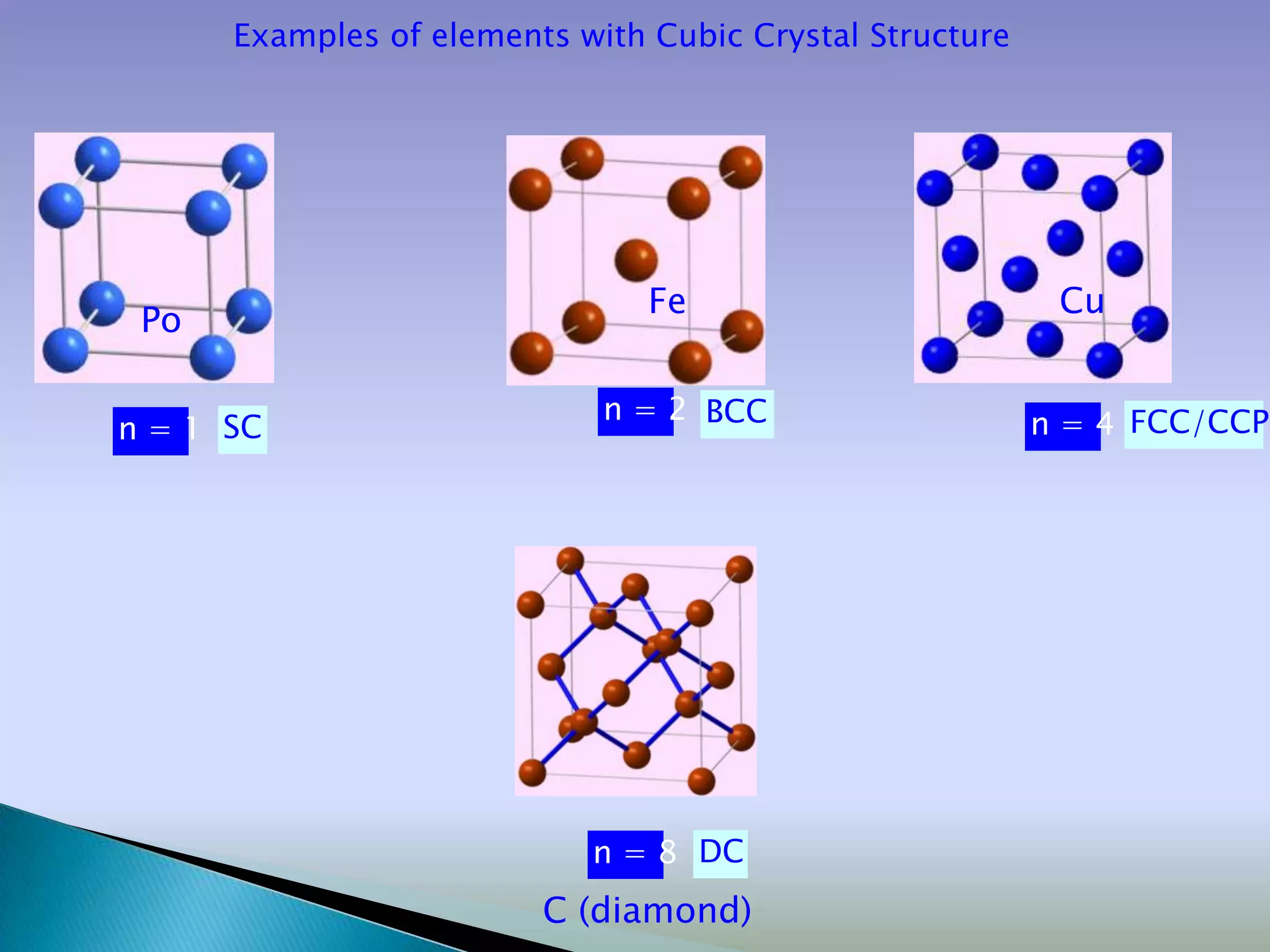
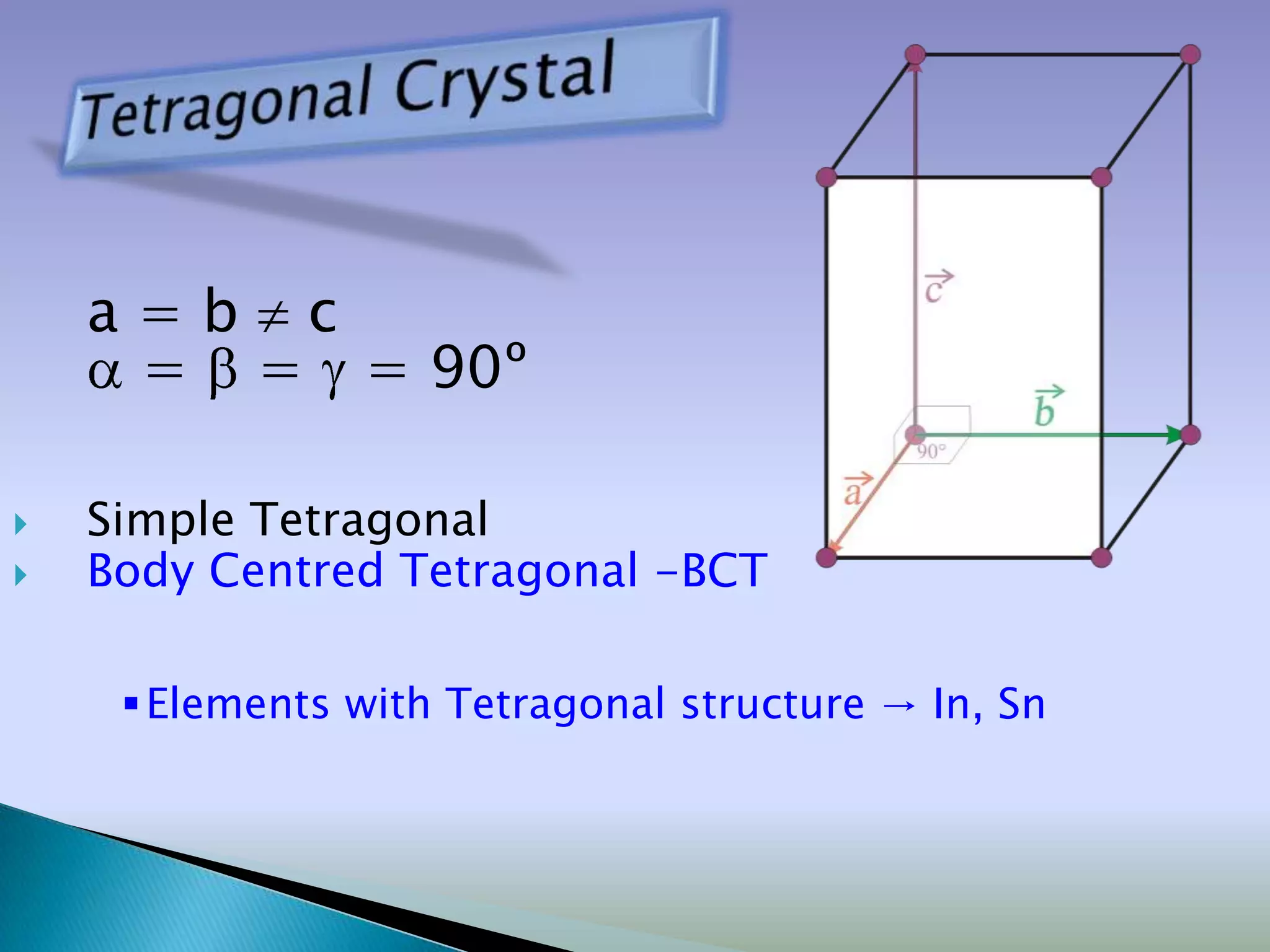
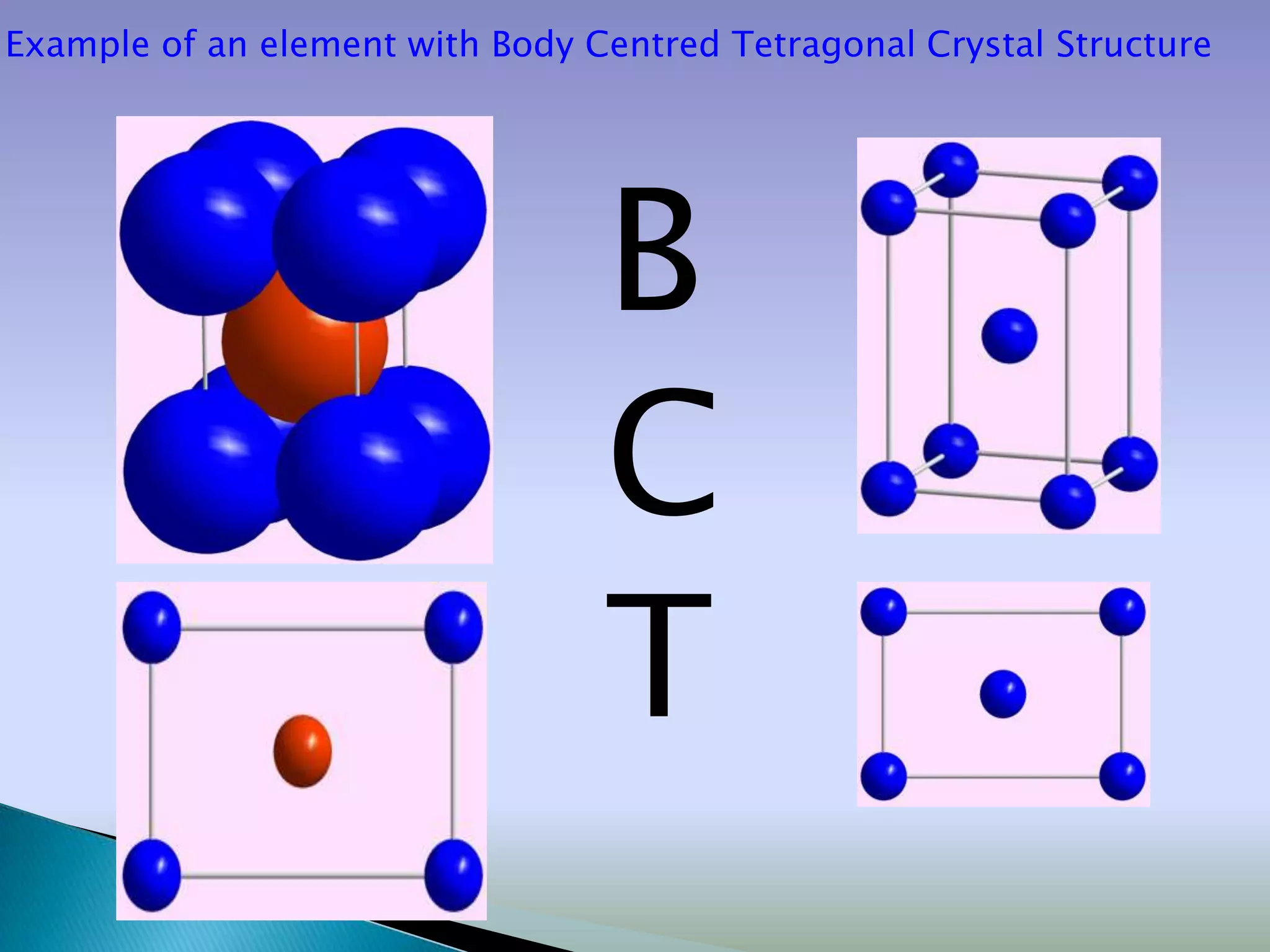
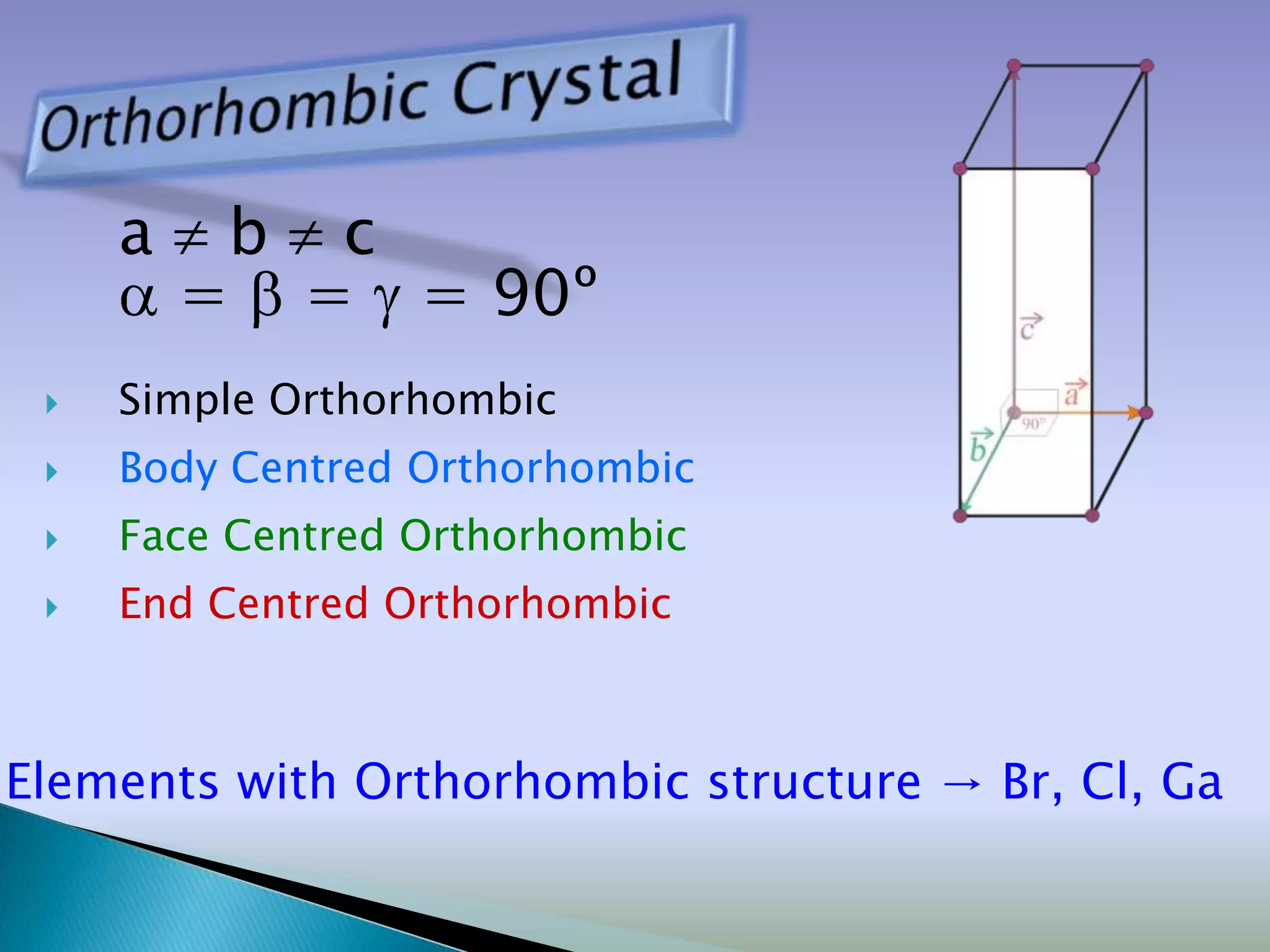
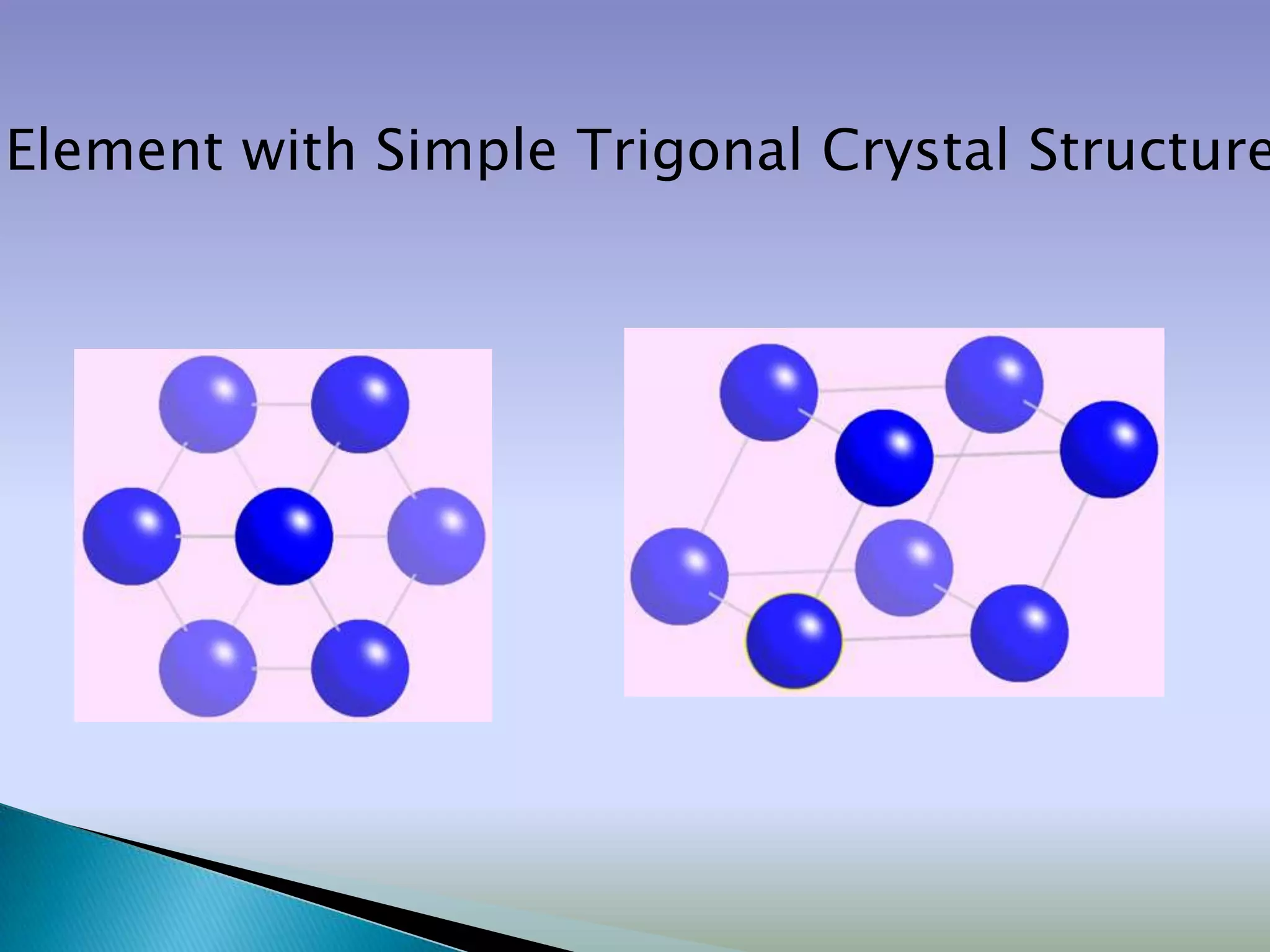
