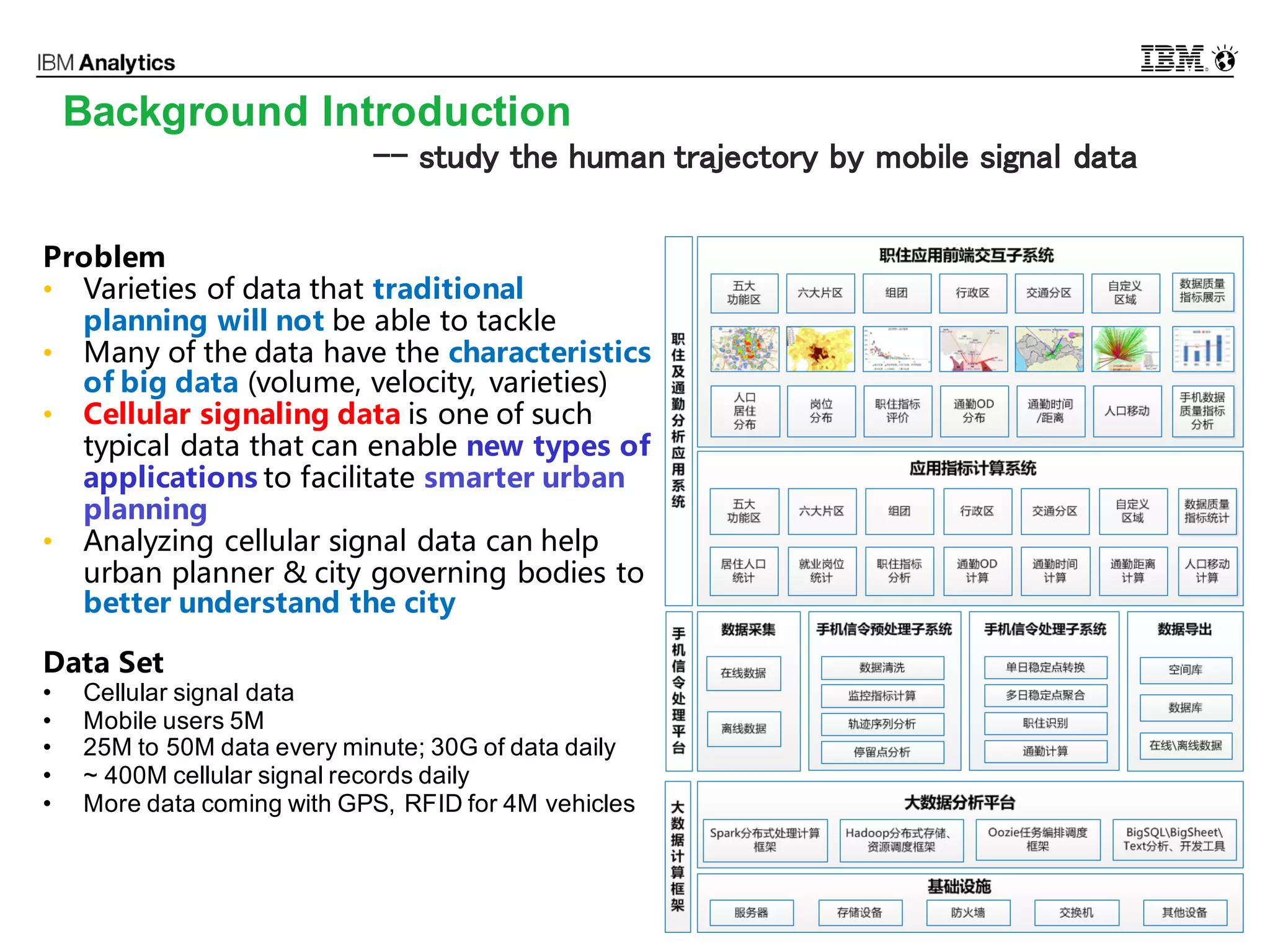
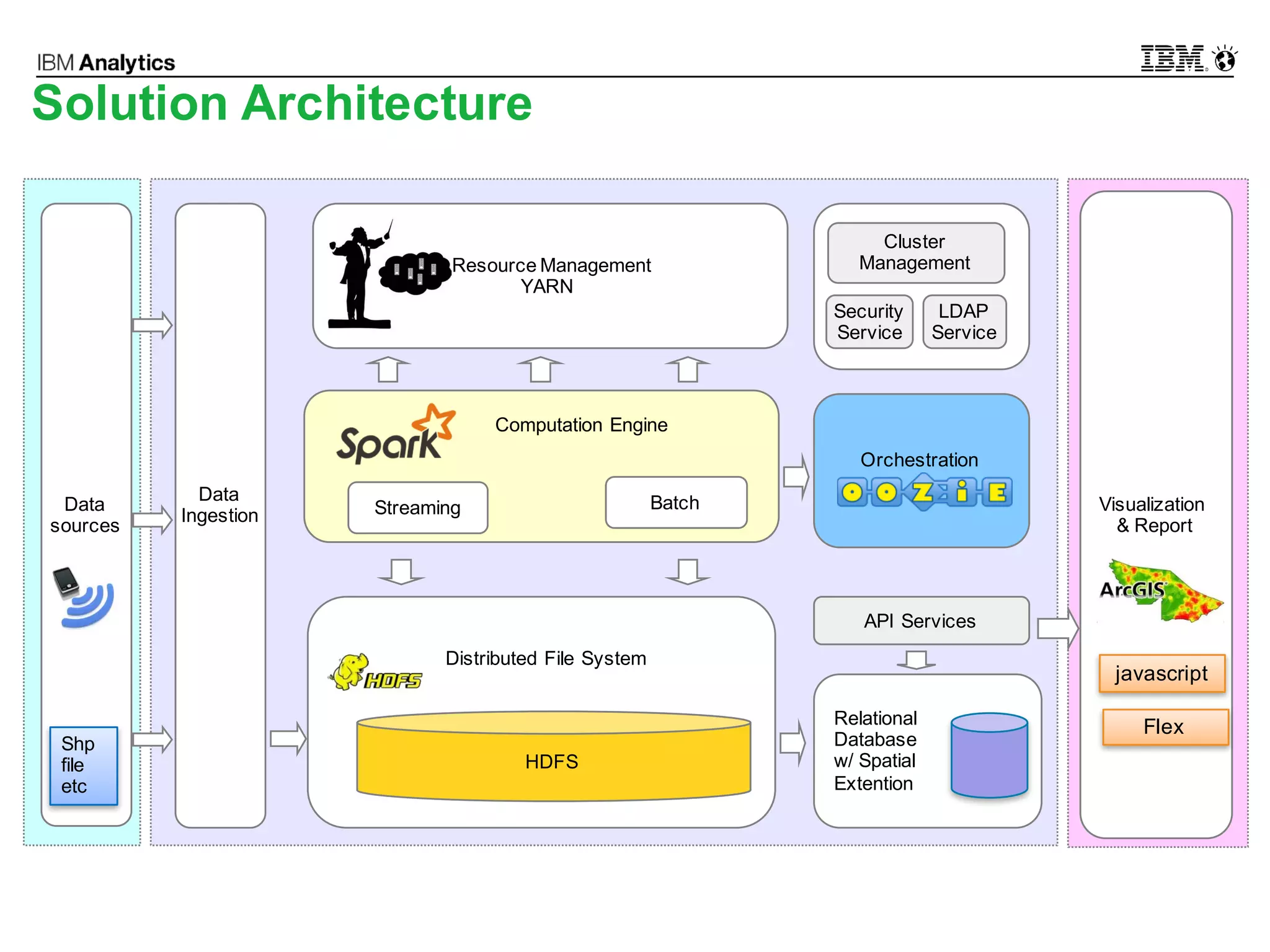
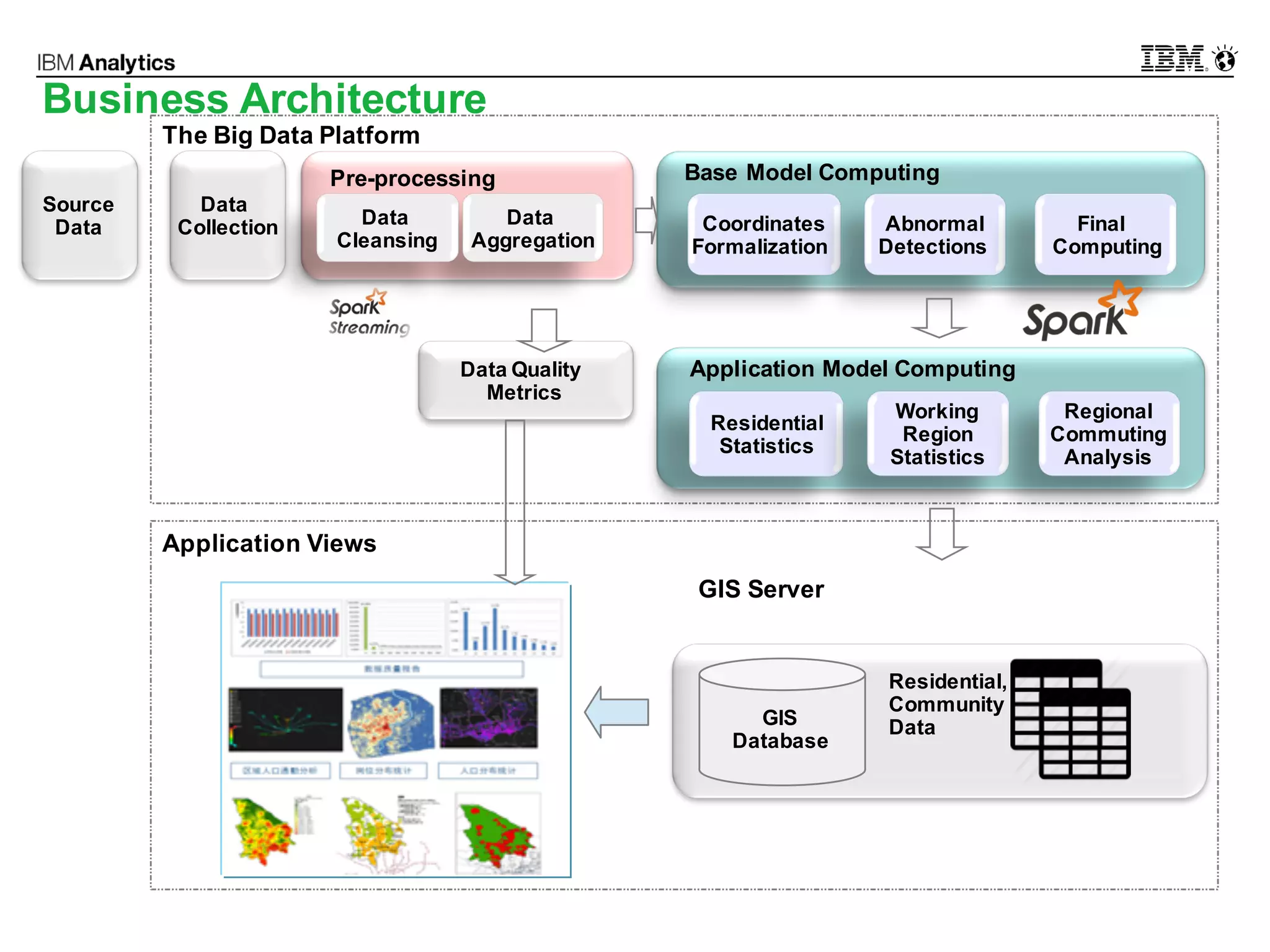
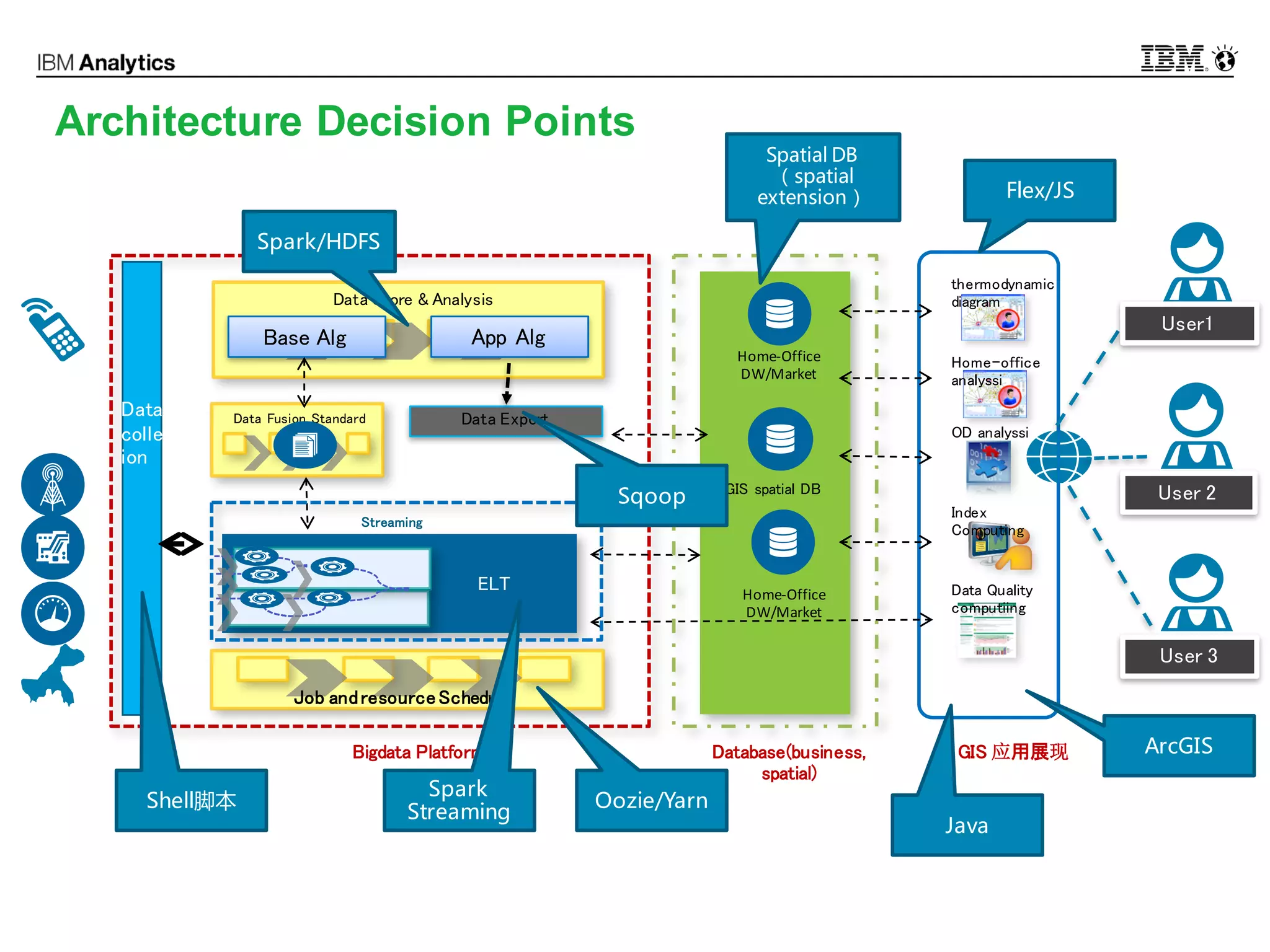
