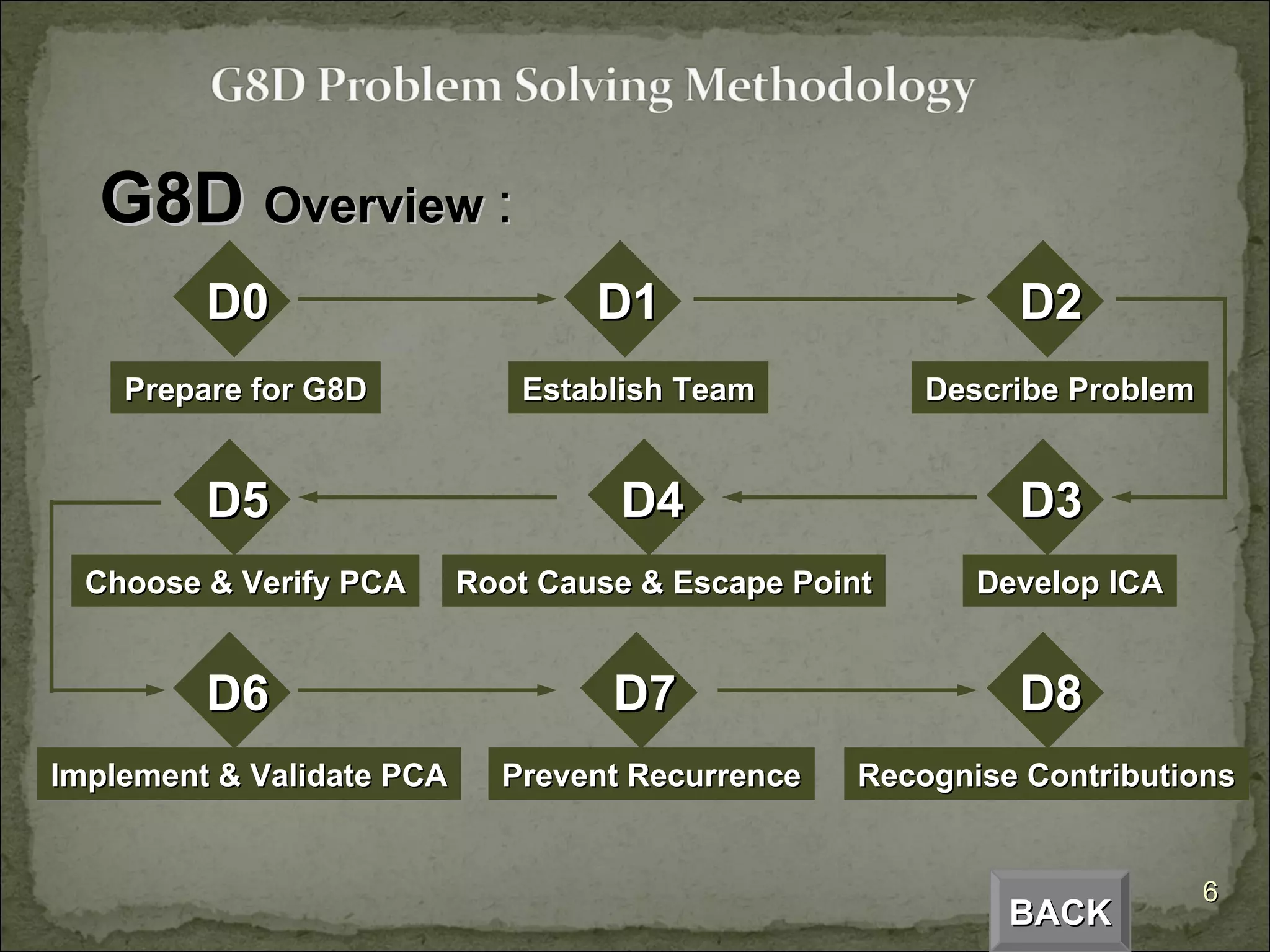
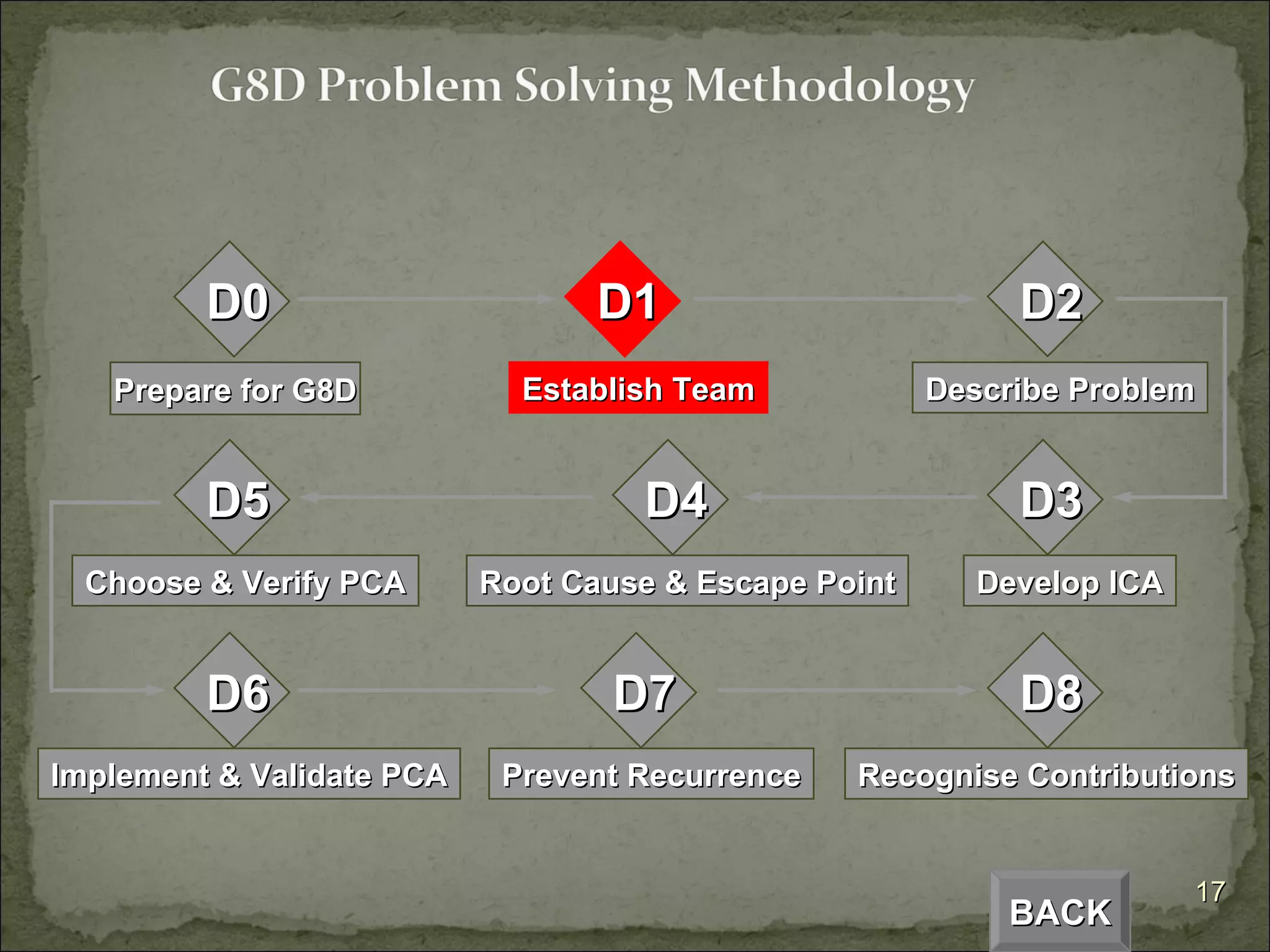
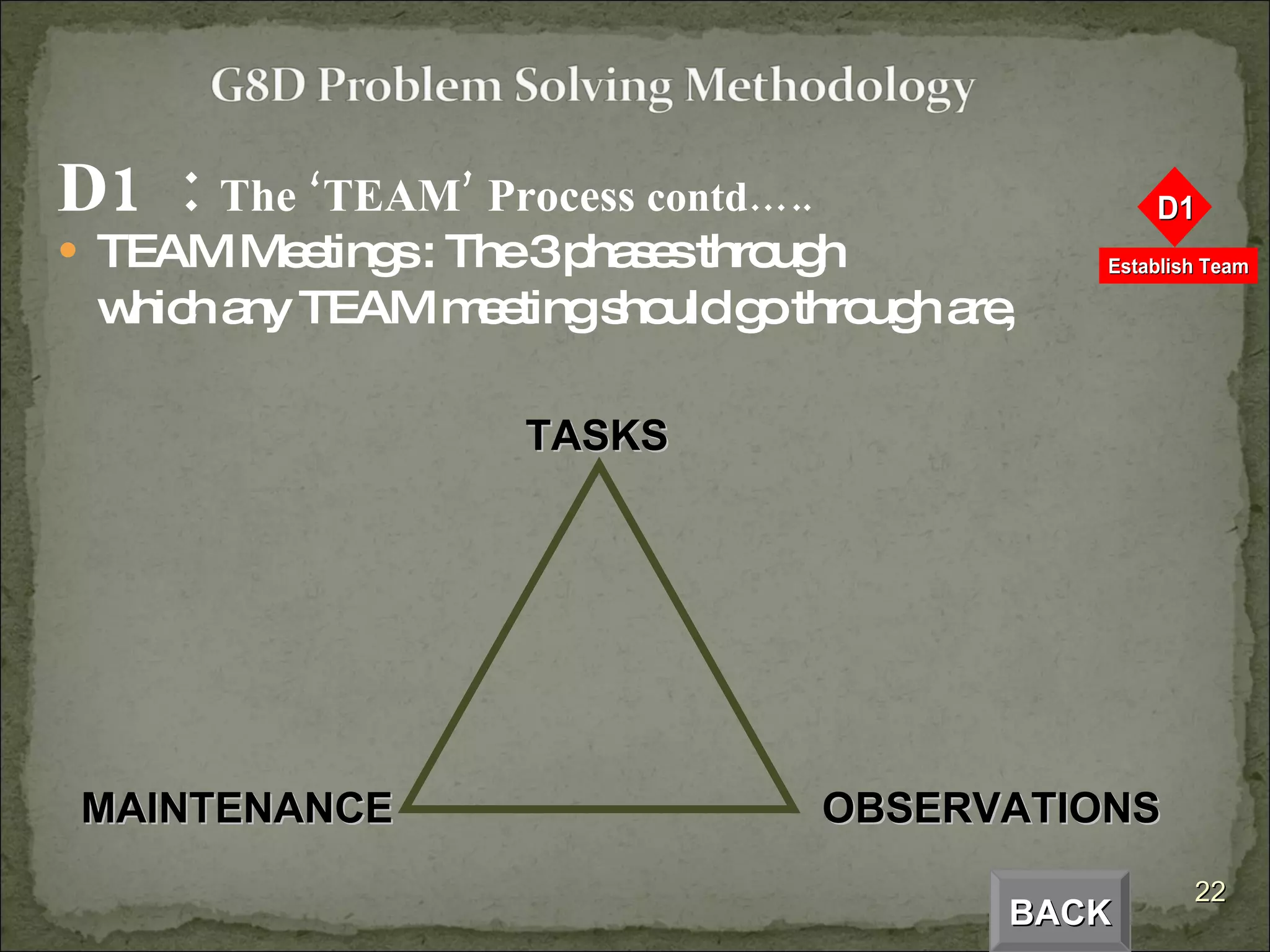