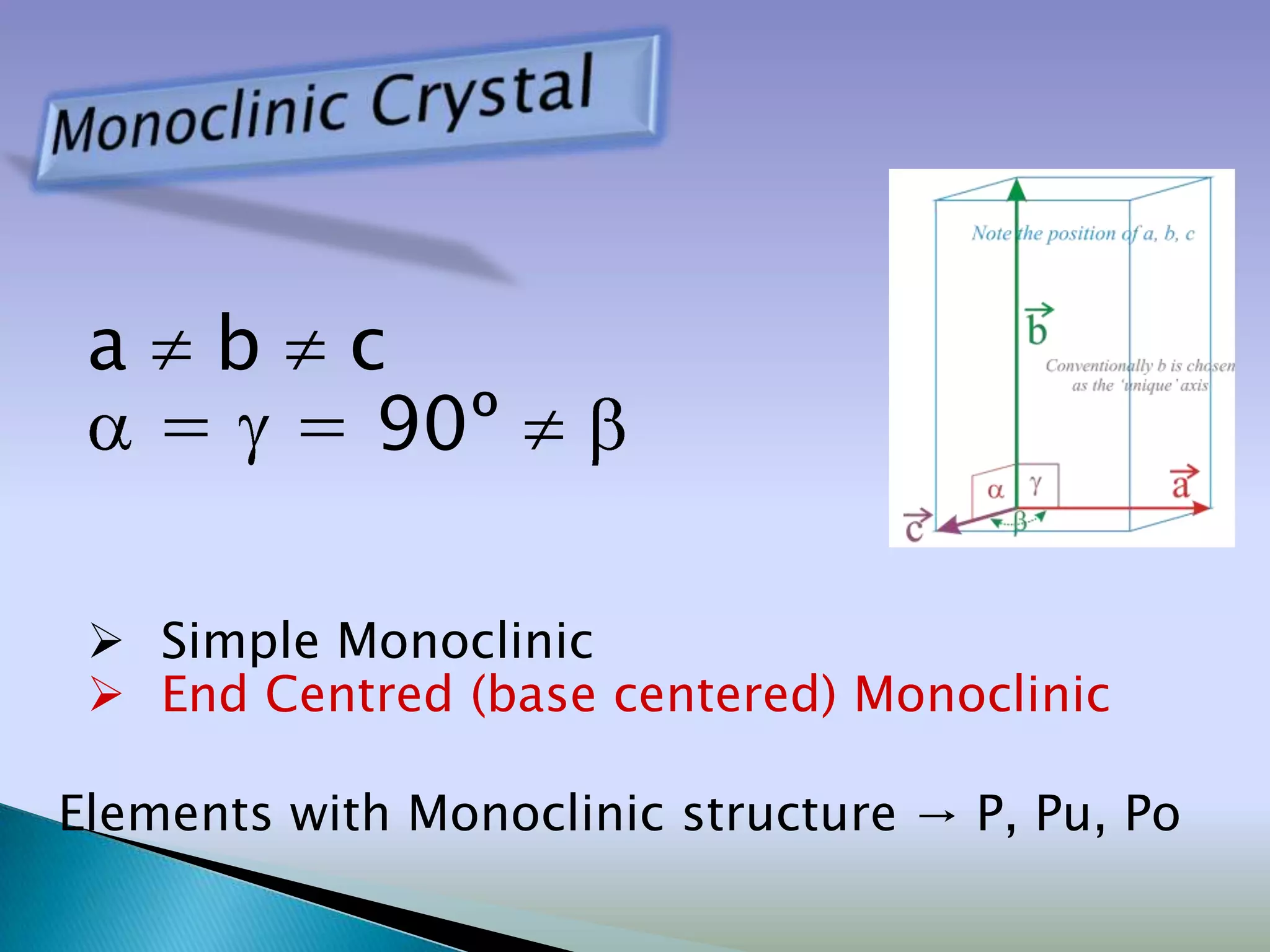
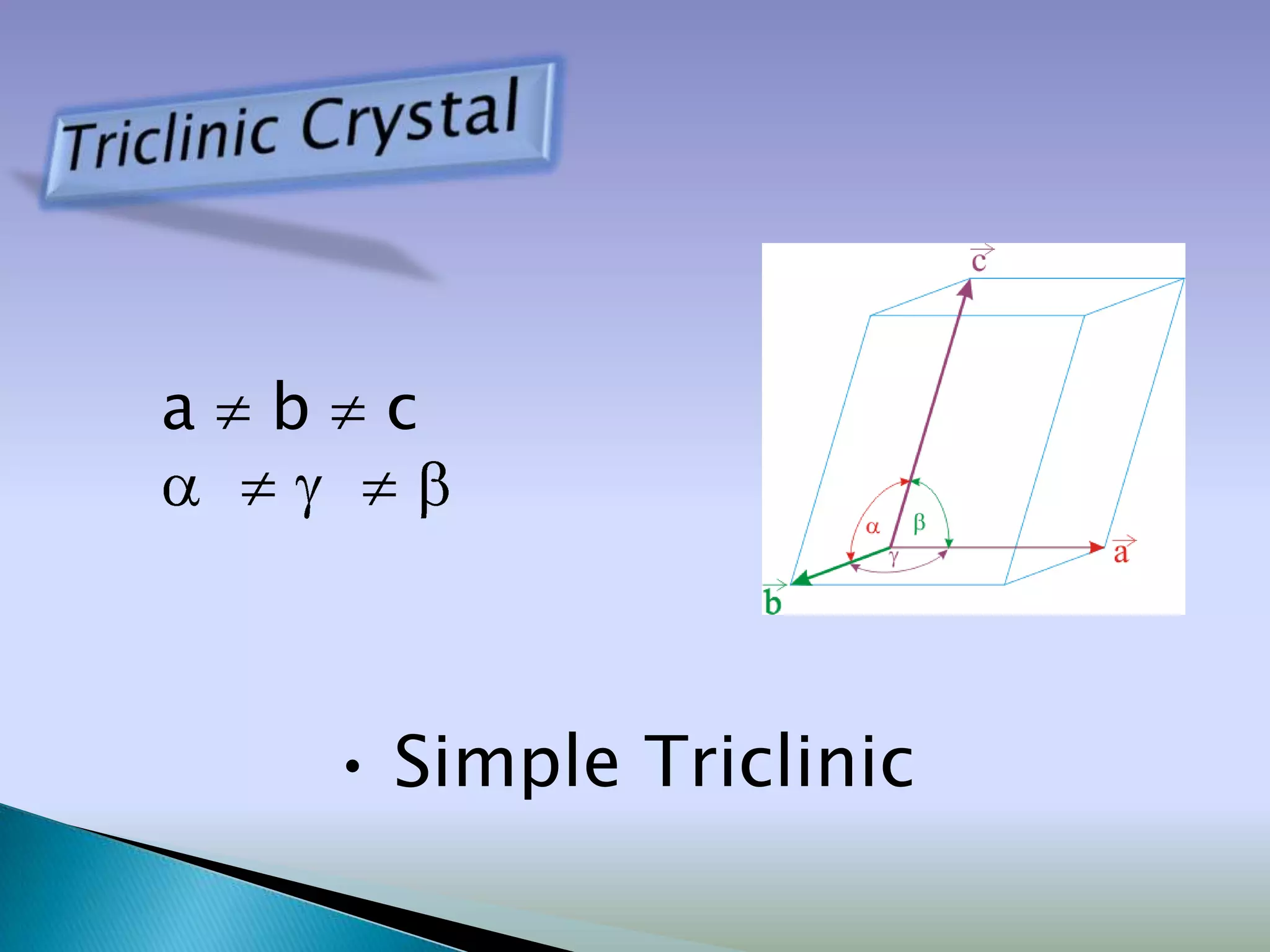
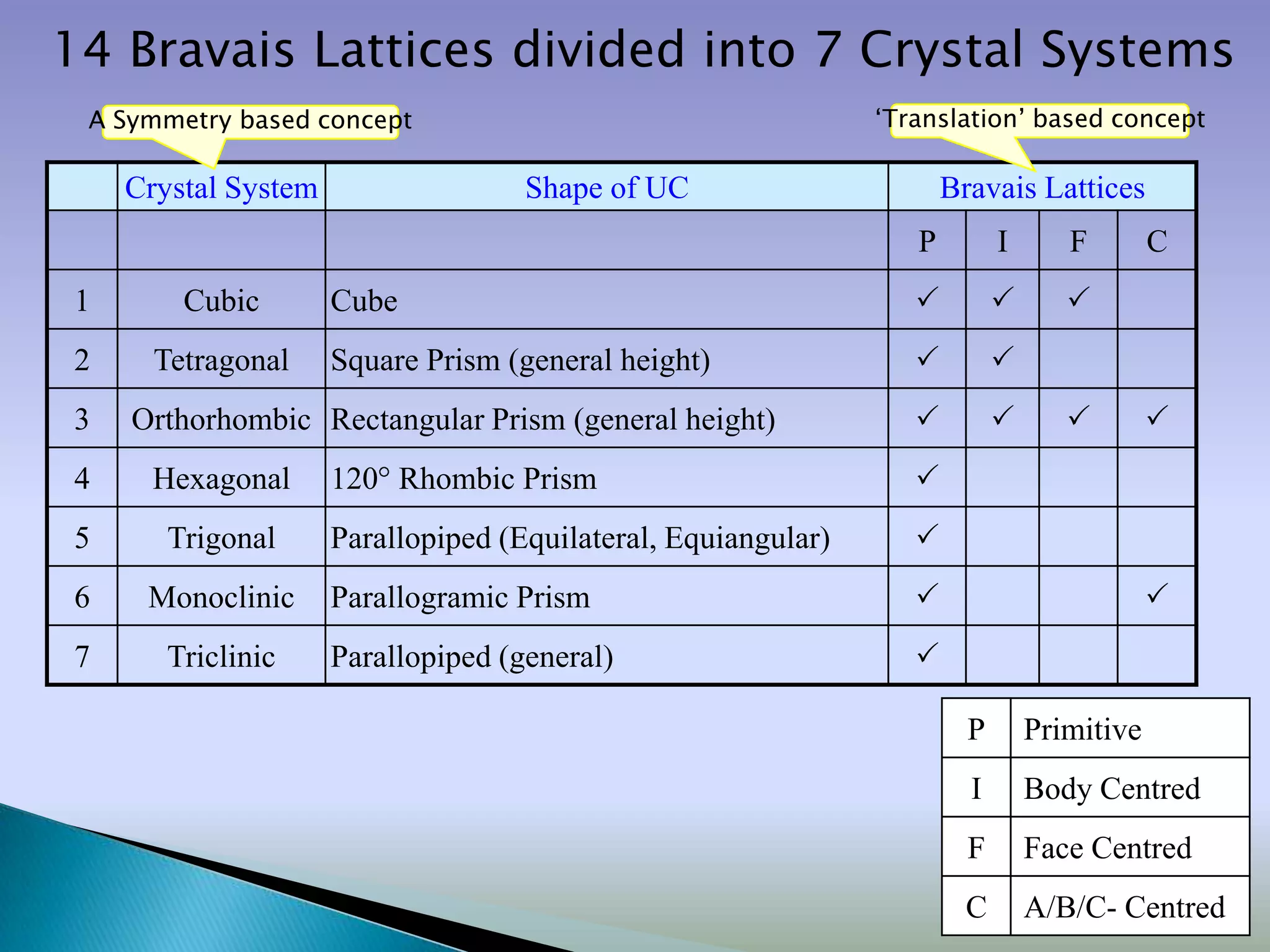
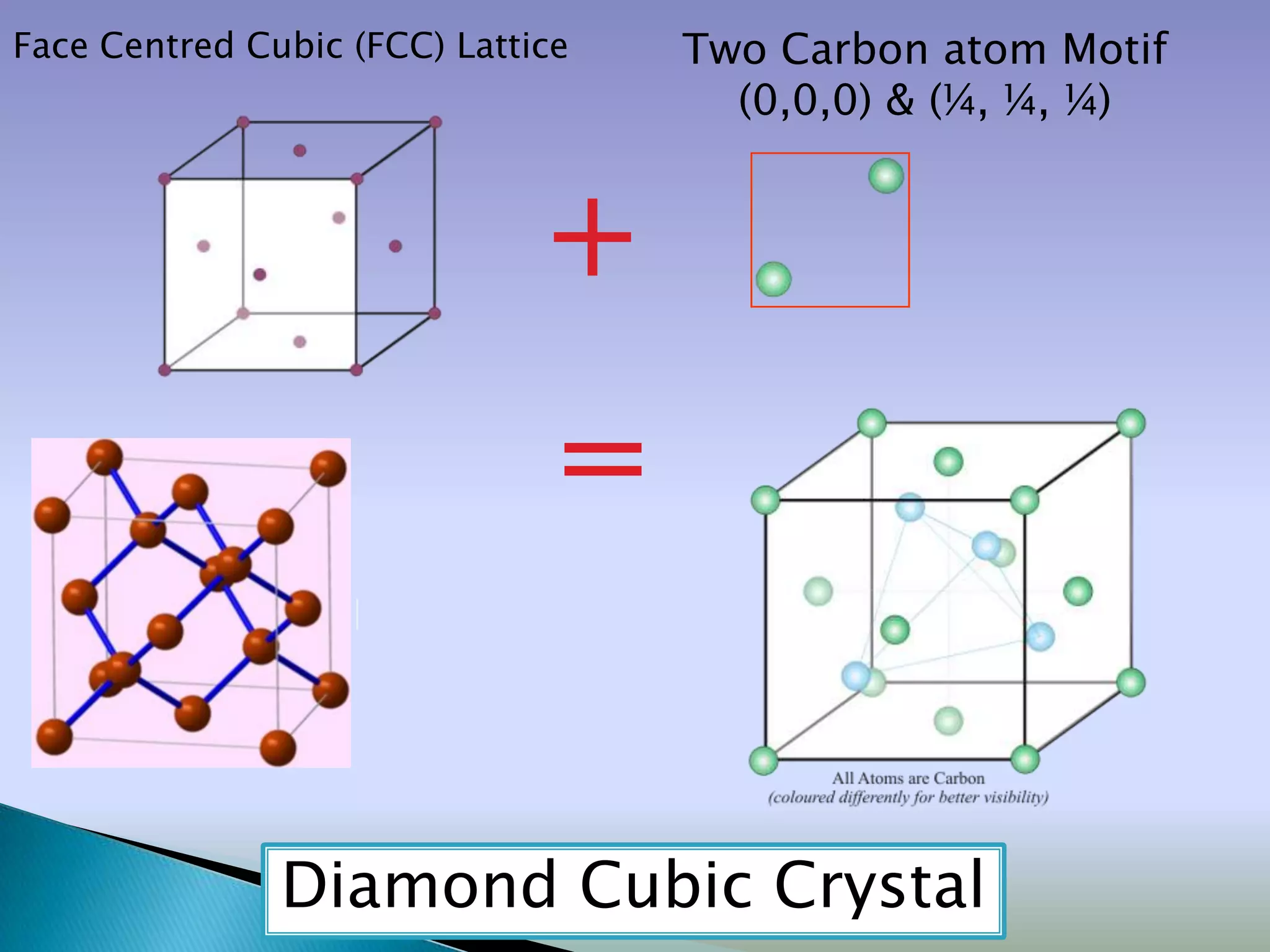