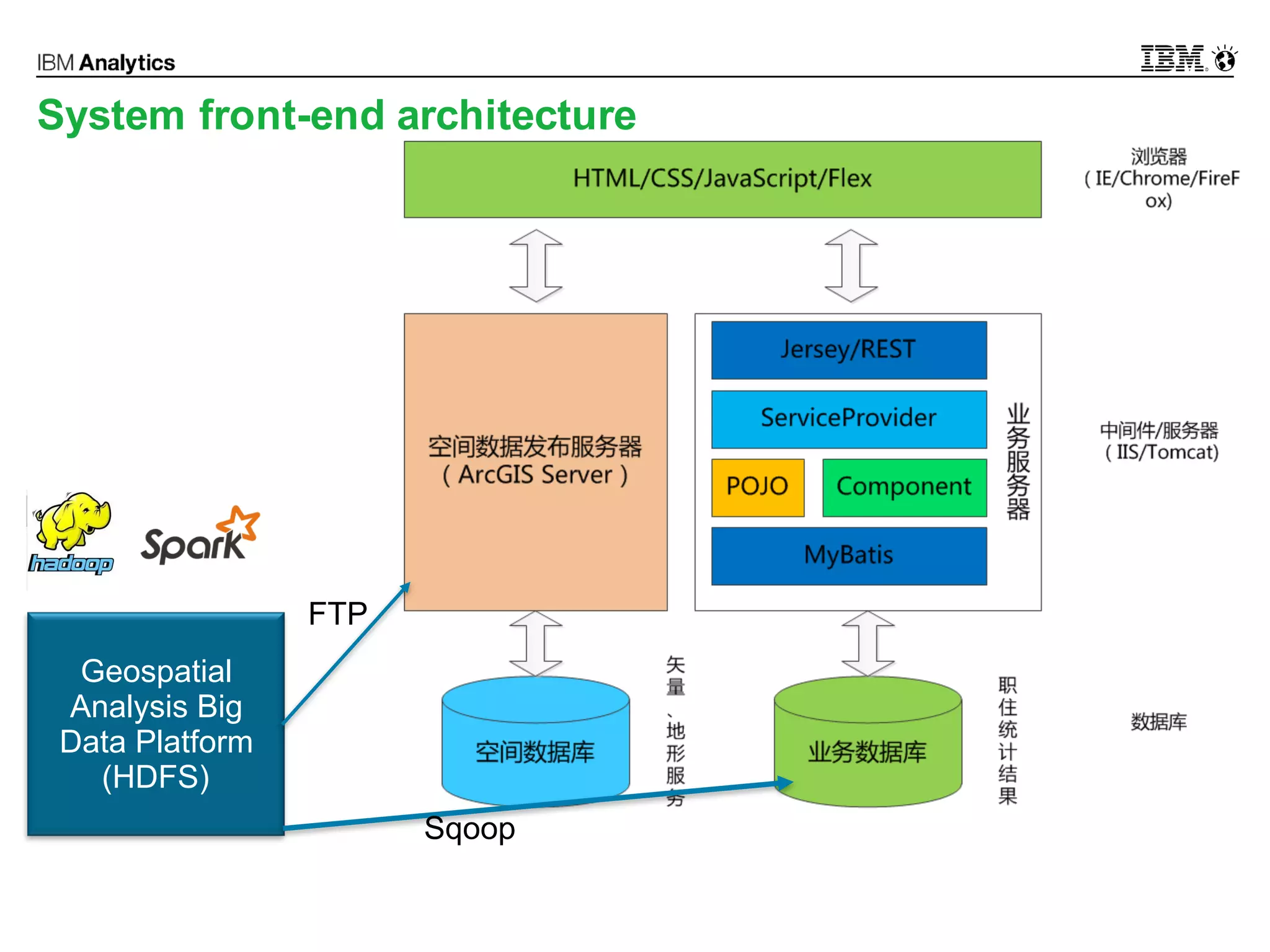
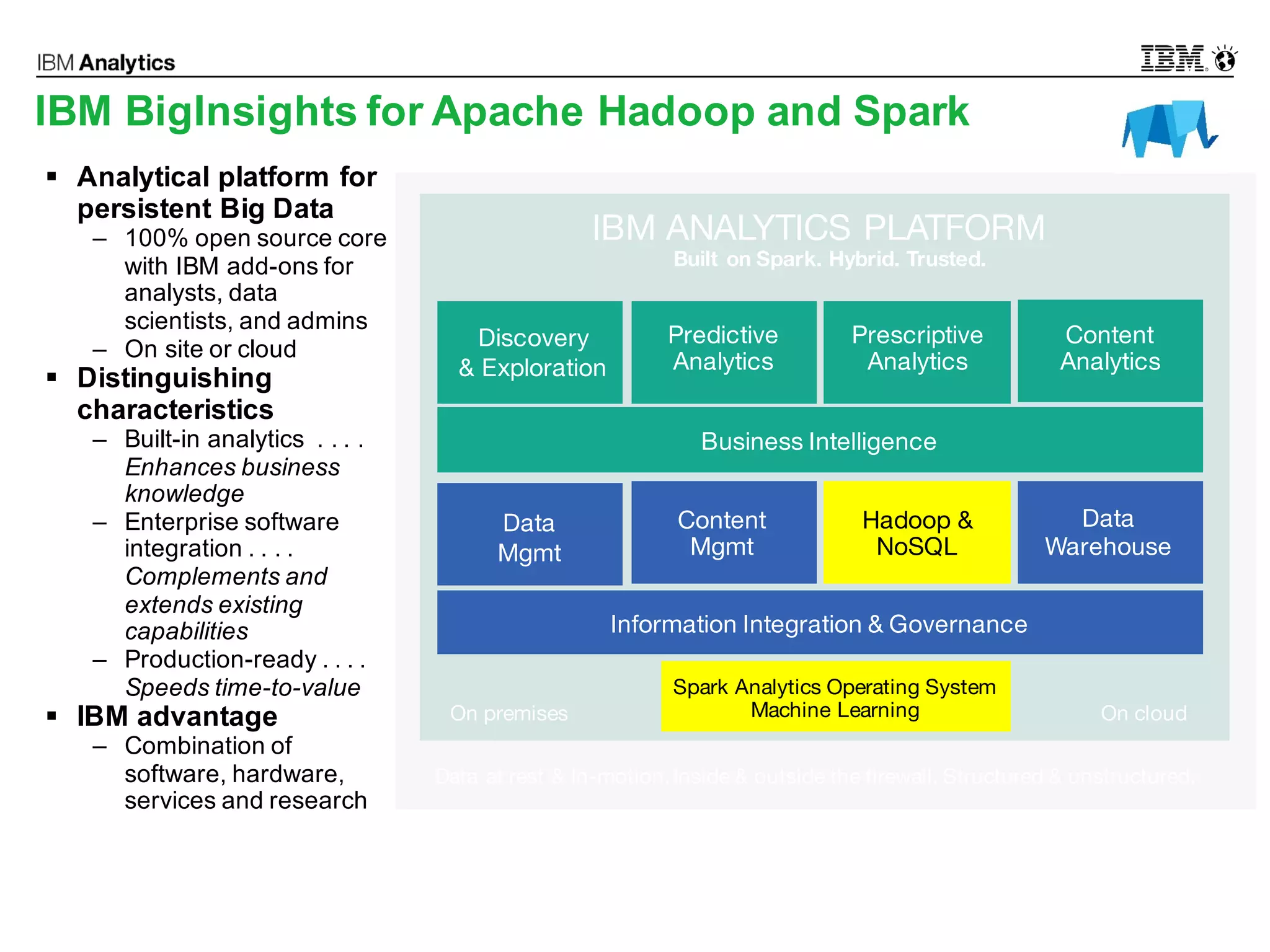
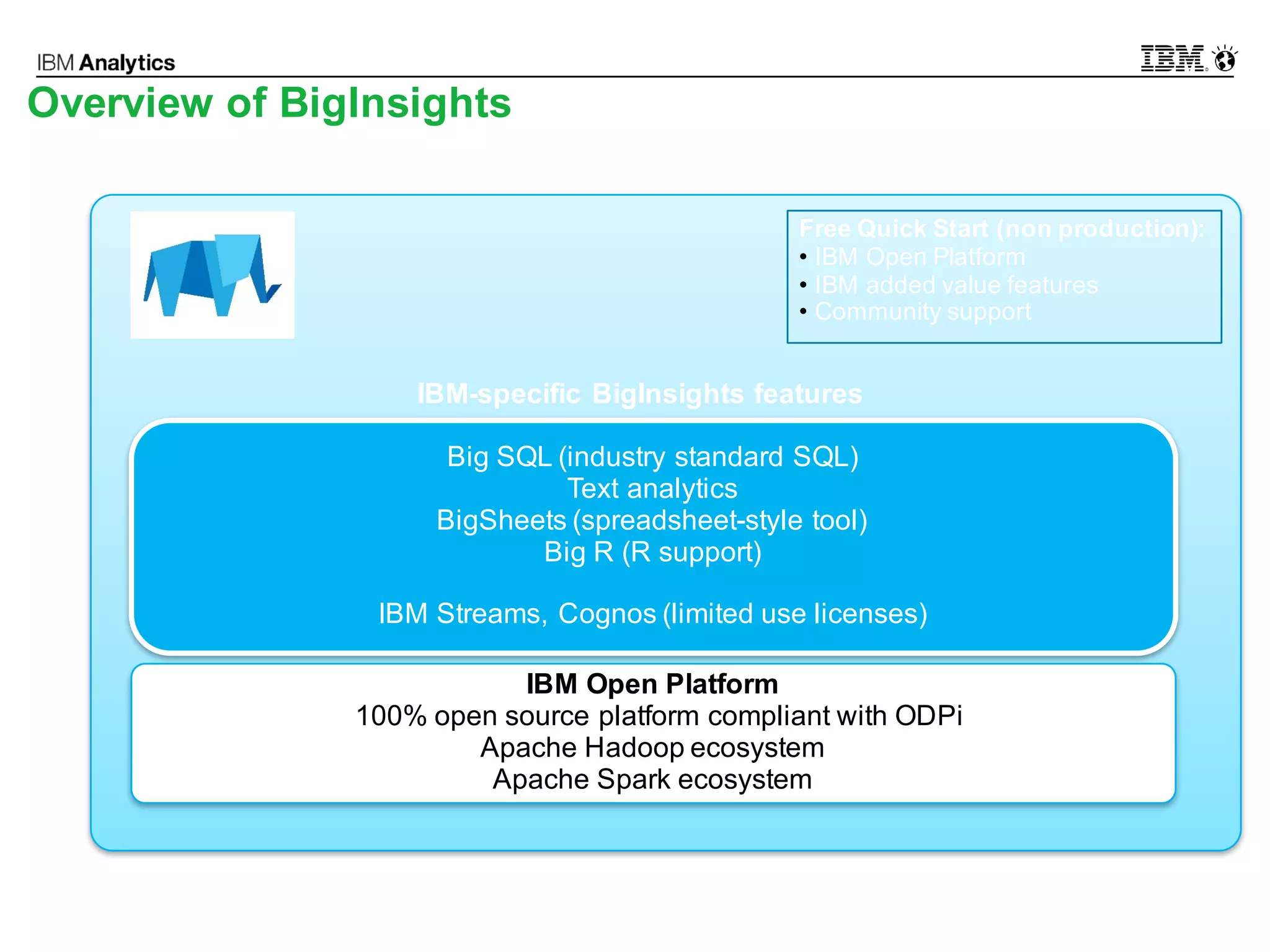
