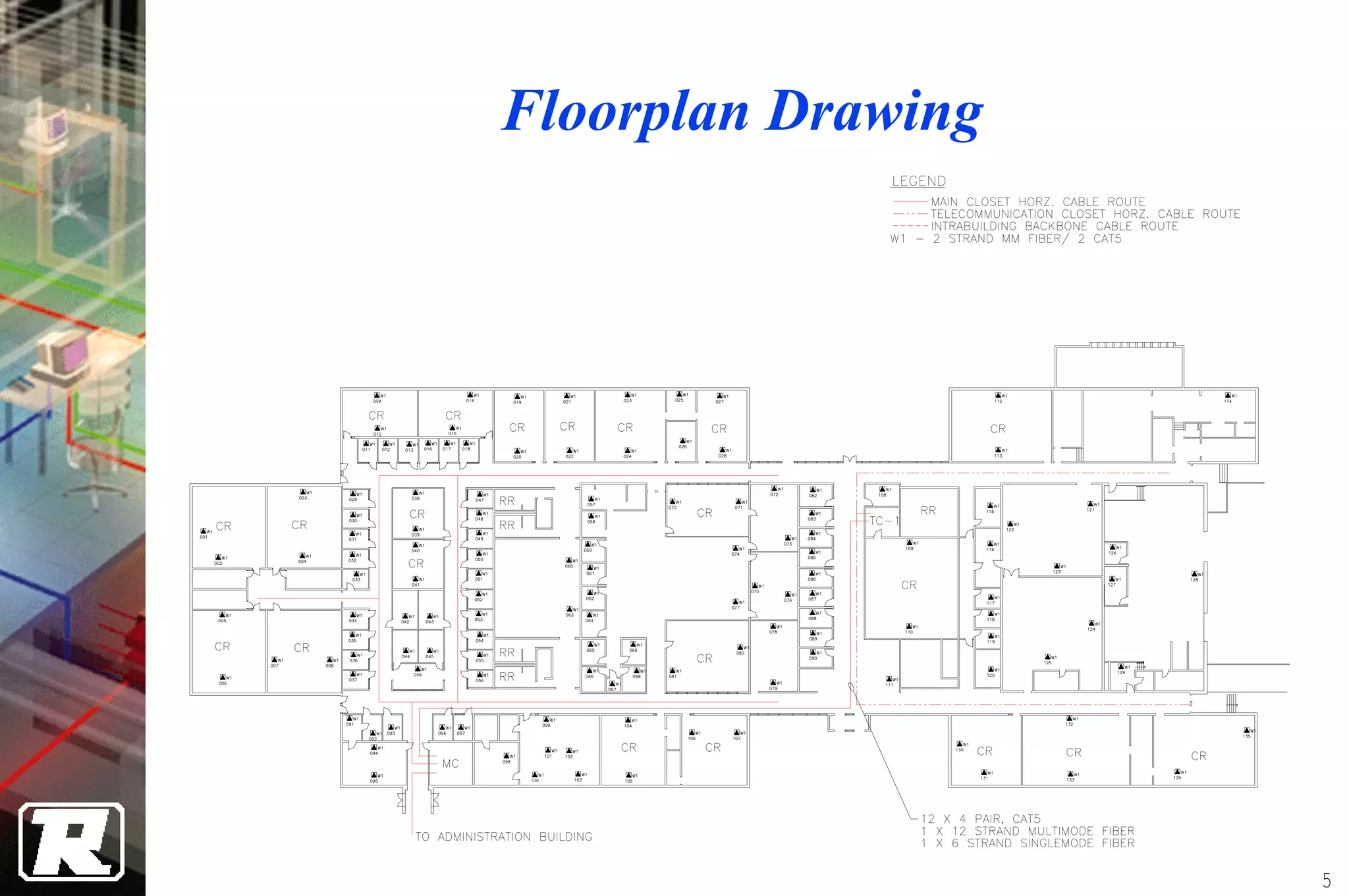
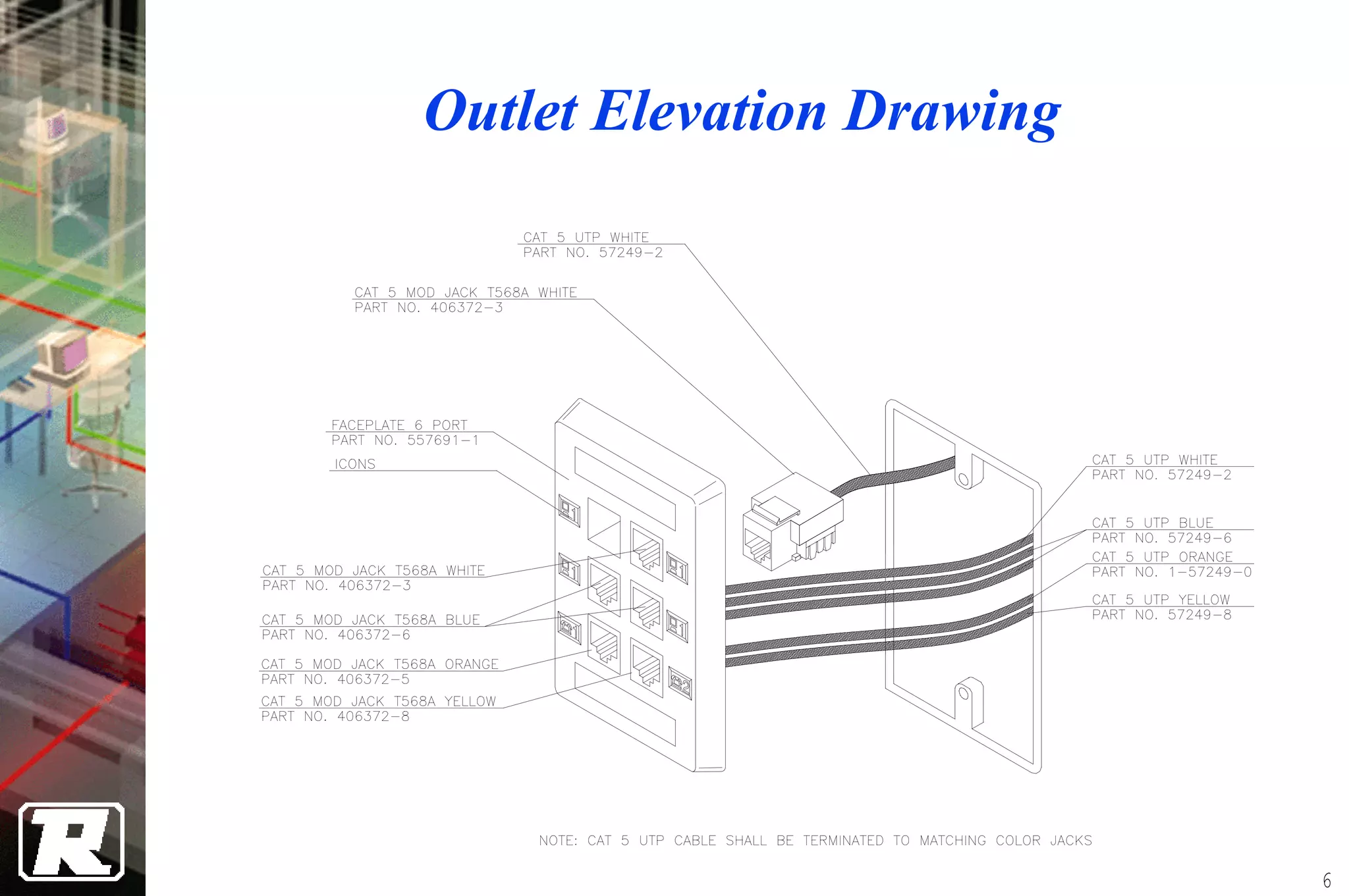
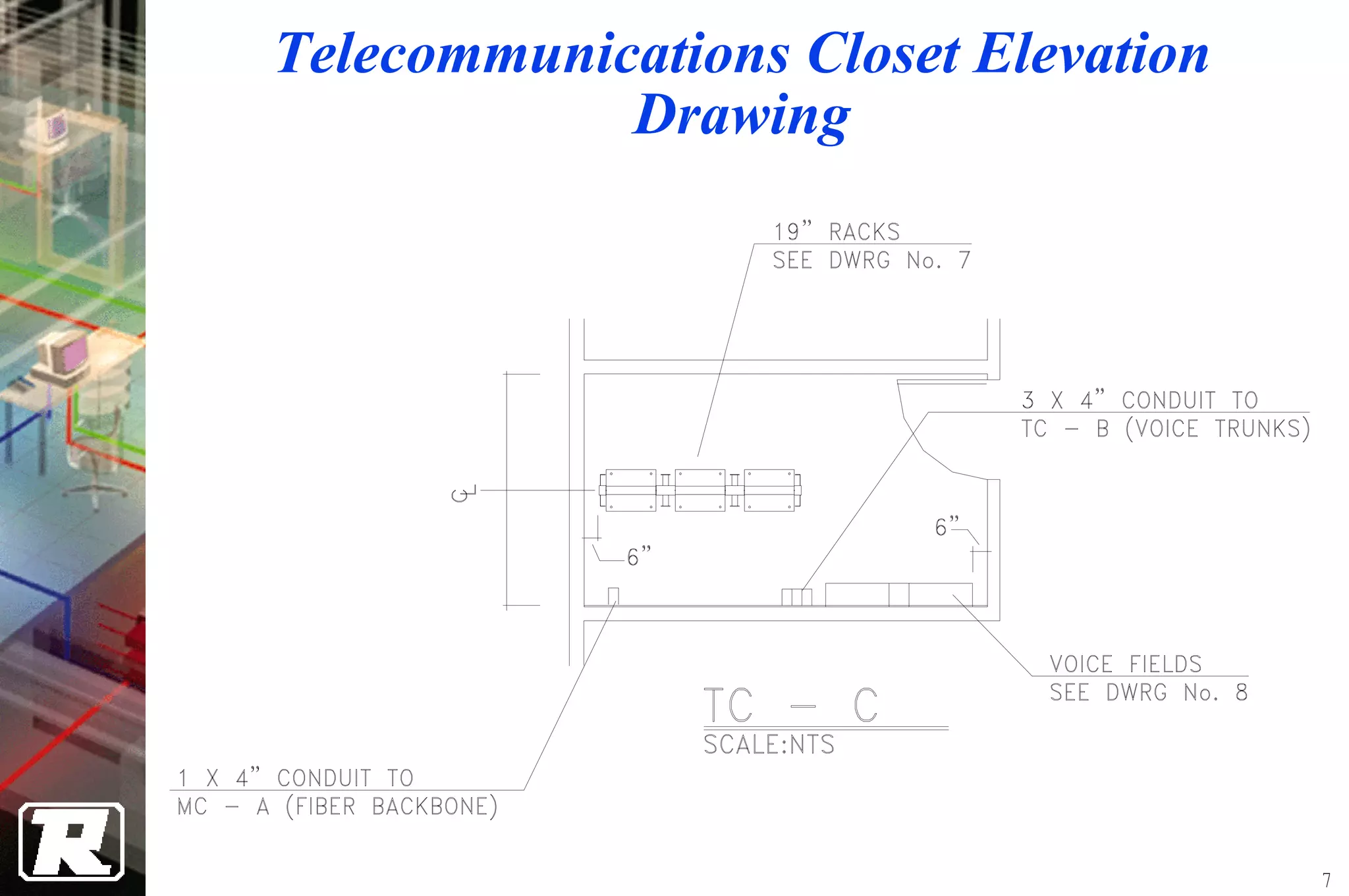
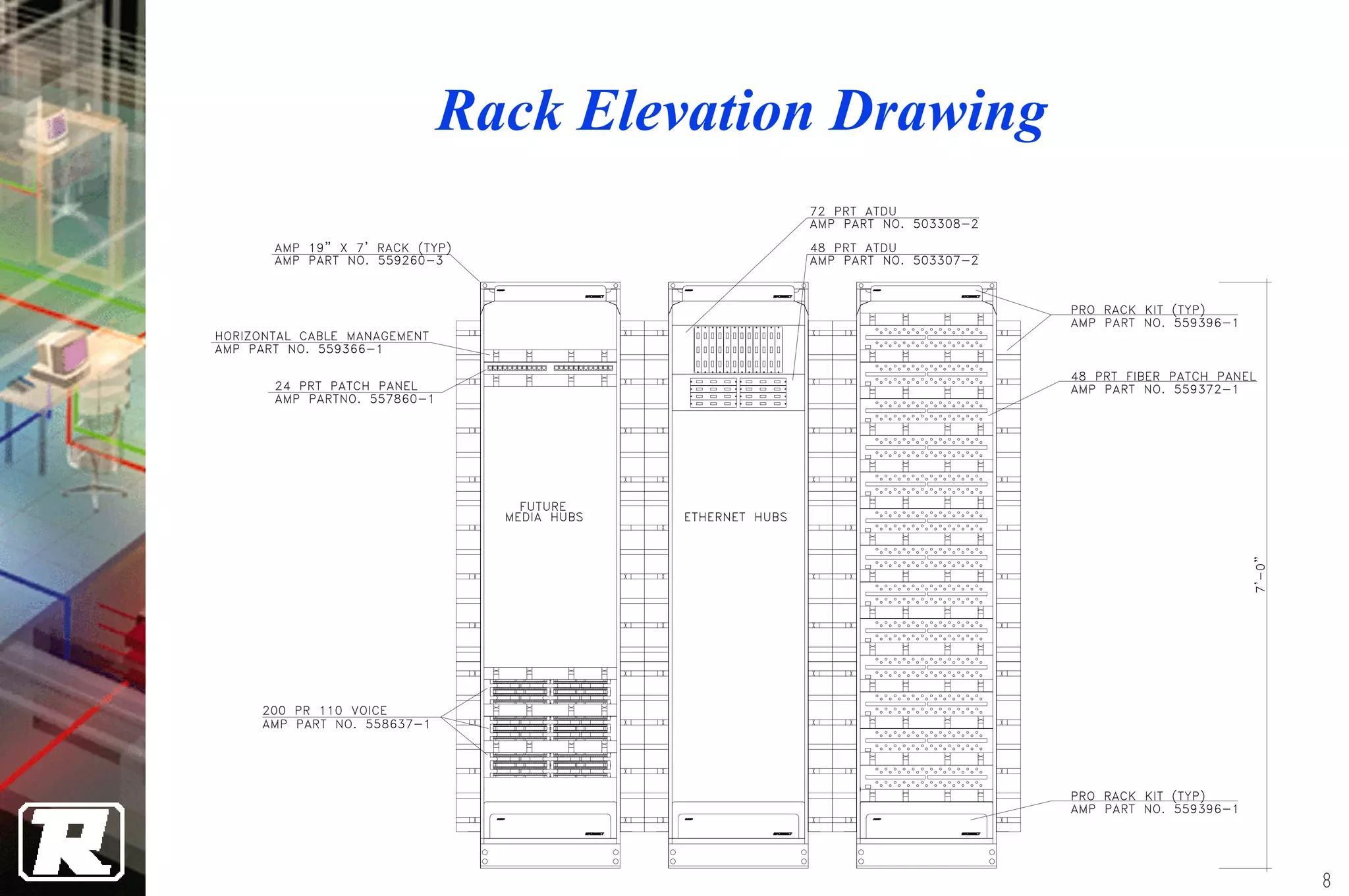
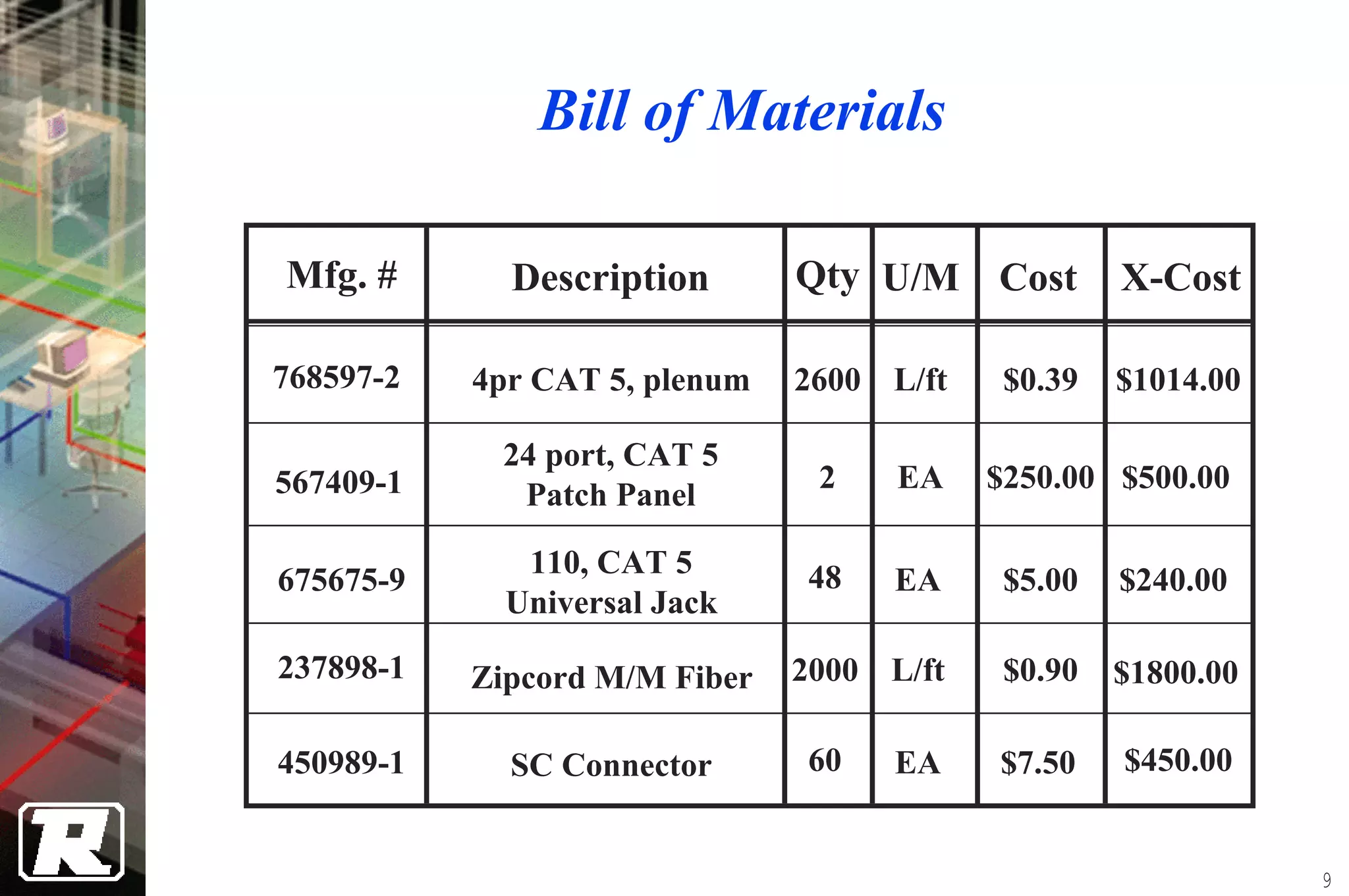
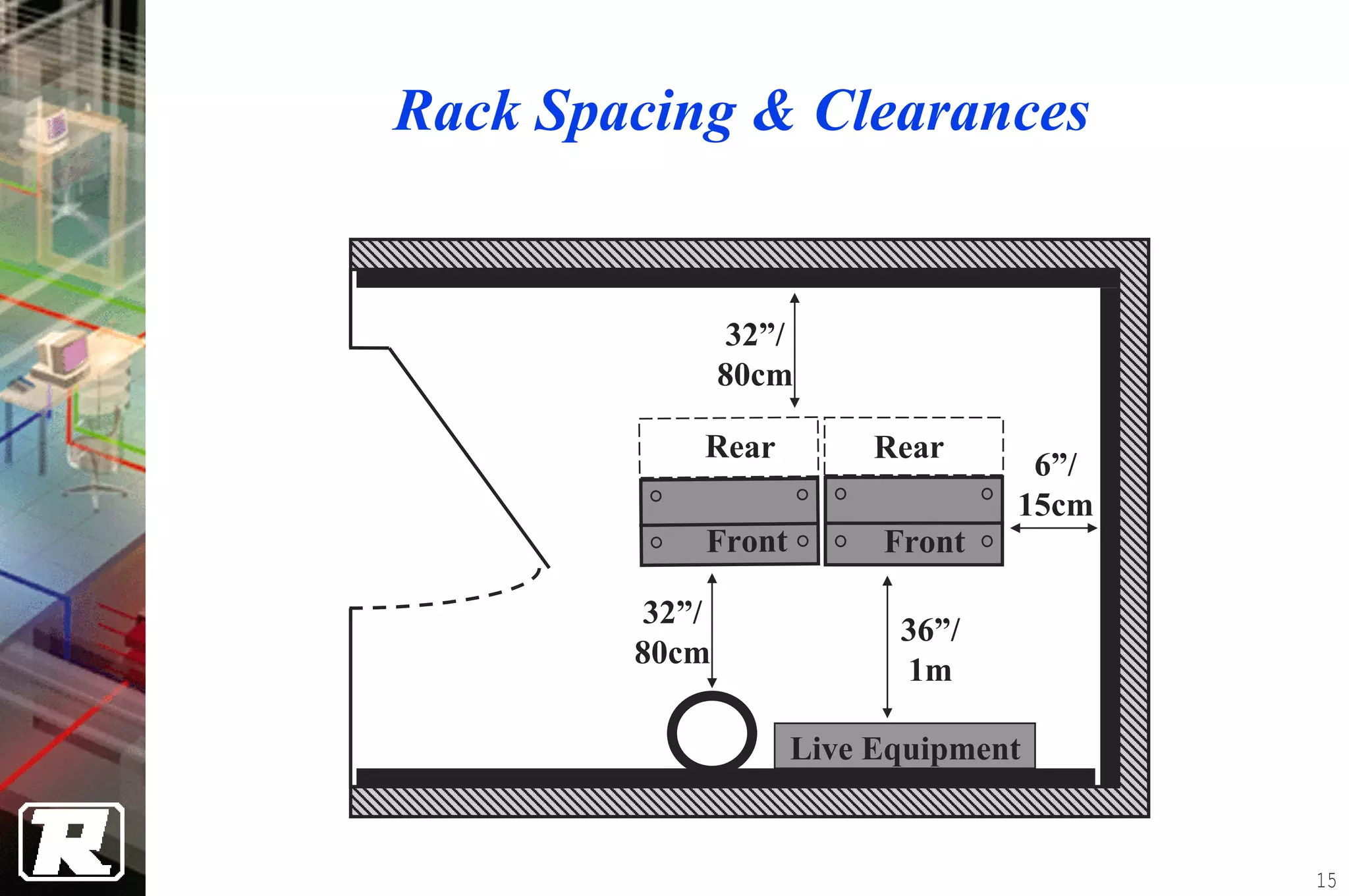
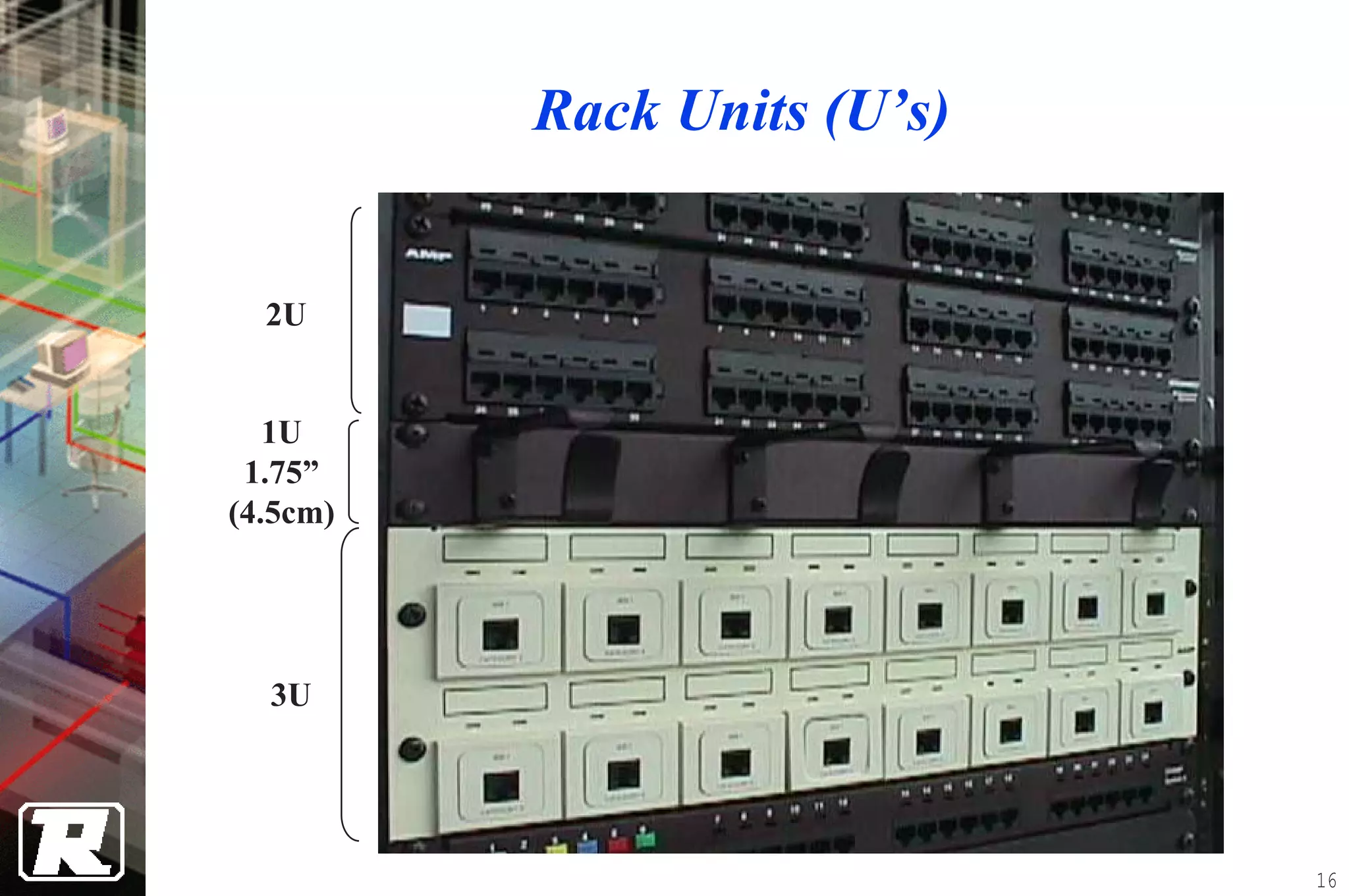
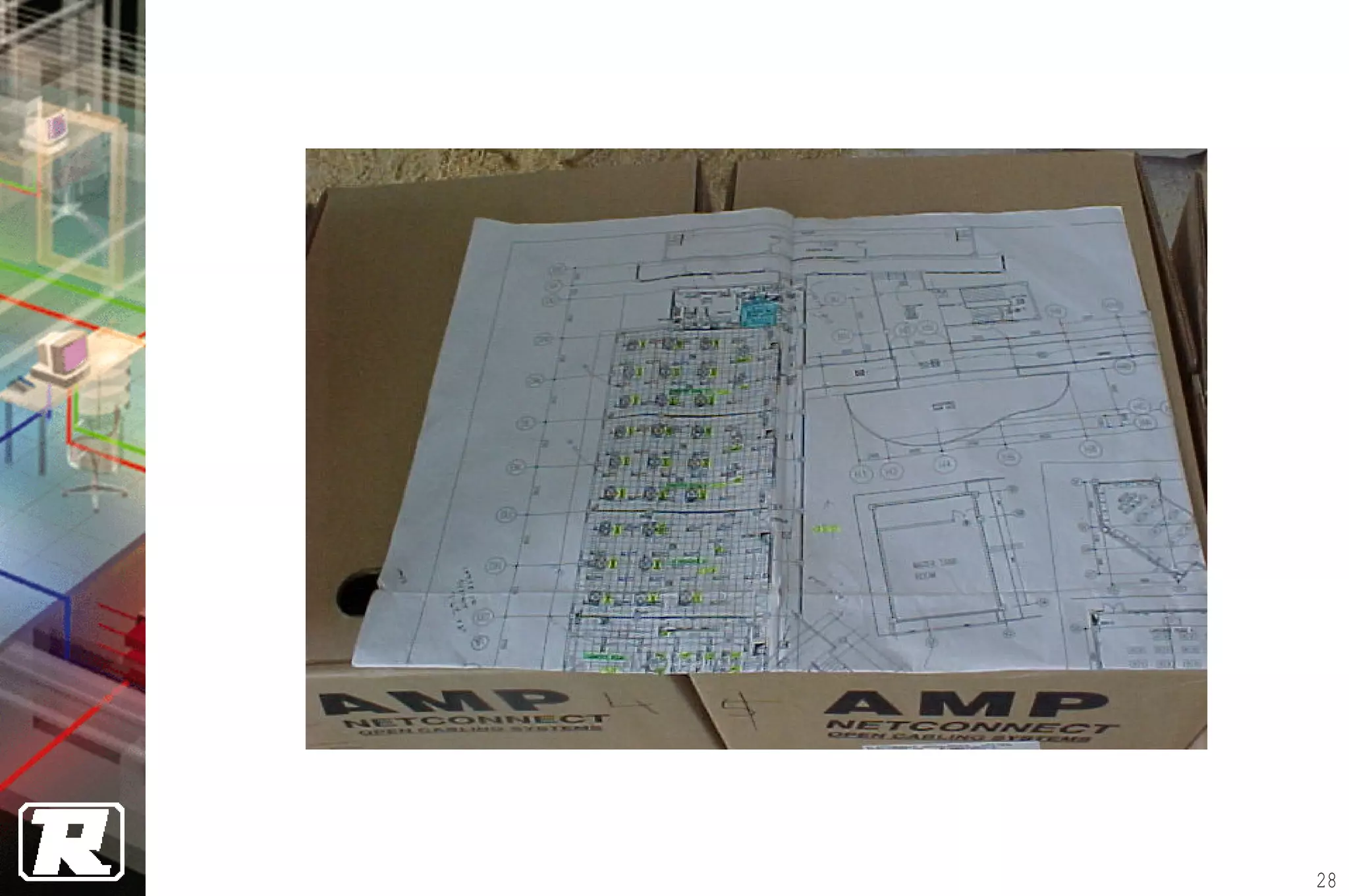