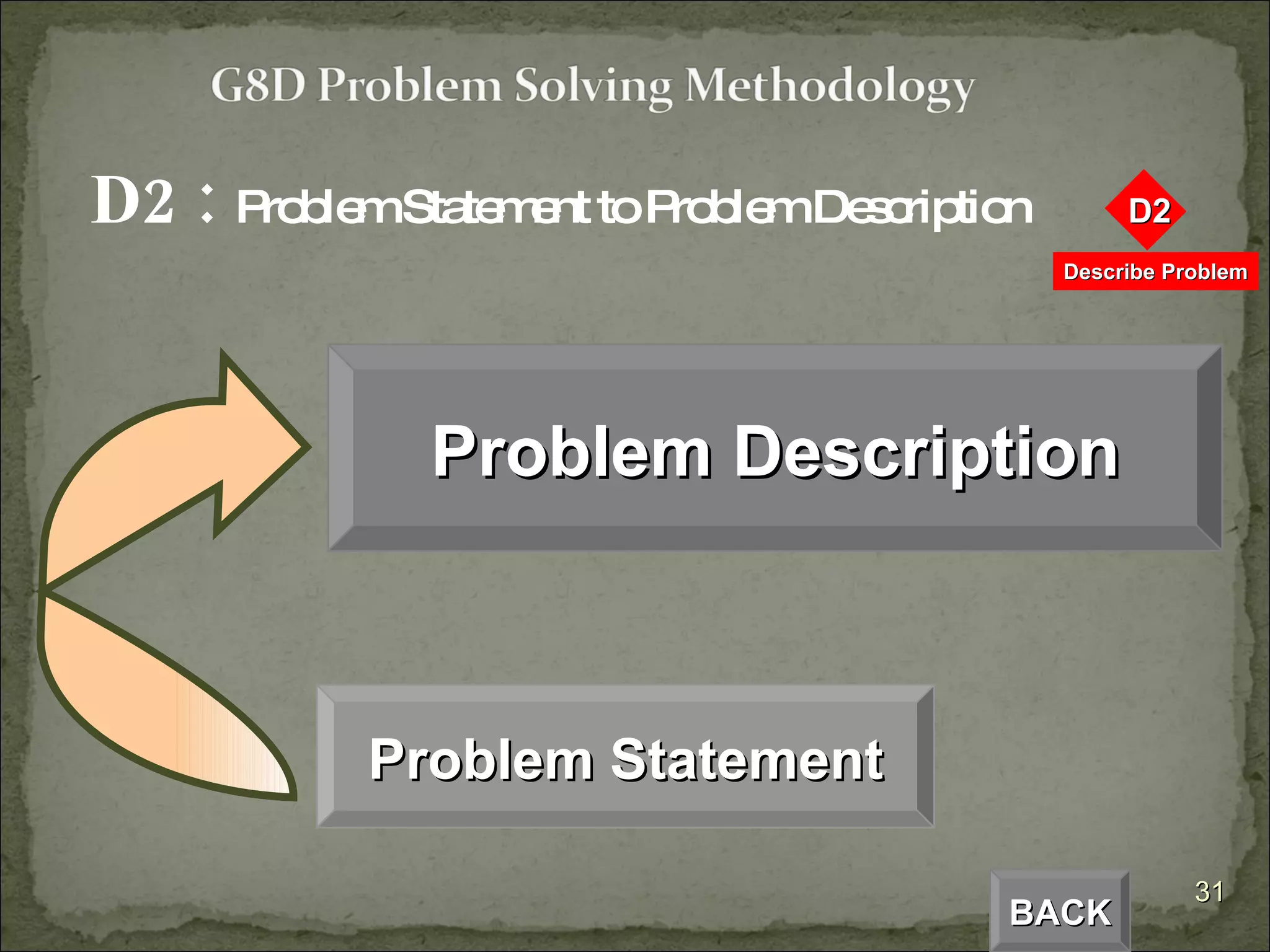
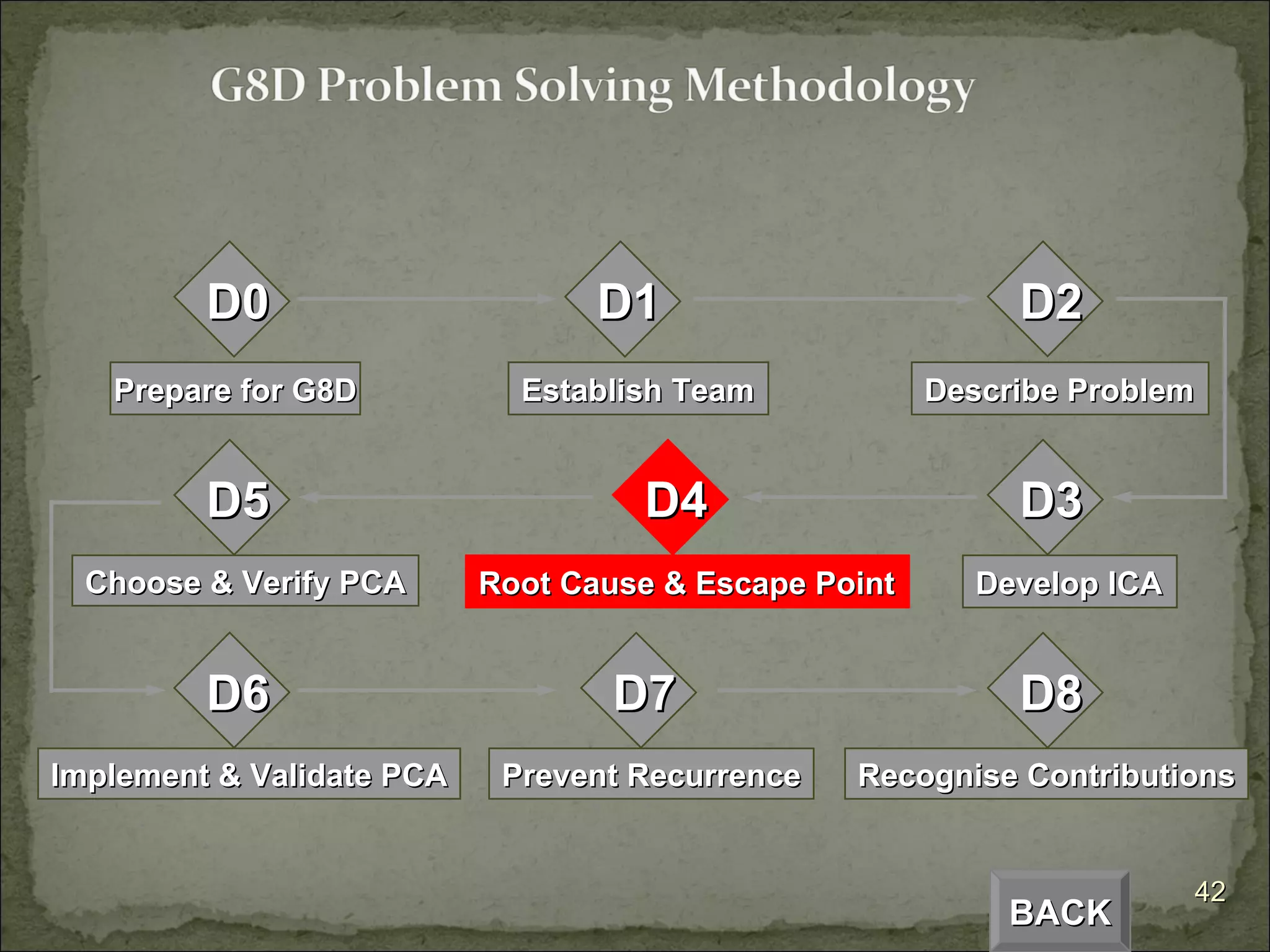
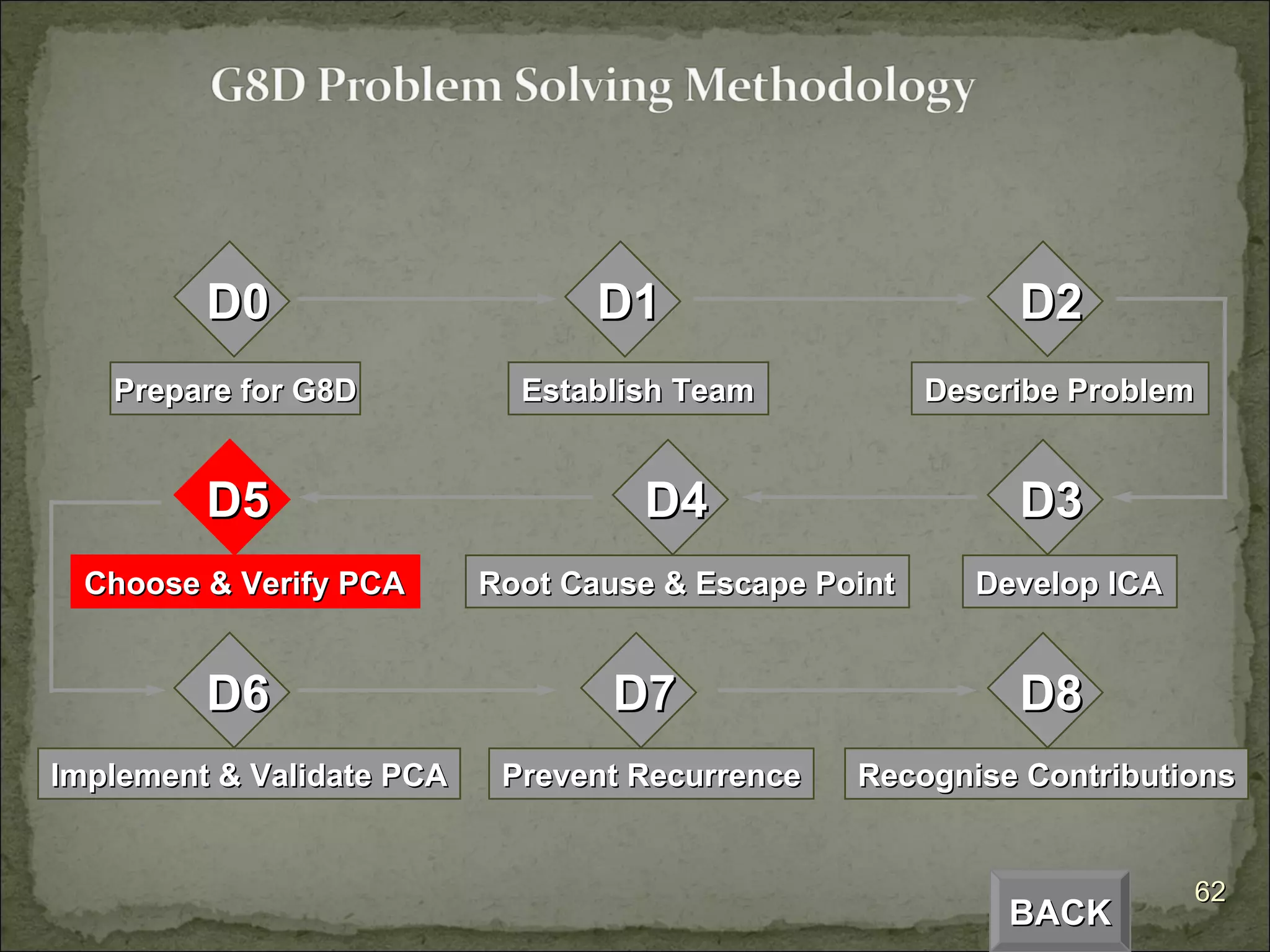
The document provides an overview of the Global 8D problem solving process. It describes the 8 steps (D0 to D8) involved in resolving issues using a standardized approach. The steps include establishing a team, describing the problem, analyzing the root cause, developing and implementing corrective actions, and ensuring the issue does not recur. The 8D process is designed to systematically drive to the root cause of problems and implement permanent solutions.