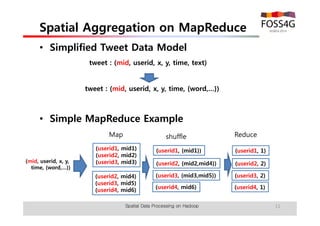
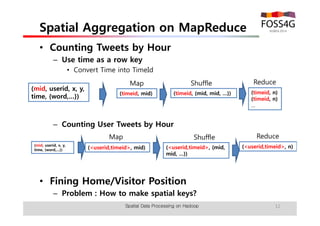
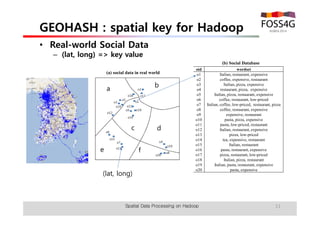
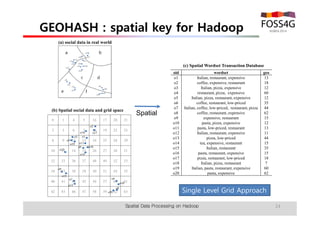
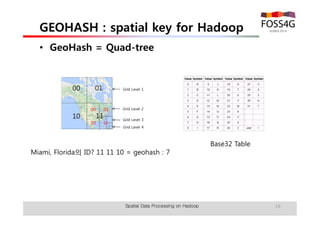
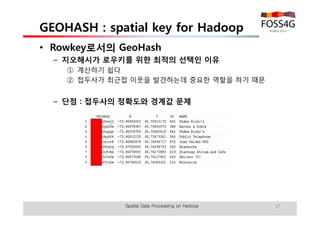
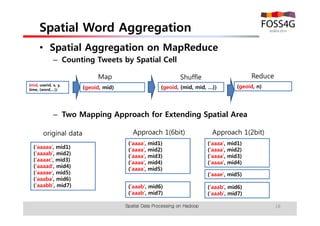
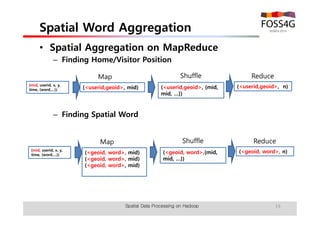
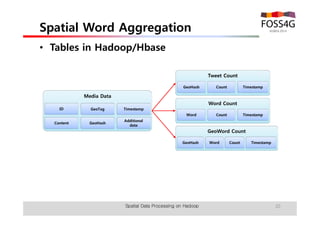
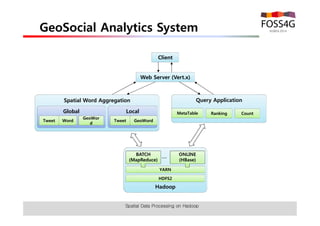
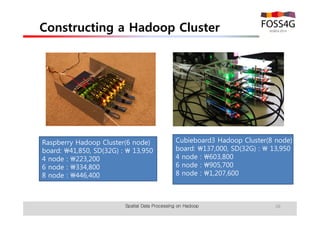
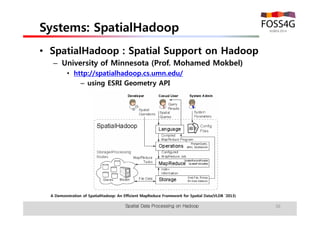
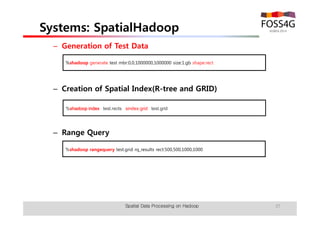
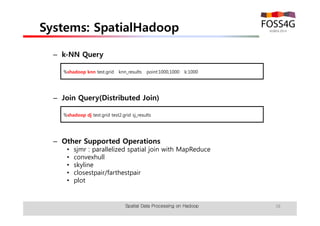
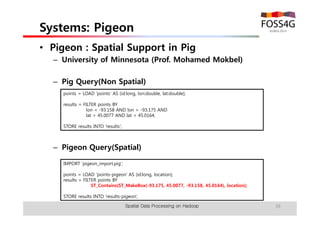
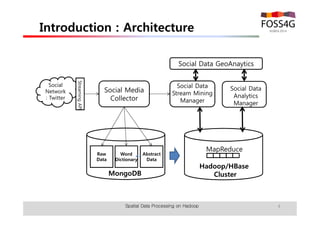
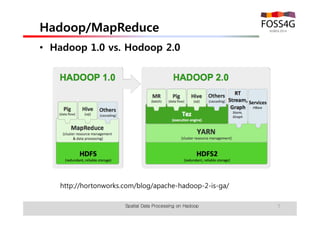
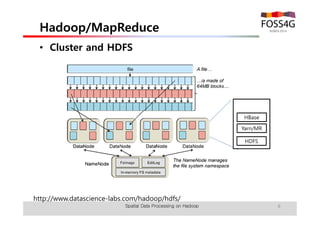
The document outlines methods for processing spatial big data using Hadoop and MapReduce, focusing on social media data, particularly Twitter streams. It describes the architecture of a Hadoop cluster, the use of geohashing for spatial keys, and spatial aggregation techniques for analyzing large datasets. The document also highlights the construction and management of big data systems, with practical insights and tools from ESRI for optimizing geospatial data processing.




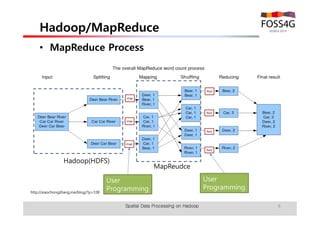
![MapReduce
• Collected Tweet Data
• Twitter Inner Data Model
1
n
n
m
n m
following
count …
1 1
follower
count
Spatial Data Processing on Hadoop 10
{
“mid” : “1234567”,
"filter_level":"medium",
"contributors":null,
"text":"역시 다 멋있다 #EVERYBODY",
"geo":{
"type":"Point",
"coordinates":[37.3604652, 127.9554015]
},
"retweeted":false,
"created_at":"Fri Oct 11 10:32:52 +0000 2013",
"lang":"ko",
"id":388613160678088700,
"retweet_count":0,
"favorite_count":0,
"id_str":"388613160678088704",
"user":{
"lang":"ko",
"id":1394439386,
"verified":false,
"contributors_enabled":false,
"name":"은지",
"created_at":"Wed May 01 11:32:39 +0000 2013",
"geo_enabled":true,
"time_zone":"Seoul",
“follower_count":93,
“following_count”:30,
“favorate_count”: 105,
"id_str":"1394439386",
}
}
user tw tweet
fol fav
• Real Collected Twitter Data
userlog tw tweet](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/foss4g2014hadoop-geohash-v02-140829035316-phpapp02/85/FOSS4G-KOREA-2014-Hadoop-MapReduce-Spatial-Big-Data-10-320.jpg)