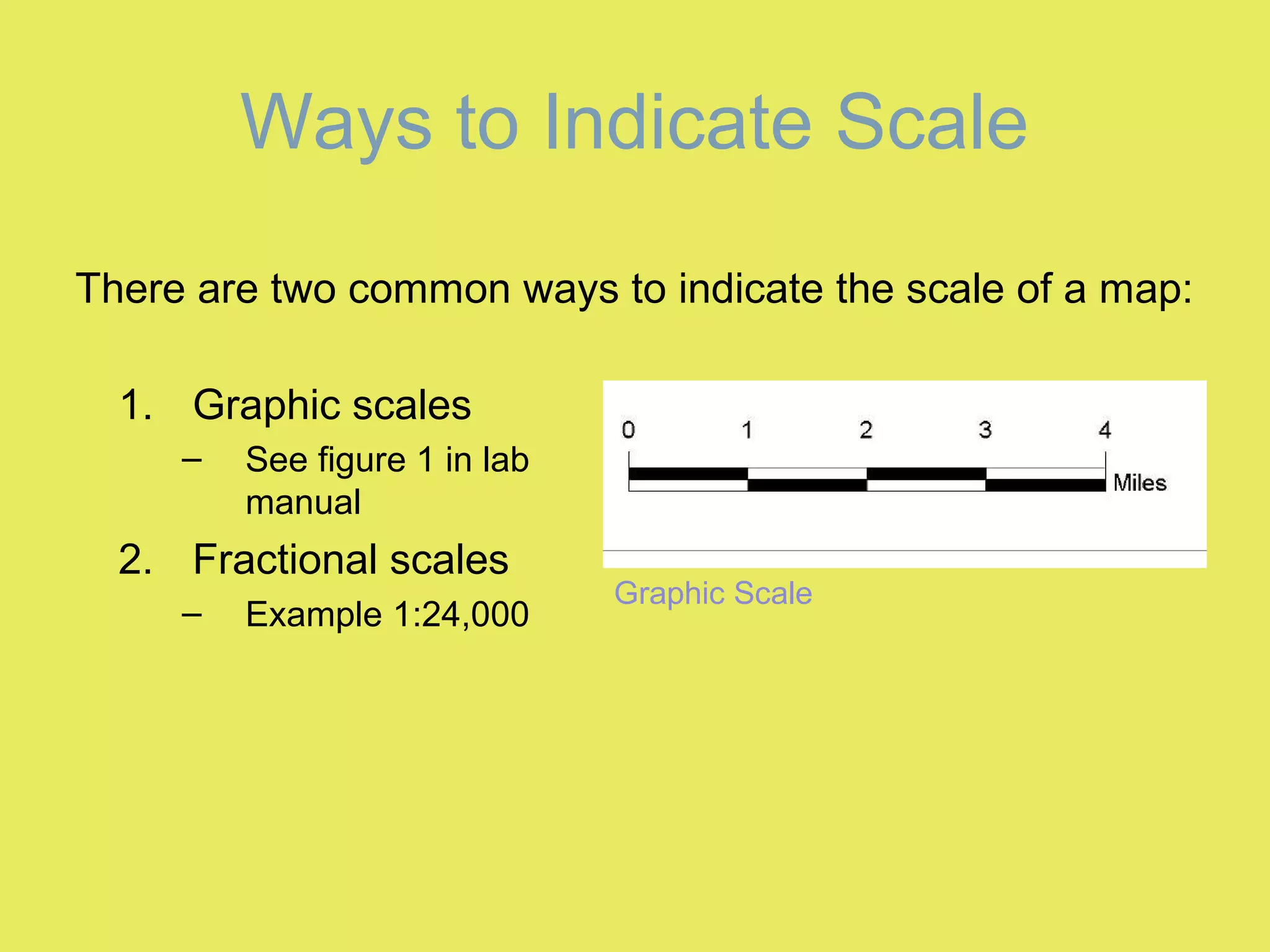
