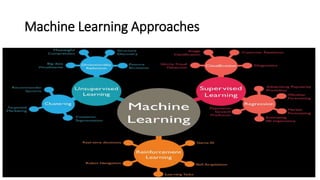
This document provides an overview of machine learning, including definitions of key terminology, the typical machine learning process, different machine learning approaches (supervised, unsupervised, semi-supervised, and reinforcement learning), applications of machine learning, and advantages and disadvantages of machine learning. It discusses how machine learning allows systems to learn from data and improve automatically without being explicitly programmed.