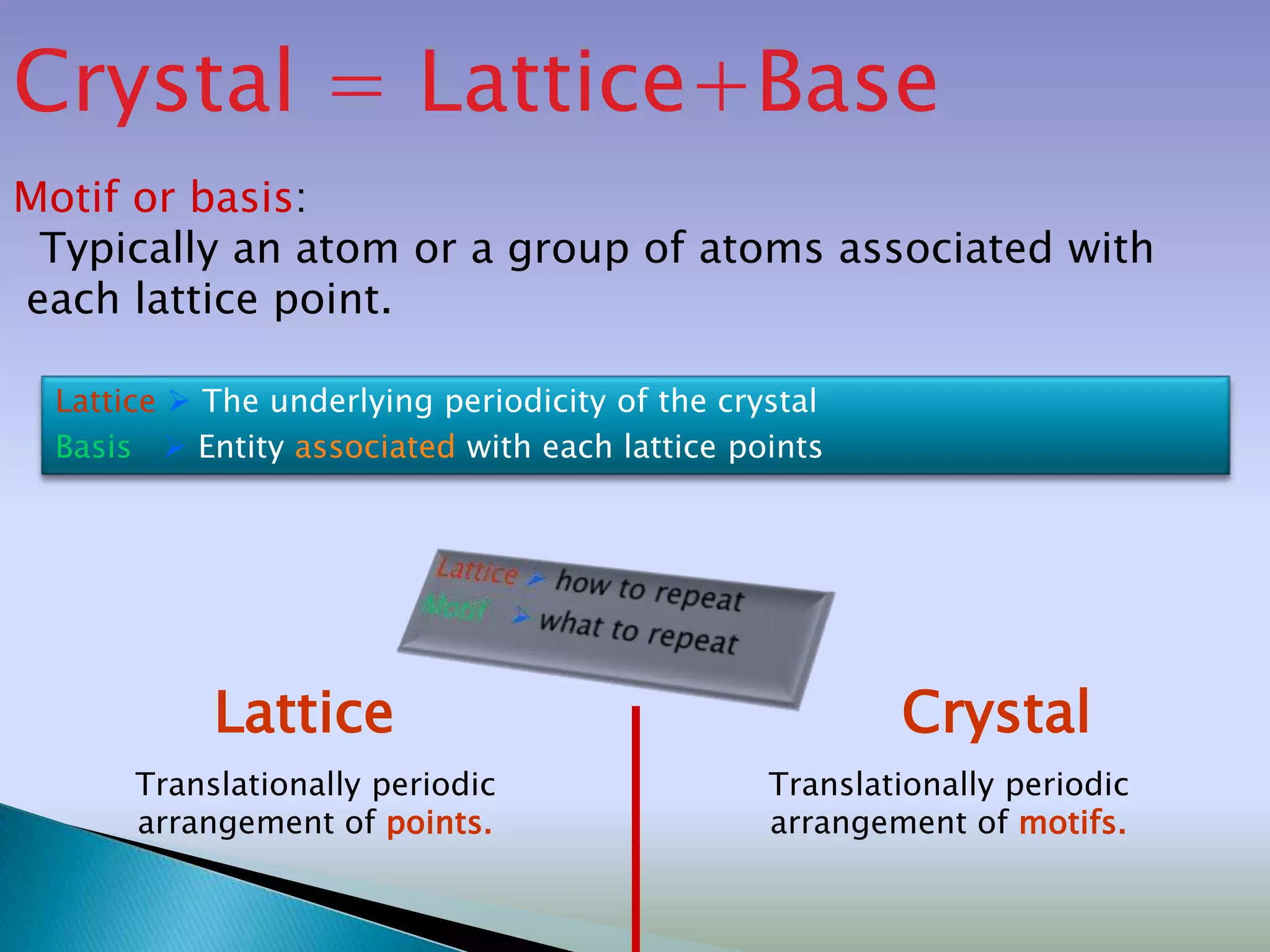
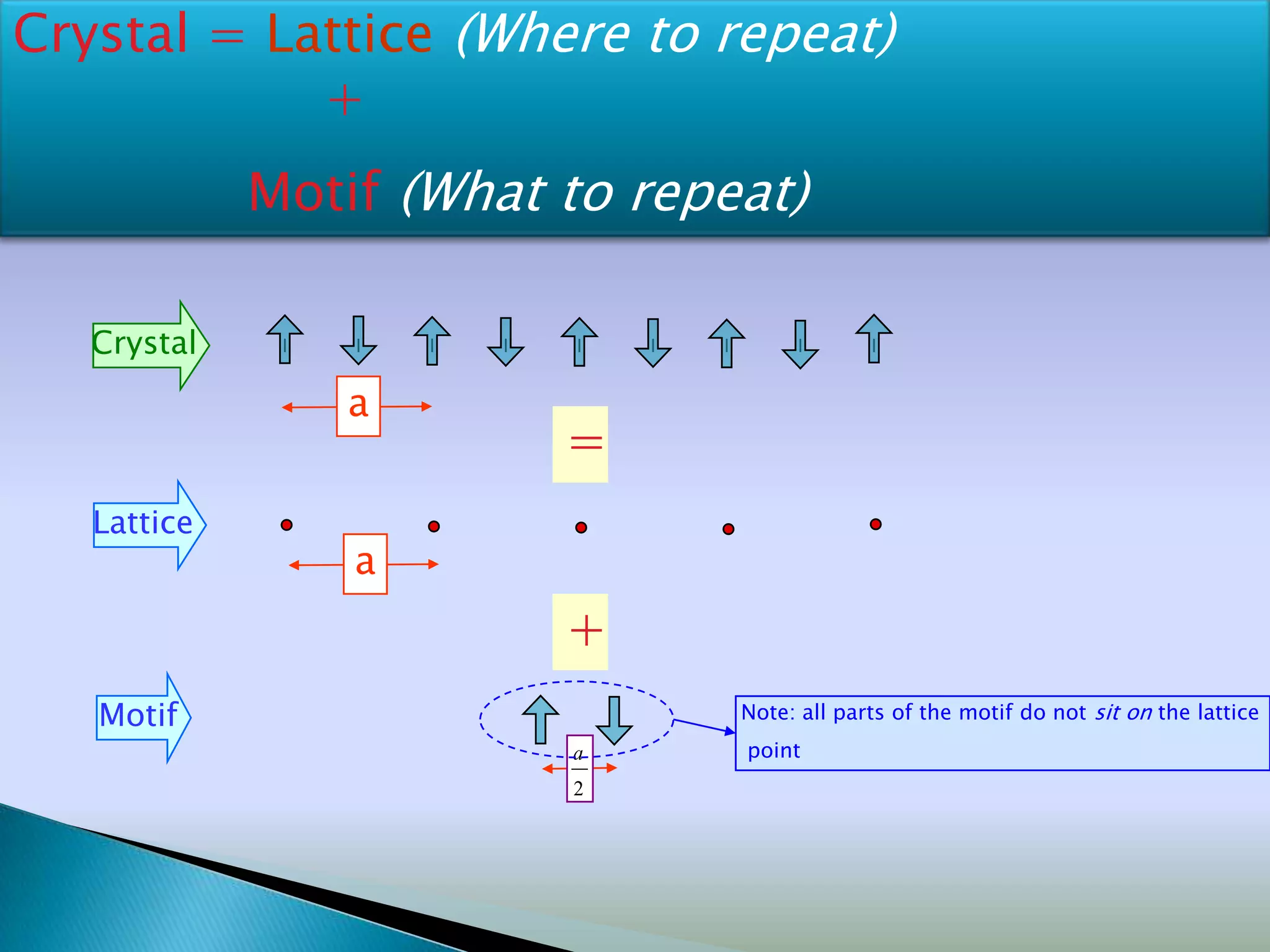
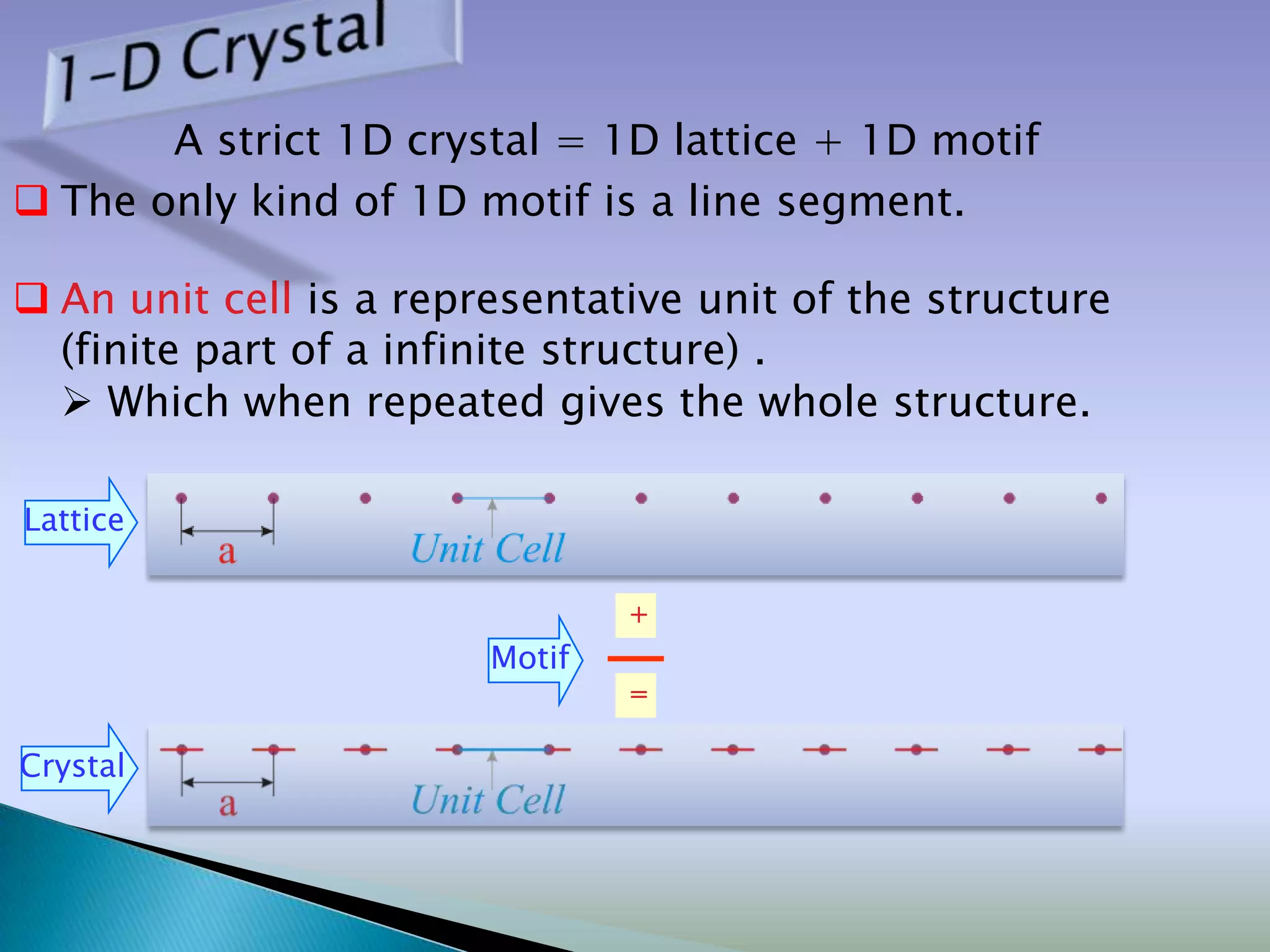
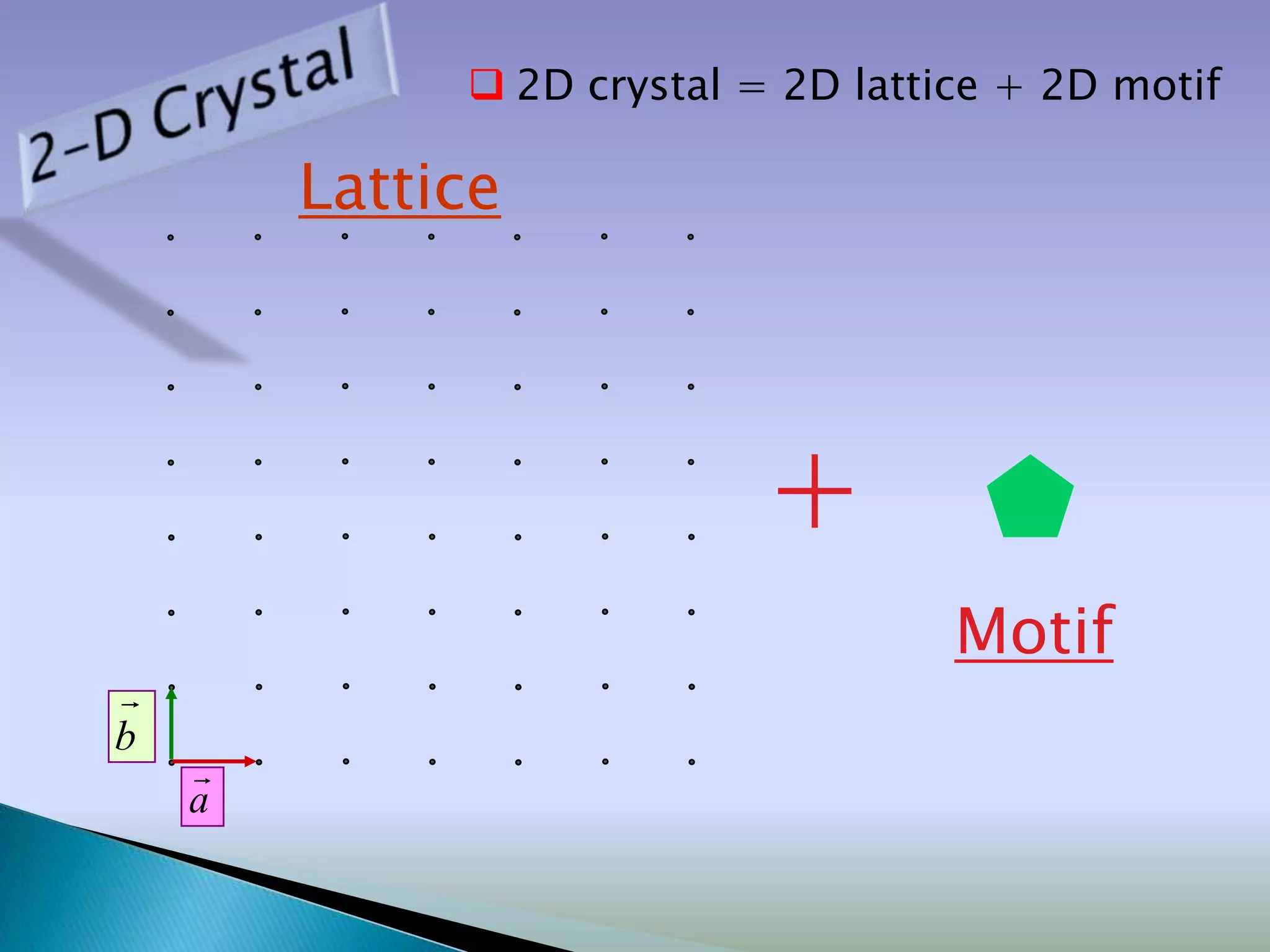
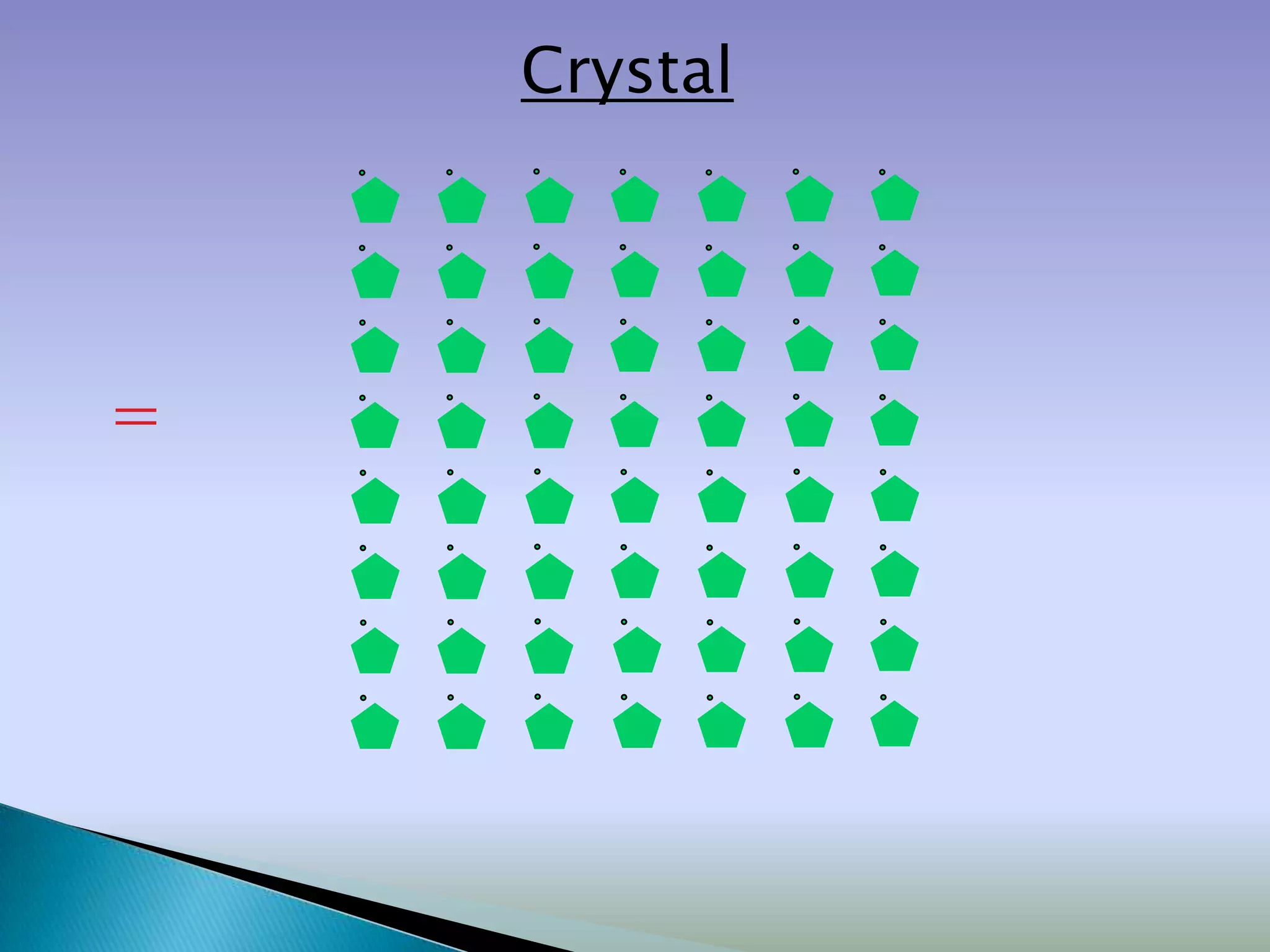