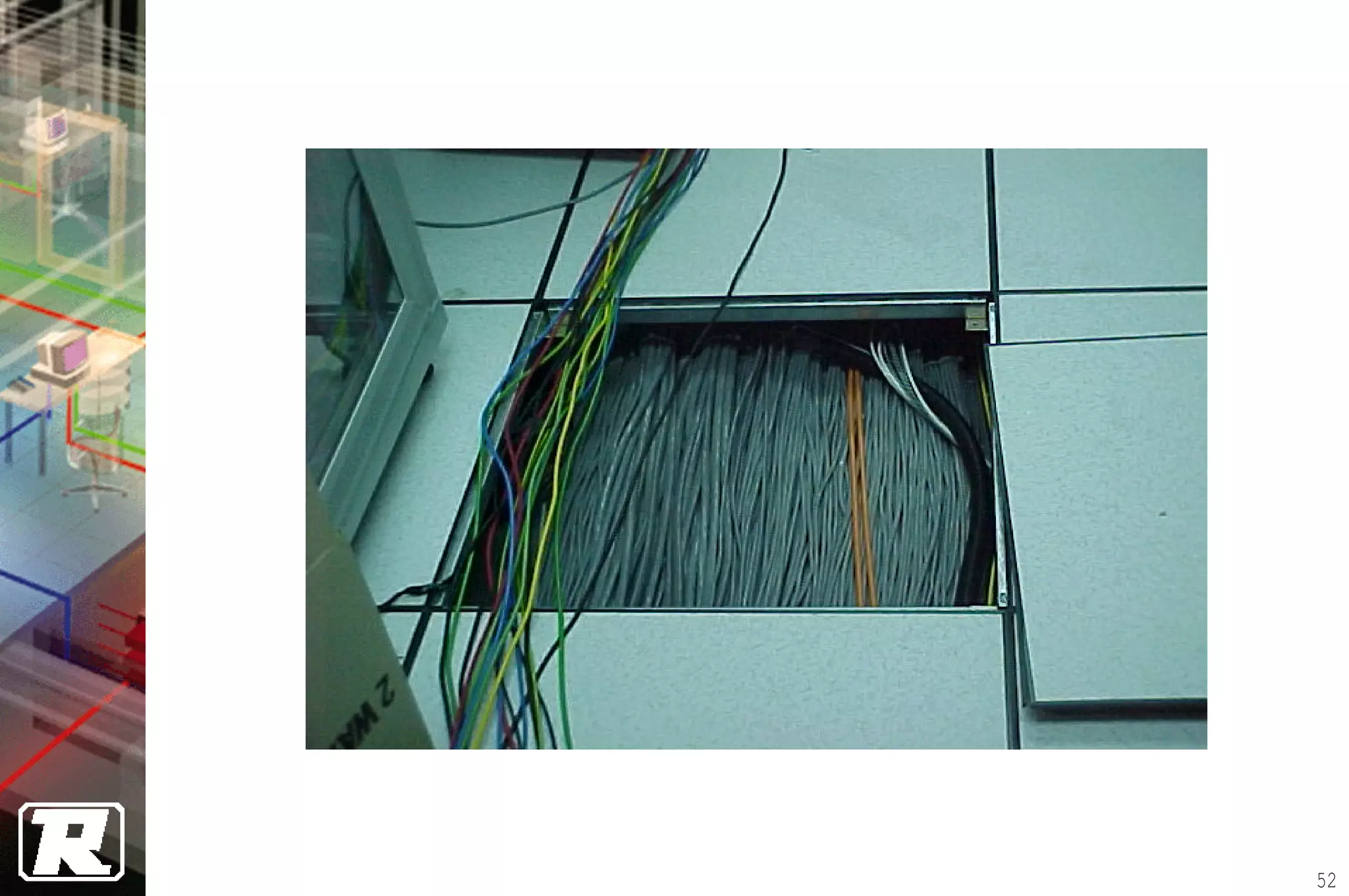
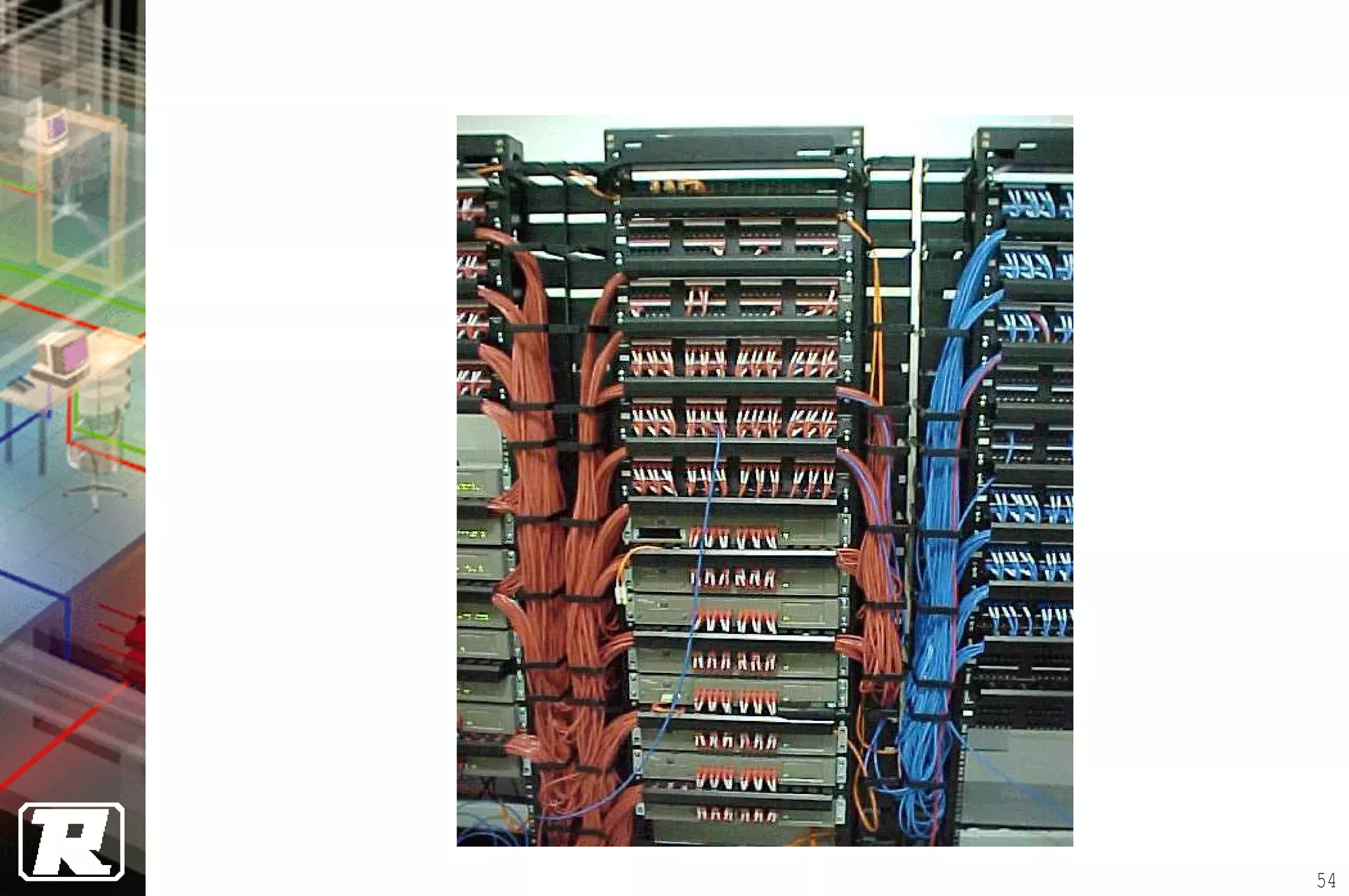
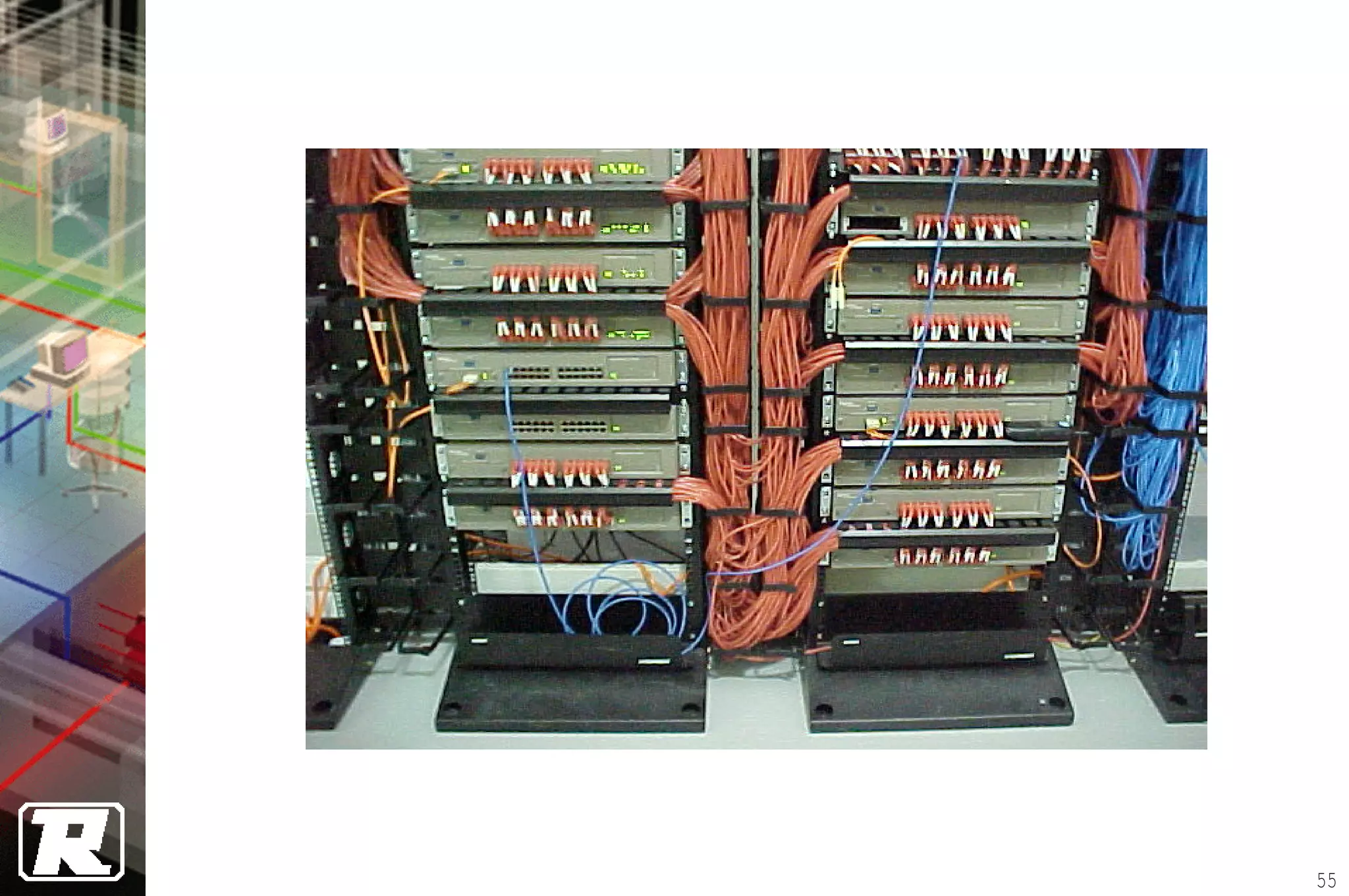
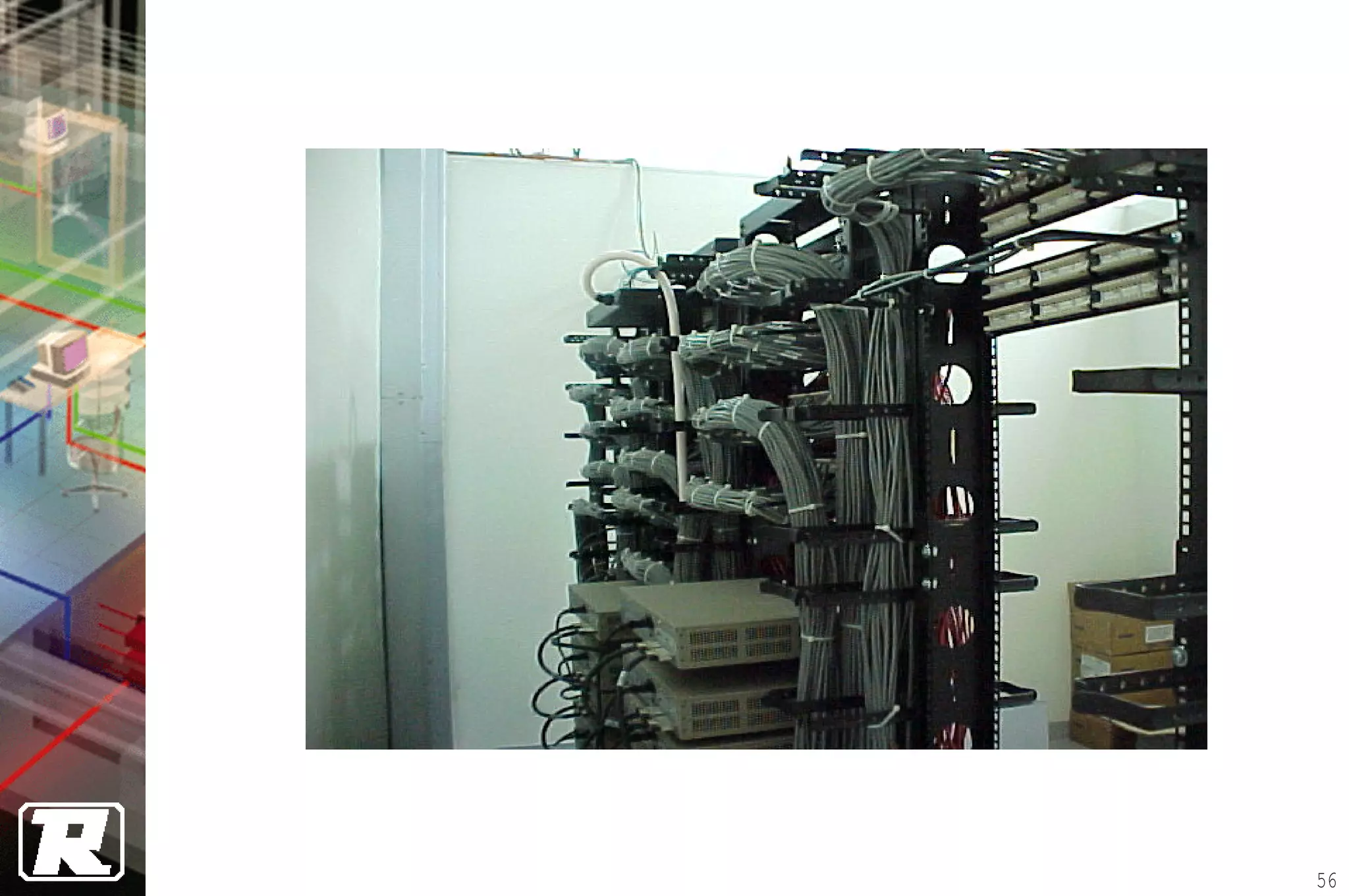
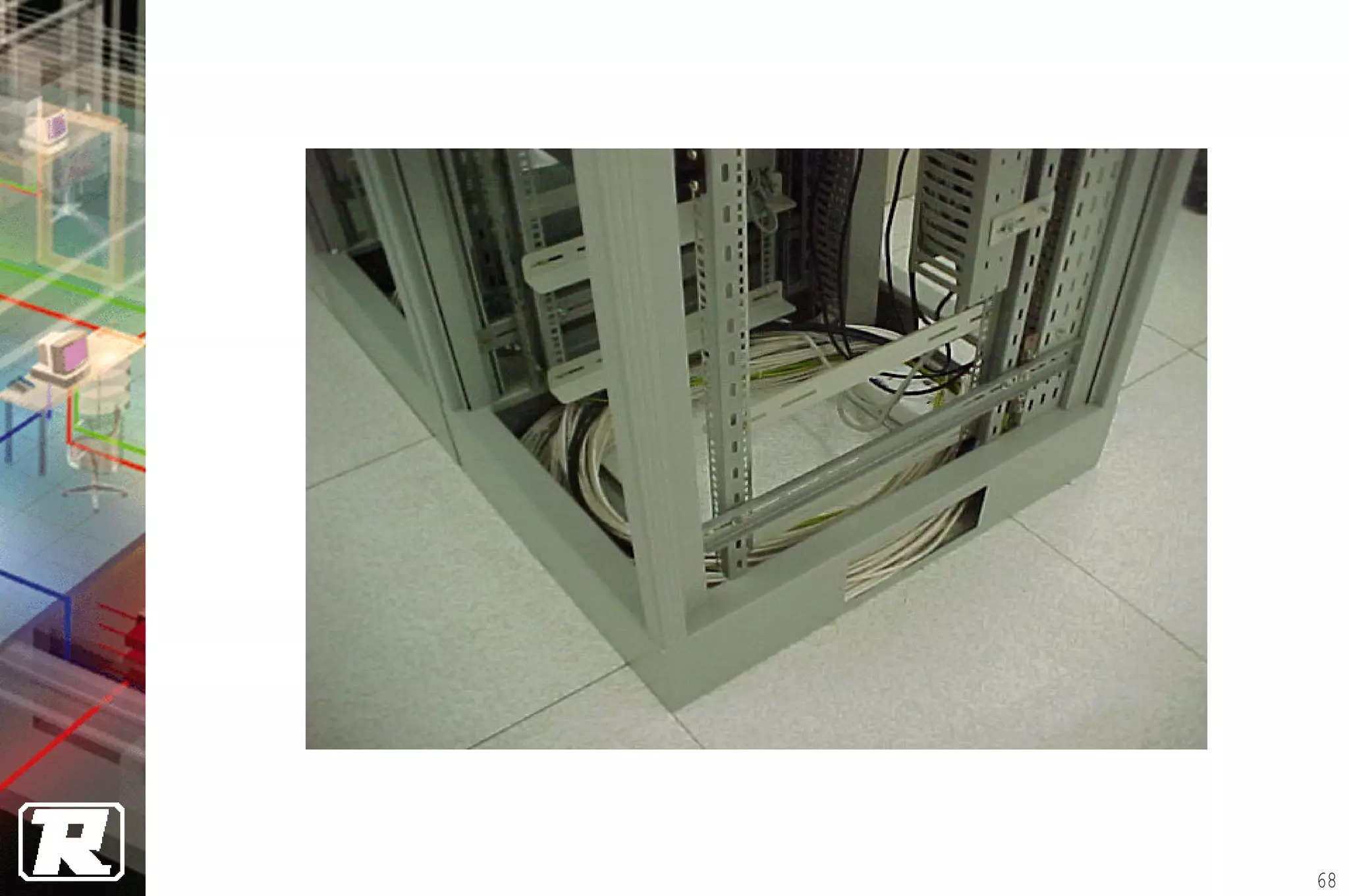
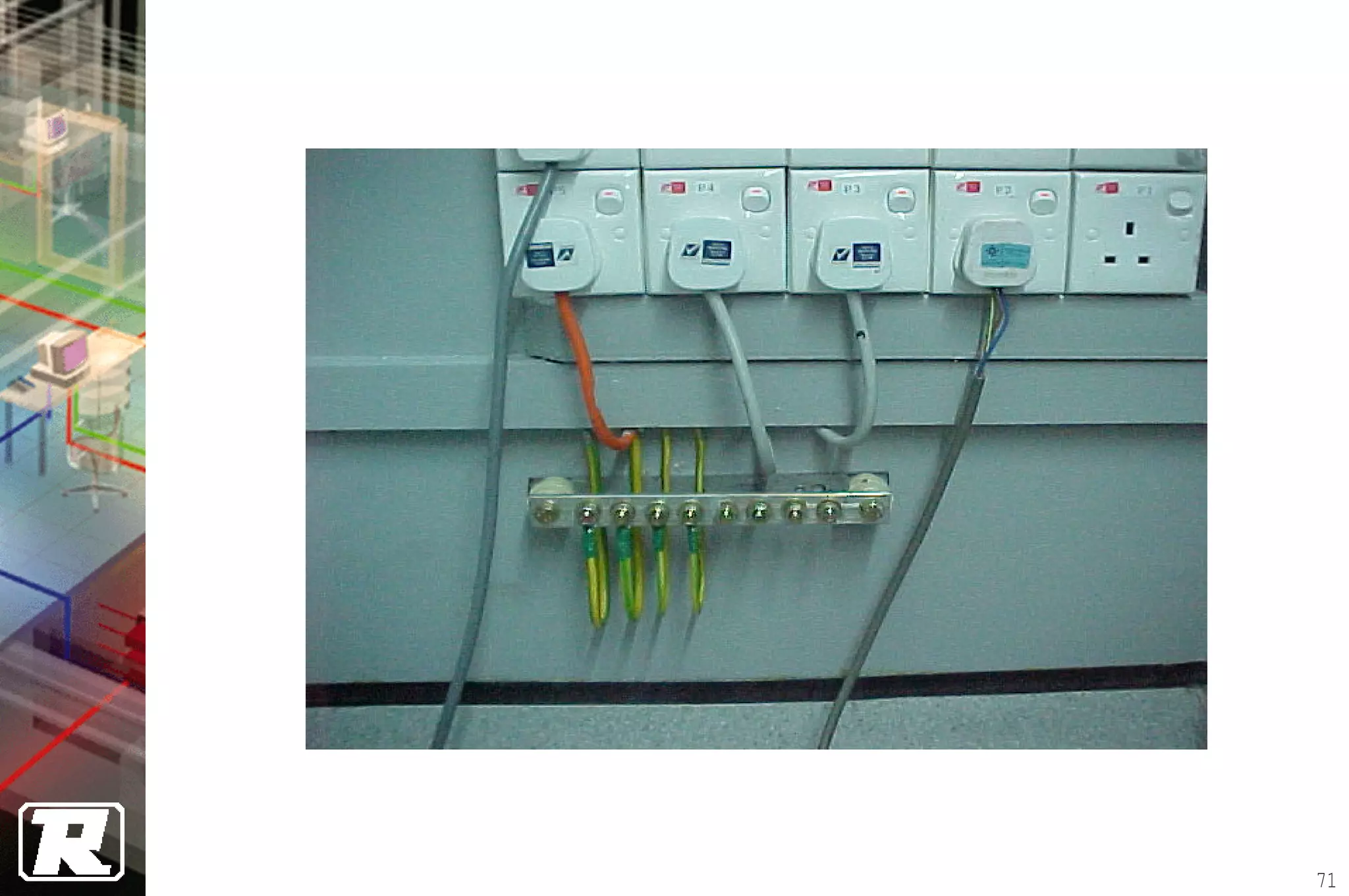
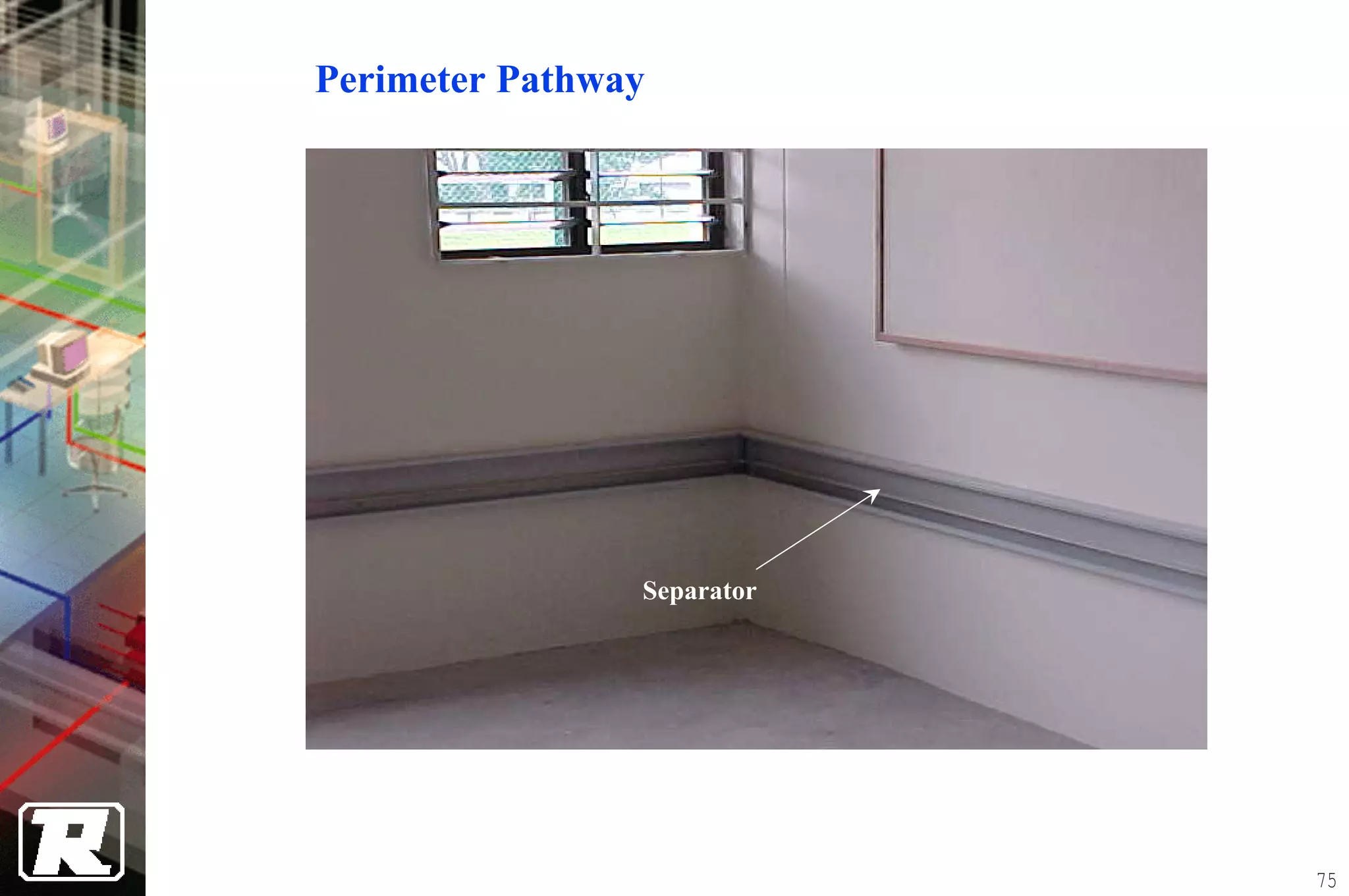
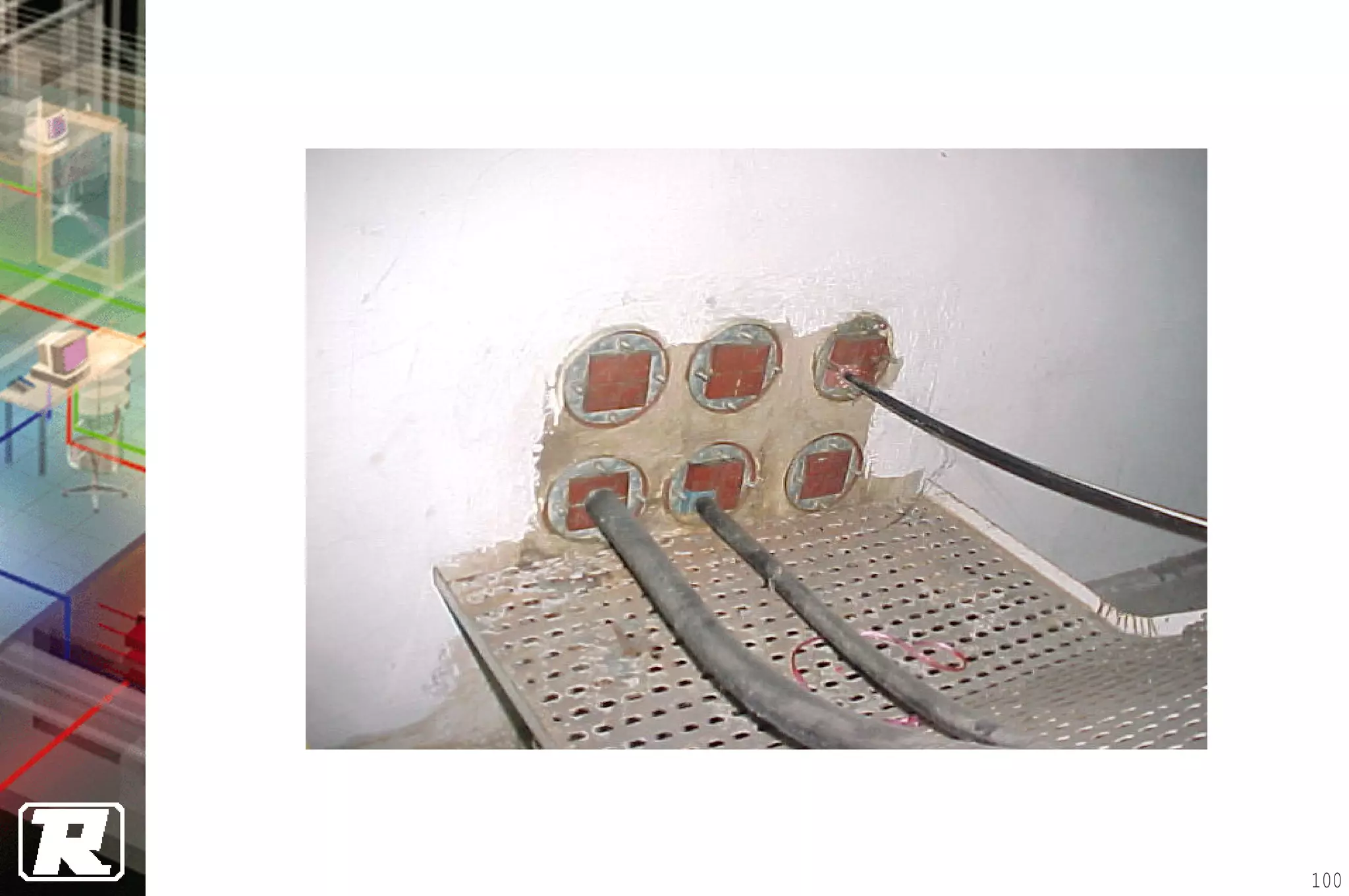
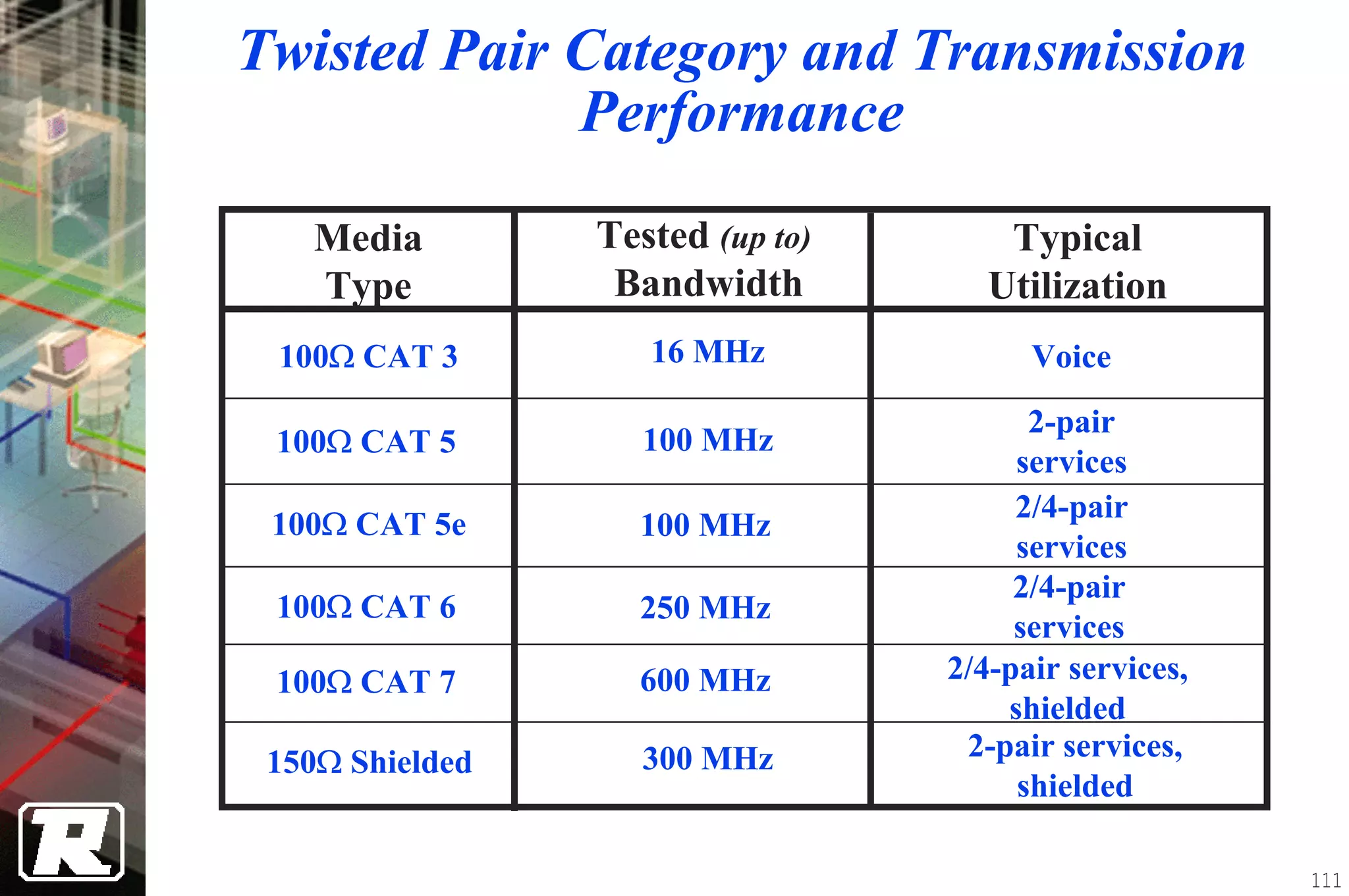
