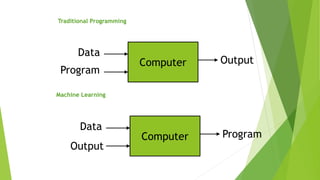
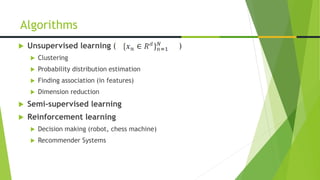
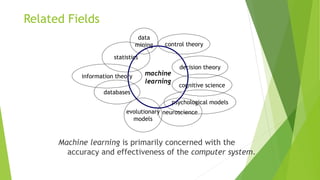
Machine learning is a subset of artificial intelligence that allows computers to learn without being explicitly programmed by improving their performance on tasks based on experience. It involves developing algorithms that can learn from and make predictions on data. There are many machine learning algorithms that differ in their representation, evaluation, and optimization methods, and algorithms can perform supervised learning (classification and regression), unsupervised learning (clustering and dimensionality reduction), semi-supervised learning, and reinforcement learning. Machine learning has applications in areas like web search, finance, e-commerce, robotics, and healthcare.