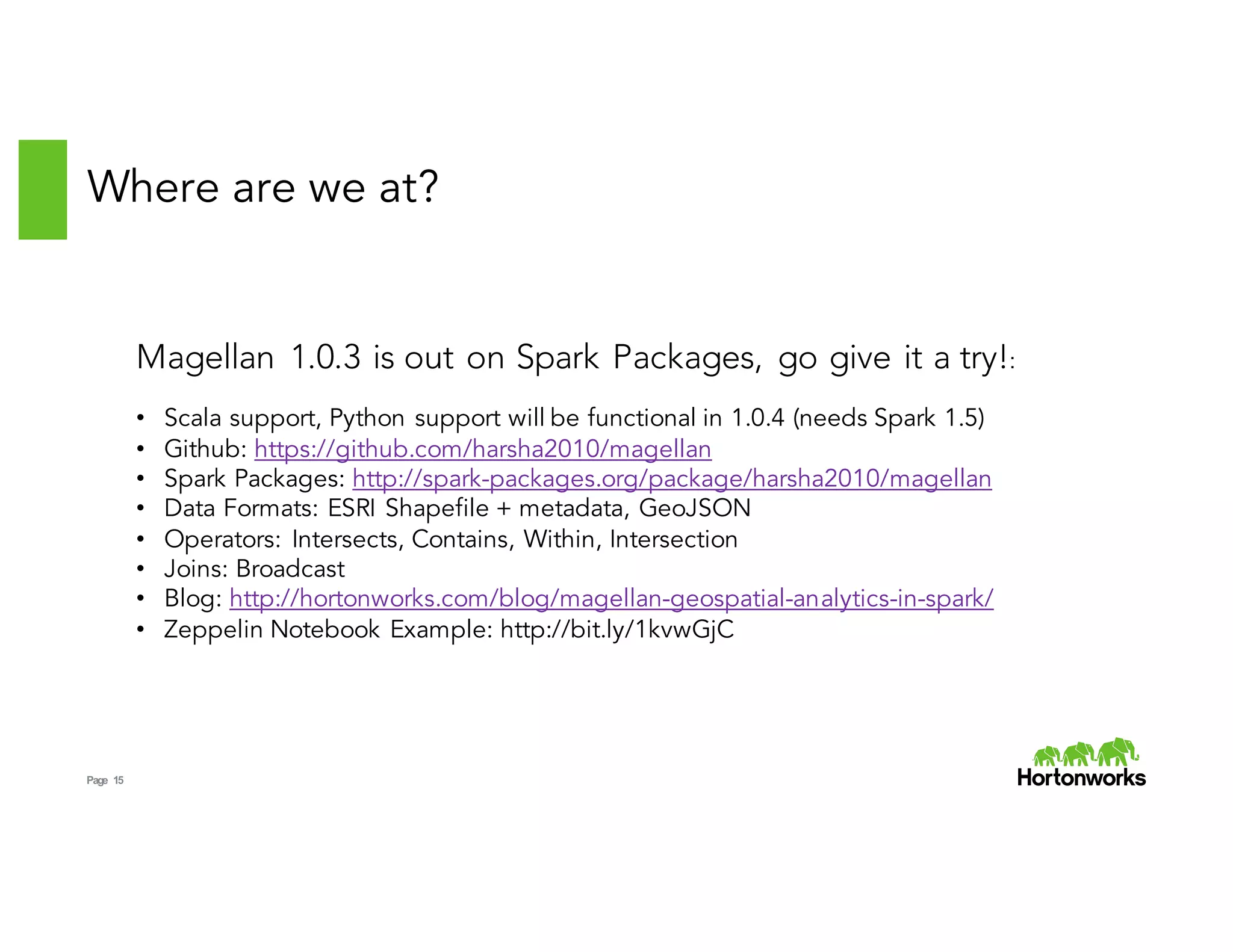
Magellan provides geospatial analytics capabilities on Spark. It allows users to read geospatial data formats like Shapefiles and GeoJSON, perform spatial queries and joins on location data, and build complete geospatial analytics applications in Spark faster using their preferred programming languages like Python and Scala. Key features include custom data types for representing spatial objects, spatial expressions for queries, optimized strategies for spatial joins, and integration with Spark SQL's Catalyst optimizer.