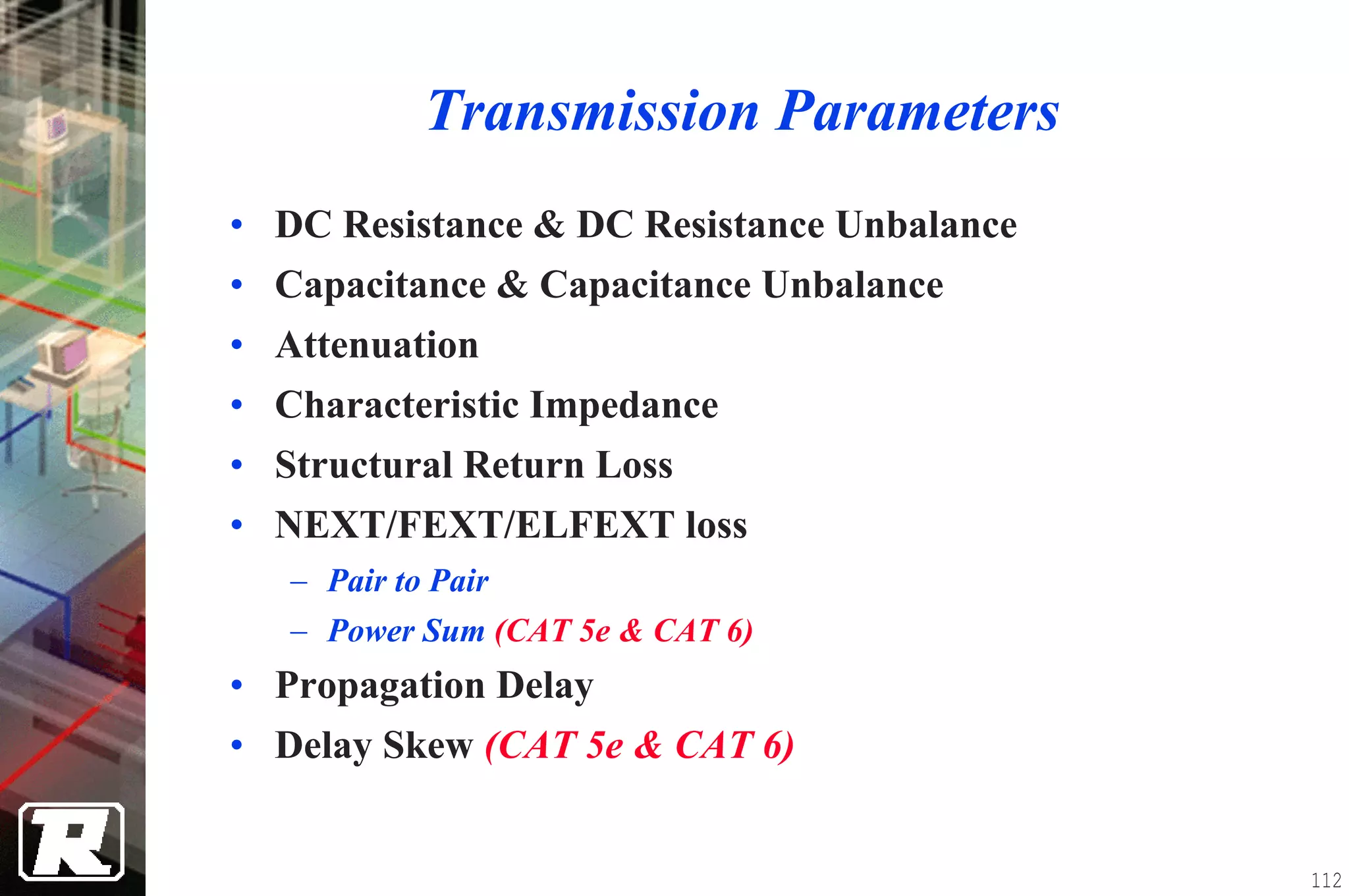
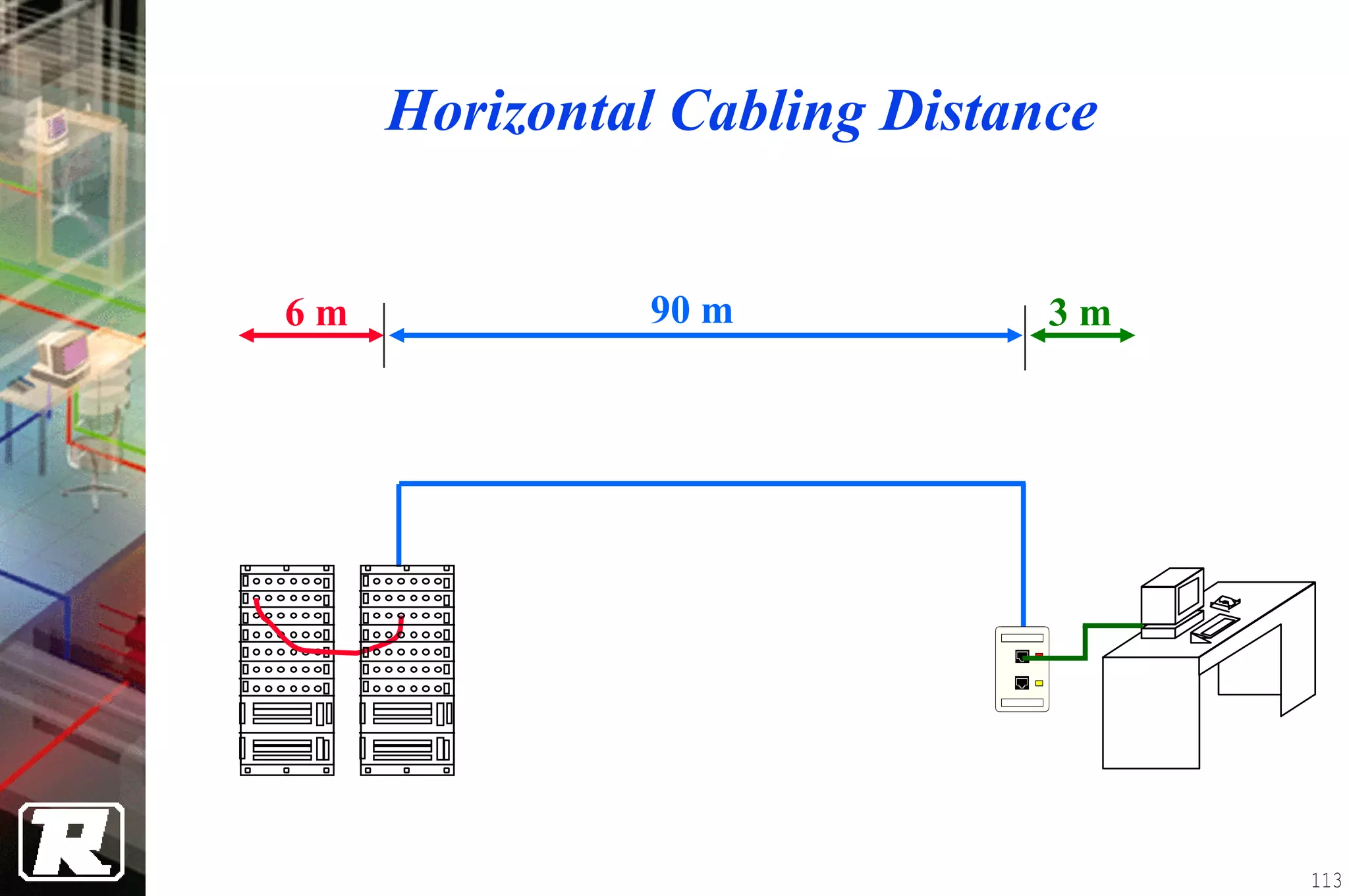
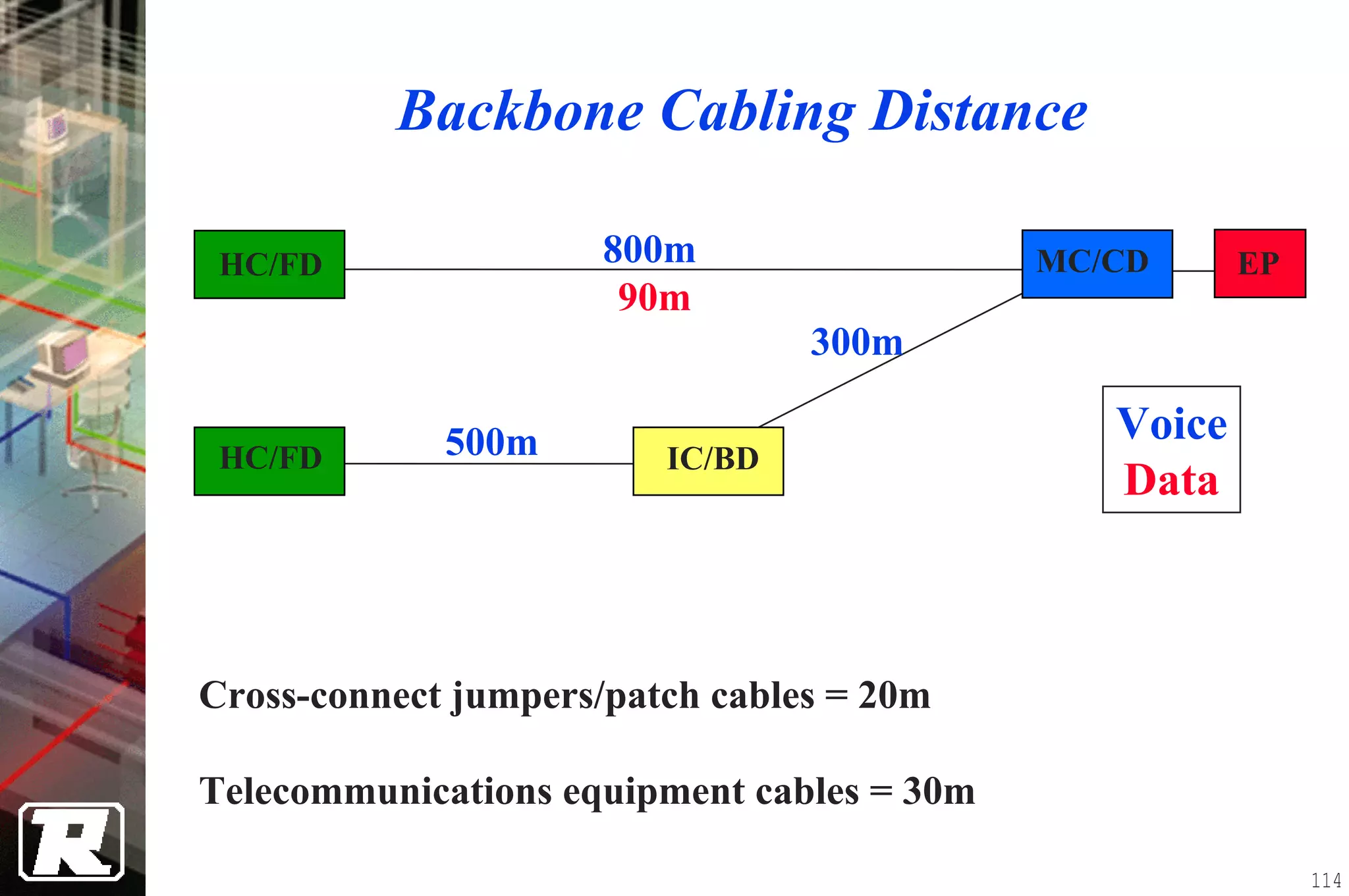
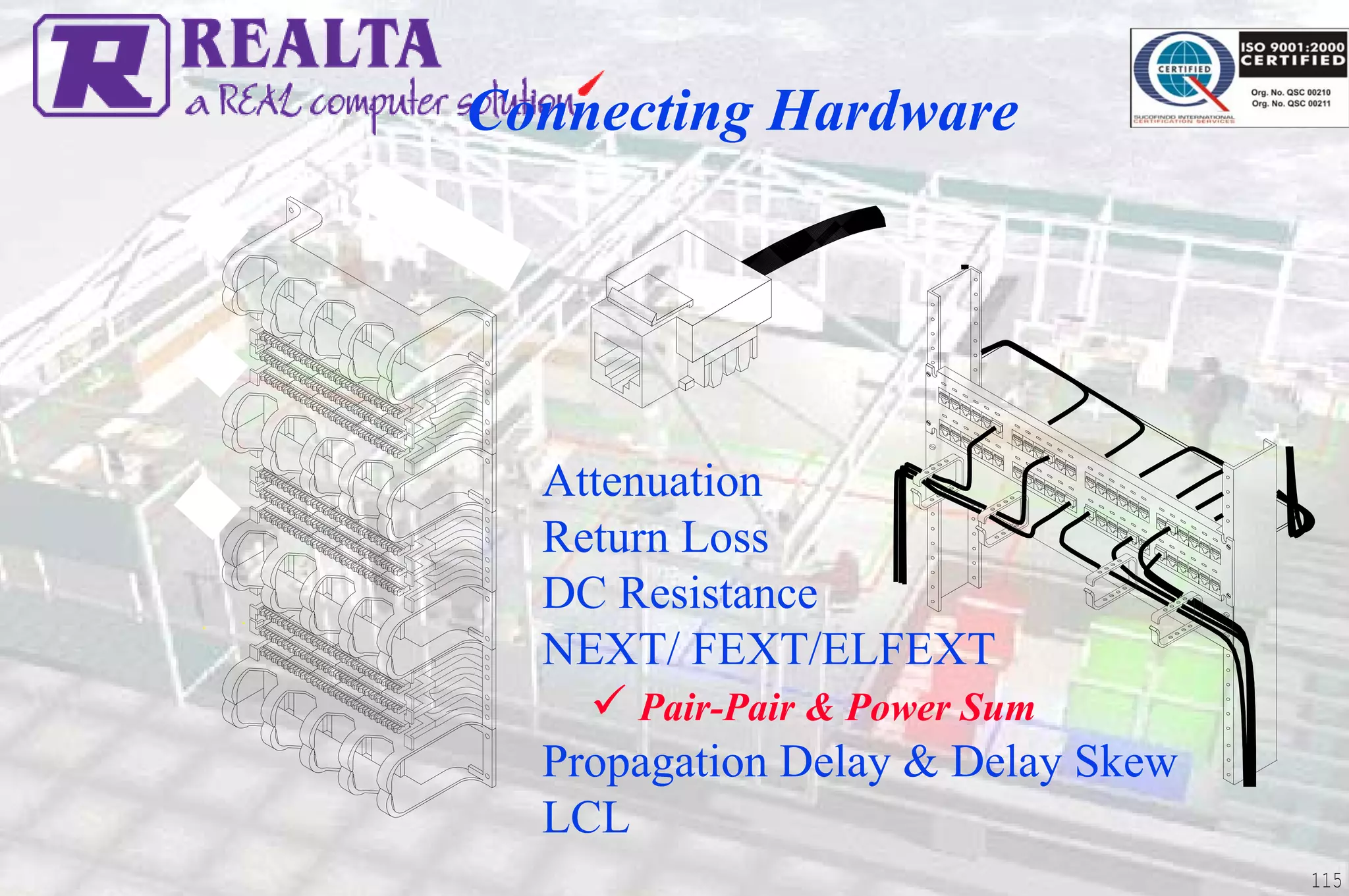
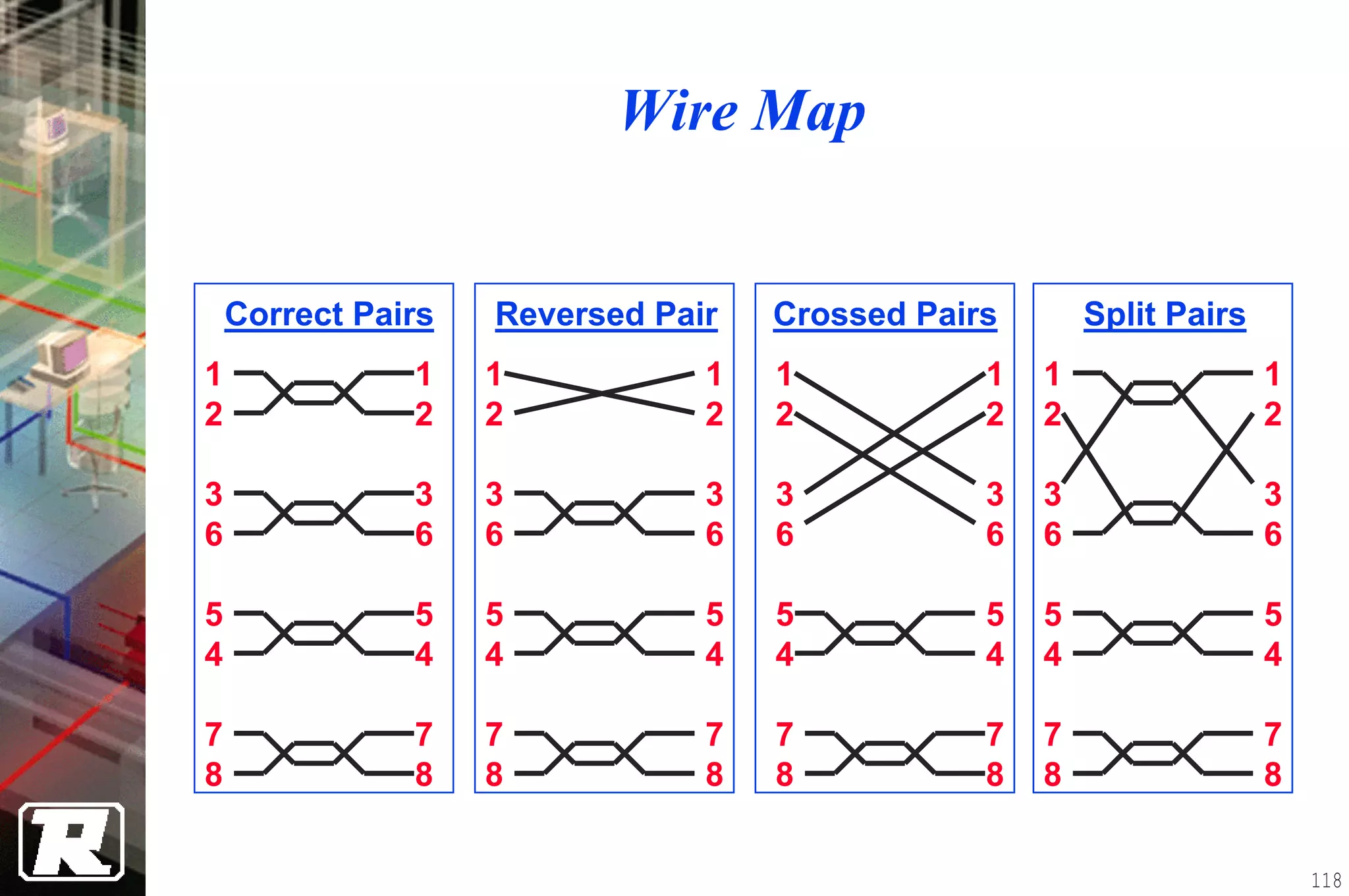
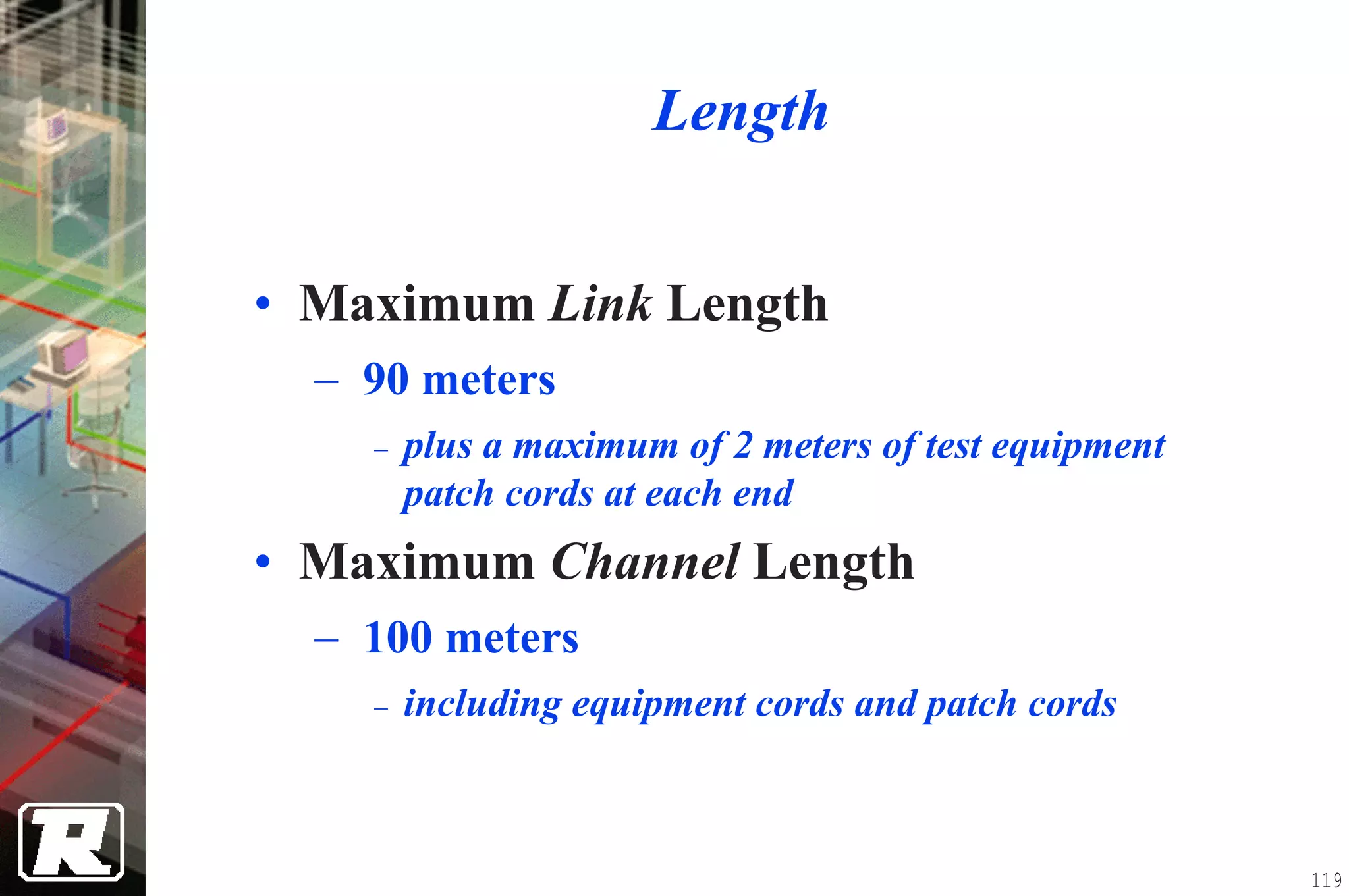
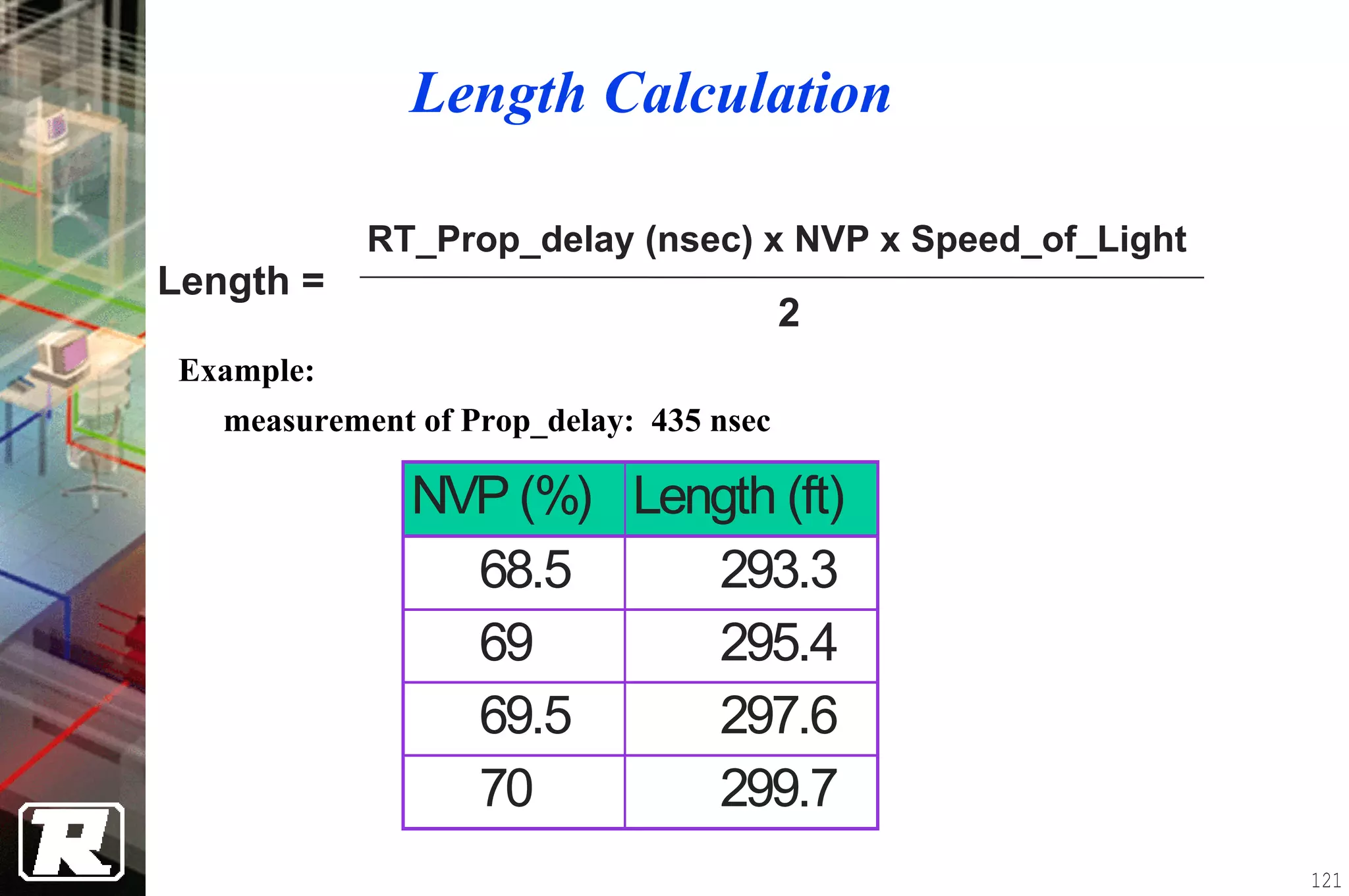
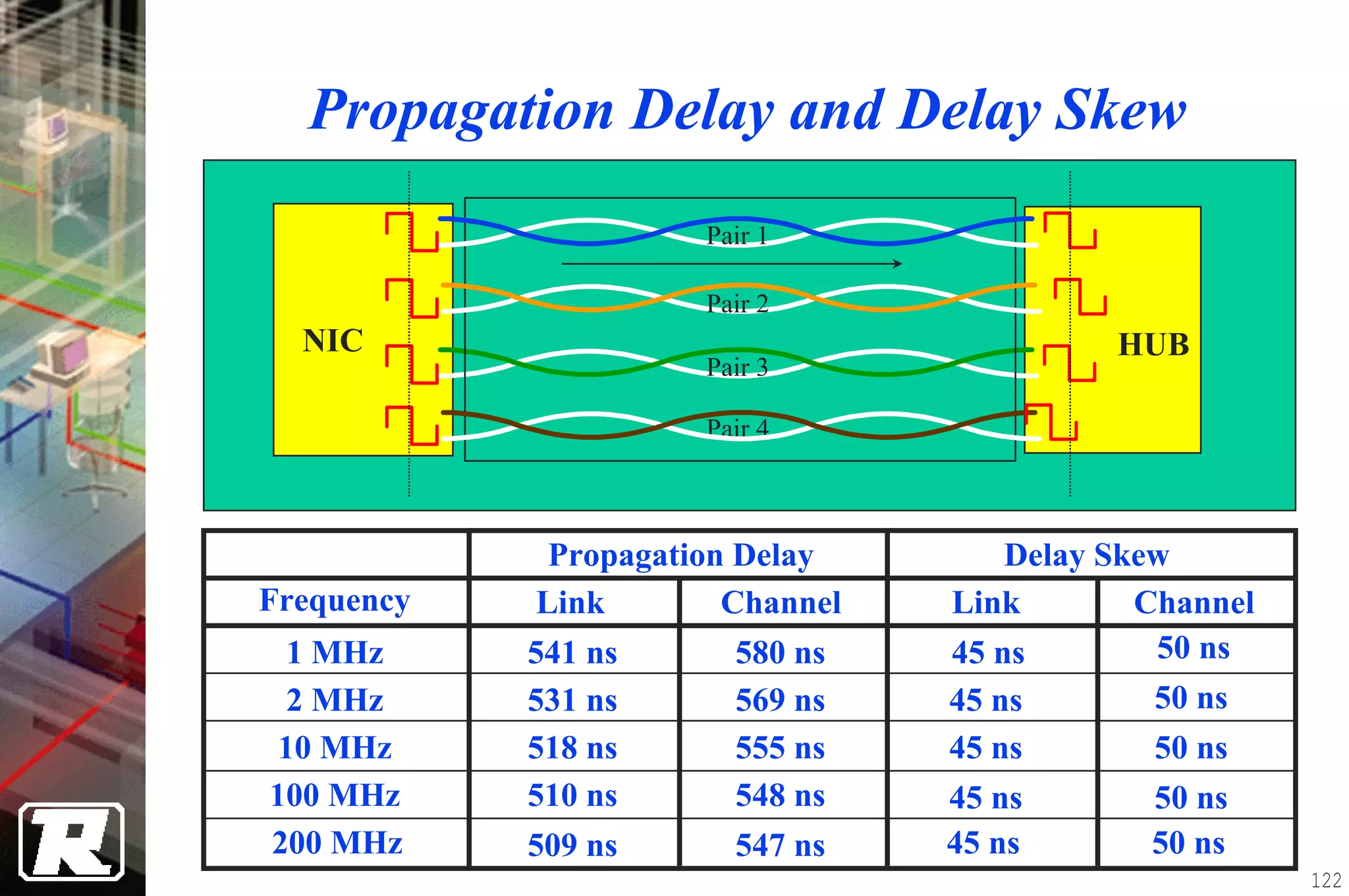