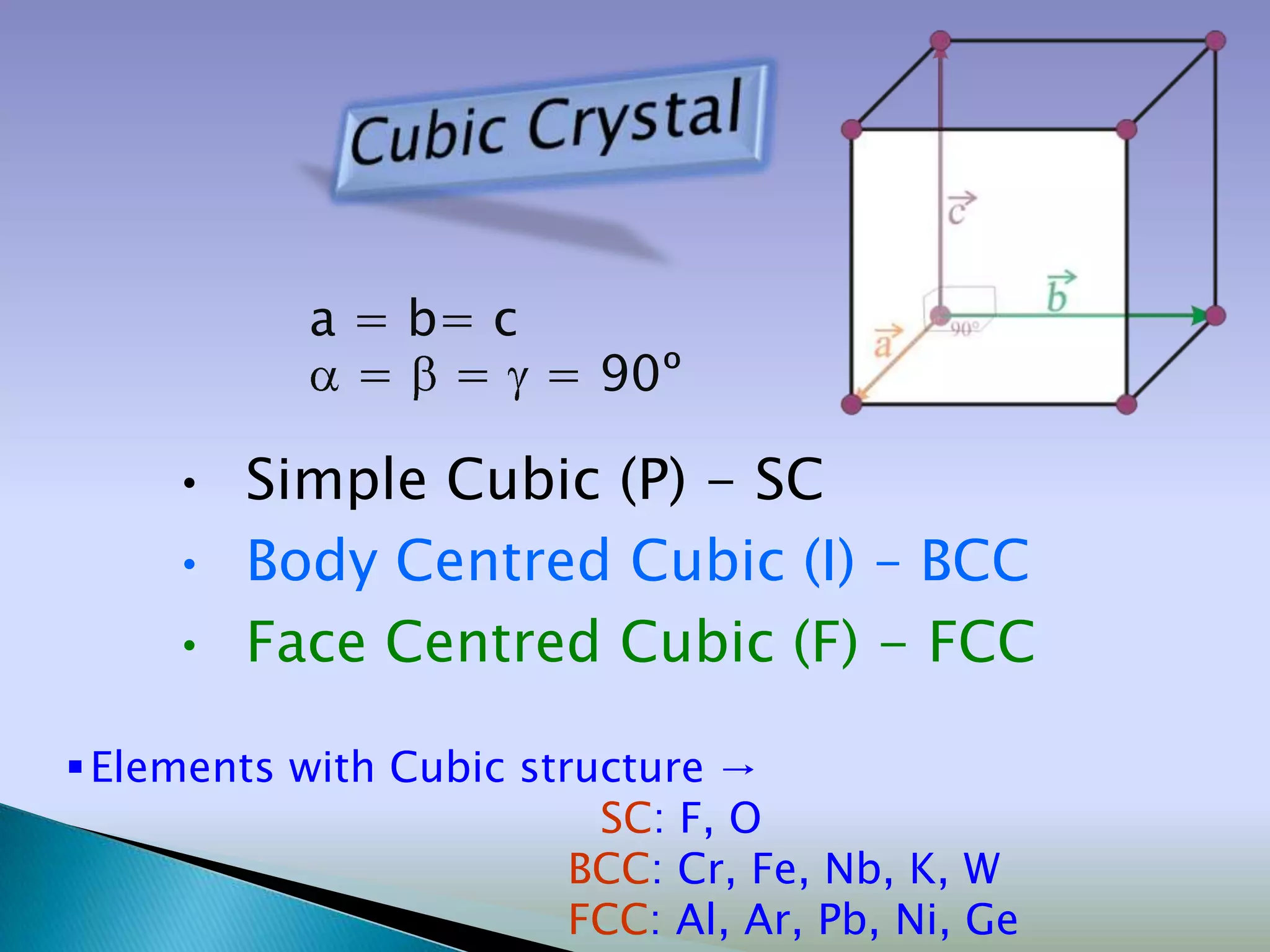
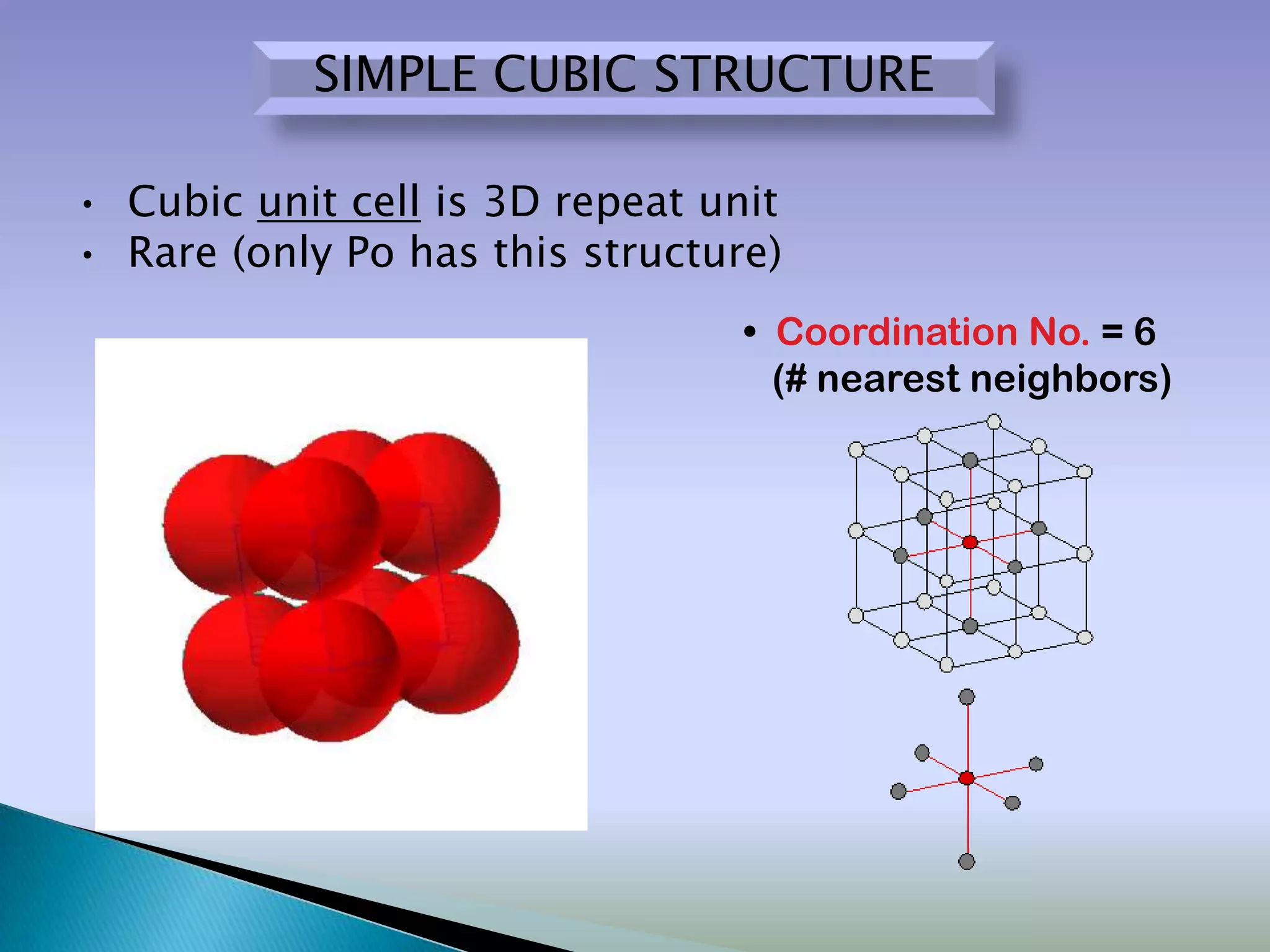
Crystals are solids with atoms arranged in a repeating pattern. They consist of a lattice, which defines the points of repetition, and a motif or basis, which defines the entity associated with each lattice point. Common crystal structures include simple cubic, body-centered cubic, and face-centered cubic, which differ in their lattice and packing arrangements. Crystals can be one-dimensional, two-dimensional, or three-dimensional depending on the dimensionality of the lattice and motif.





