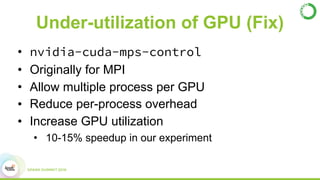
GPU Computing With Apache Spark And Python
- Python is a popular language for data science and analytics due to its large ecosystem of libraries and ease of use, but it is slow for number crunching tasks. GPU computing is a way to accelerate Python workloads.
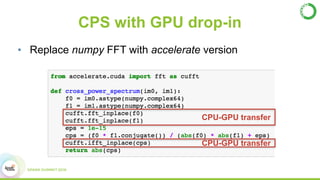
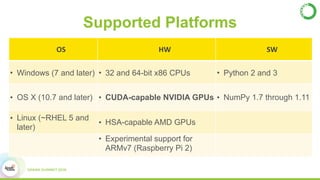
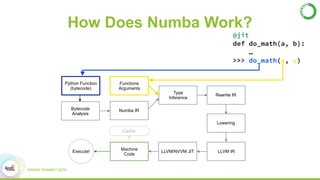
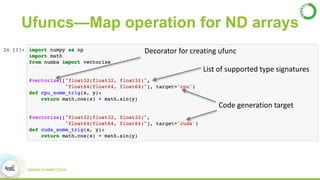
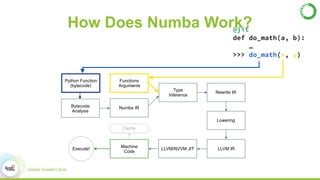
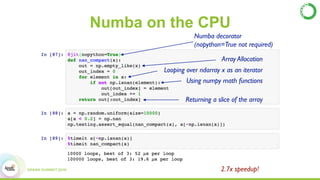
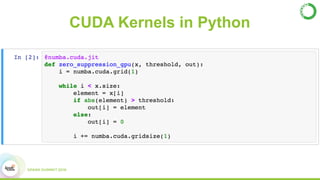
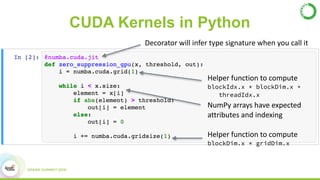
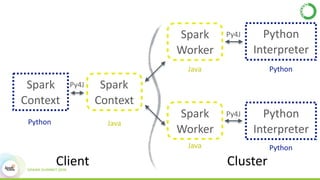
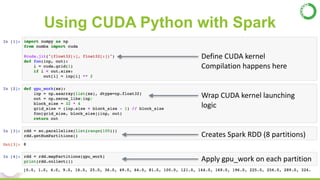
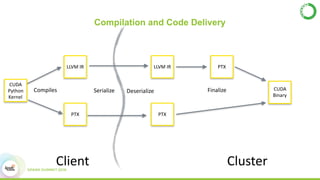
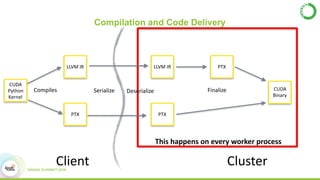
- This presentation demonstrates using GPUs with Apache Spark and Python through libraries like Accelerate, which provides drop-in GPU-accelerated functions, and Numba, which can compile Python functions to run on GPUs.
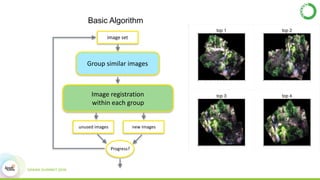
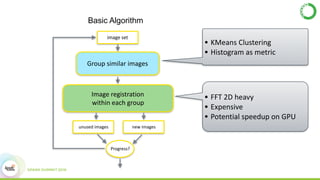
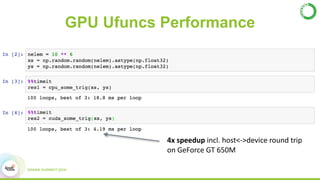
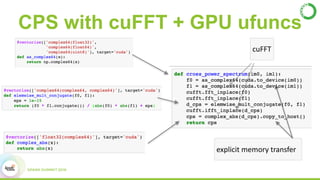
- As an example, the task of image registration, which involves computationally expensive 2D FFTs, is accelerated using these GPU libraries within a PySpark job, achieving a 2-4x speedup over CPU-only versions