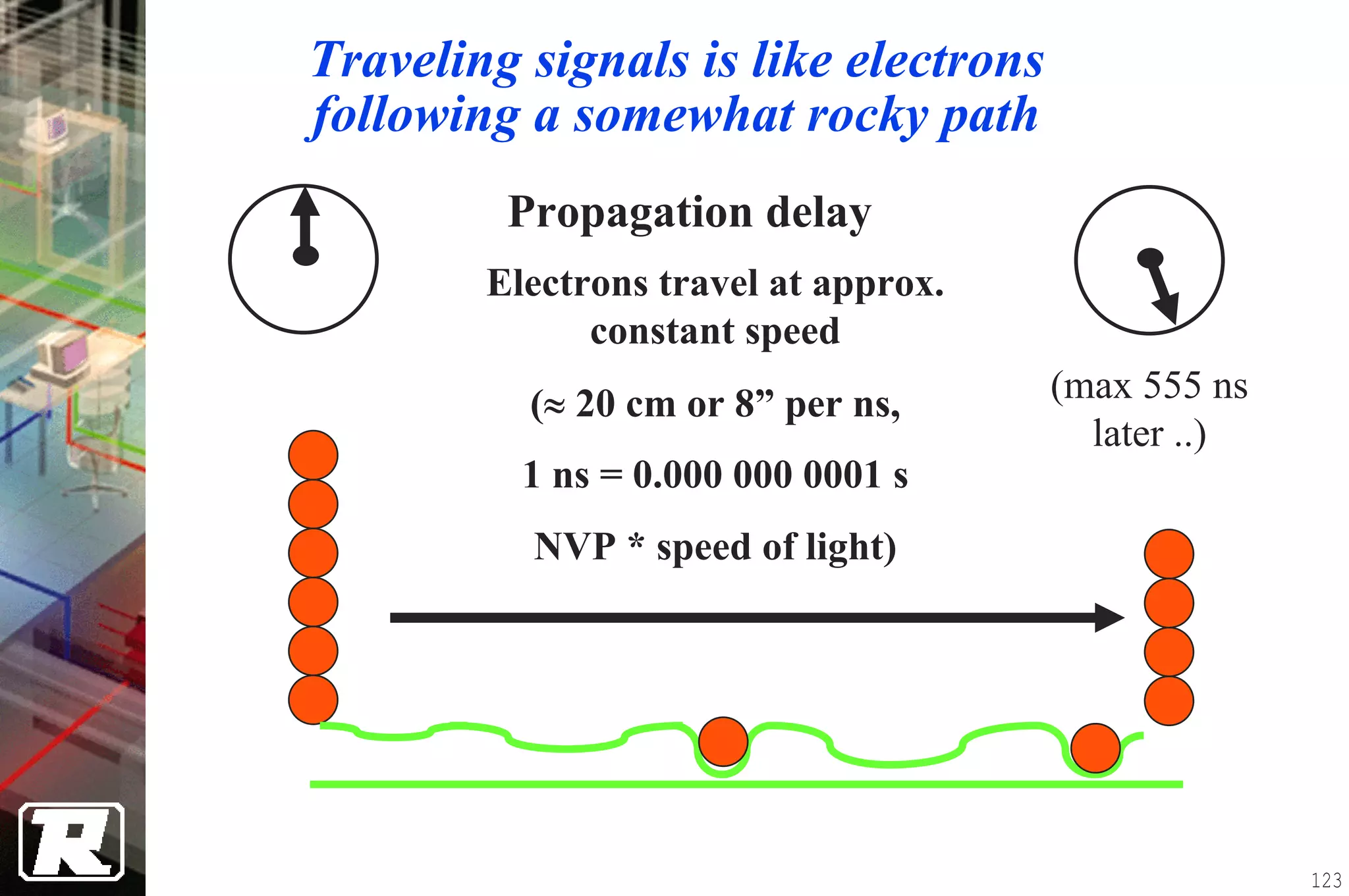
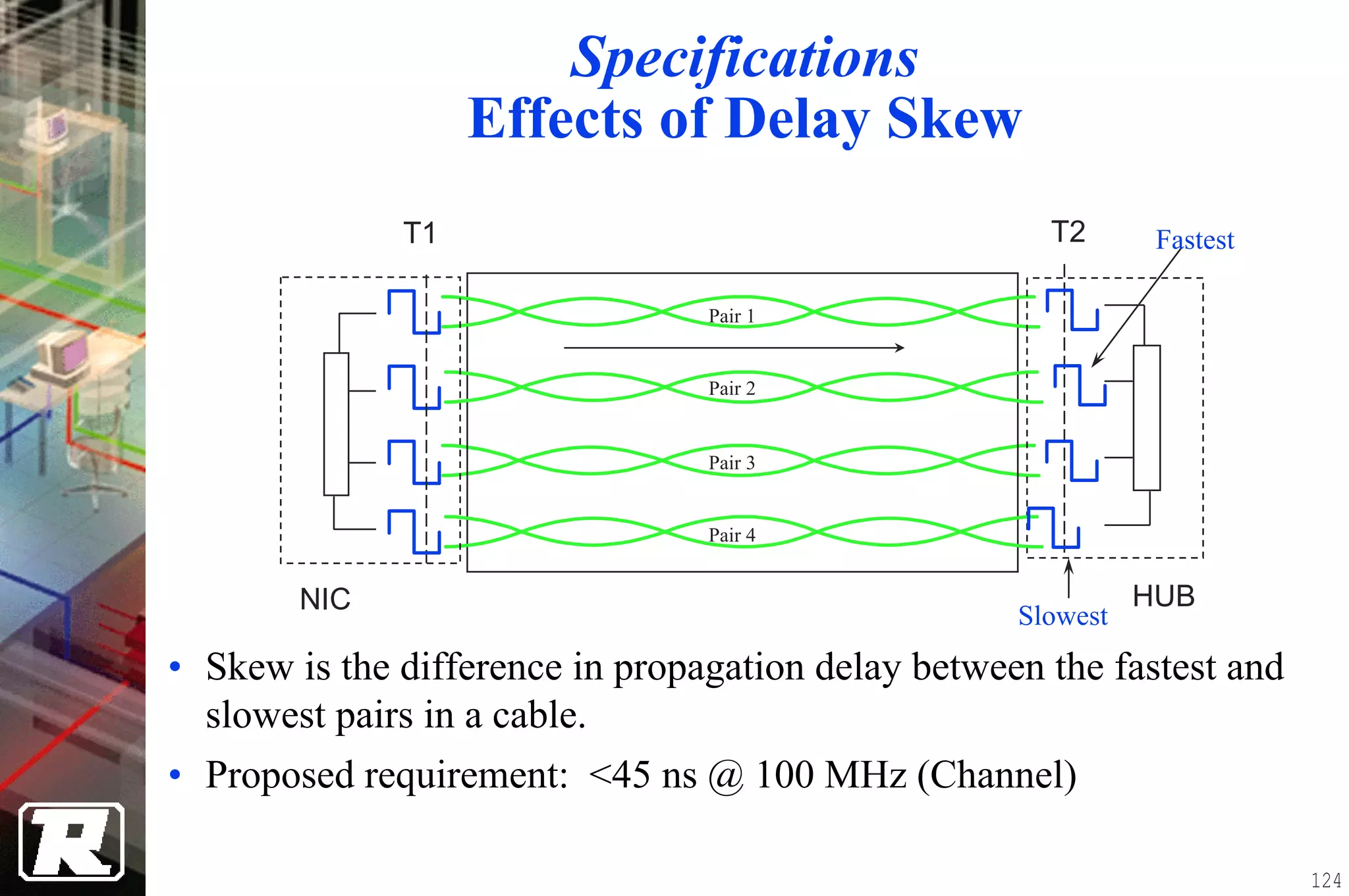
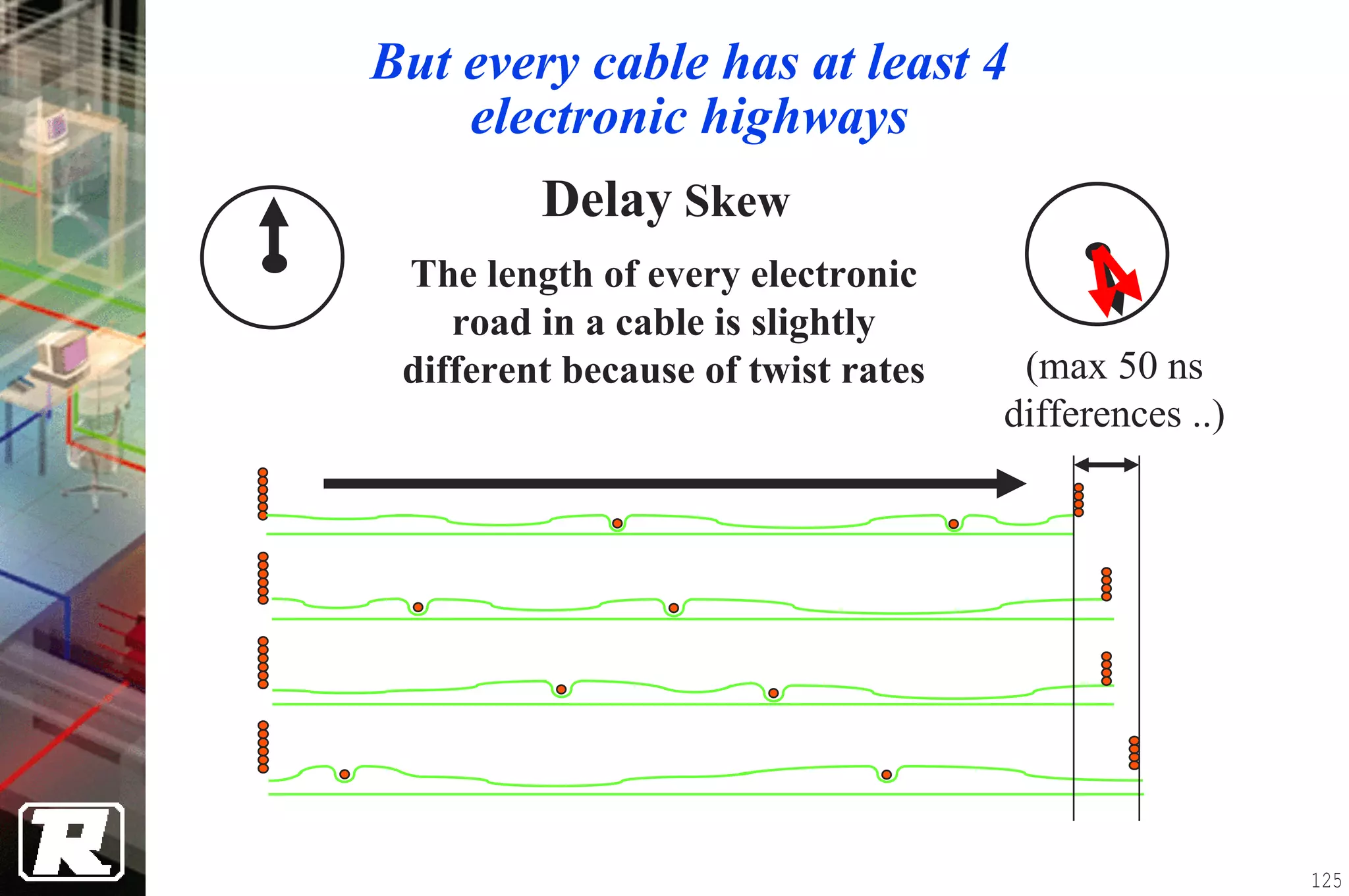
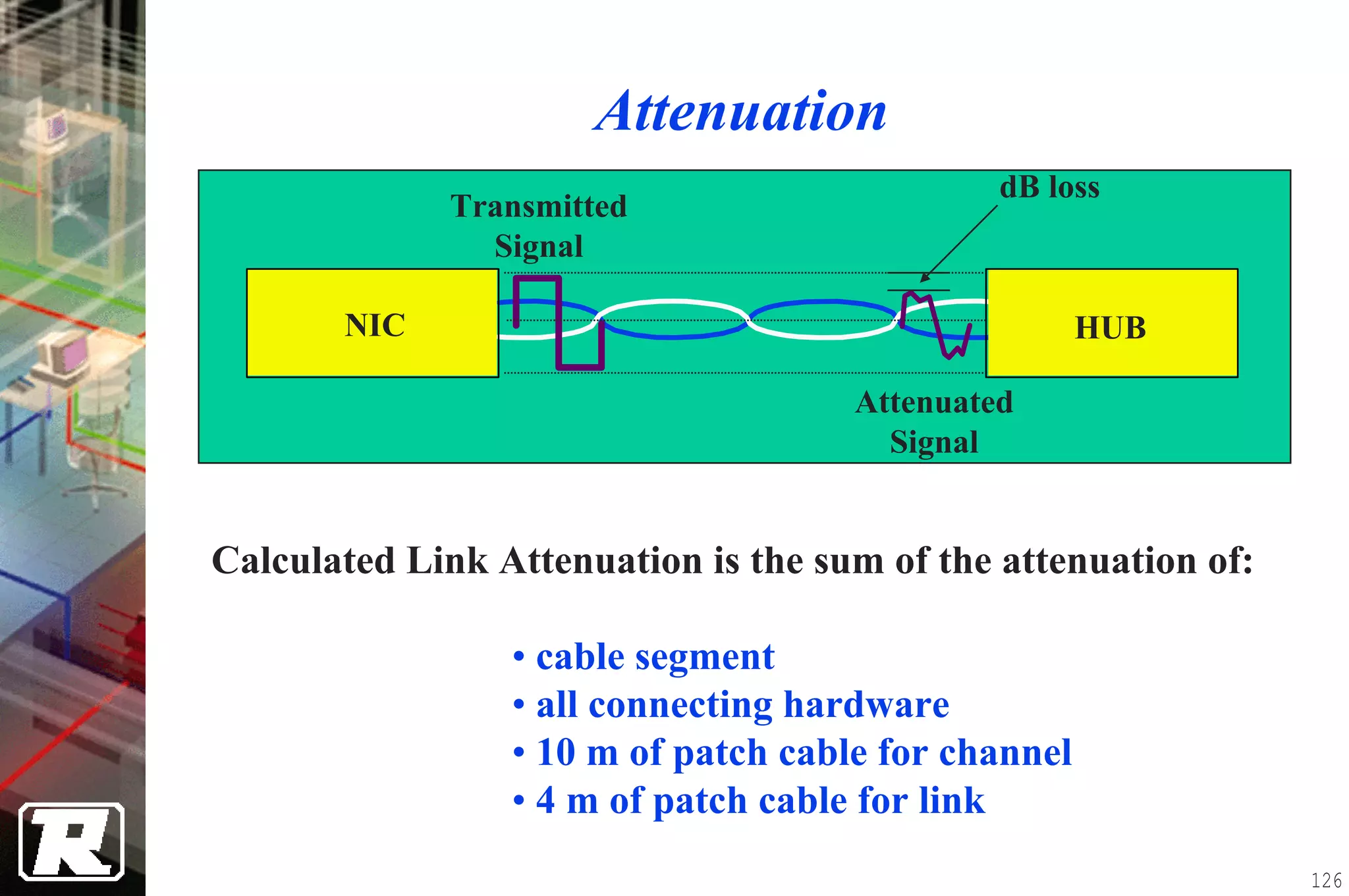
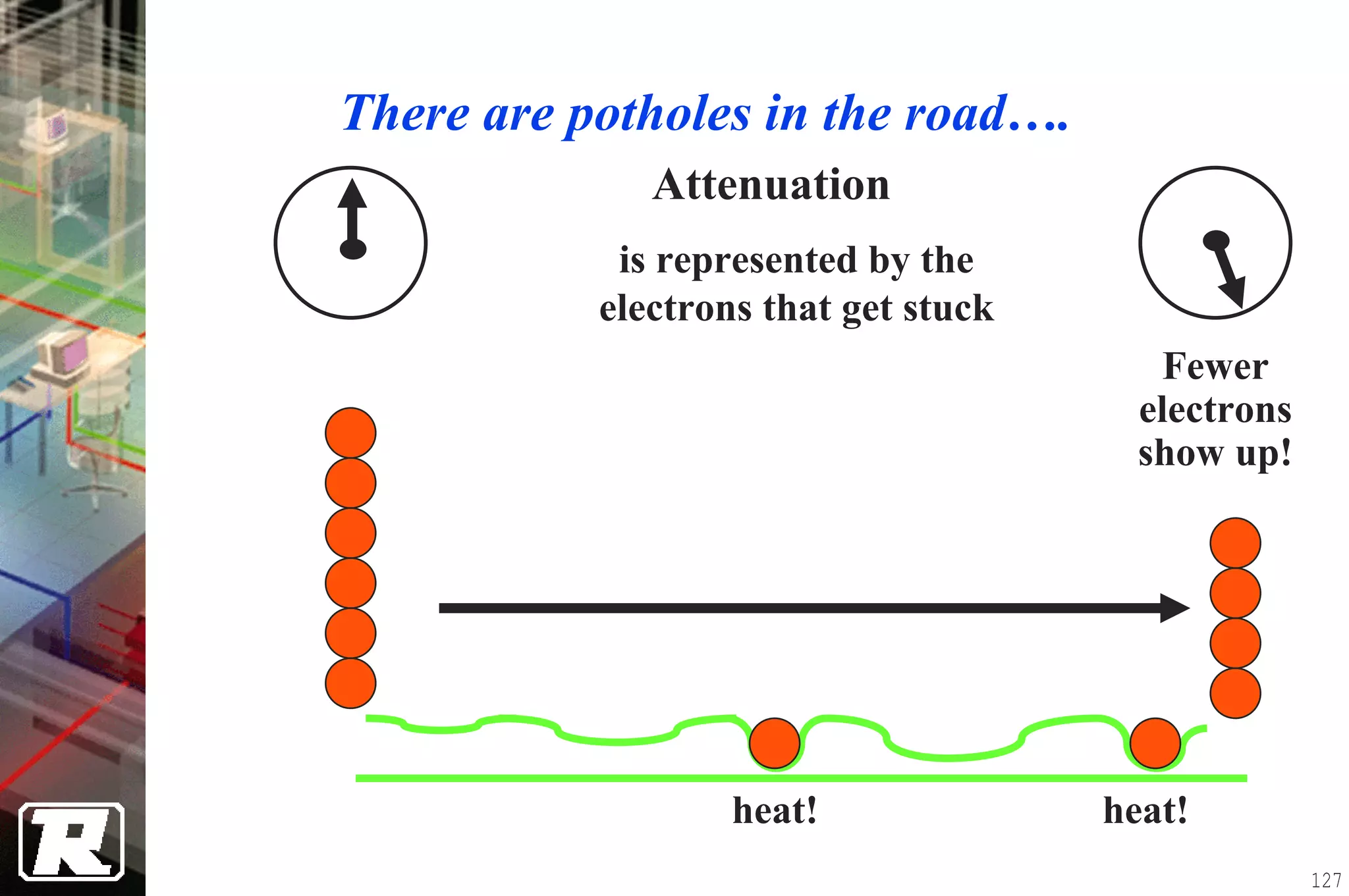
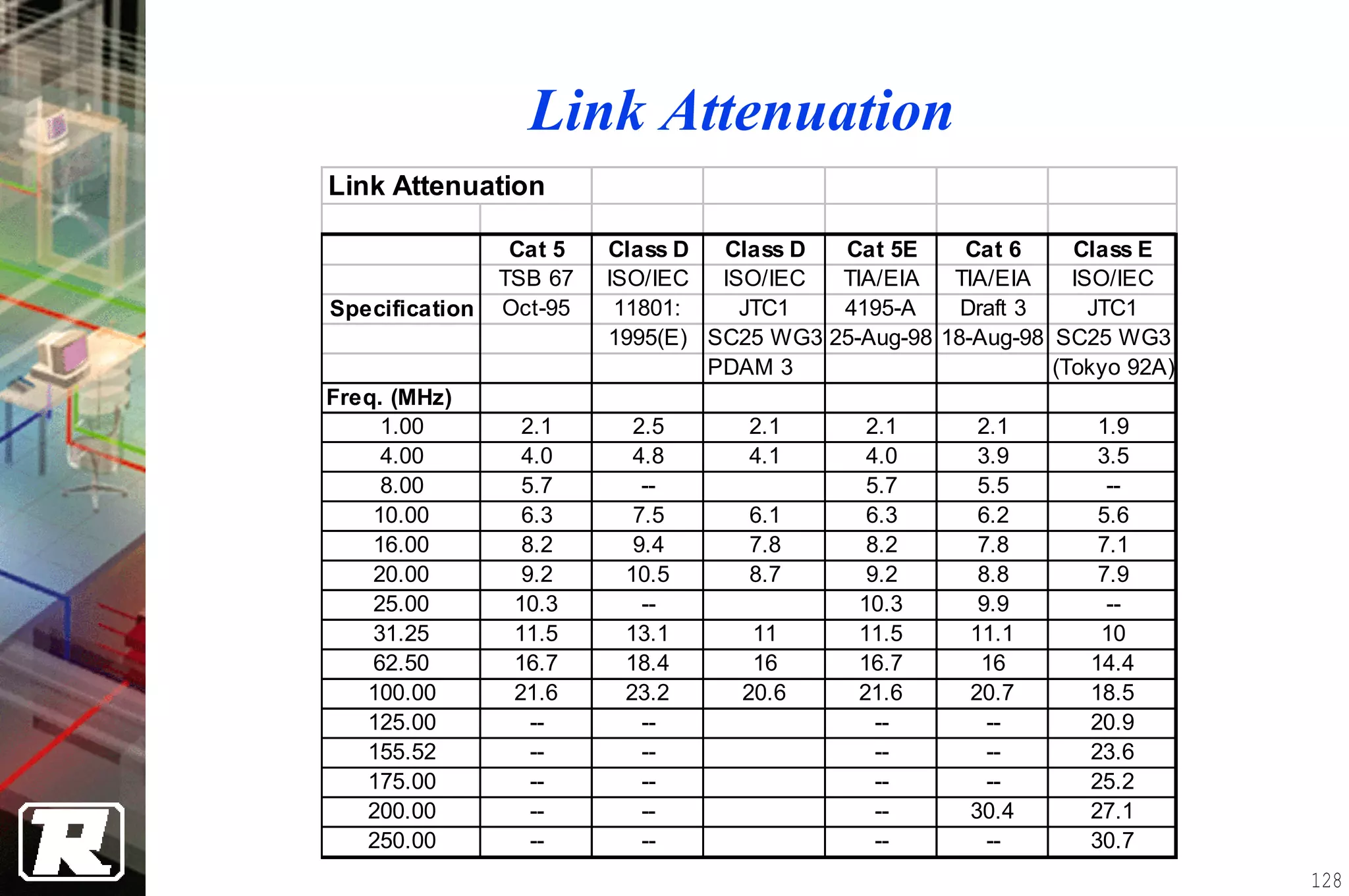
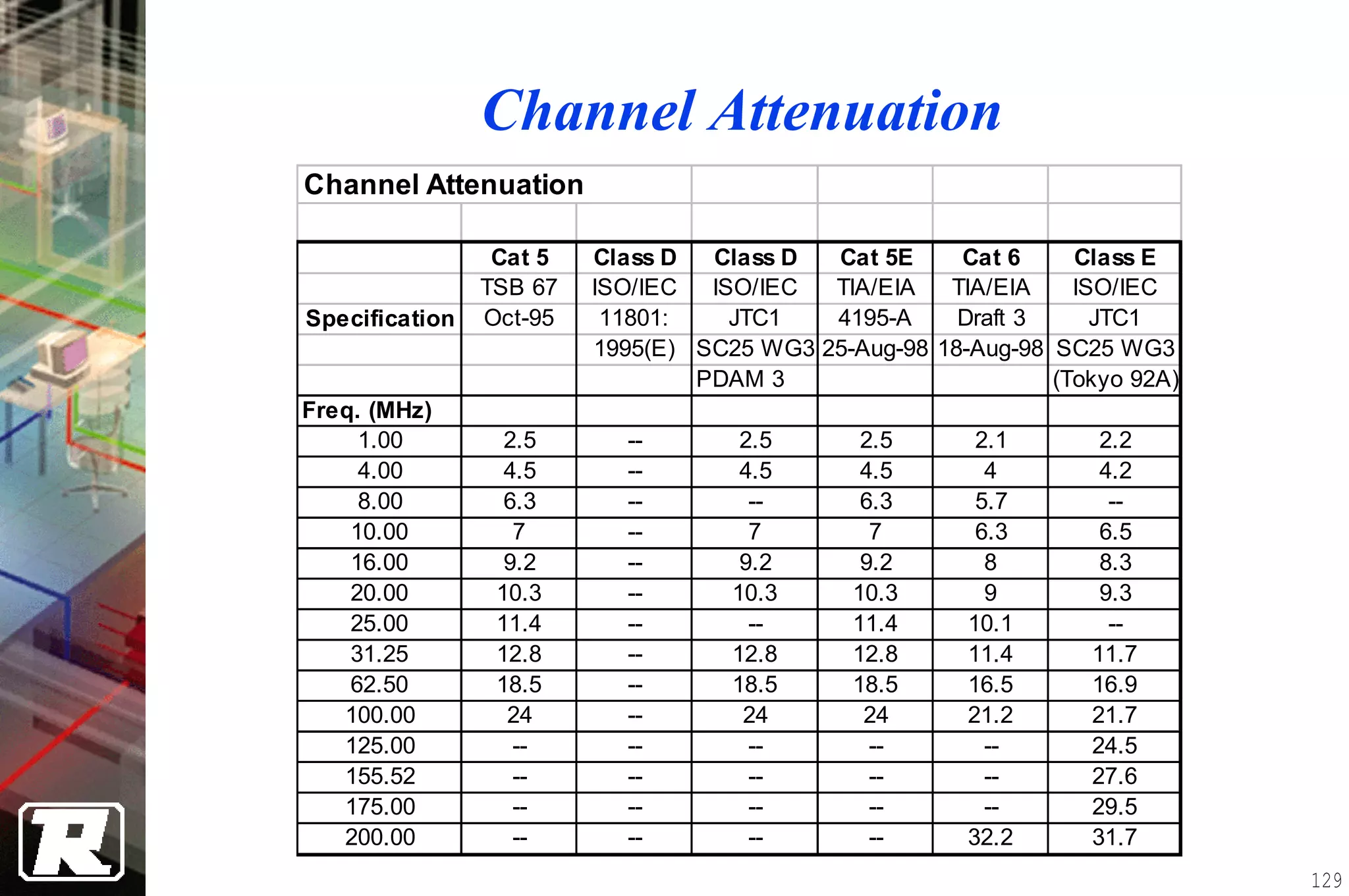
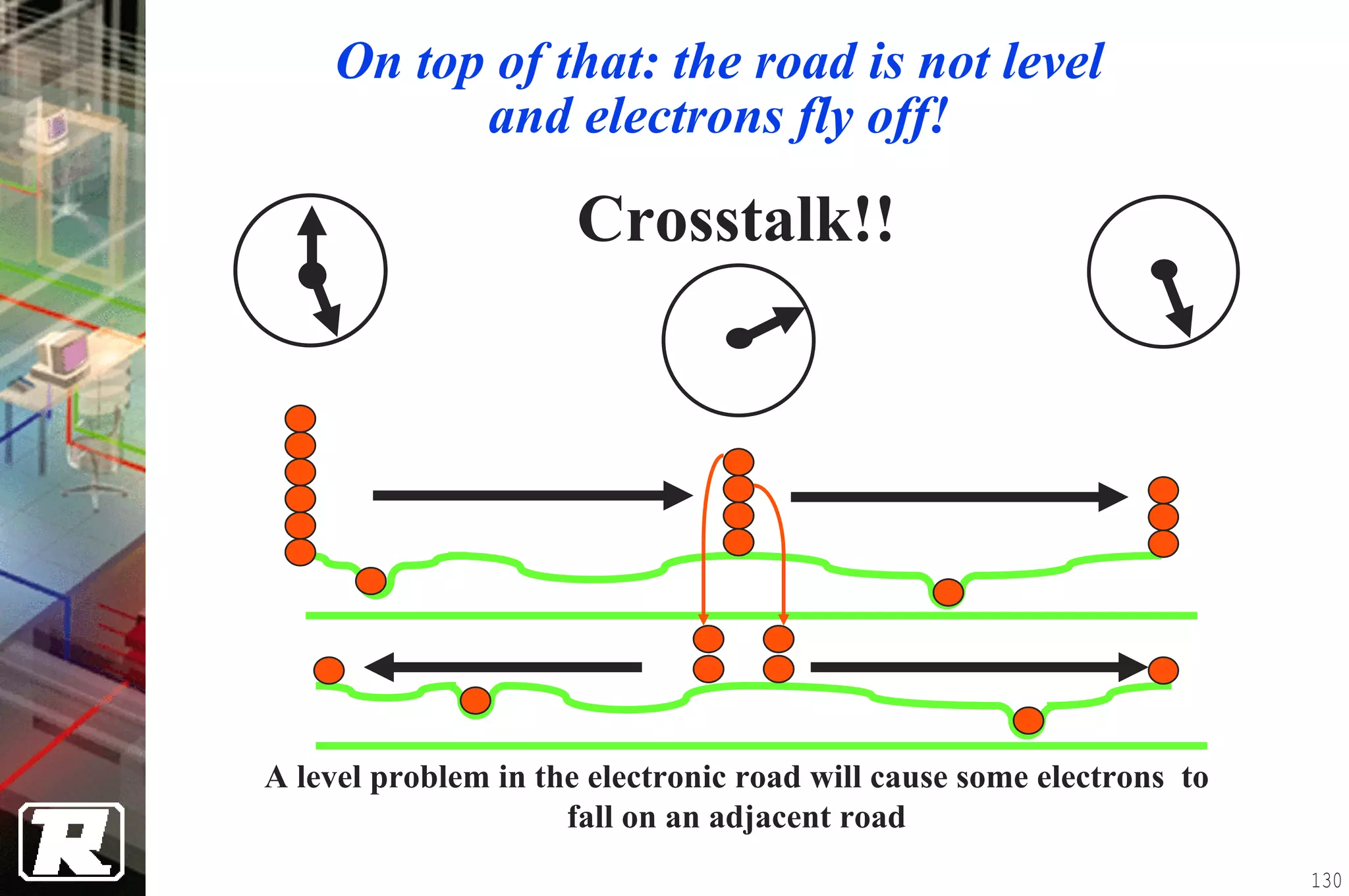