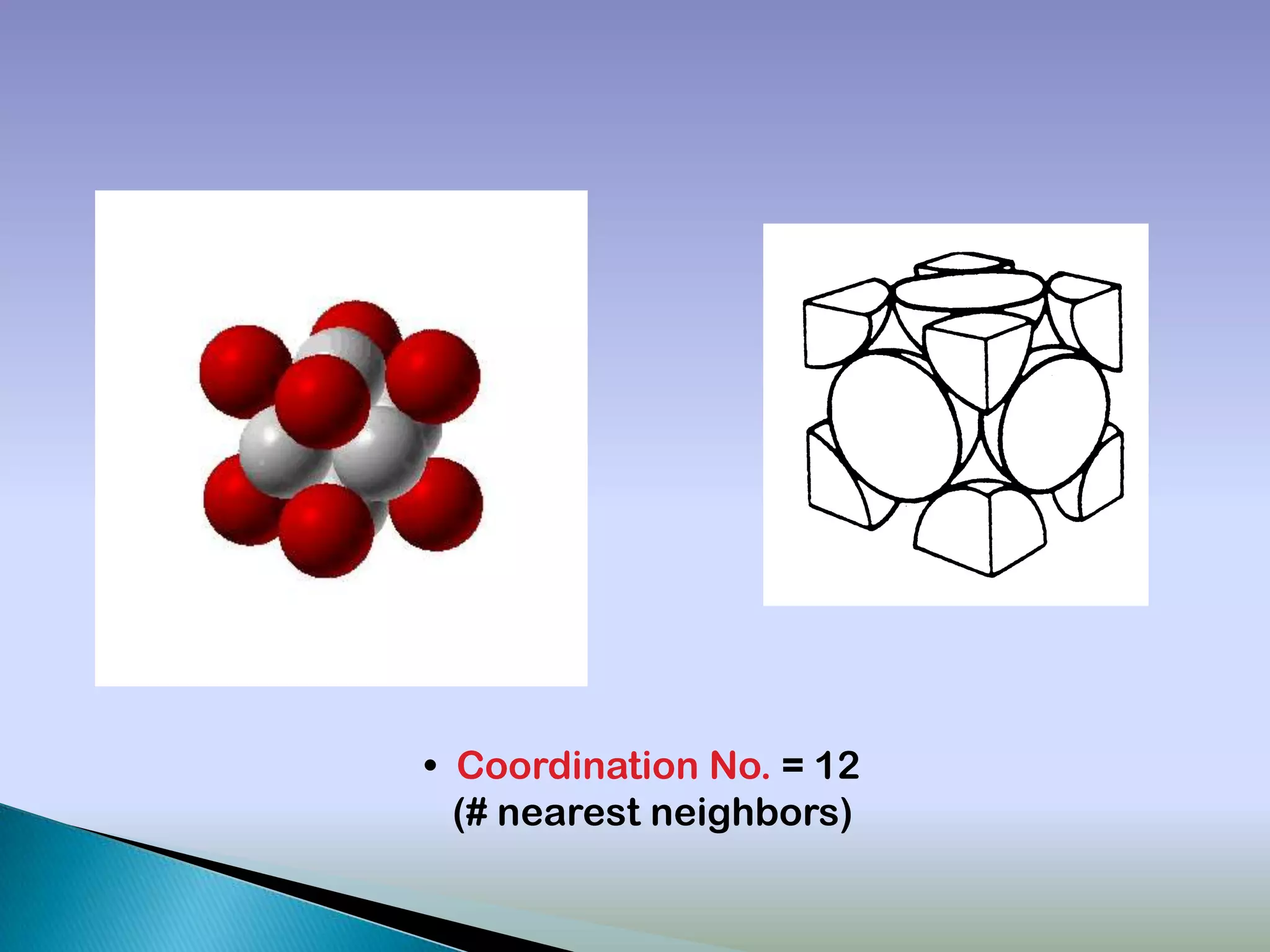
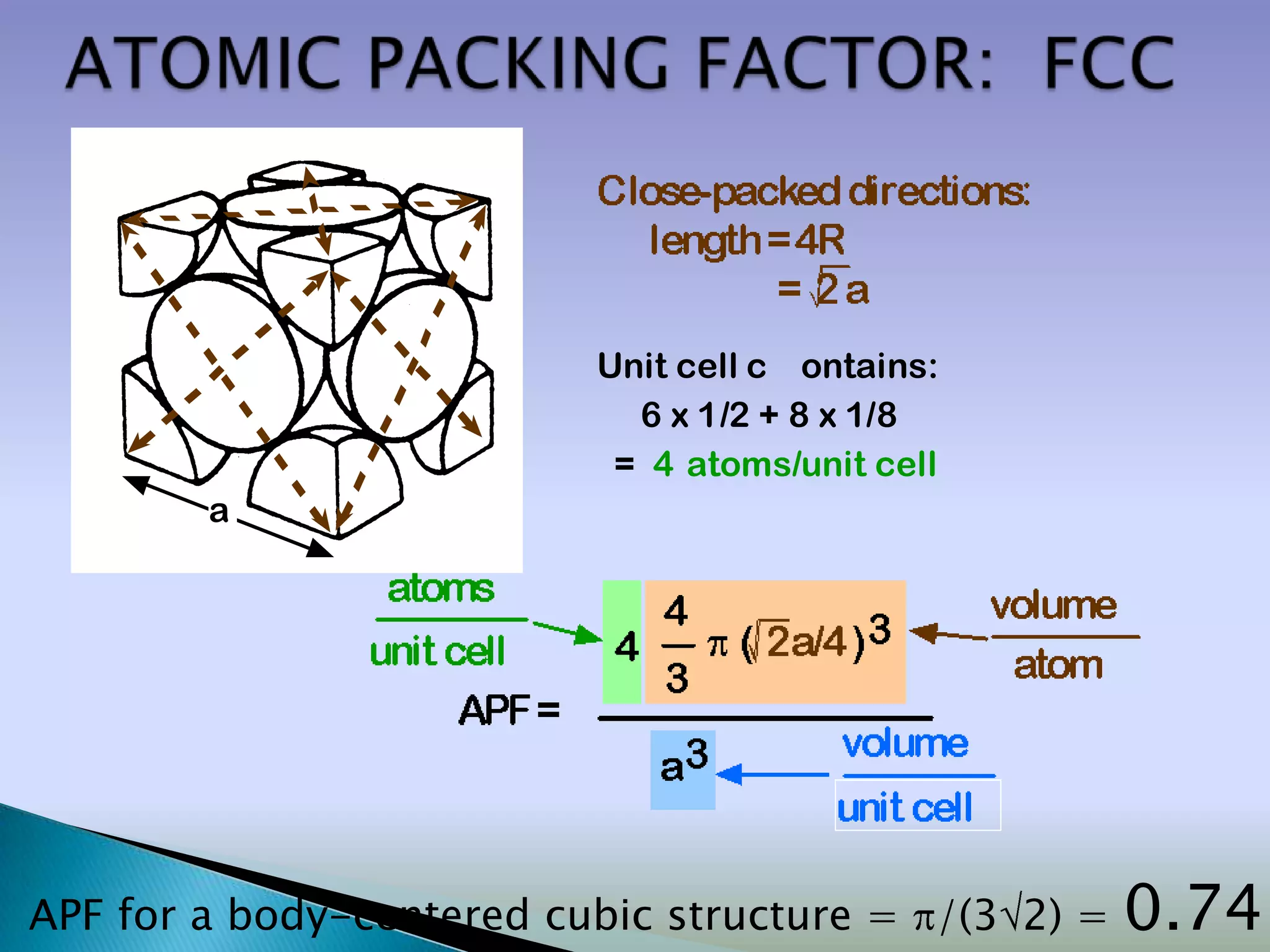
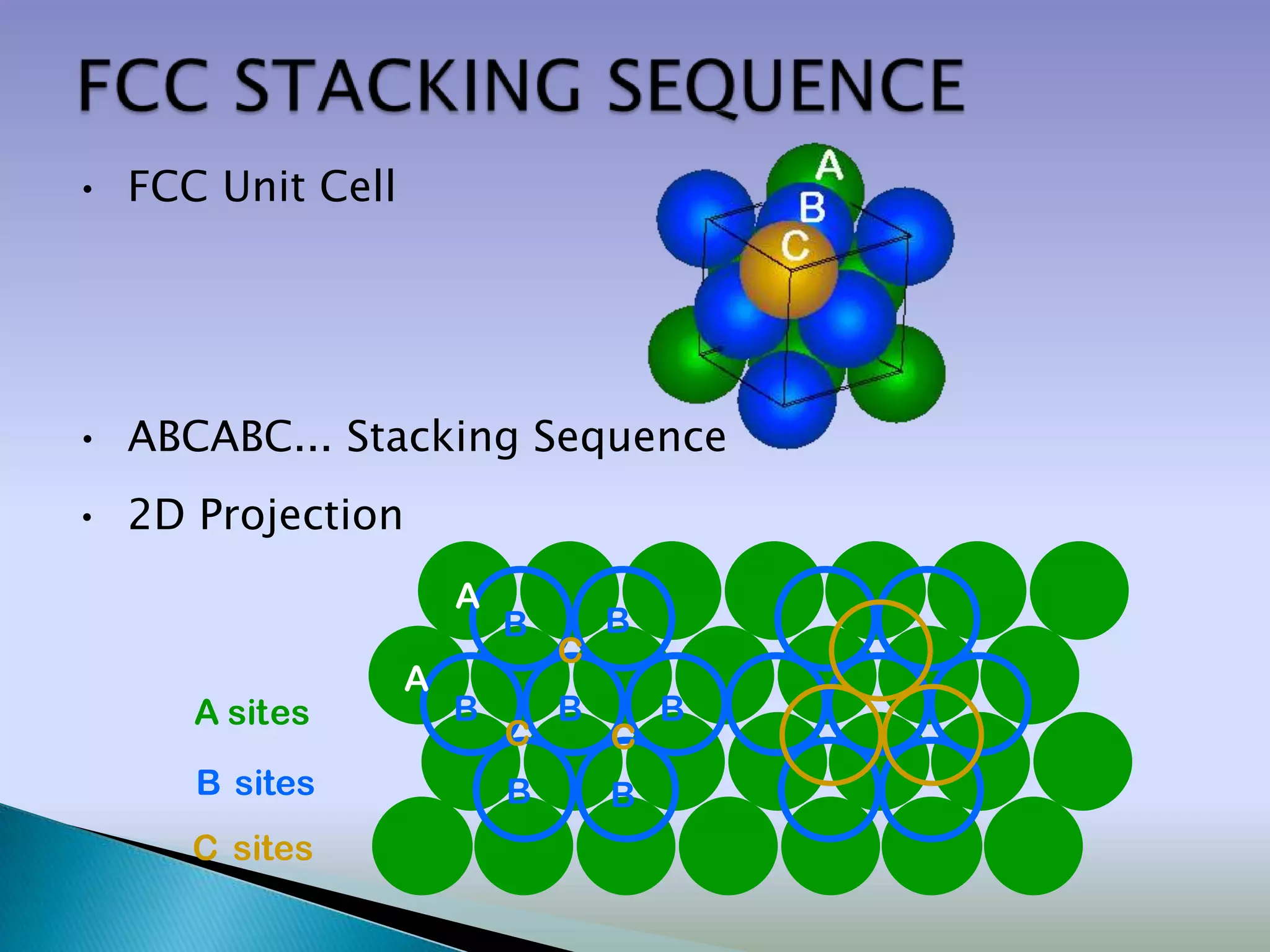
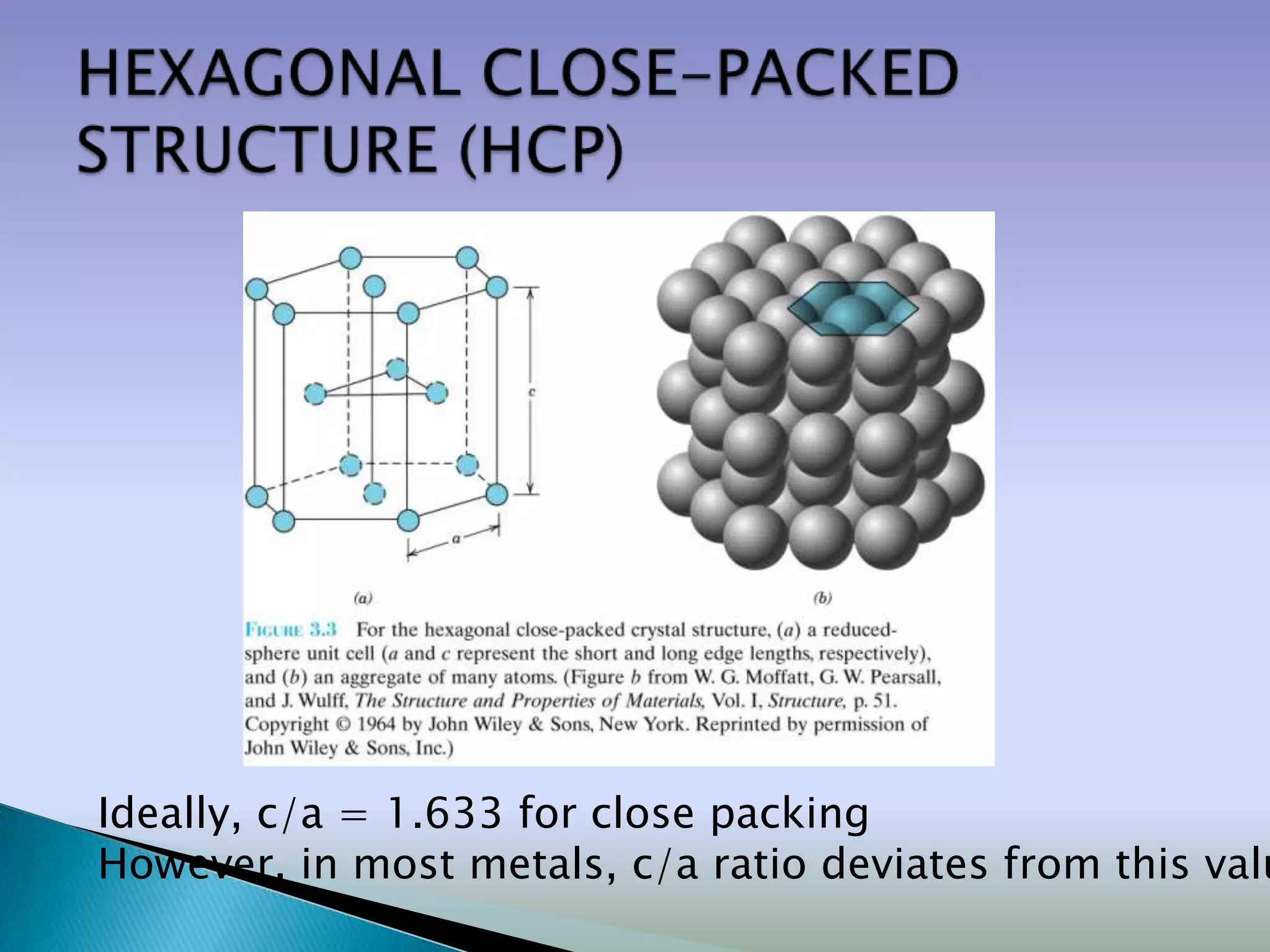
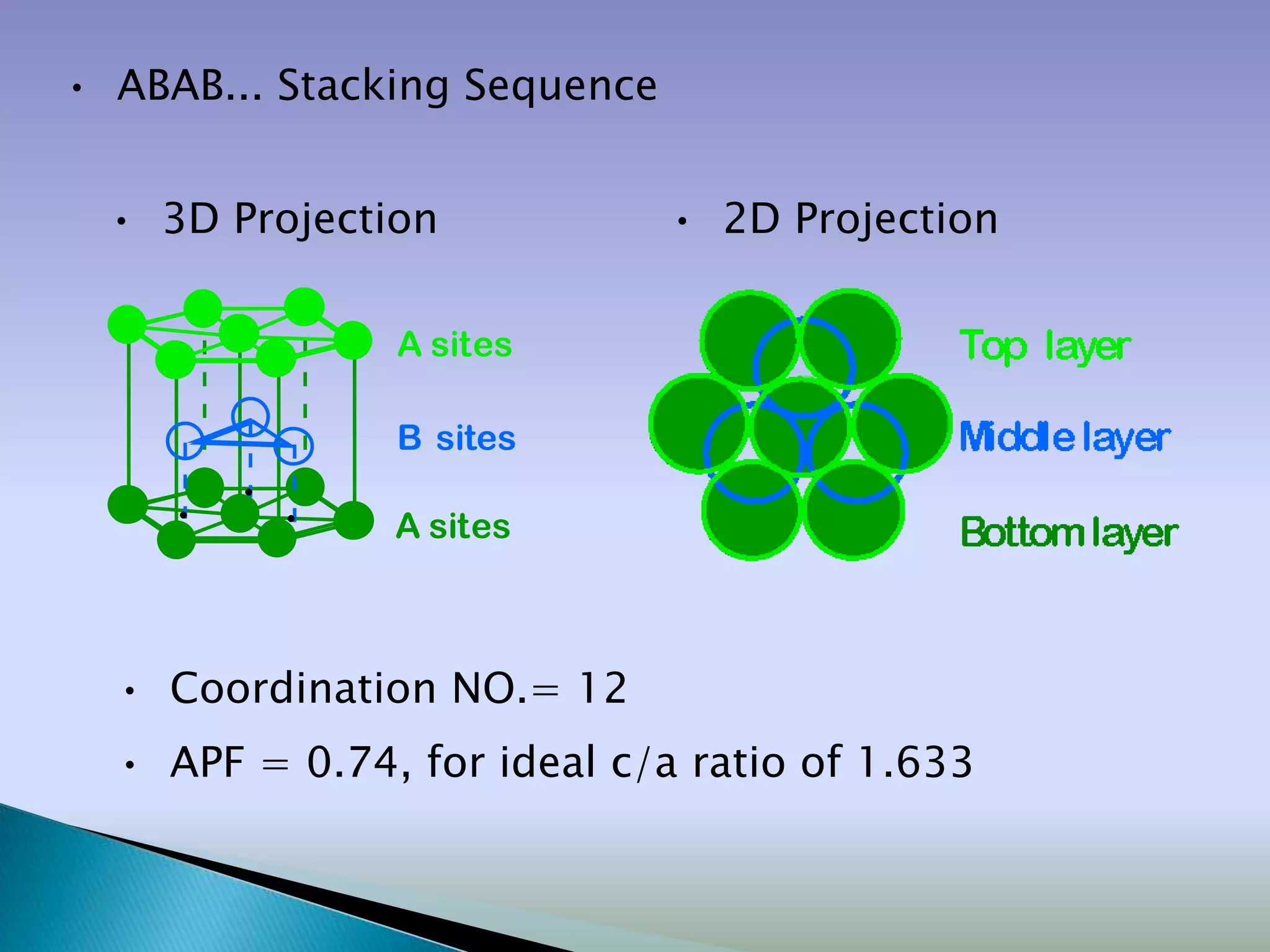
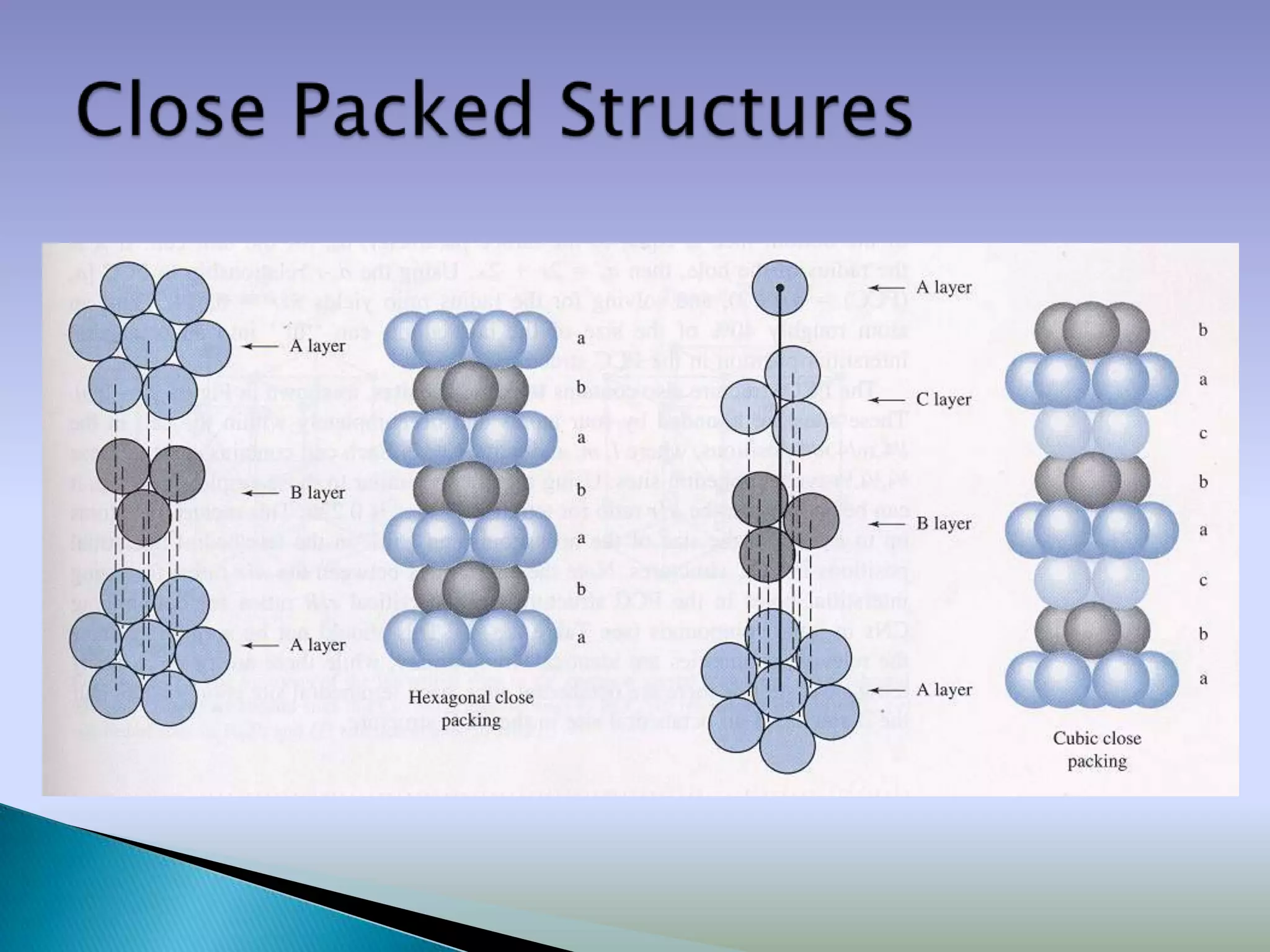
![Close packed crystals
A plane
B plane
C plane
A plane
…ABCABCABC… packing …ABABAB… packing
[Face Centered Cubic (FCC)] [Hexagonal Close Packing (HCP)]](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/structure-120416115117-phpapp01/75/Crystal-structures-Packing-Fraction-23-2048.jpg)