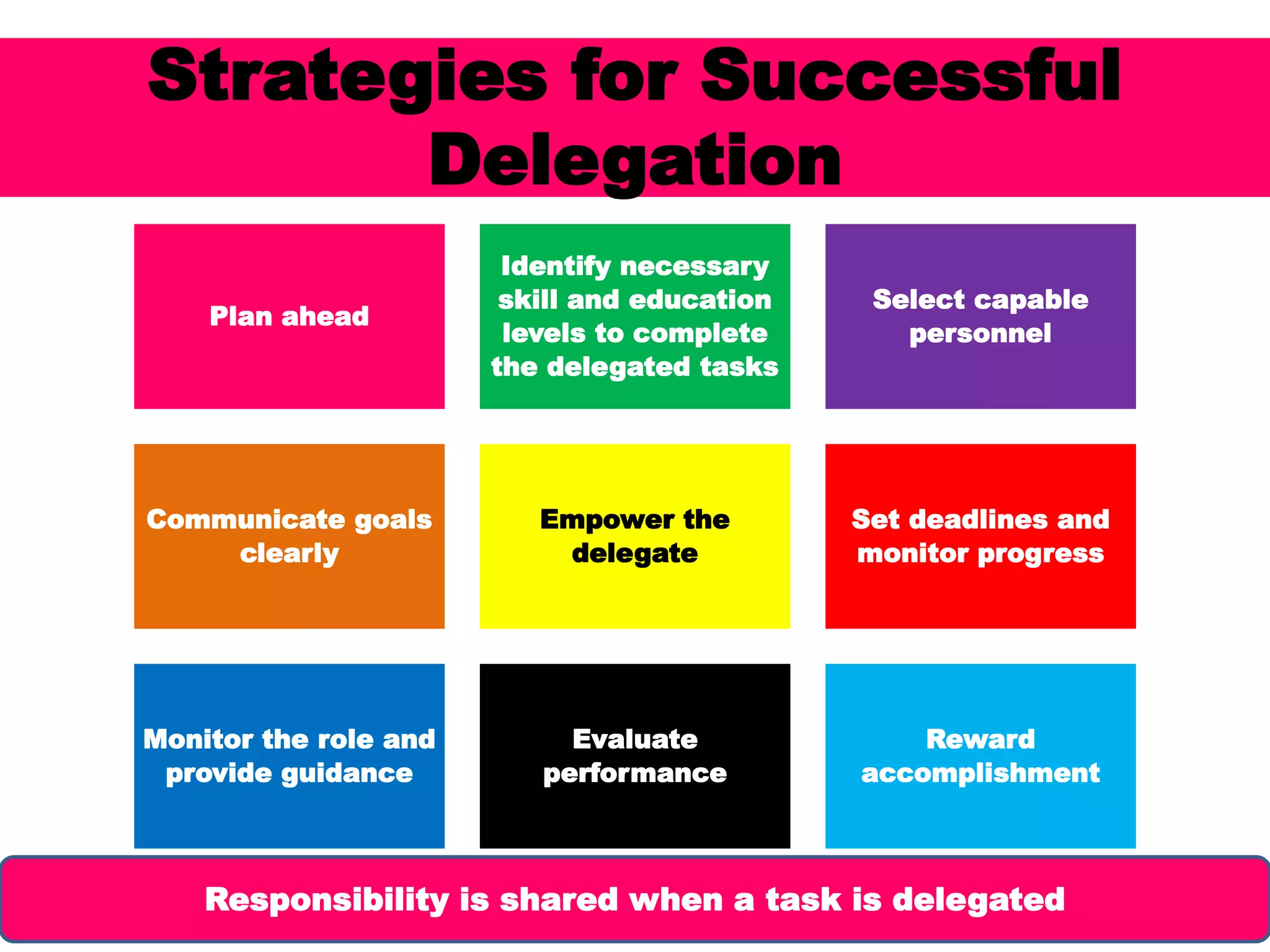
Delegation involves entrusting authority and empowering others to act on your behalf. It is important for handling complex problems and providing learning opportunities. Successful delegation requires planning, selecting capable people, clear communication, empowering delegates, monitoring progress, and evaluating performance. Common errors include underdelegating due to lack of trust or time, overdelegating due to poor time management or insecurity, and improper delegation by assigning the wrong task, person, direction or level of supervision. Creating motivation involves understanding intrinsic versus extrinsic motivation and factors like cultural differences that influence behavior.