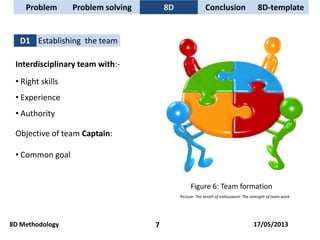
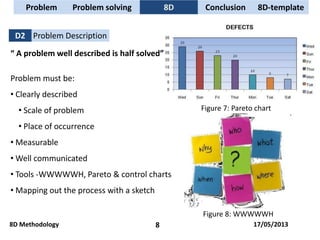
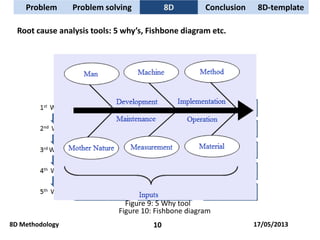
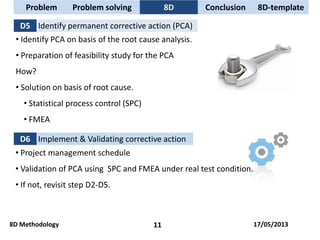
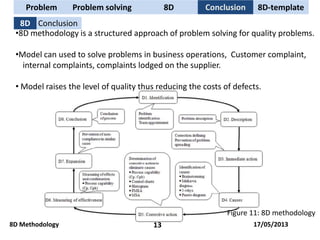
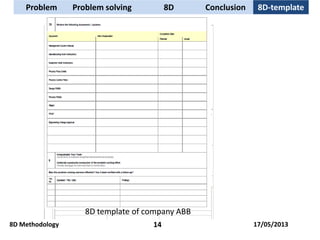
The document discusses problem solving techniques, specifically the 8D methodology. It provides an overview of the 8D methodology, which is an eight-step problem solving process used to solve quality problems. The eight steps are: 1) establishing a team, 2) describing the problem, 3) containment actions, 4) root cause analysis, 5) identifying permanent corrective actions, 6) implementing and validating corrective actions, 7) preventing recurrence, and 8) congratulating the team. Tools that can be used with each step, such as fishbone diagrams, Pareto charts, and 5 whys, are also described.



![Problem Problem solving 8D Conclusion
8D Methodology 15
References
• Gerald F Smith, Quality problem solving, American society of quality, 1998.
• 6ixsigma.org, 8D book,
Available at: http://6ixsigma.org/8d-book.aspx [Accessed: 25 Apr 2013]
• Problem solving, Quality Management handbook, December 2005.
• Uzair Rajput, 8D- problem solving method, Quality management handbook
• Fideltronik, 8D-problem solving methodology
• Marjanca Krajnc, 8D-methodology, Journal of universal excellence, October 2012.
• Bill Arnott, 8D-problem solving methodology, Canada.
• ABB, 8D problem solving template, http://www05.abb.com/global[Accessed: 25 Apr 2013]
17/05/2013](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/improblemsolvingassignment1sandeep-130625024041-phpapp01/85/8D-problem-solving-15-320.jpg)