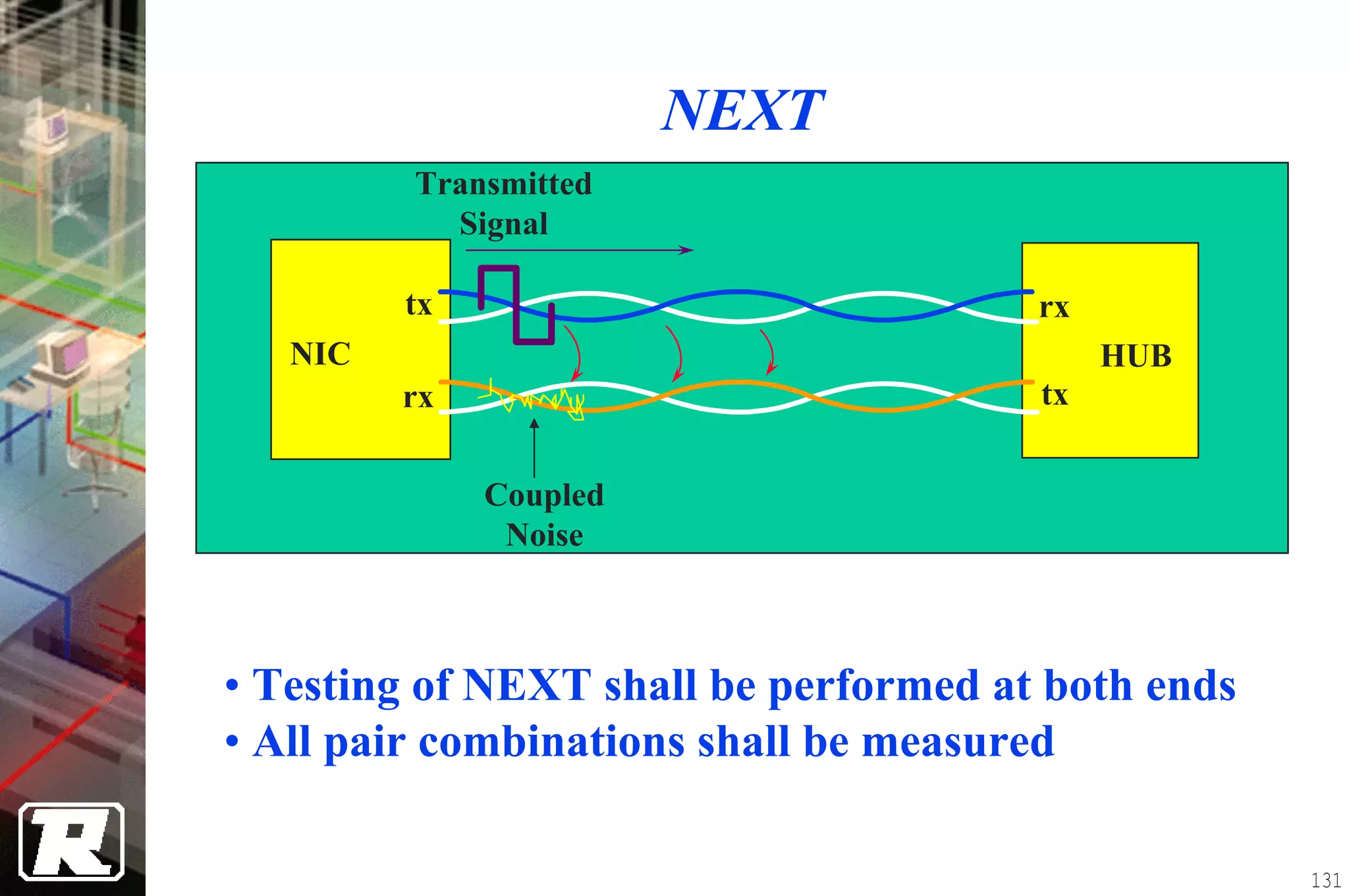
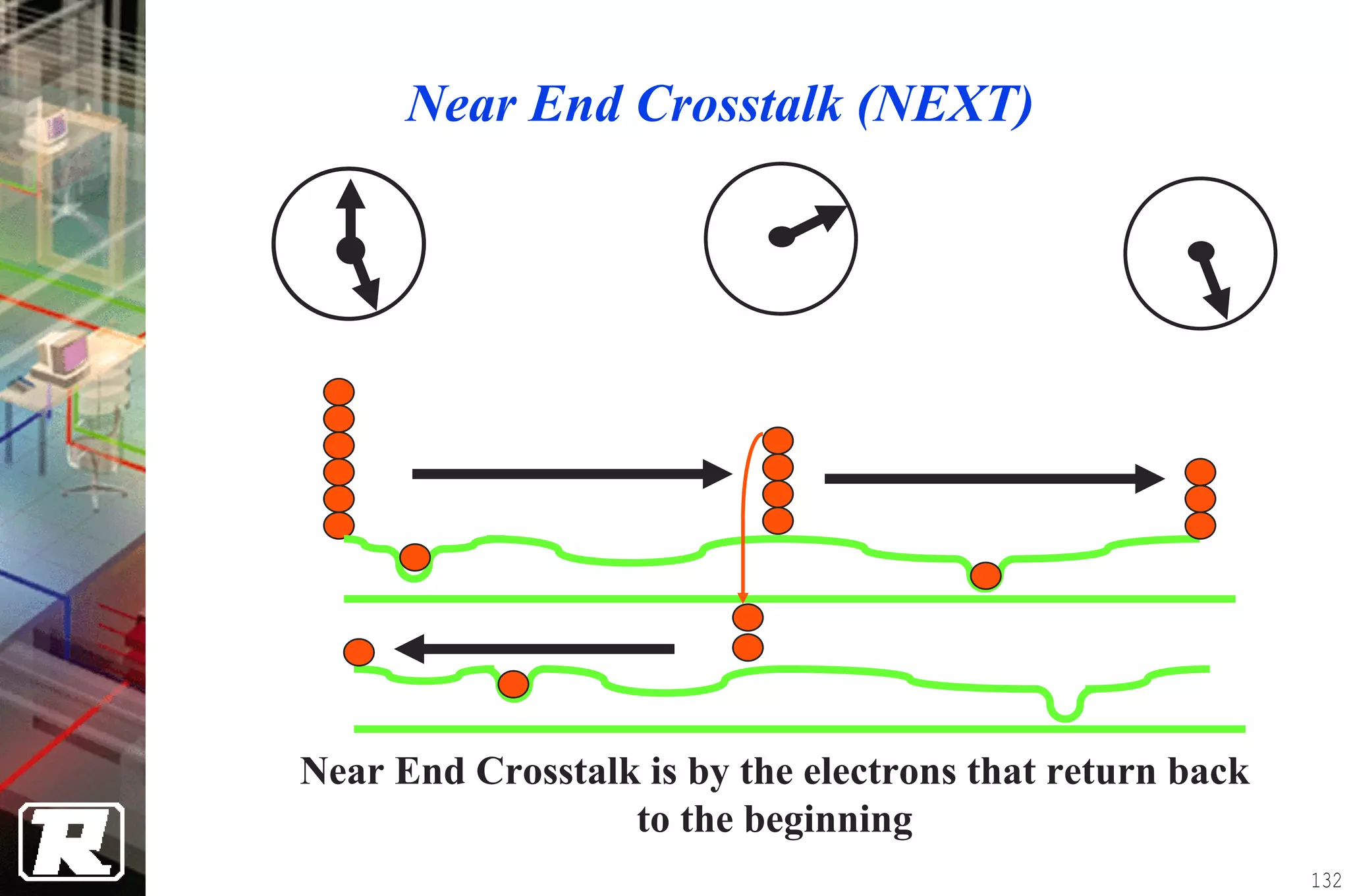
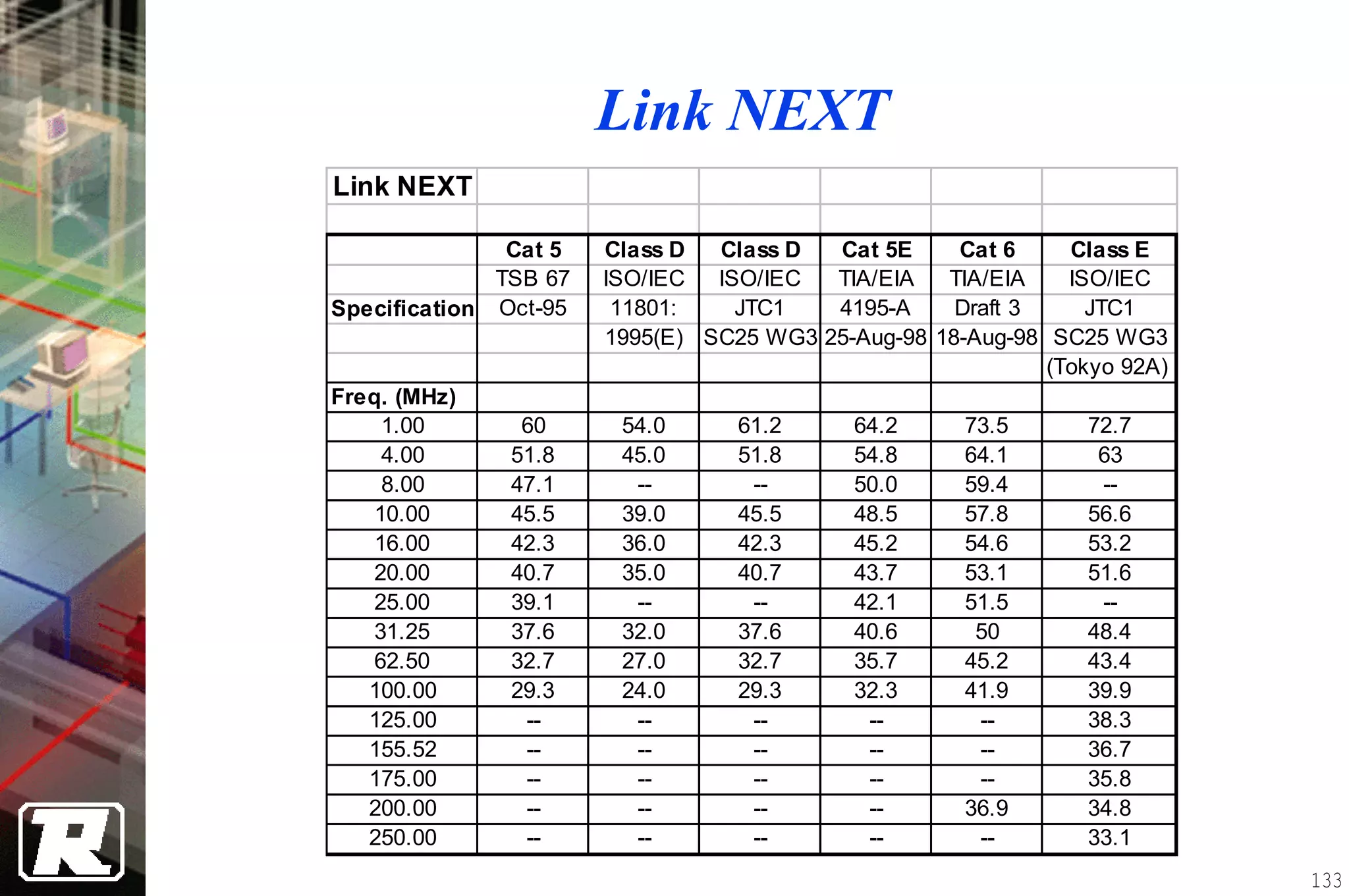
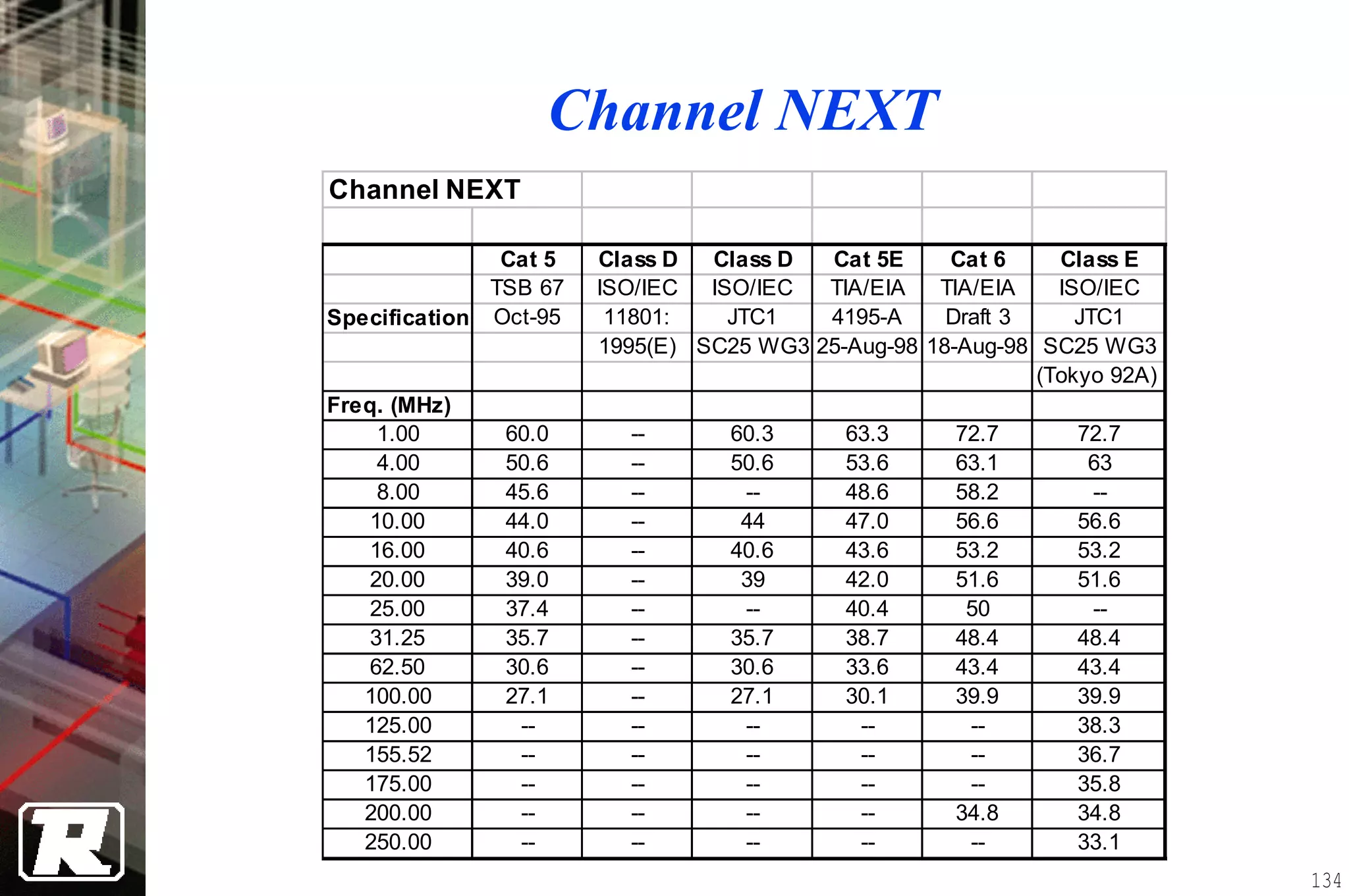
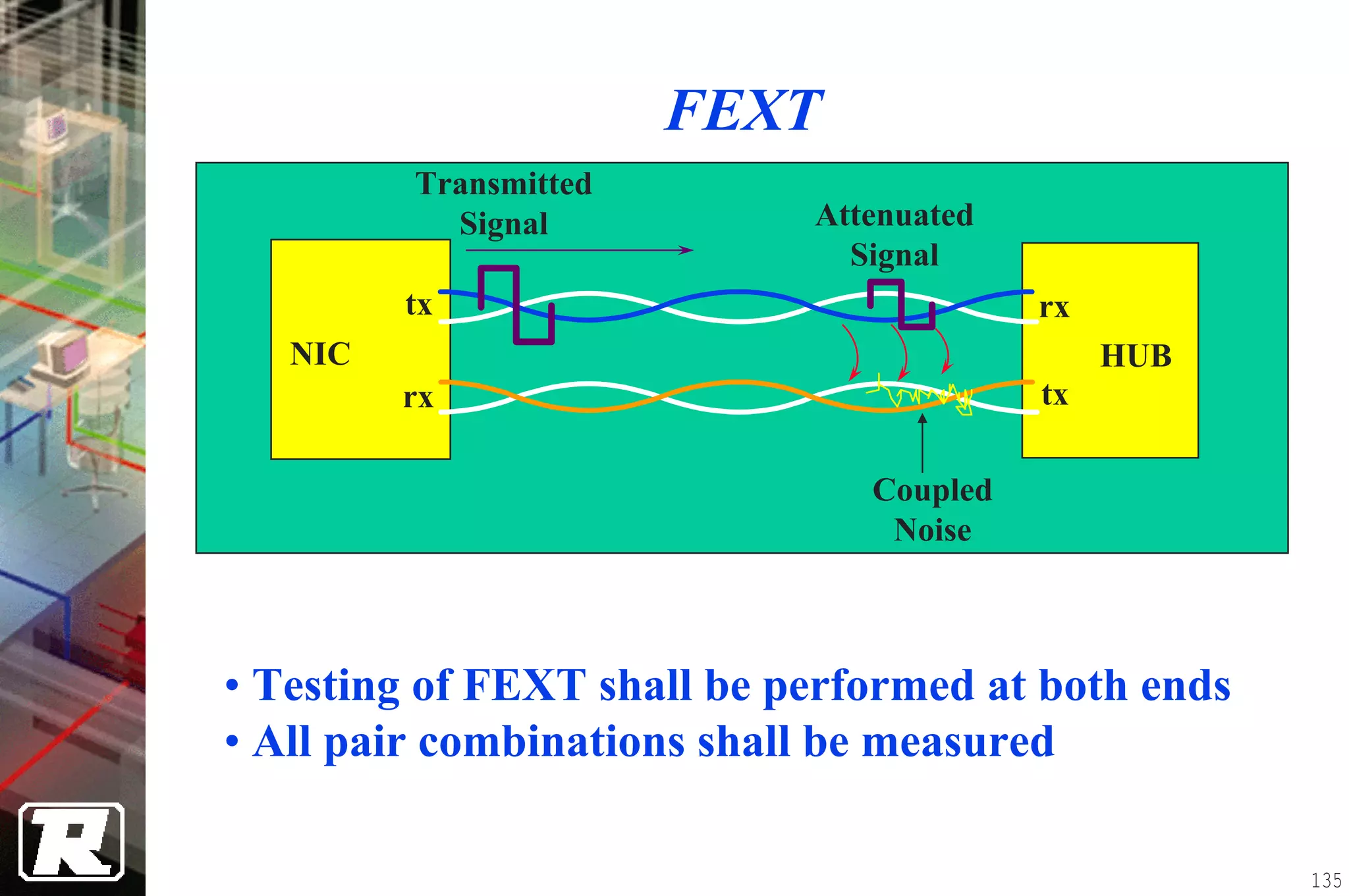
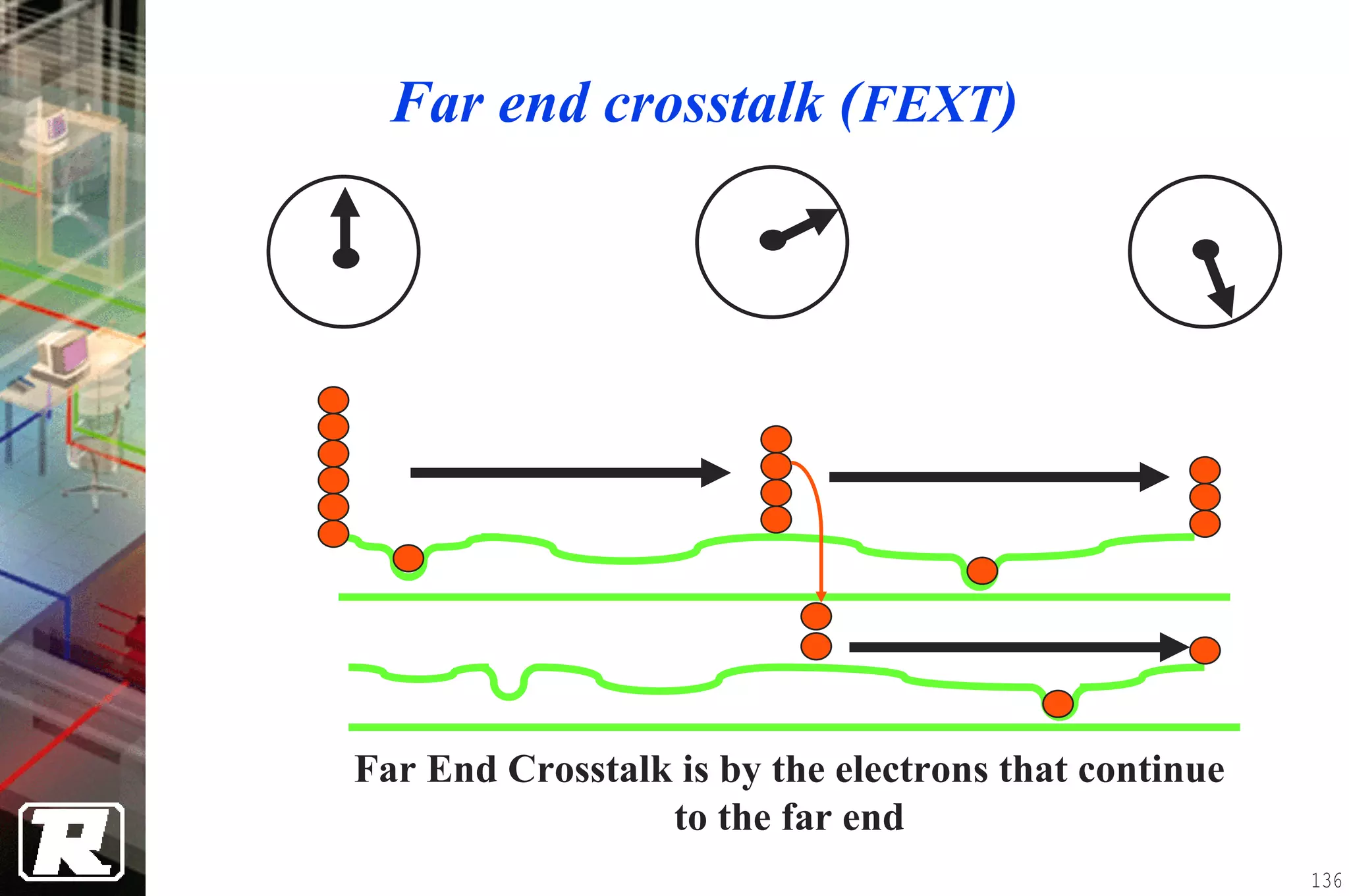
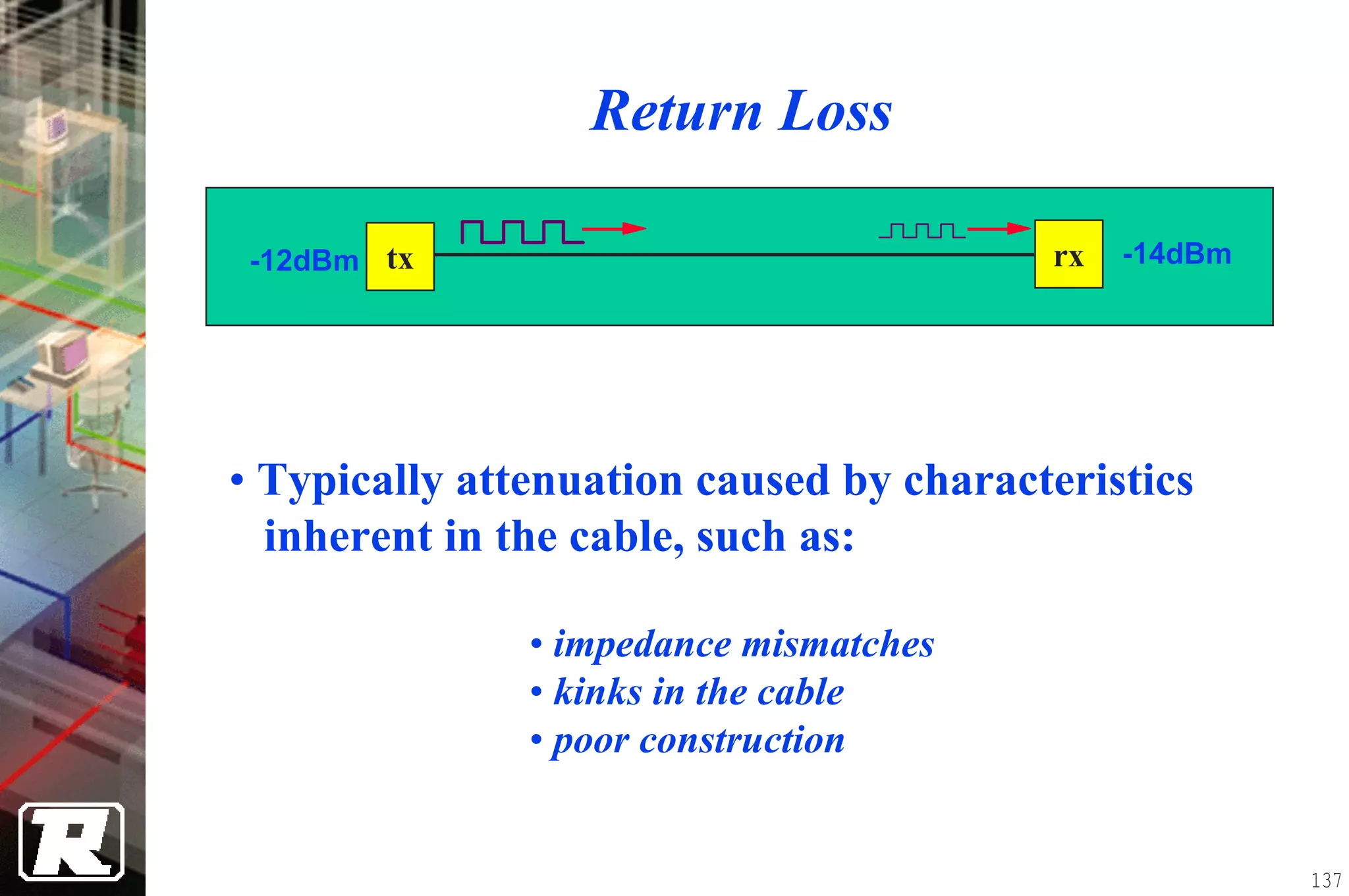
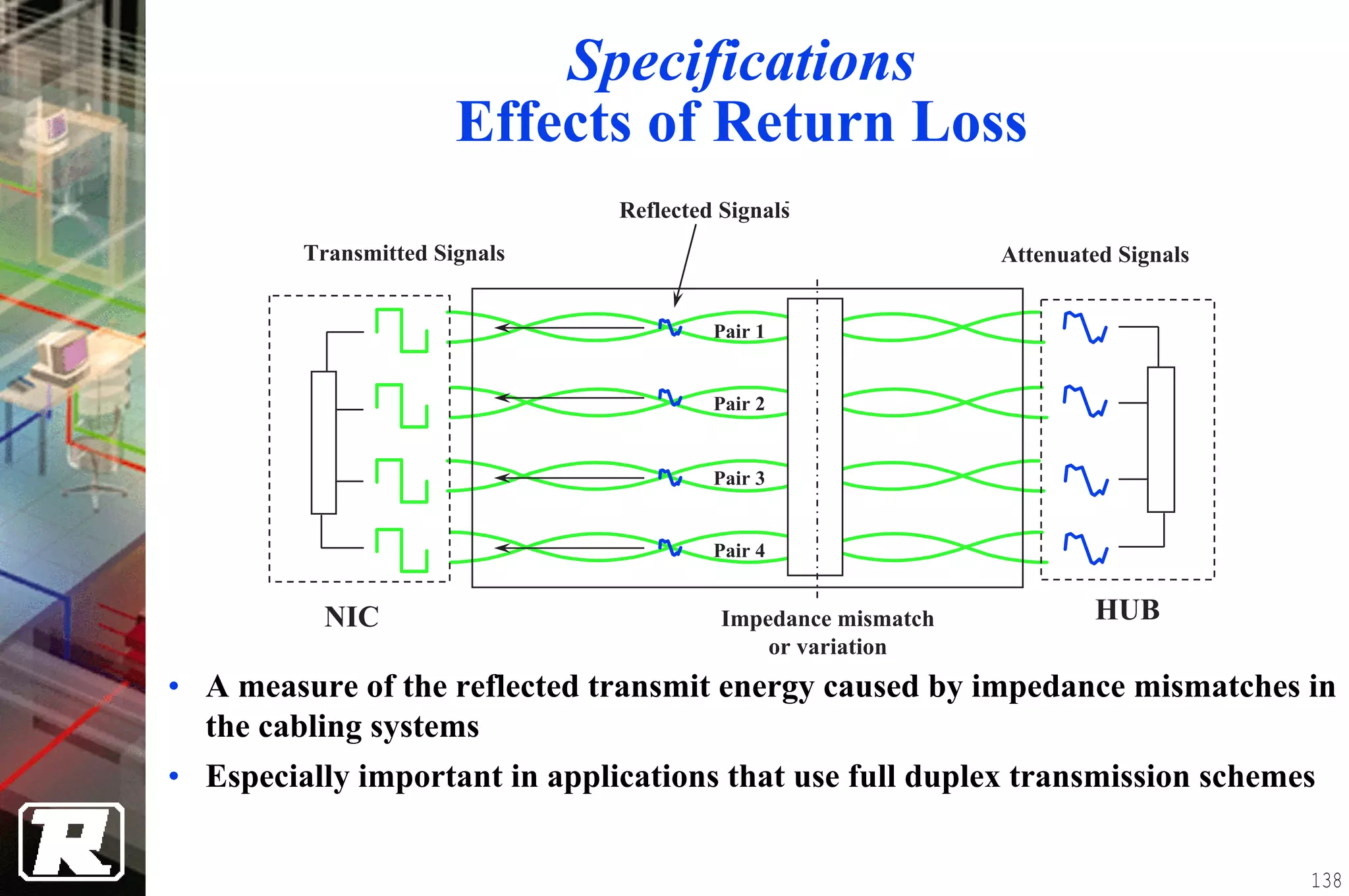
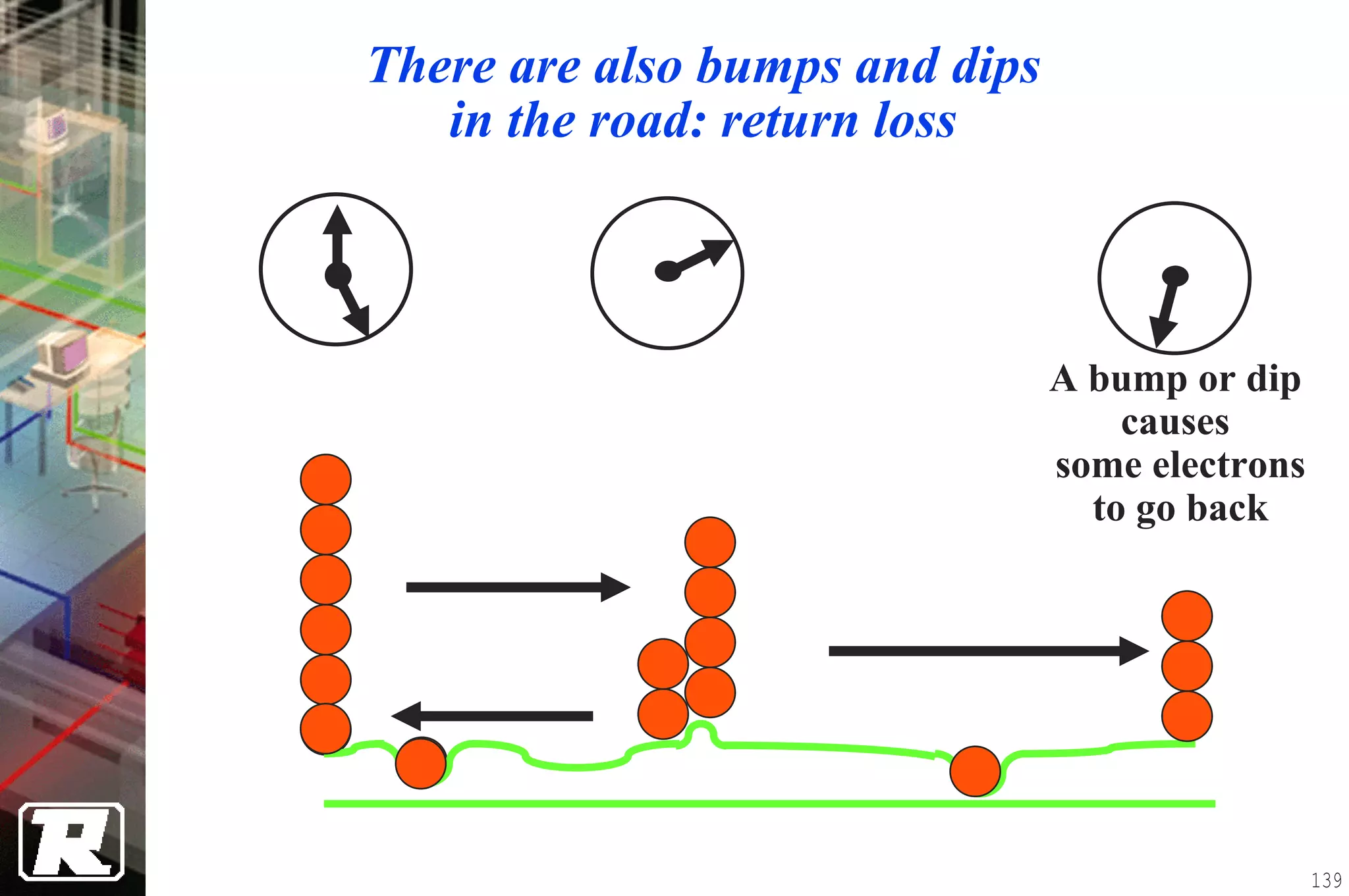
