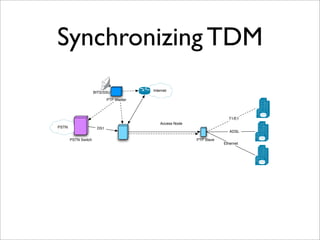
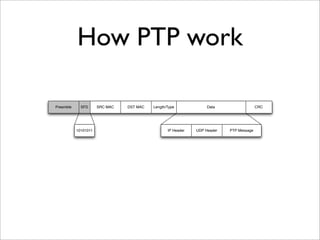
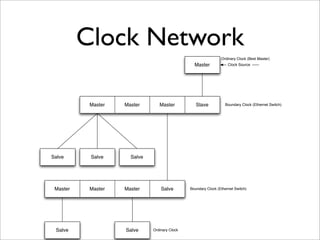
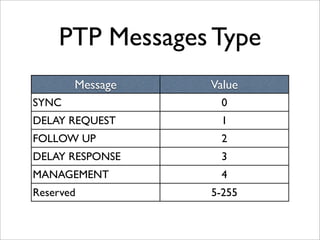
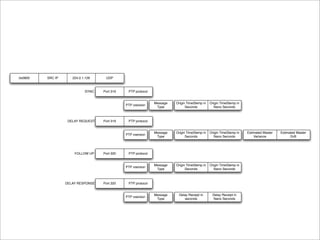
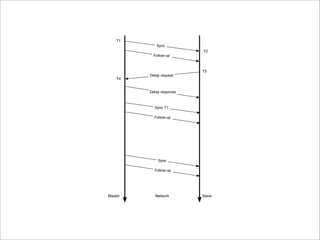
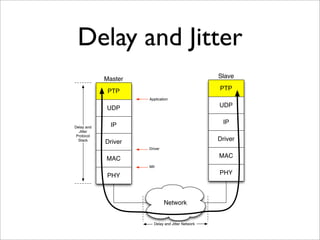
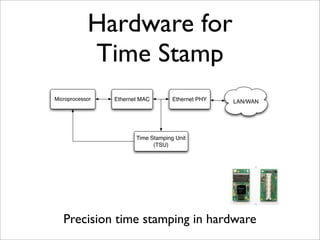
IEEE Standard 1588 defines the Precision Time Protocol (PTP) to synchronize clocks over packet networks. PTP is needed for applications that require precise timing such as Time Division Multiplexing (TDM) over IP. PTP uses network messages and timestamps to synchronize slave clocks to a master clock with nanosecond precision. PTP messages include sync, delay request, follow up, and delay response. Hardware time stamping is often required to achieve high precision with low delay and jitter. PTP is a cheaper and more scalable solution than alternatives like GPS or atomic clocks for synchronizing networks to within 50 parts per billion.