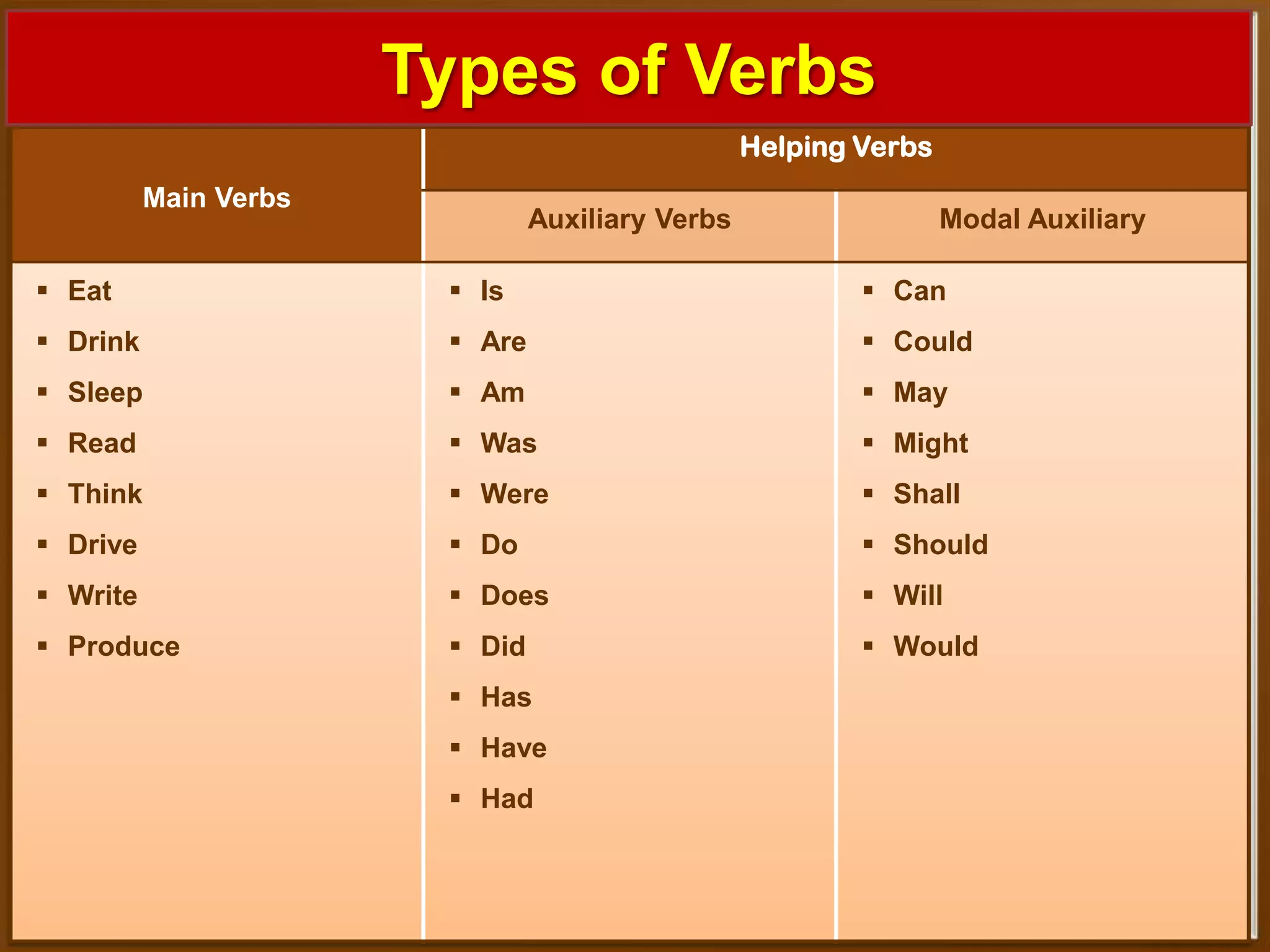
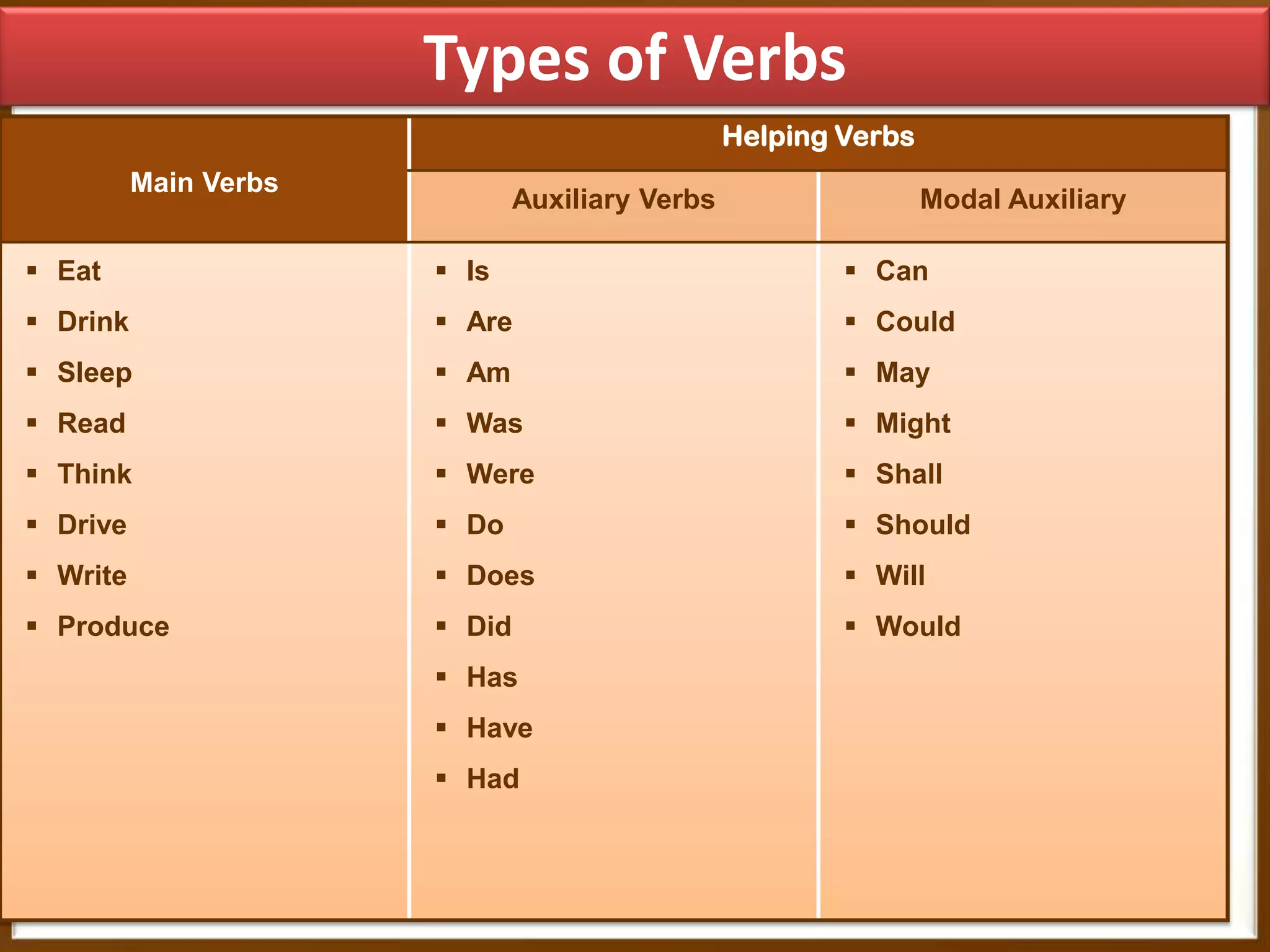
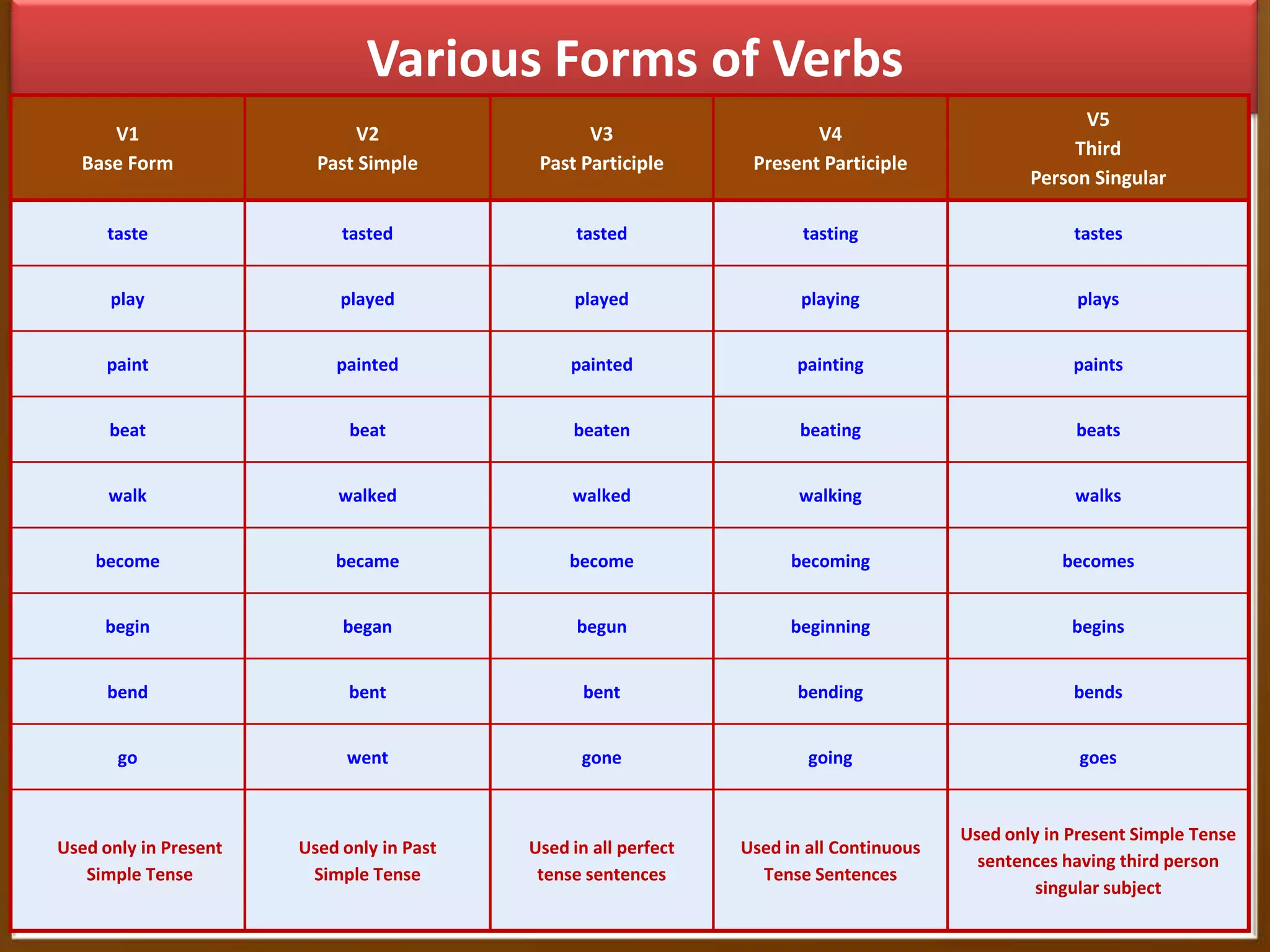
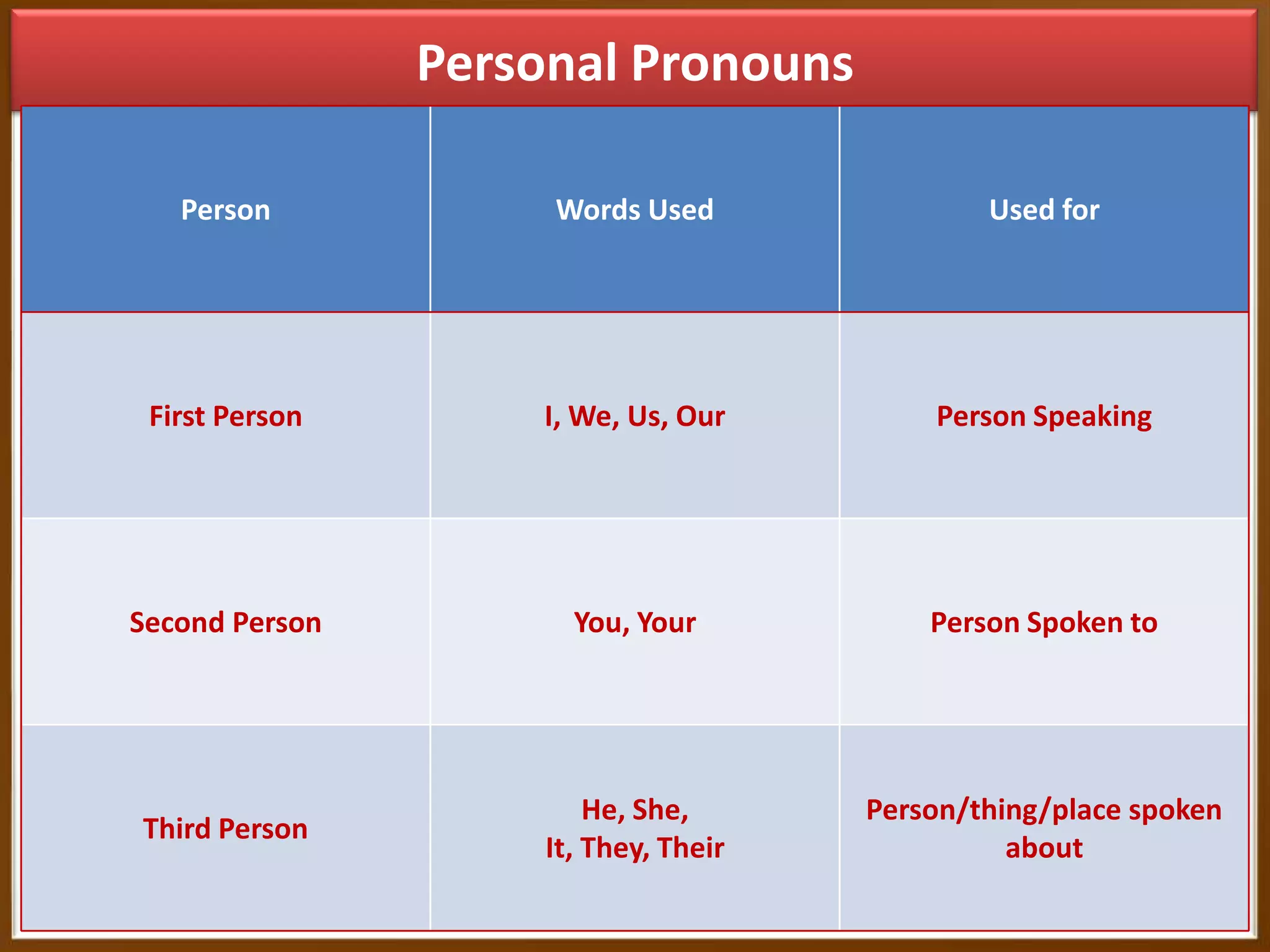
The document provides information on transforming sentences from affirmative to negative and interrogative. It discusses the three types of sentences - affirmative, negative, and interrogative. For negative sentences, it outlines adding "not" between the helping verb and main verb for sentences with helping verbs, and using "do/does/did + not" before the main verb for sentences without helping verbs. For interrogative sentences, it describes starting sentences with a helping verb or wh-word and placing wh-words before sentences with helping verbs. Formulas and examples are given for changing sentence structures.