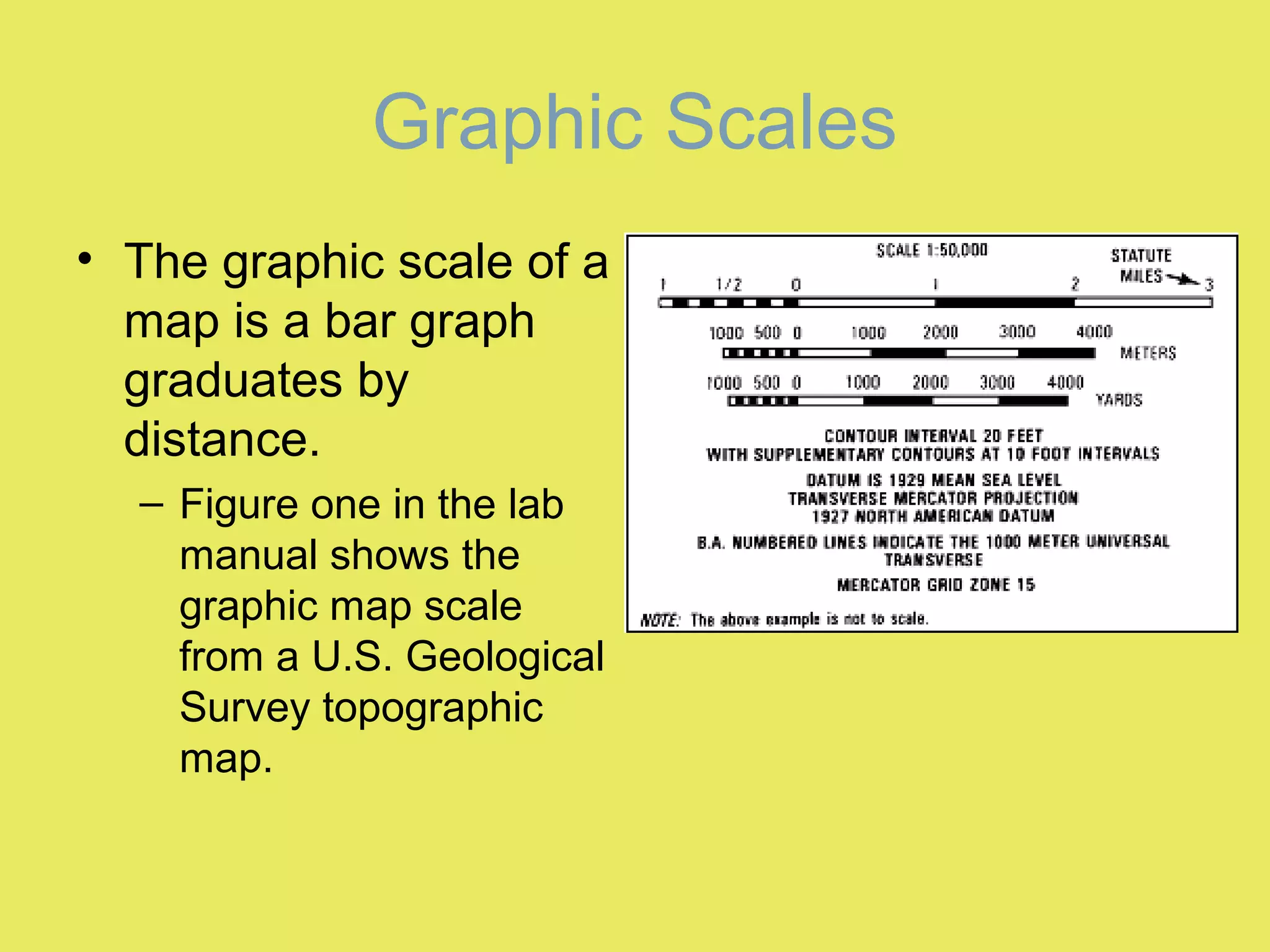