![Page 13
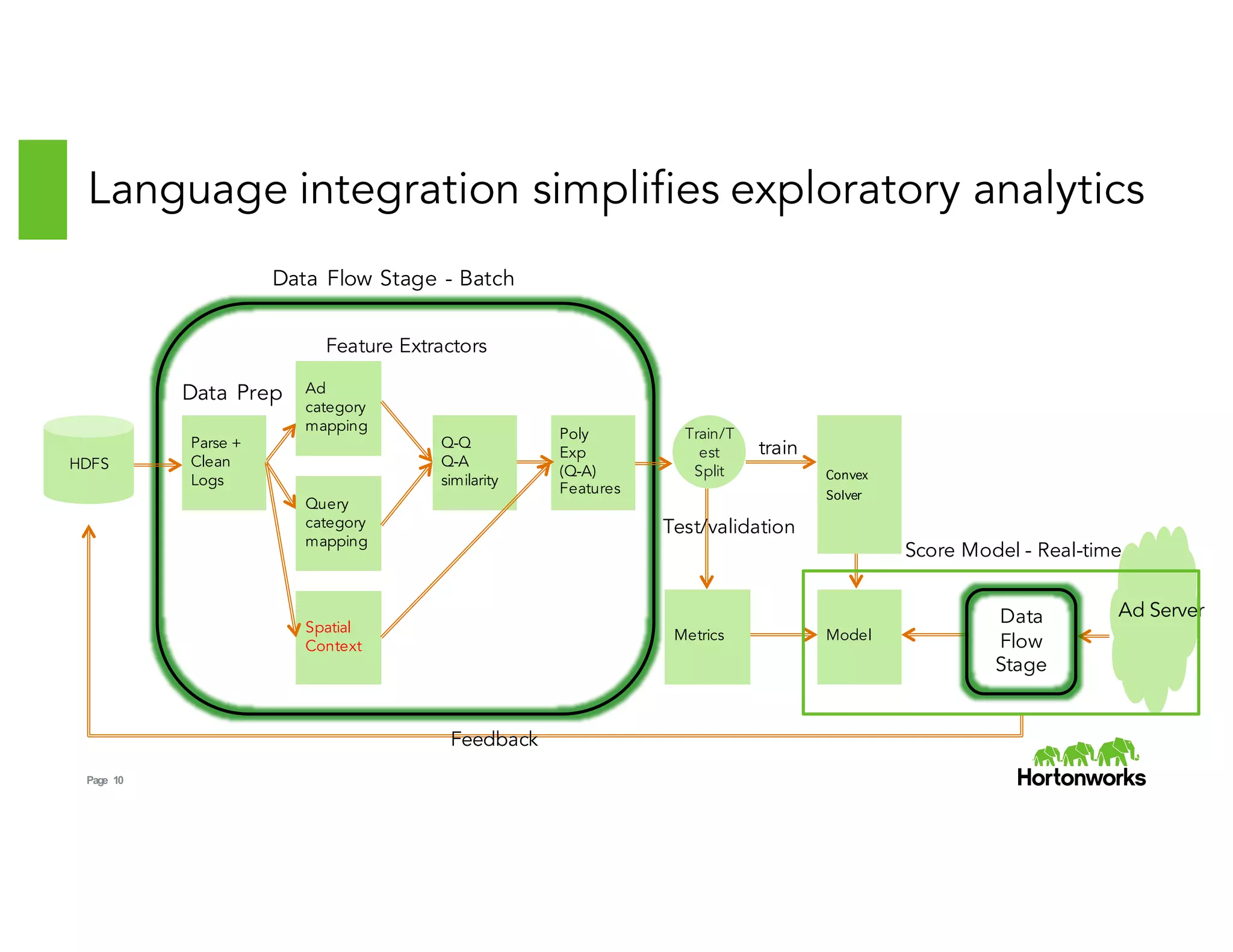
How does it work?
Custom Data Types for Shapes:
• Point, Line, PolyLine, Polygon extend Shape
• Local Computations using ESRI Java API
• No need for Scala -> SQL serialization
Expressions for Operators:
• Literals e.g point(-122.4, 37.6)
• Boolean Expressions e.g Intersects, Contains
• Binary Expressions e.g Intersection
Custom Data Sources:
• Schema = [point, polyline, polygon, metadata]
• Metadata = Map[String, String]
• GeoJSON and Shapefile implementations
Custom Strategies for Spatial Join:
• Broadcast Cartesian Join
• Geohash Join (in progress)
• Plug into Catalyst as experimental strategies](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/02ramsriharsha-151104001213-lva1-app6892/75/Magellen-Geospatial-Analytics-on-Spark-by-Ram-Sriharsha-13-2048.jpg)