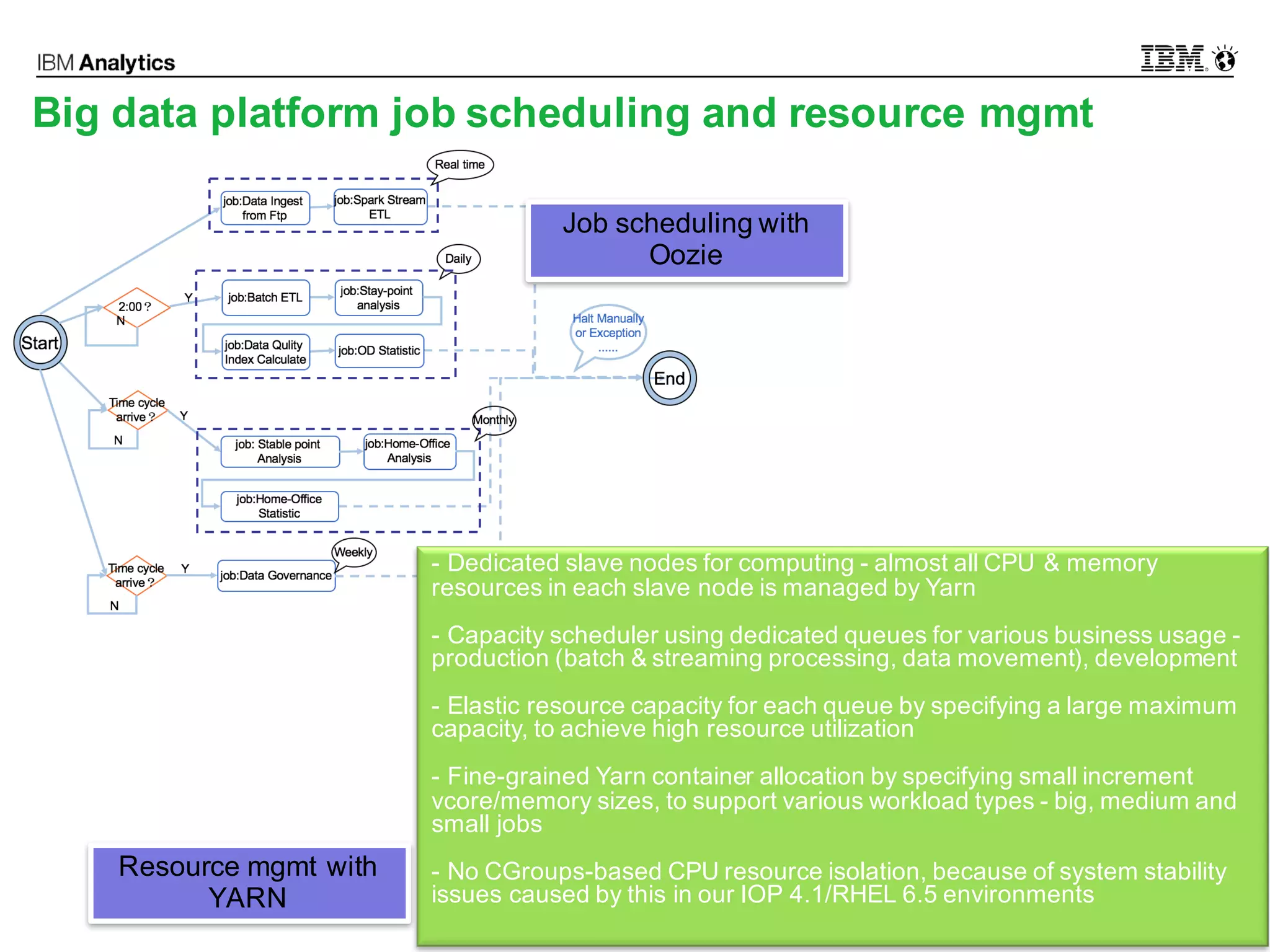
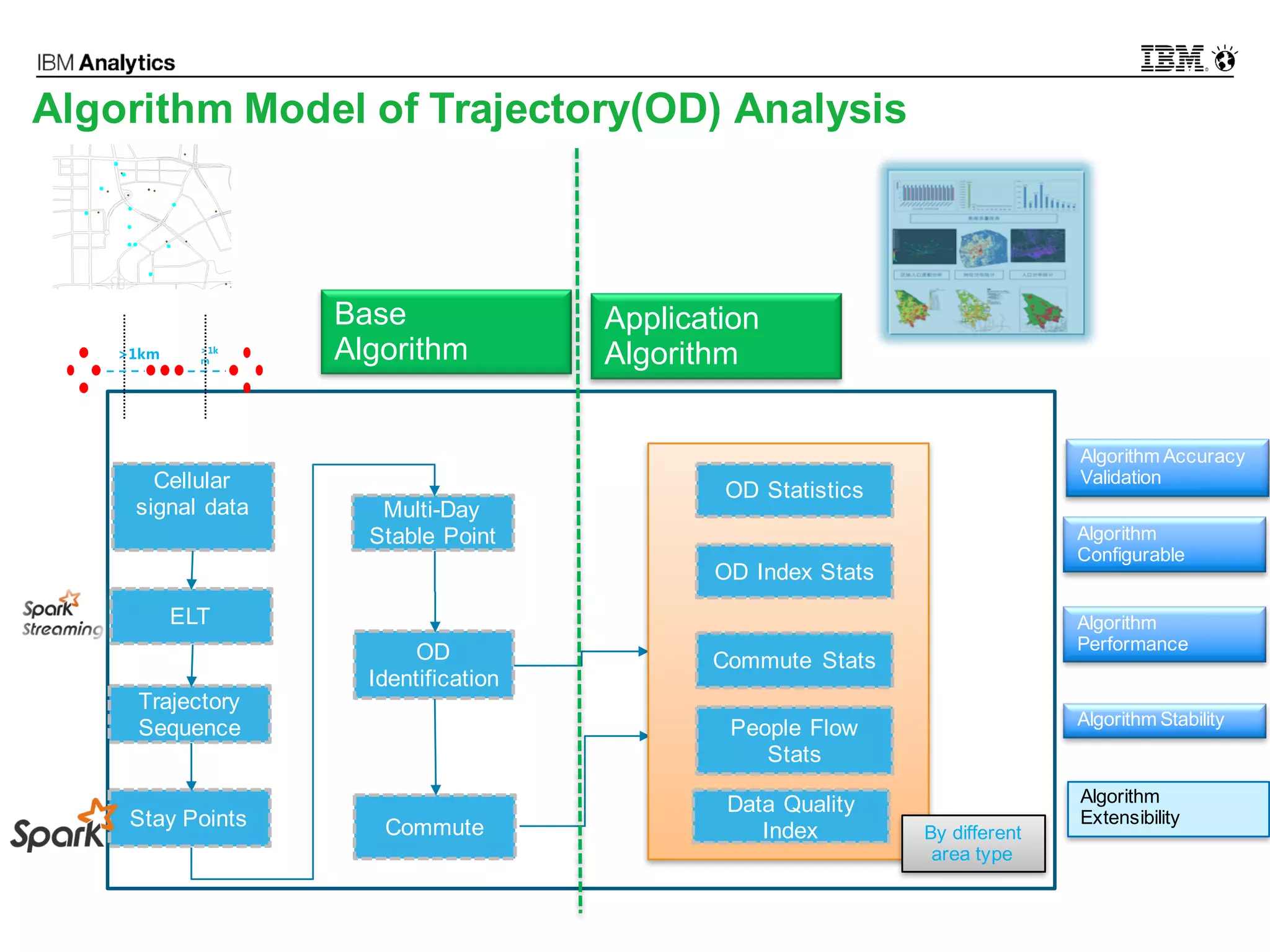
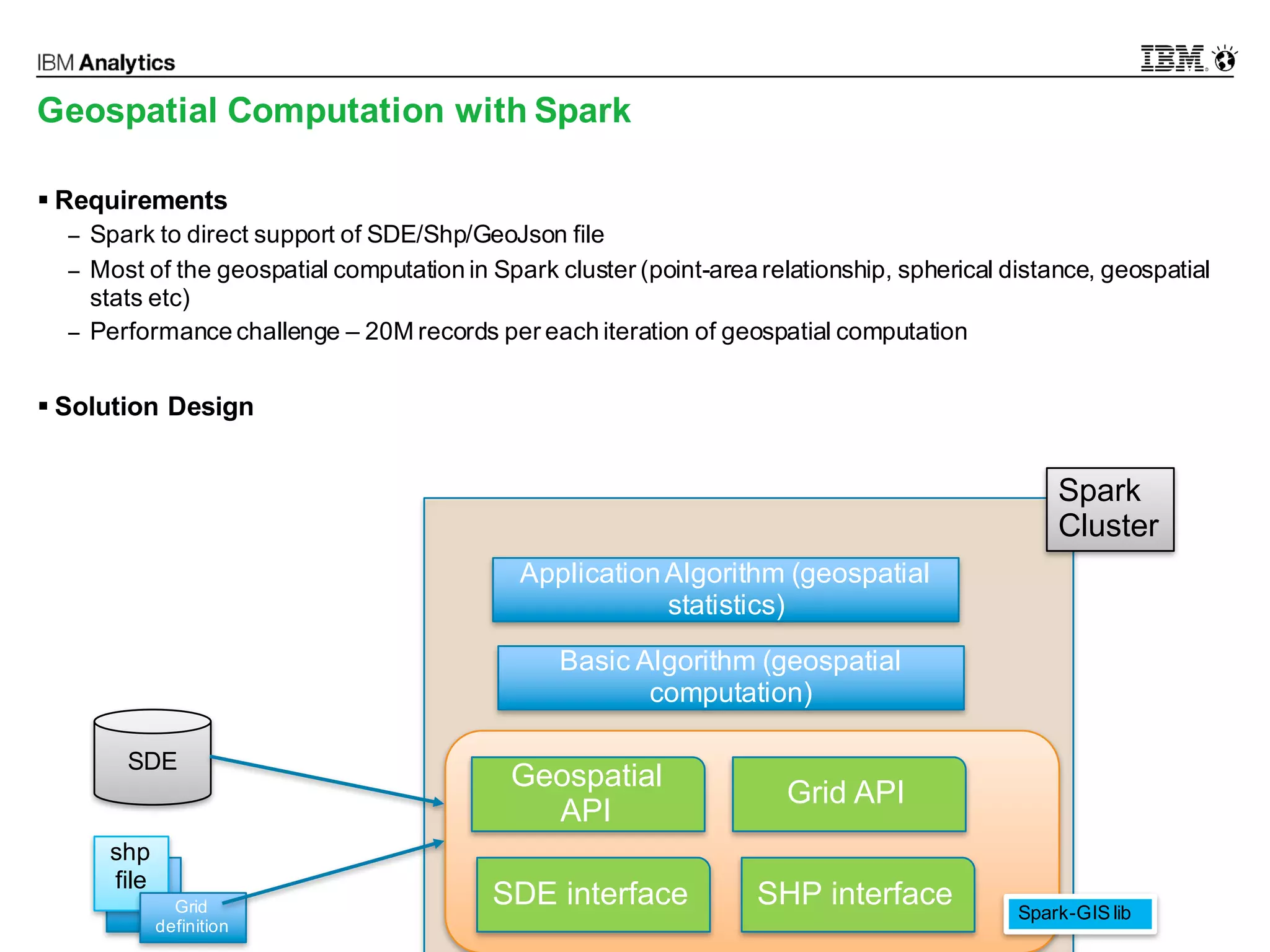
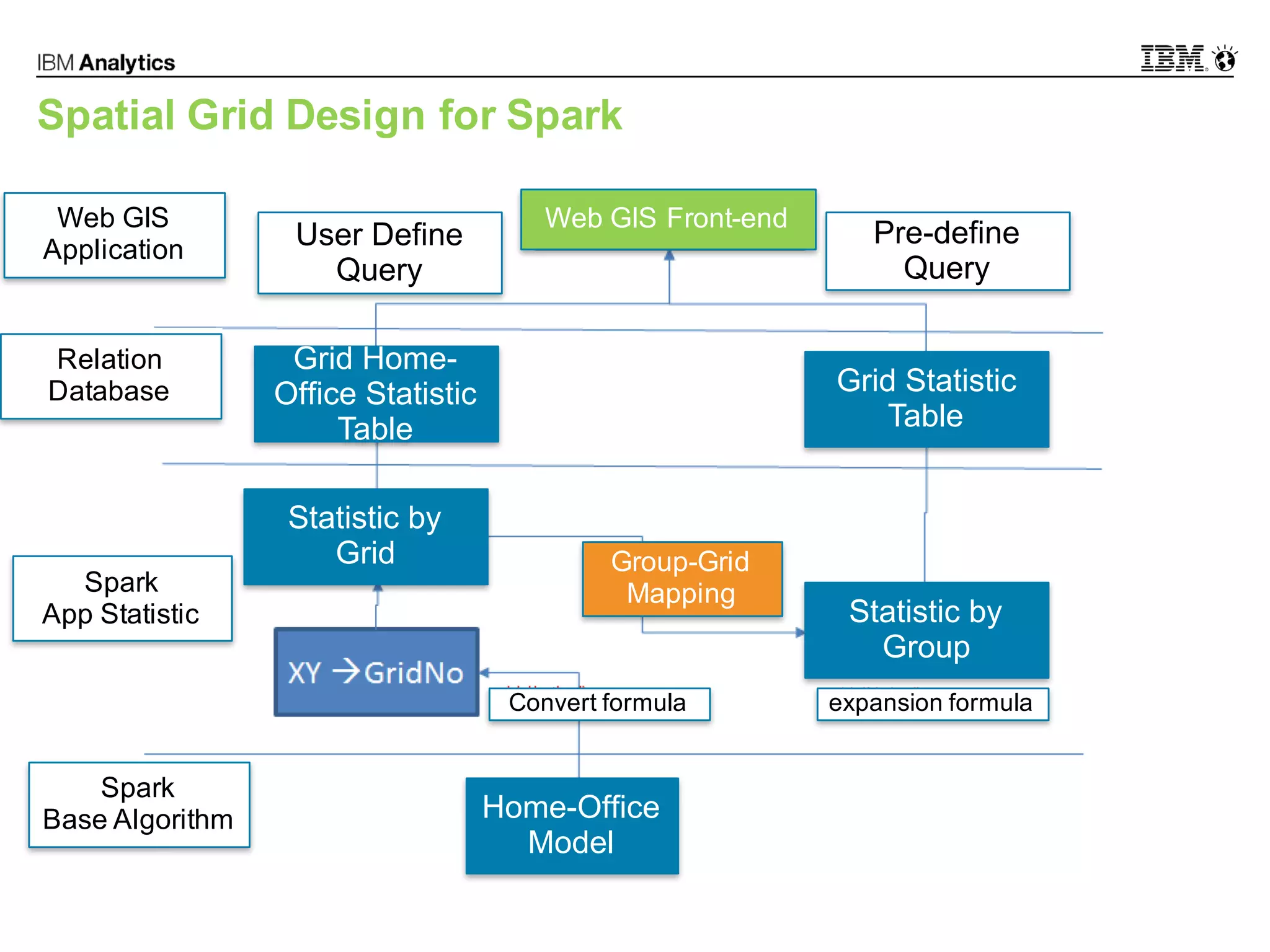
