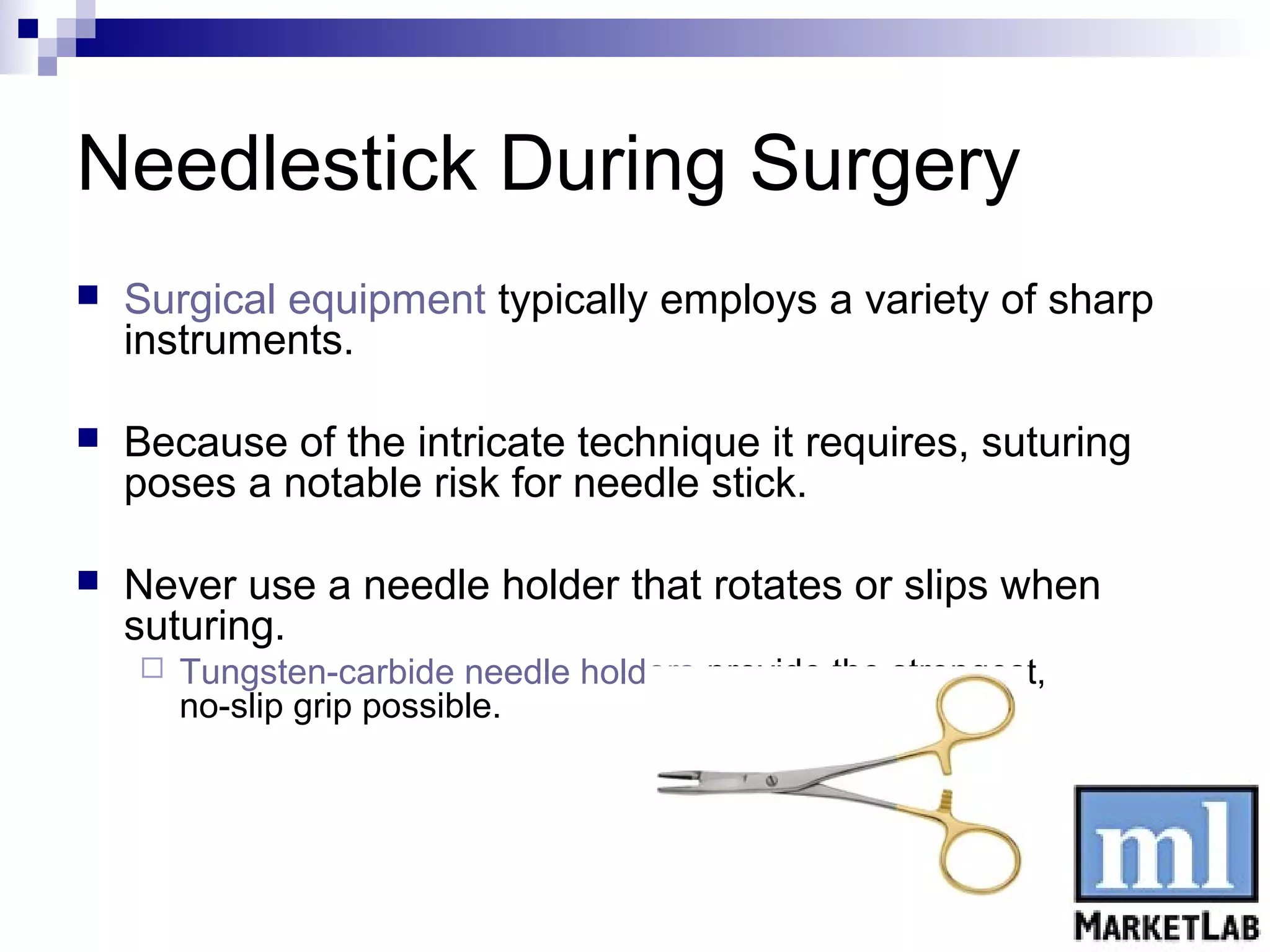
Needlestick injuries pose significant risks for healthcare workers, with an estimated 600,000 to 800,000 incidents occurring annually in the U.S., leading to high treatment costs and potential infections from blood-borne diseases. Preventive measures include using engineered safety devices, proper needle disposal, and following established safety protocols. In case of a needlestick injury, immediate washing, reporting, and possible testing are crucial for minimizing infection risks.