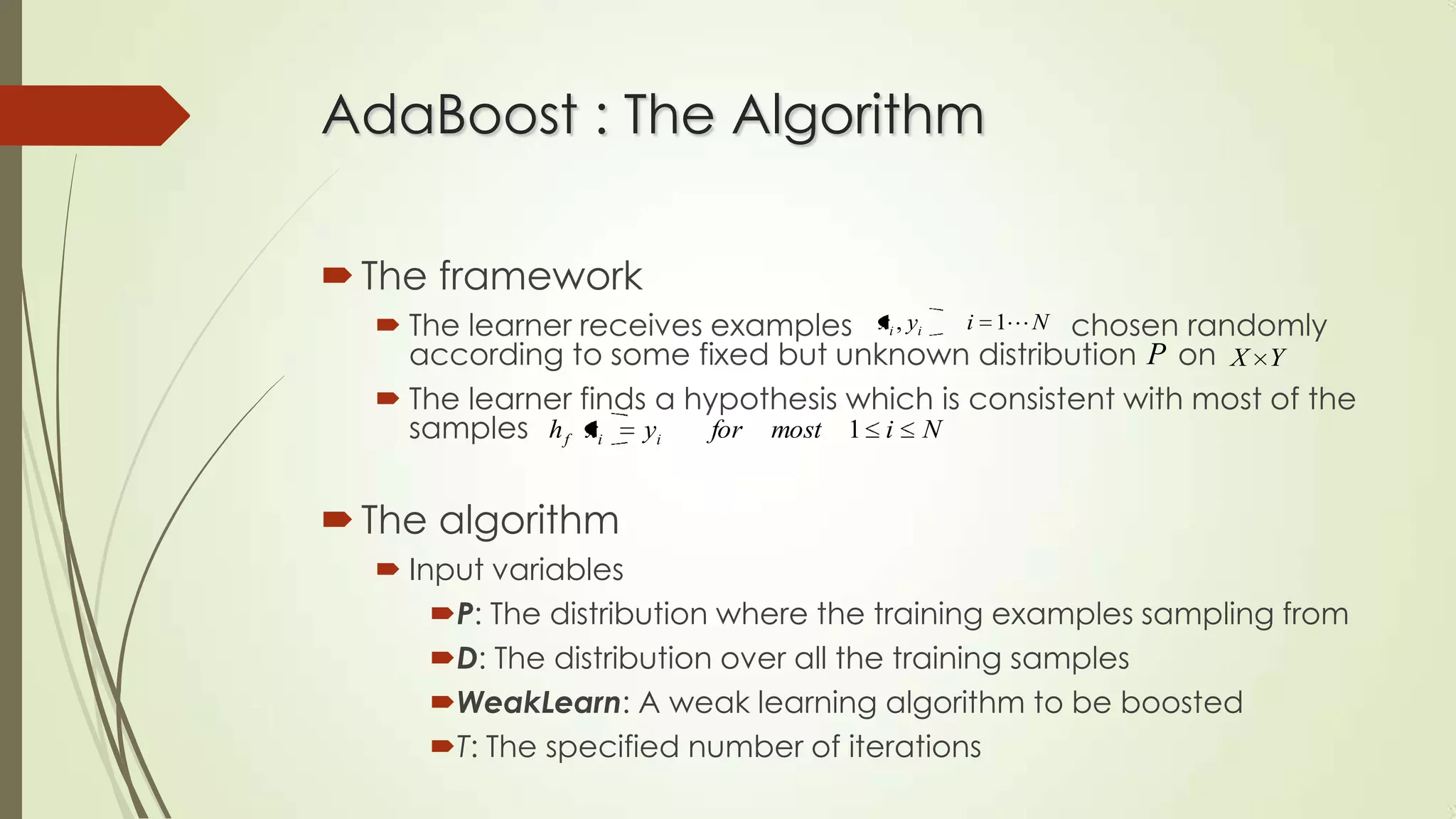
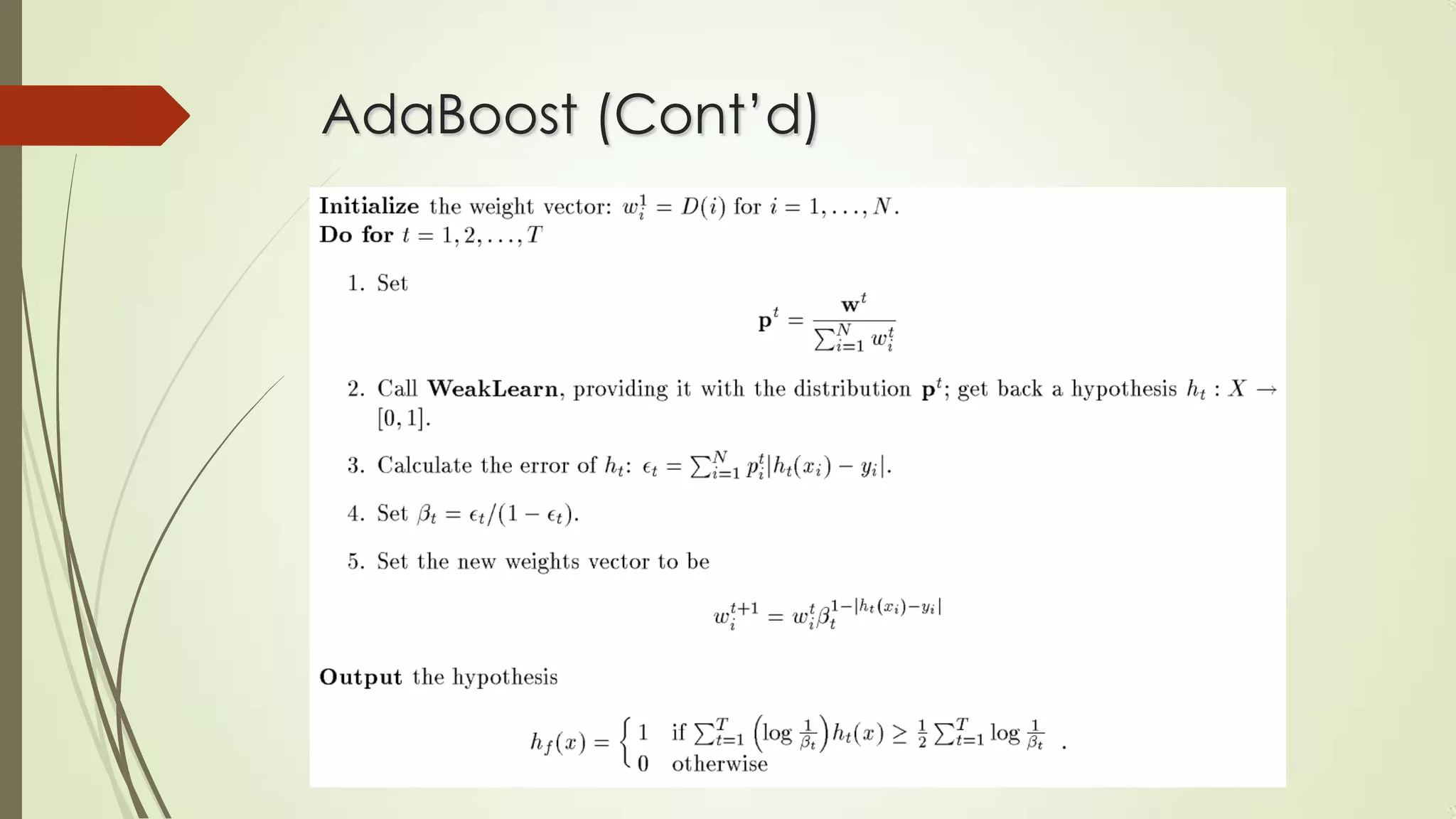
This document discusses machine learning and artificial intelligence. It defines machine learning as a branch of AI that allows systems to learn from data and experience. Machine learning is important because some tasks are difficult to define with rules but can be learned from examples, and relationships in large datasets can be uncovered. The document then discusses areas where machine learning is influential like statistics, brain modeling, and more. It provides an example of designing a machine learning system to play checkers. Finally, it discusses machine learning algorithm types and provides details on the AdaBoost algorithm.