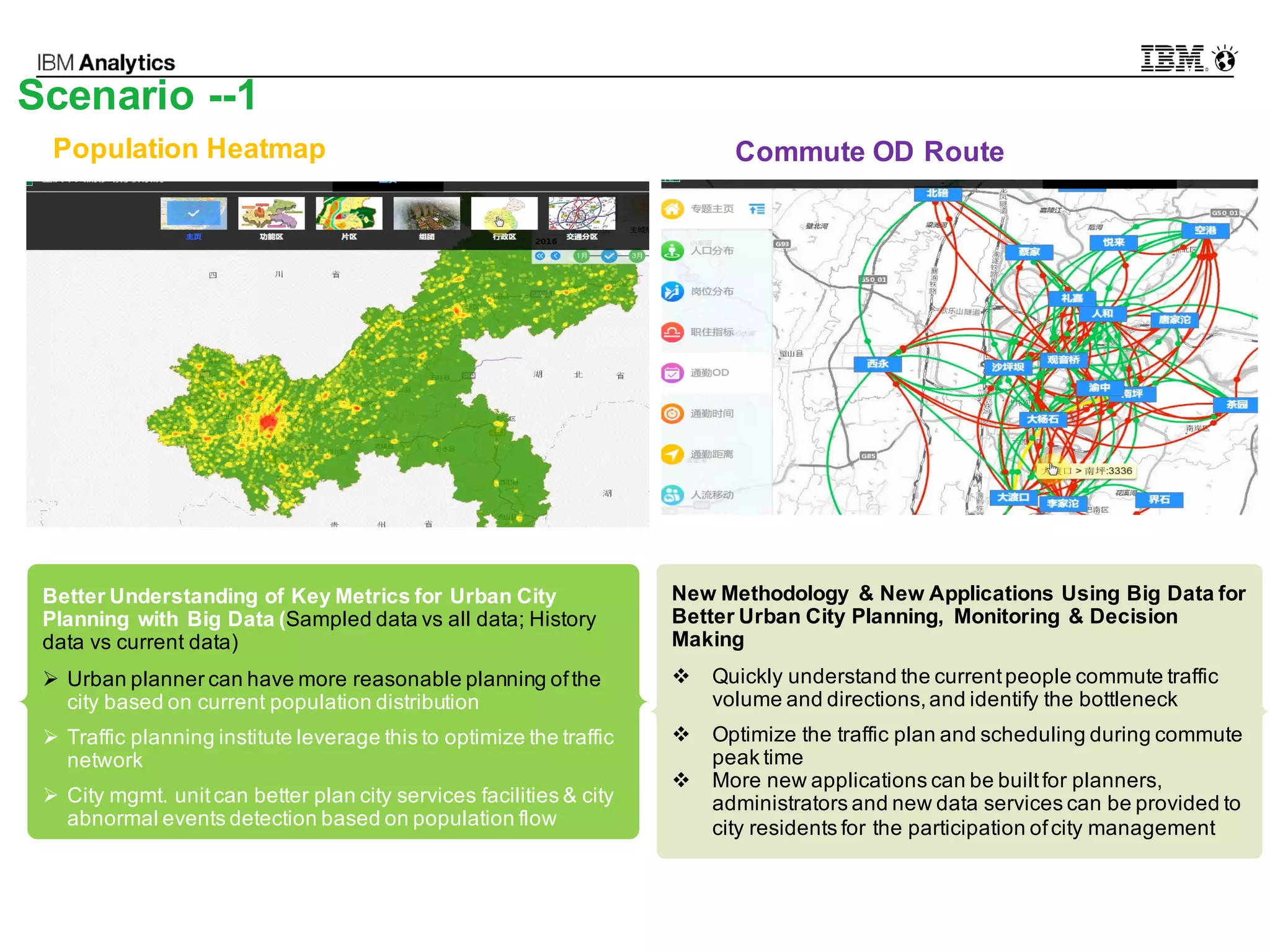
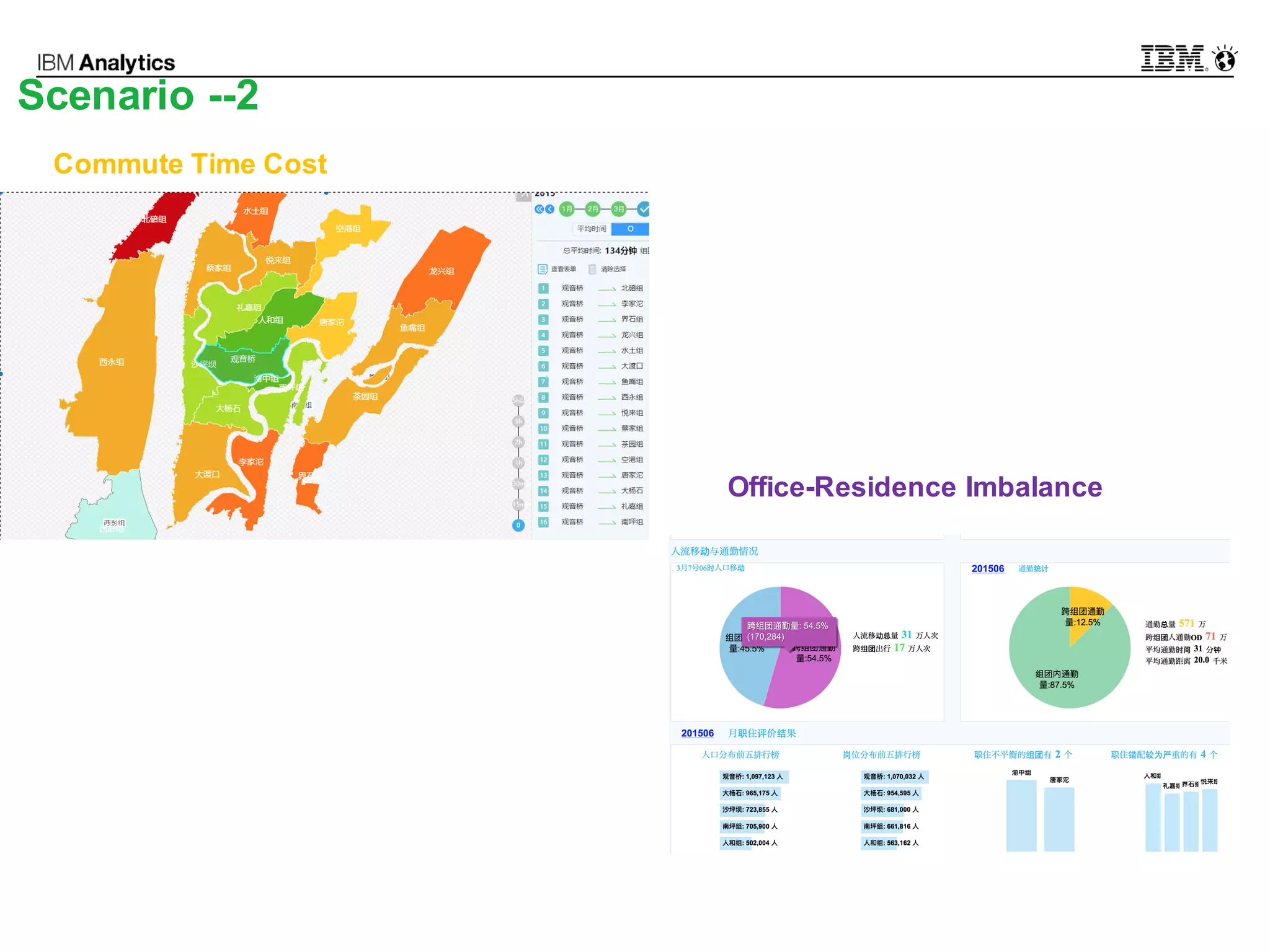
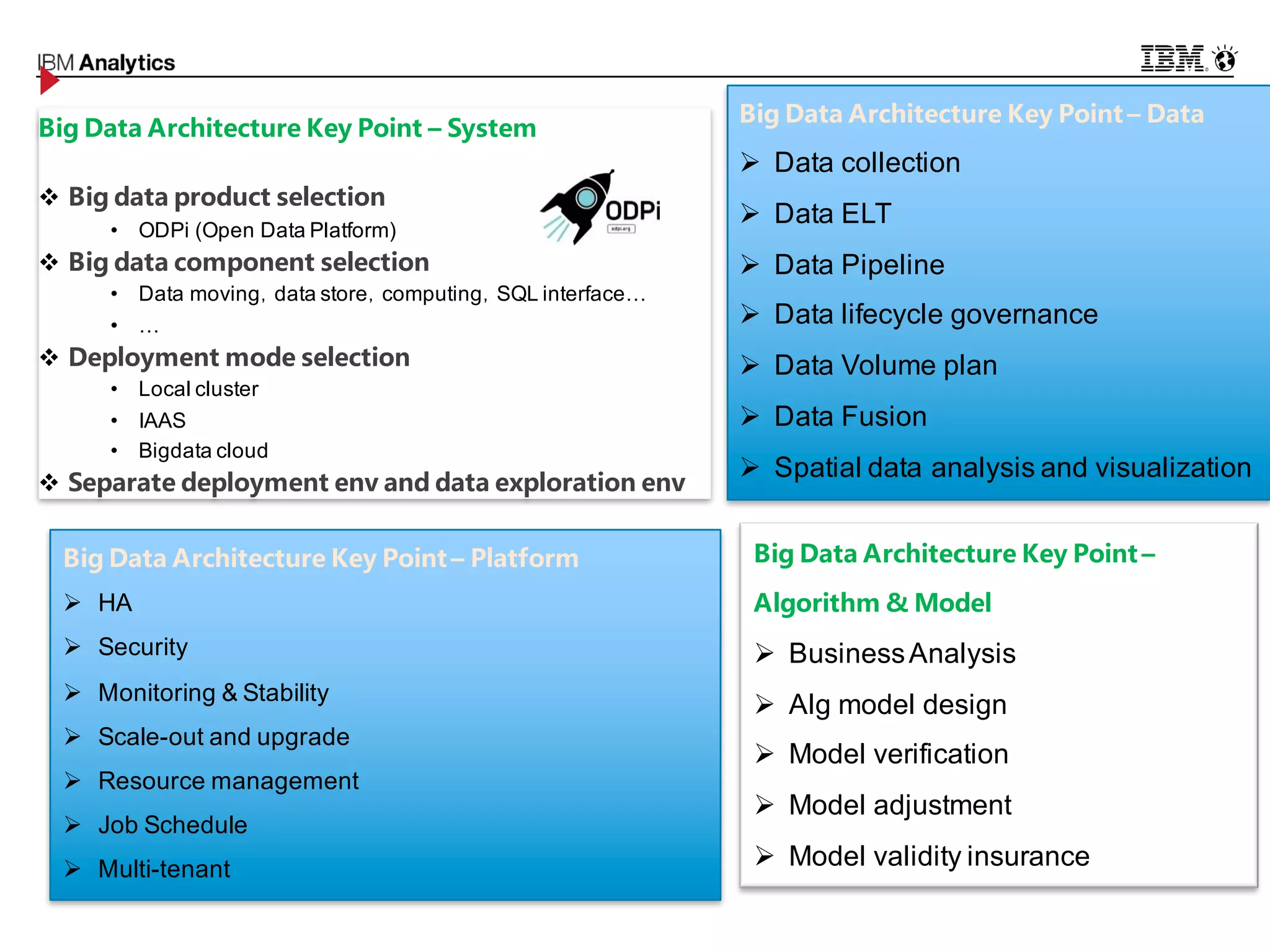
