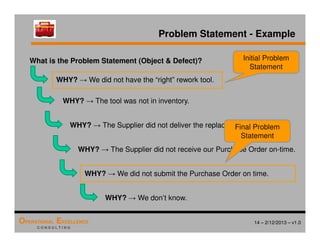
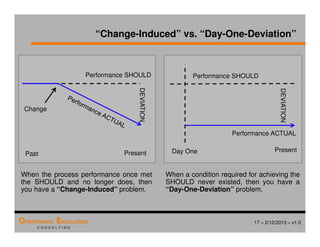
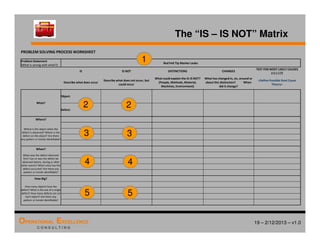
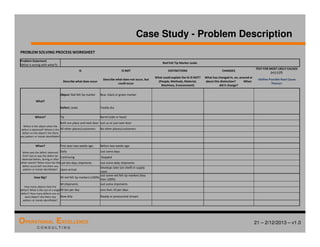
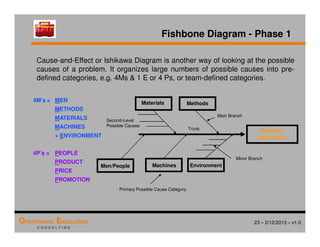
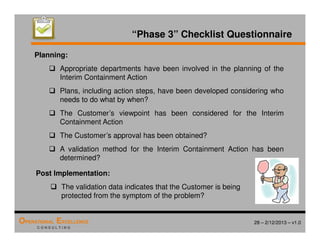
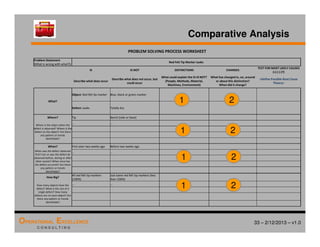
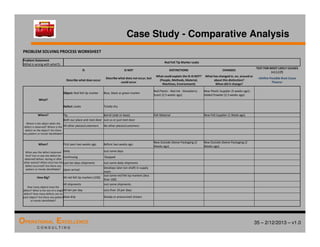
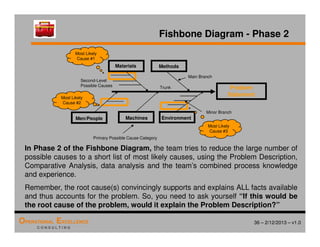
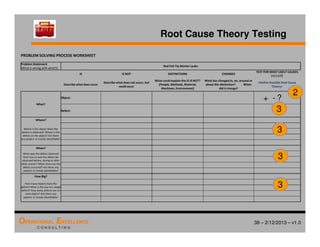
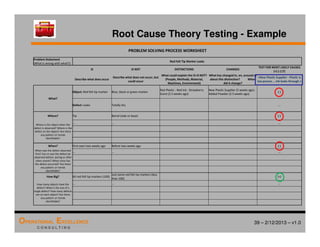
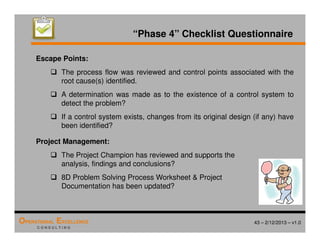
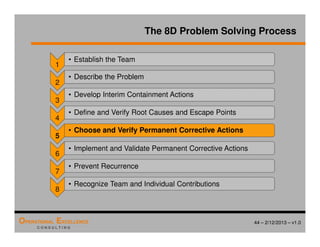
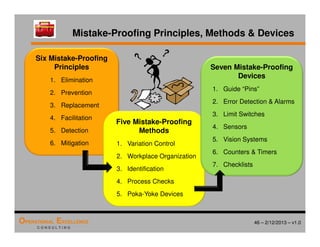
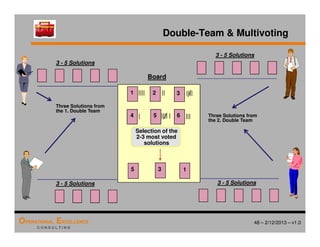
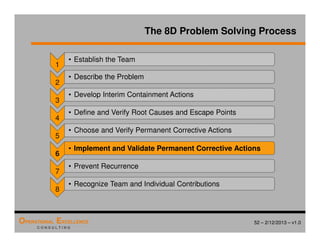
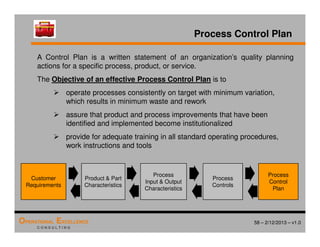
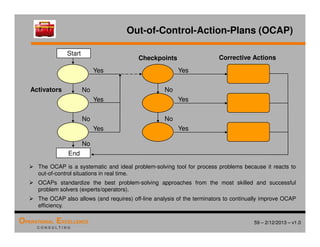
The document provides an overview of the 8D problem solving process, outlining the key activities and tools used in each phase to define and solve problems. It discusses establishing a problem solving team, describing the problem through a problem statement and analysis tools, developing interim containment actions, and defining and verifying root causes. A case study example is used throughout to demonstrate how to apply the concepts and tools.