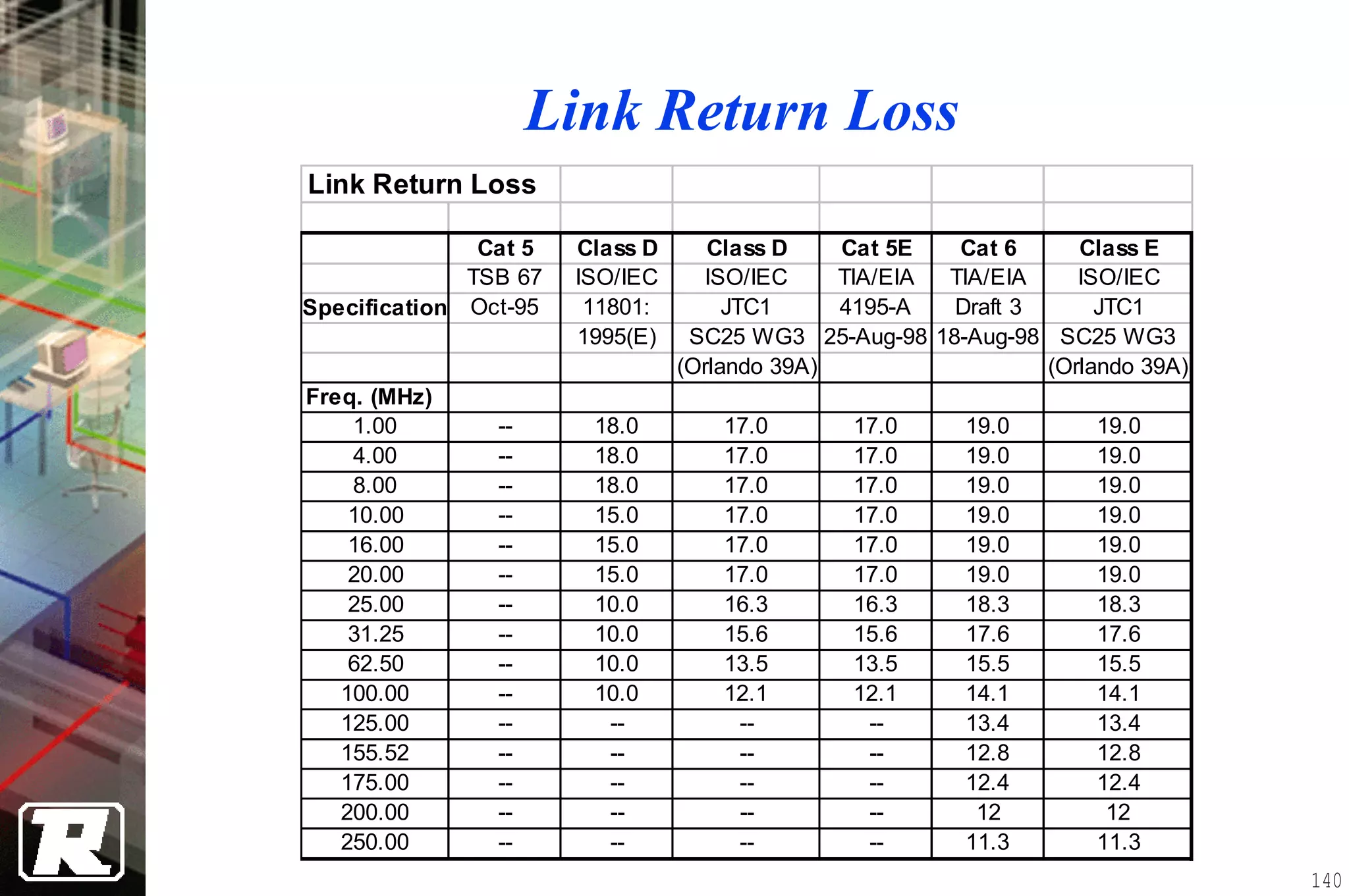
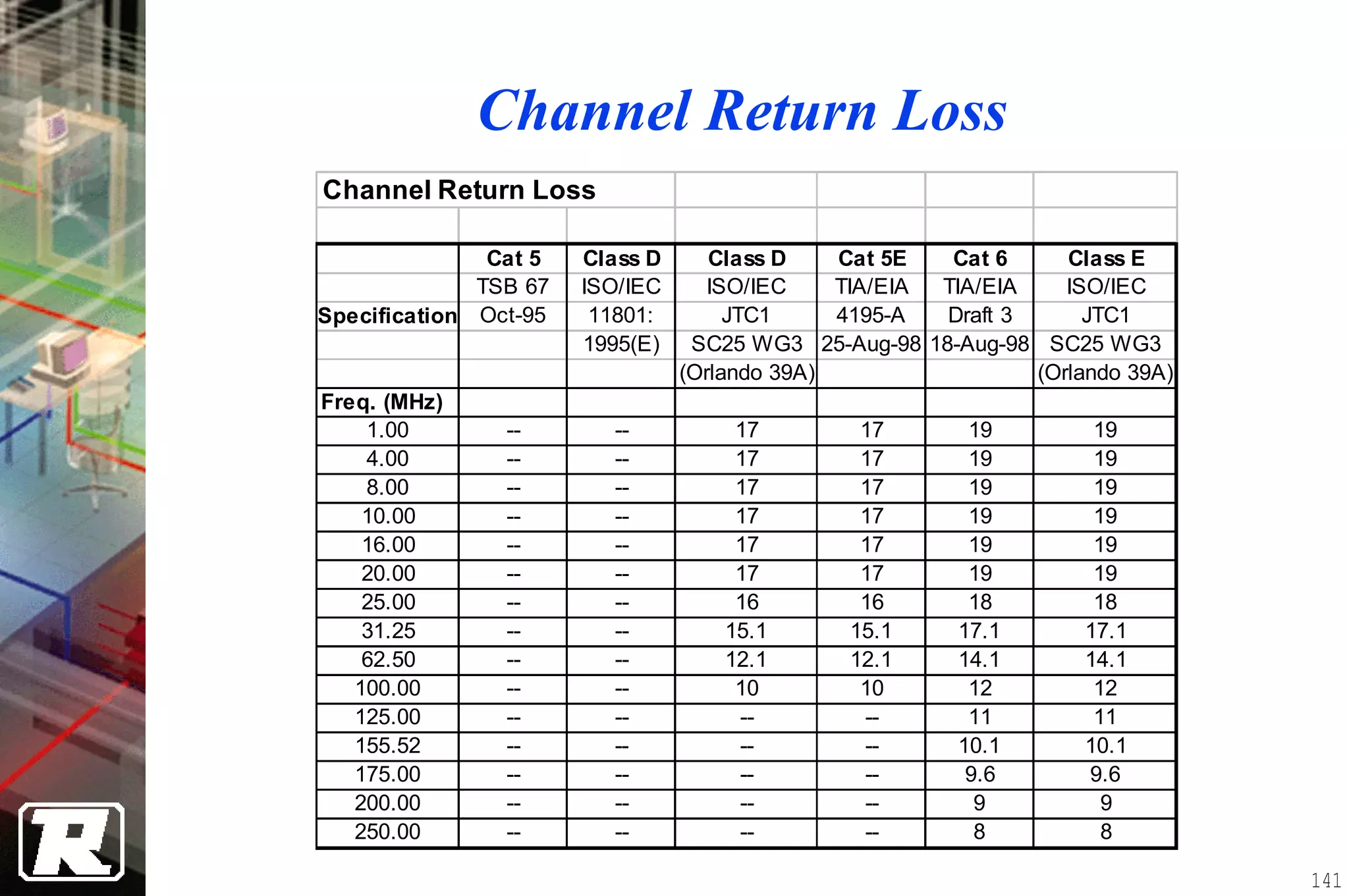
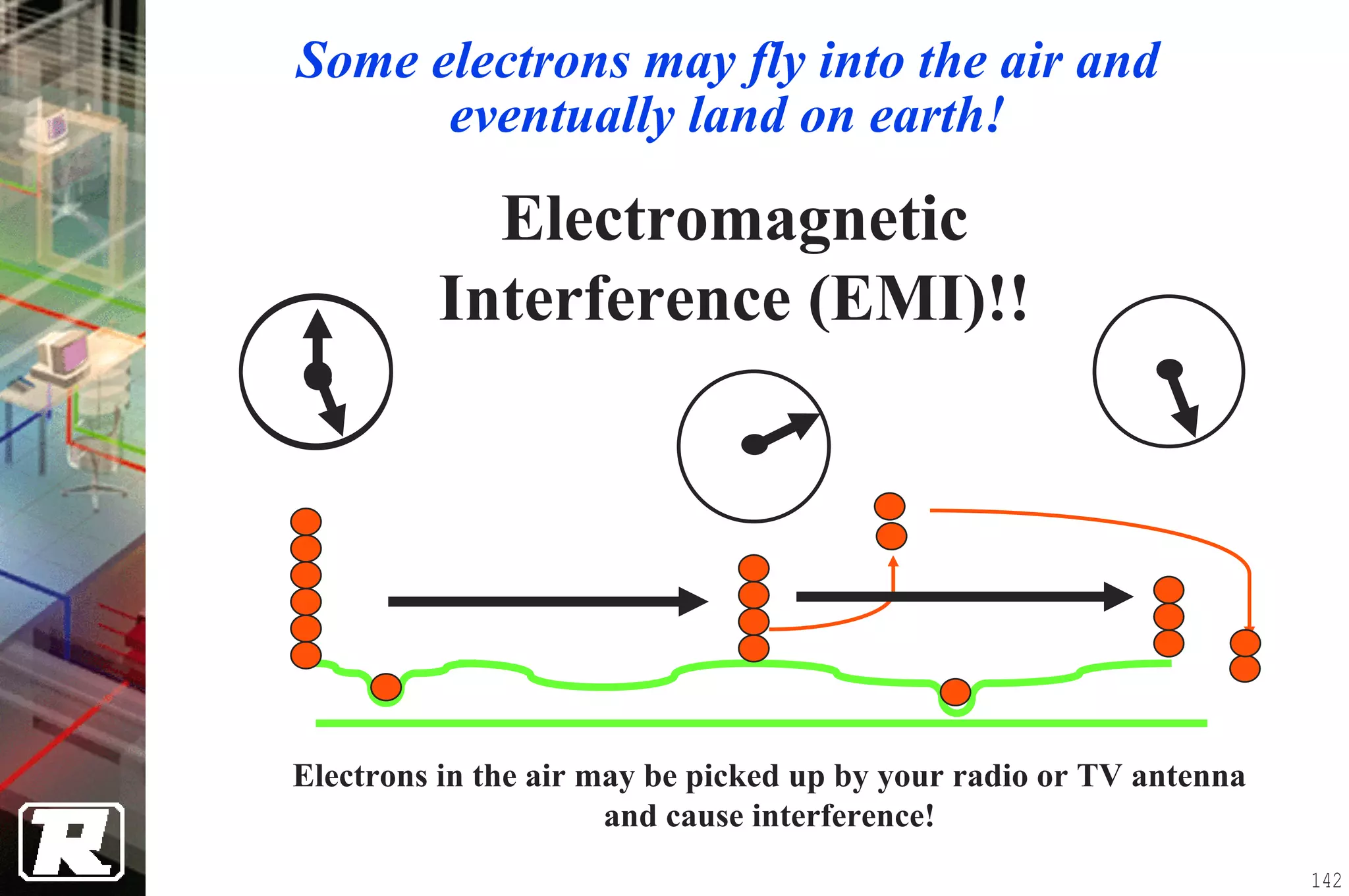
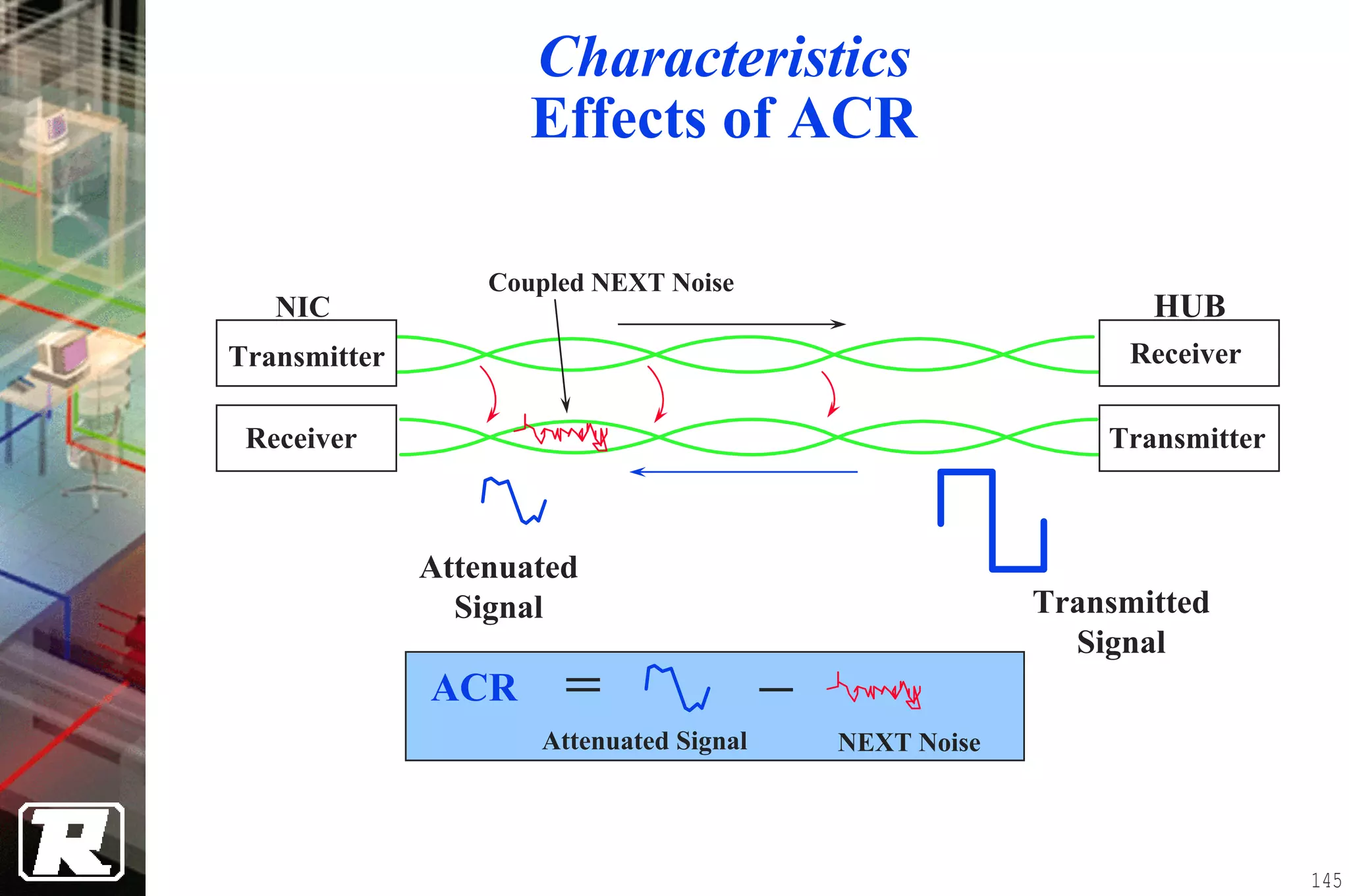
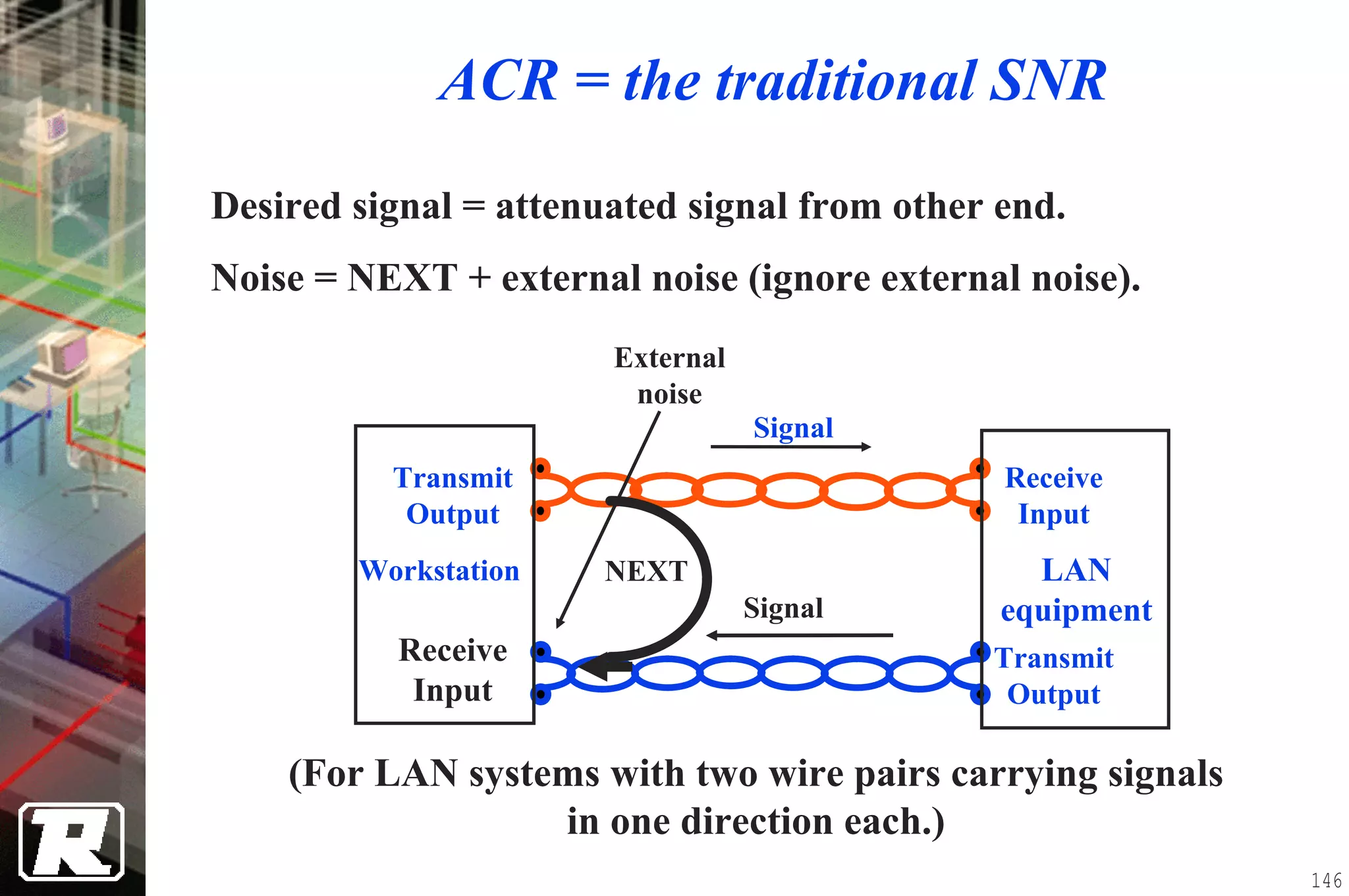
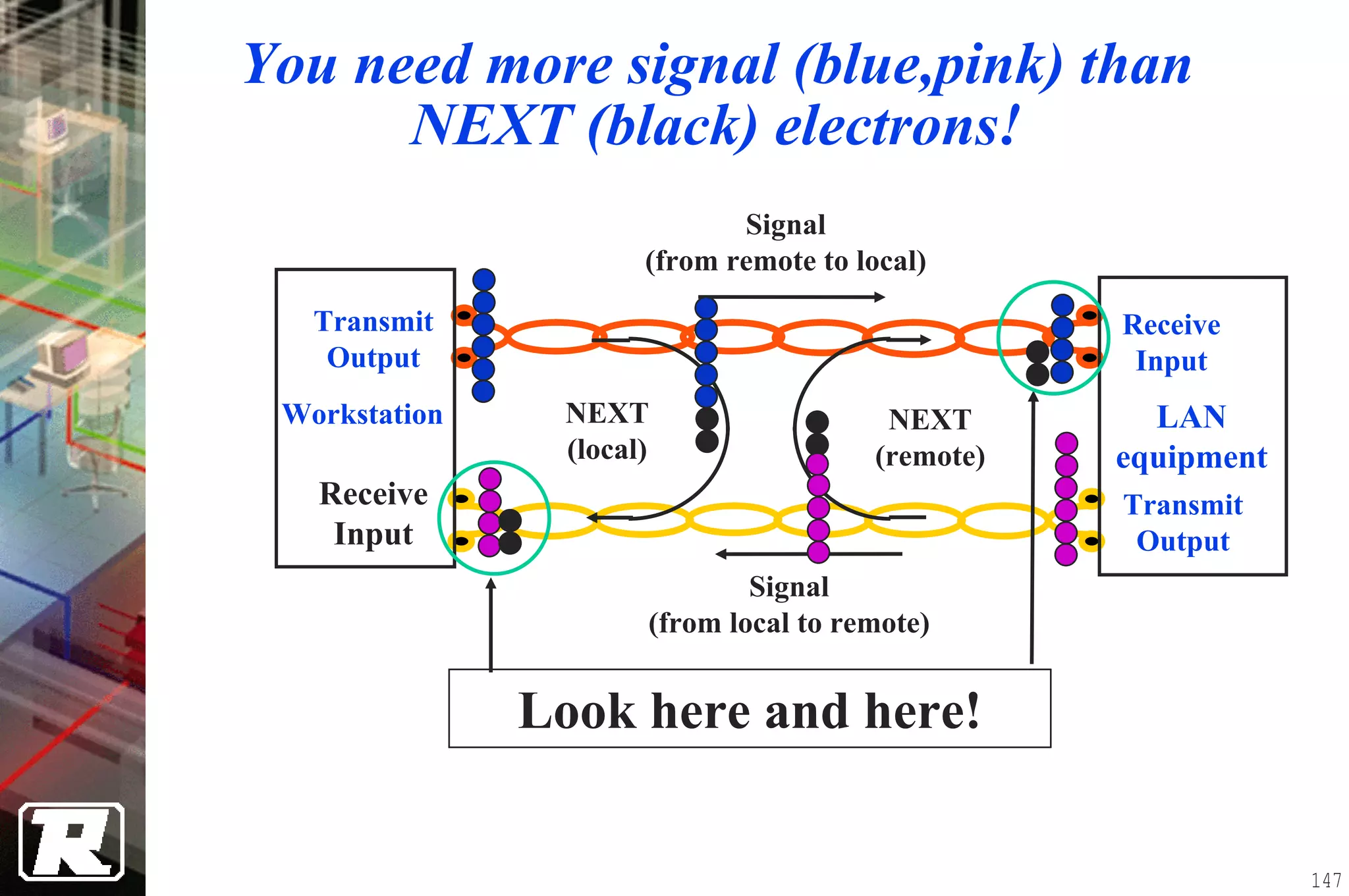
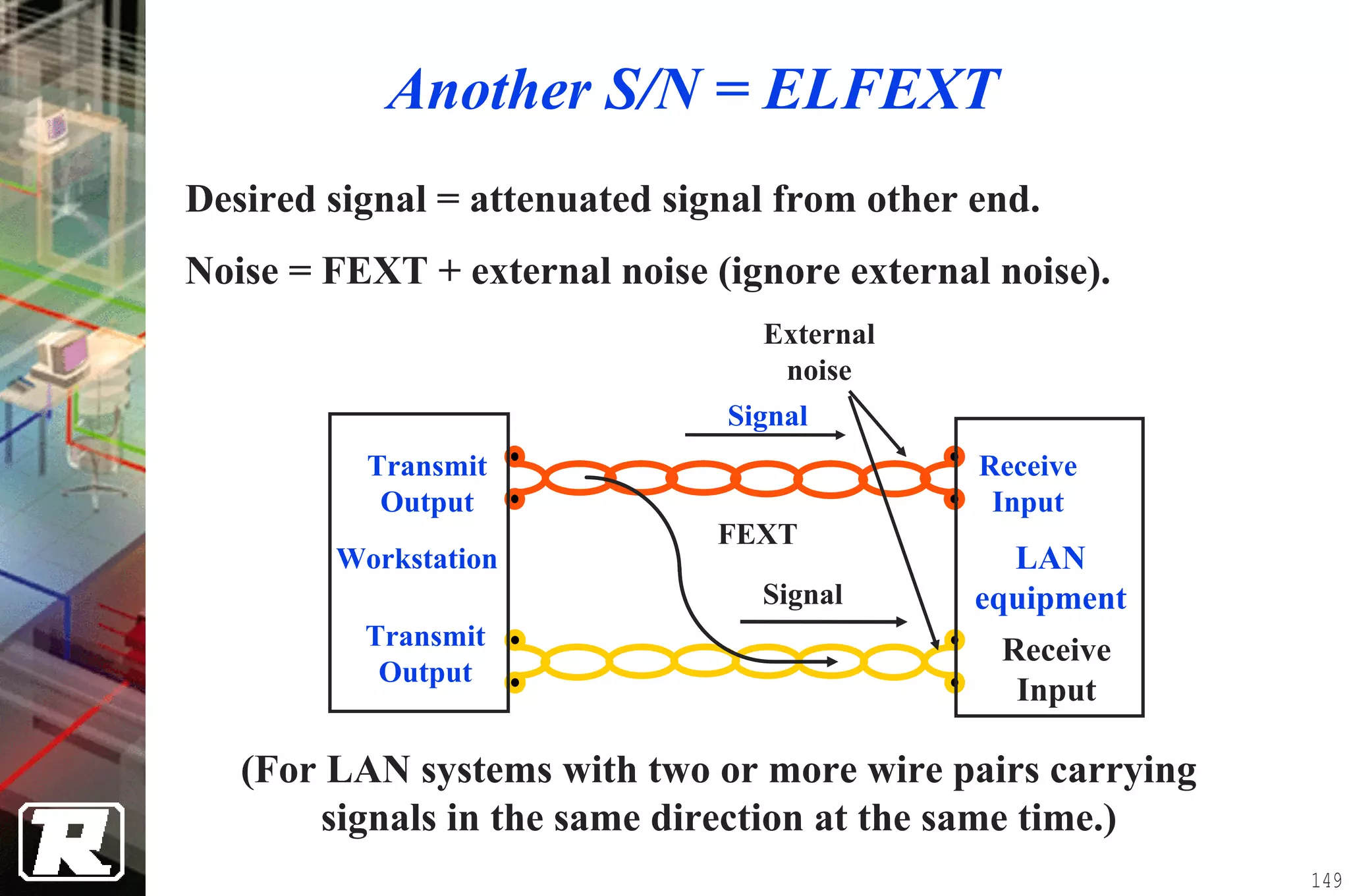
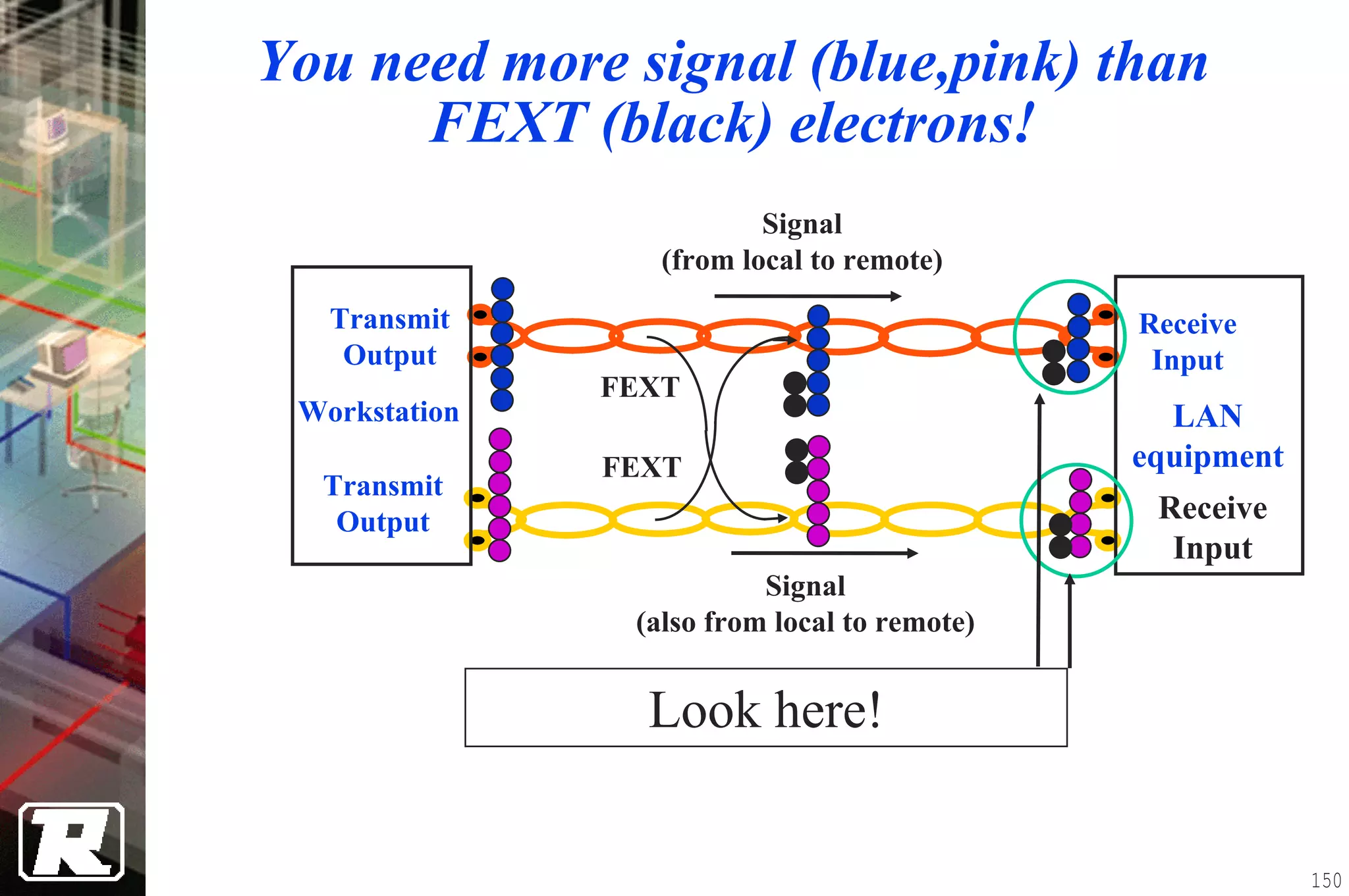