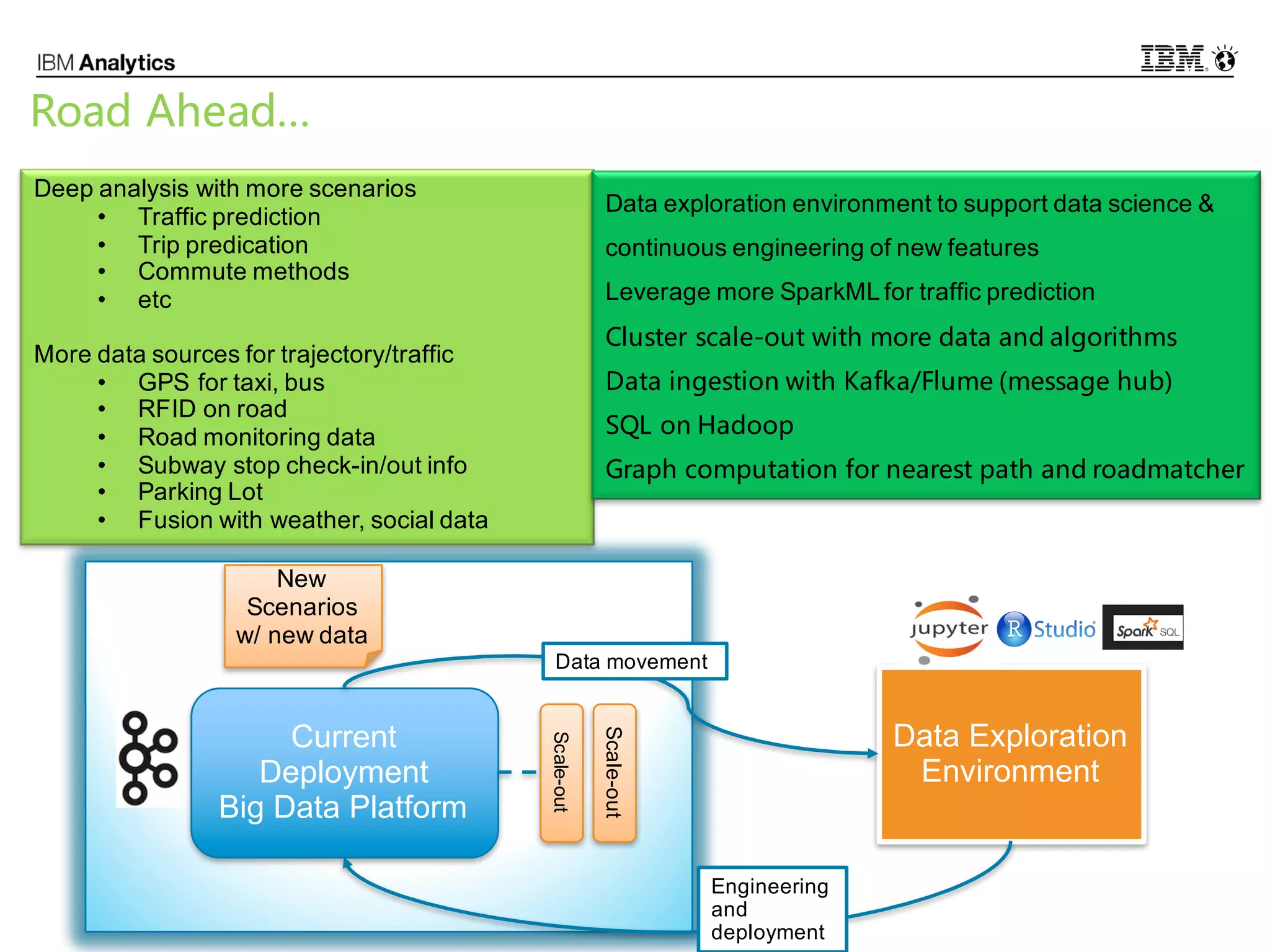
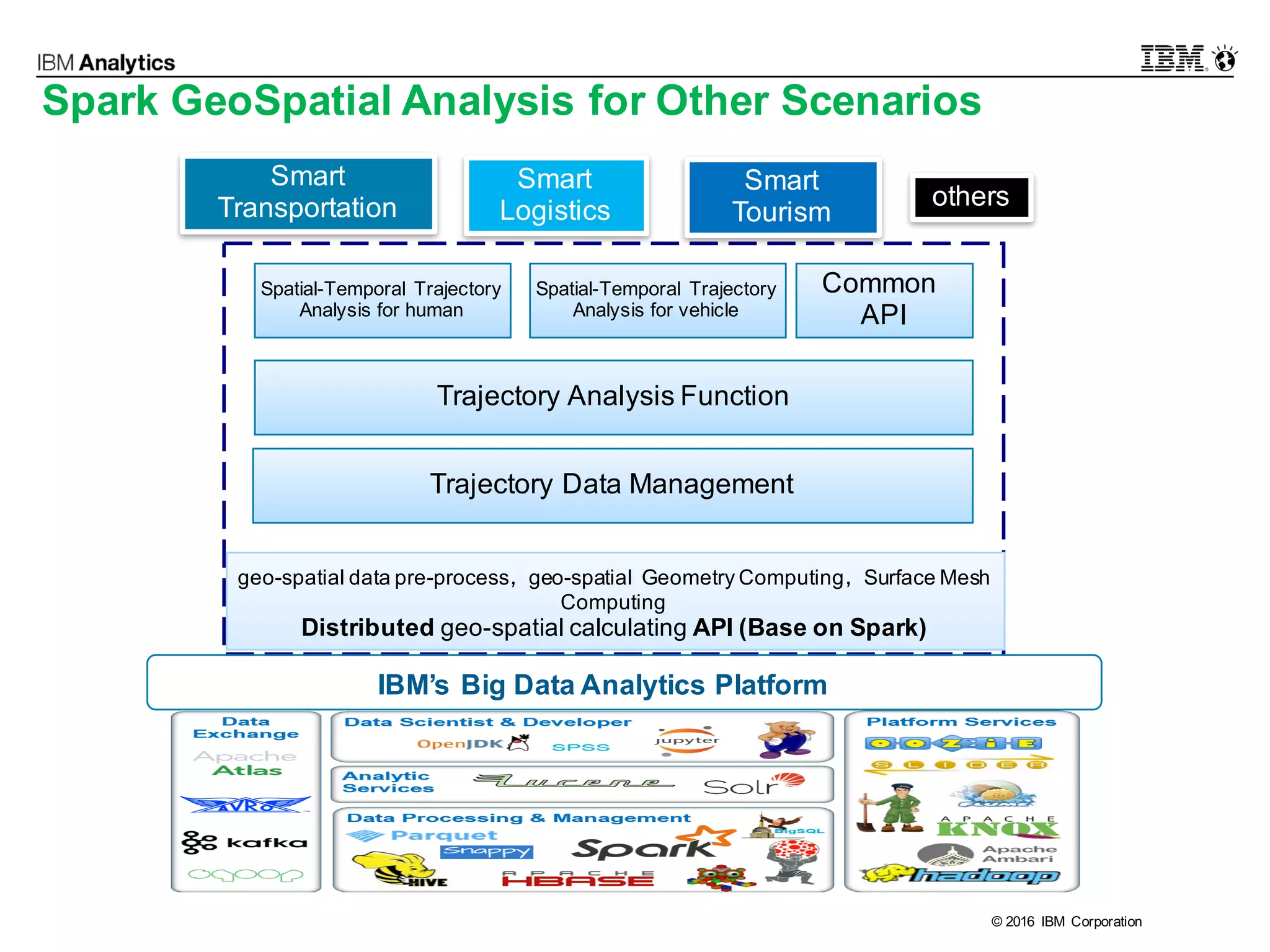
This document discusses high performance spatial-temporal trajectory analysis using Spark. It covers the background of analyzing mobile signaling data to enable smarter urban planning. The solution architecture includes data sources, distributed file system, computation engine, and visualization. Technical designs address the big data platform, data governance, algorithm models, and Spark spatial computing. Example scenarios are presented for population heatmaps, commute routes, and office-residence imbalance analysis.