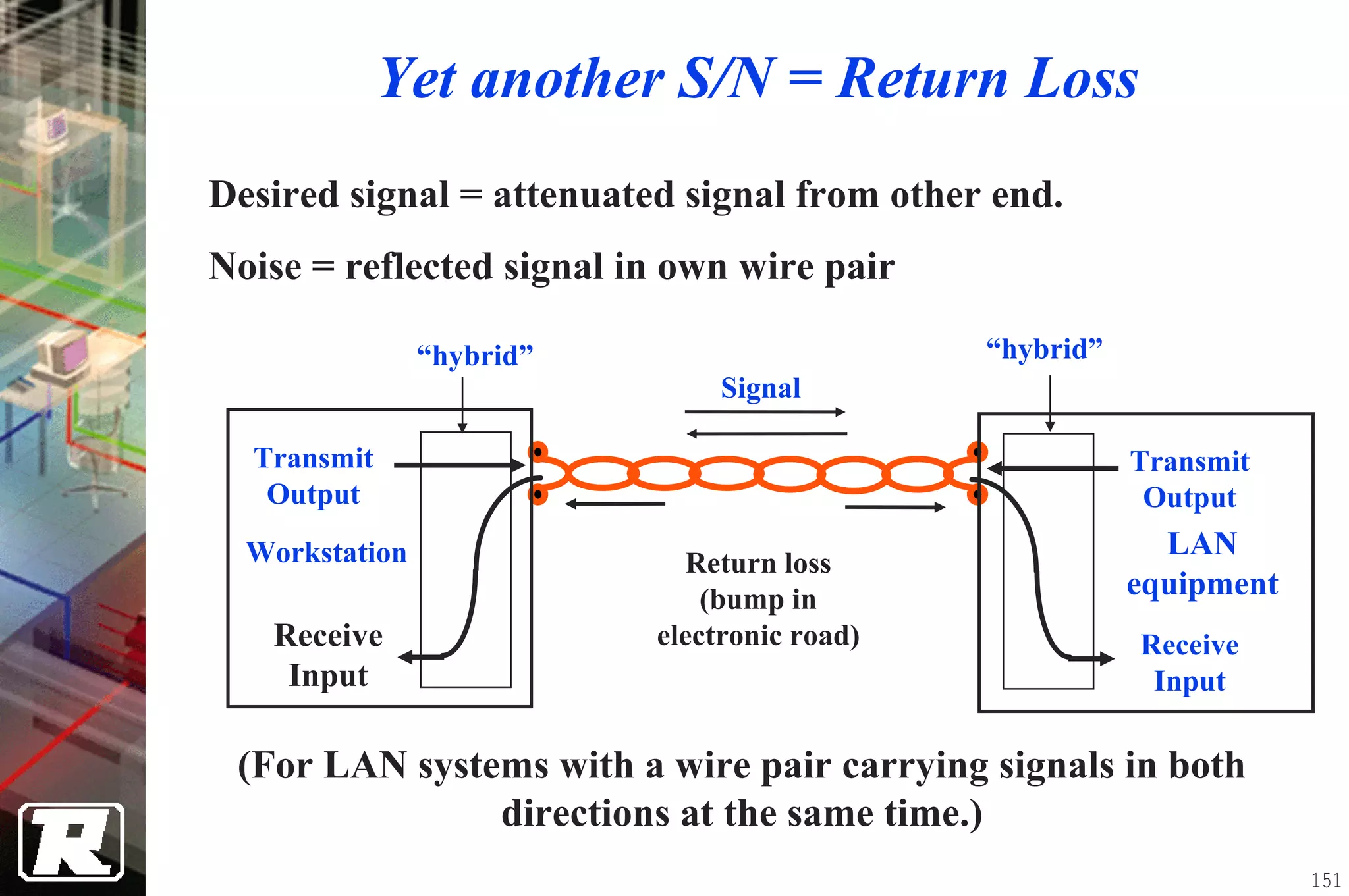
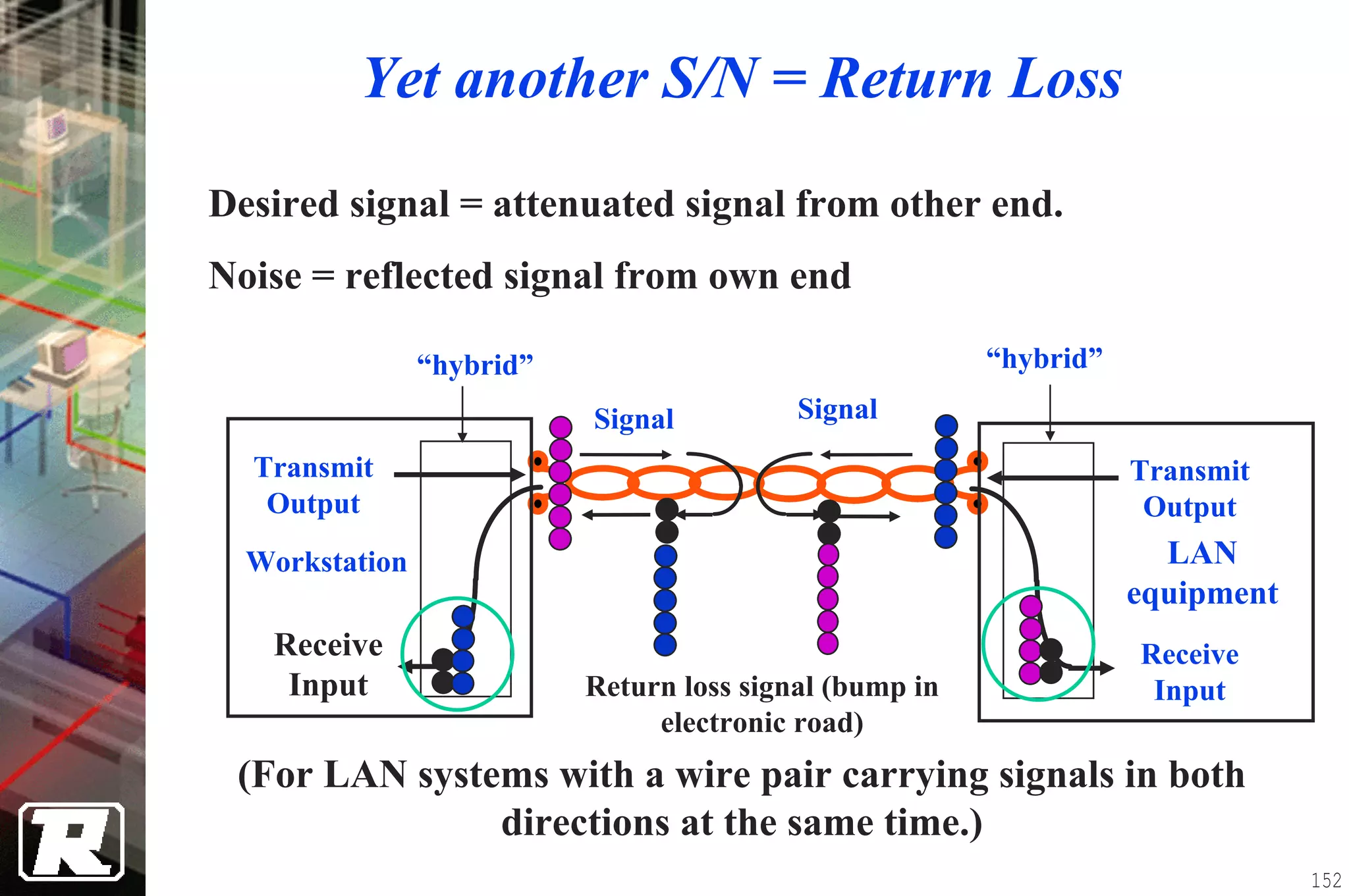
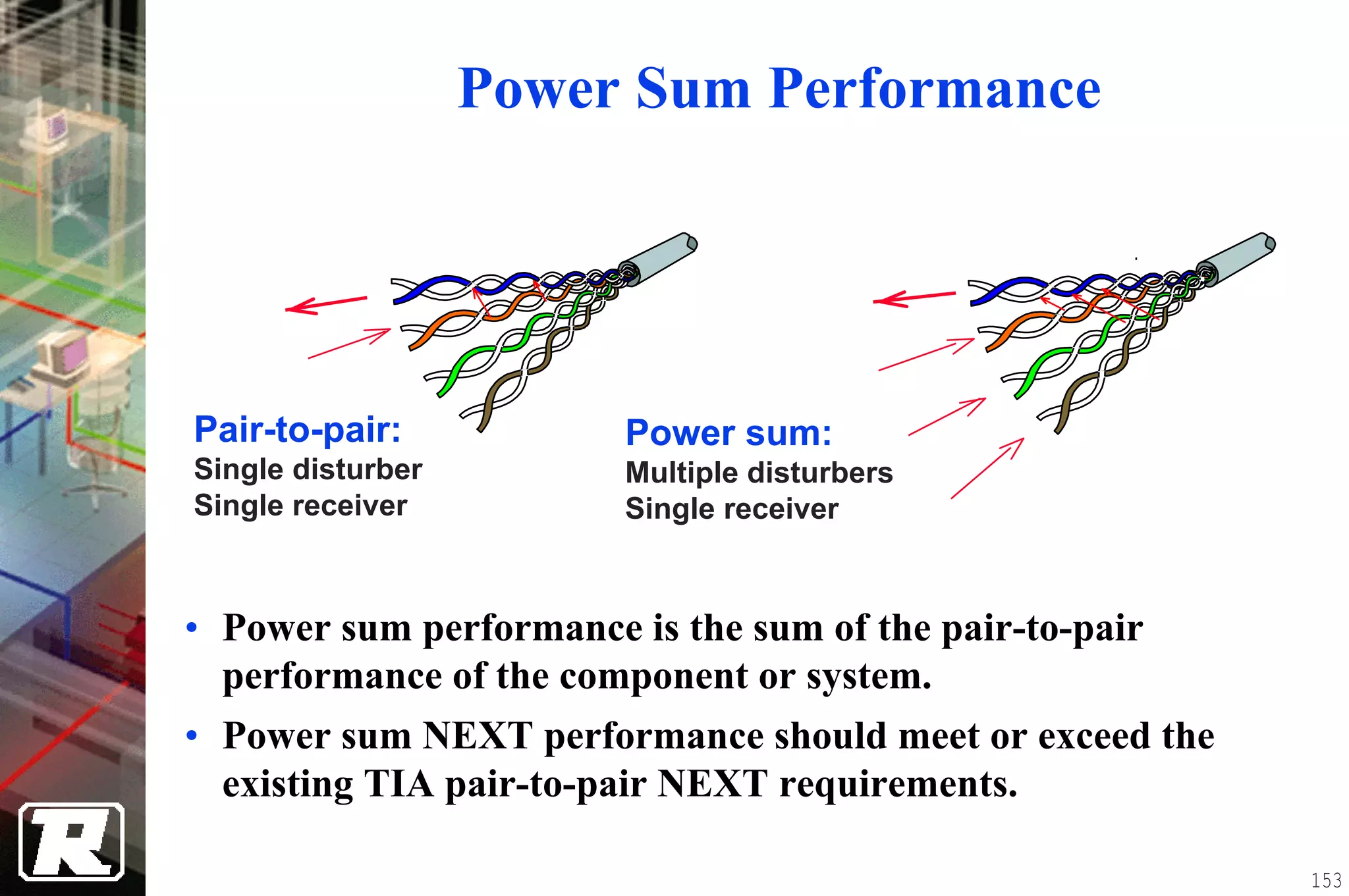
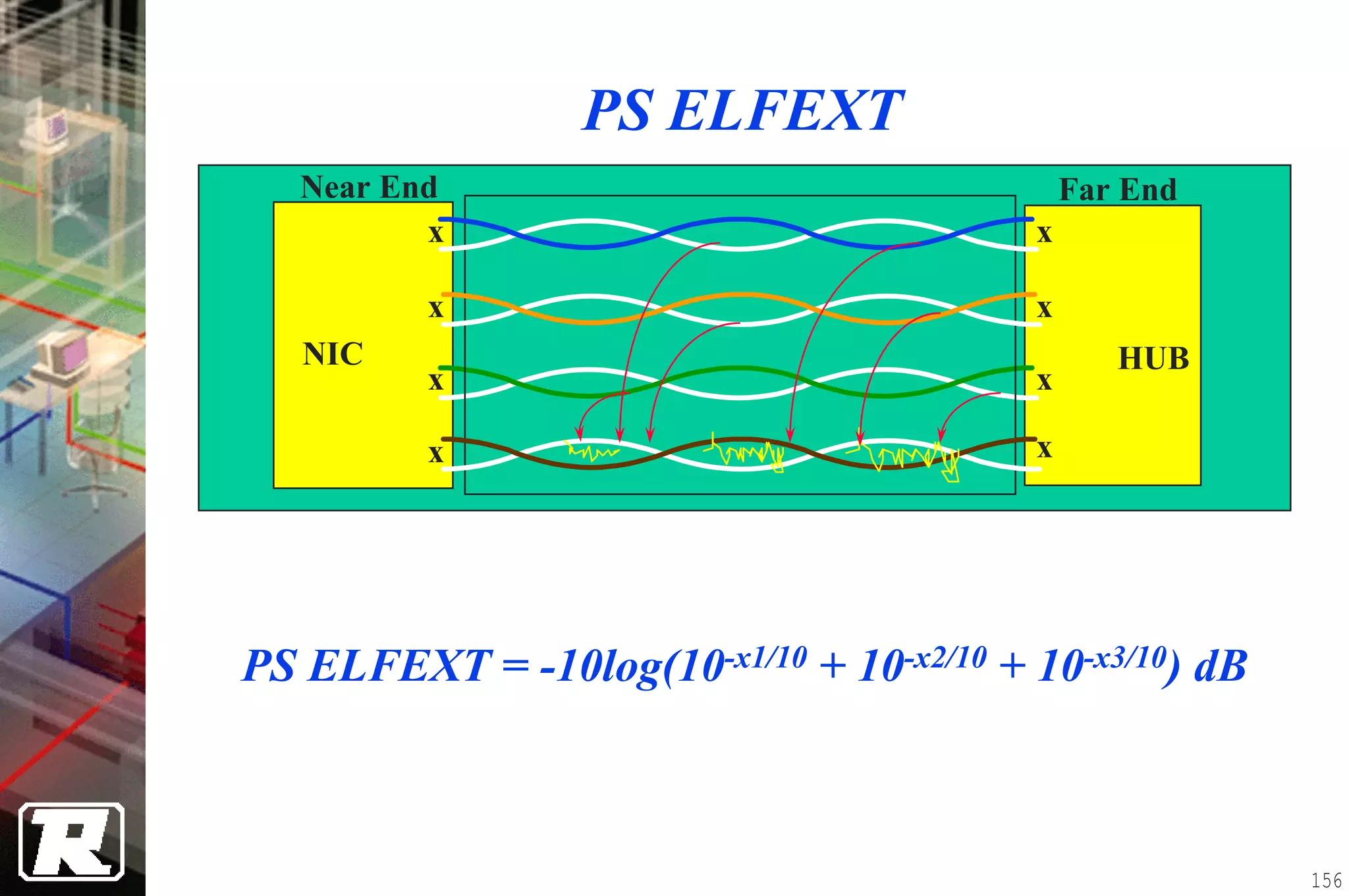
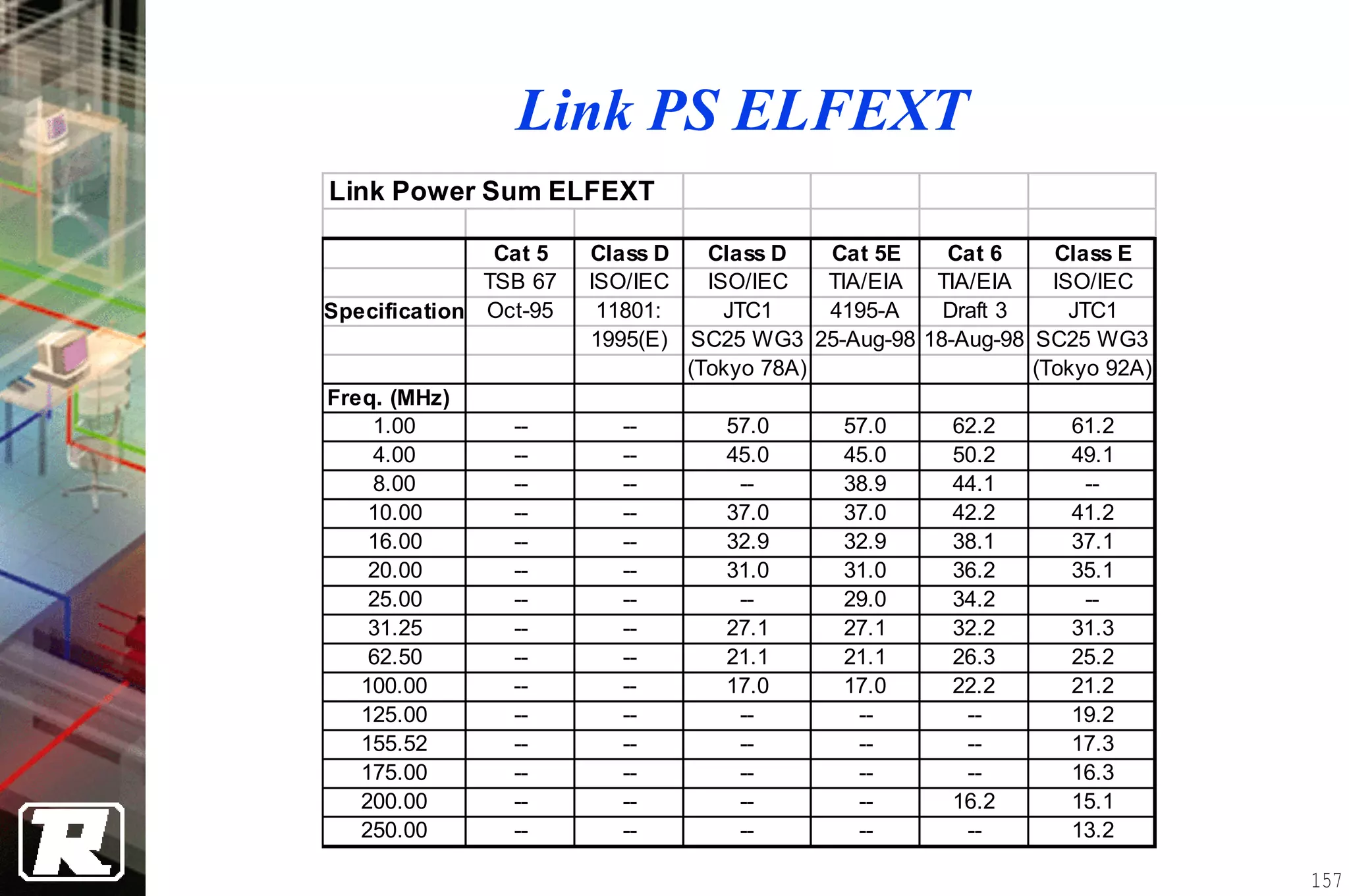
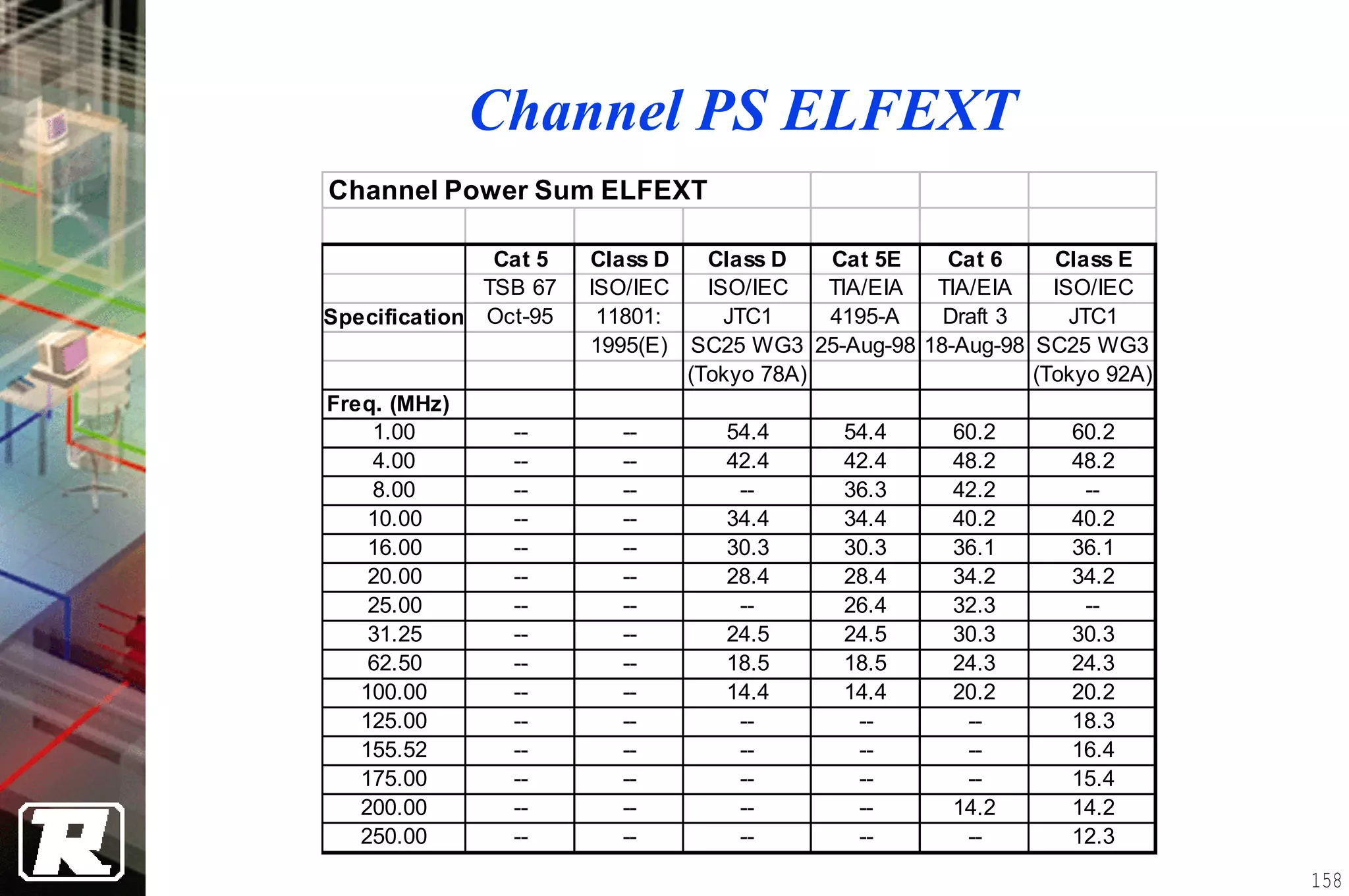
This document provides an overview of UTP installation, including rough-in procedures and specifications. It discusses items needed for rough-in like plans, materials lists, and tools. Installation specifications cover standards, placement of raceways and cables, labeling, and testing. Diagrams show outlet types, rack layouts, and bends and clearances. Performance parameters like attenuation, crosstalk, and length are also summarized.