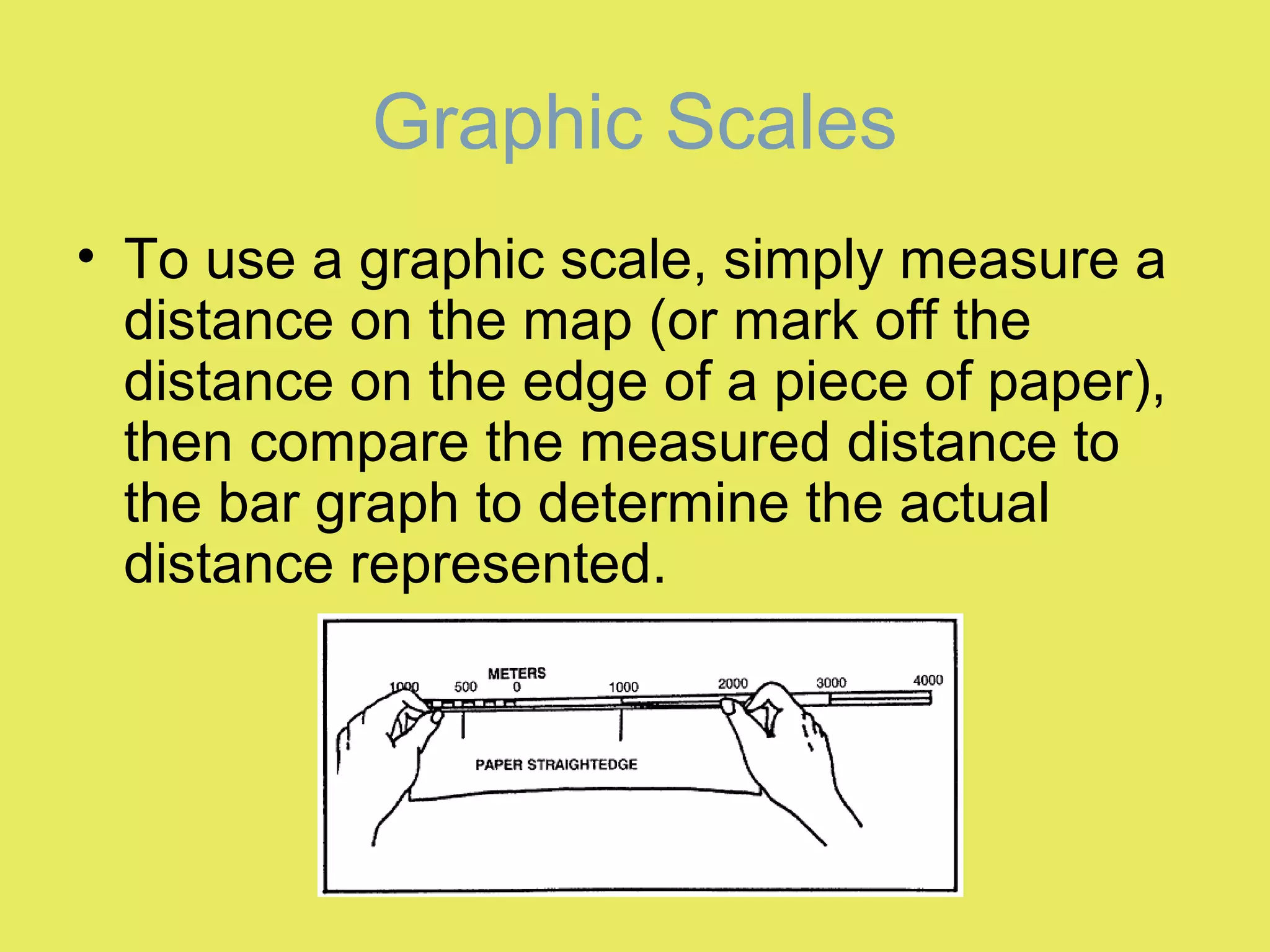
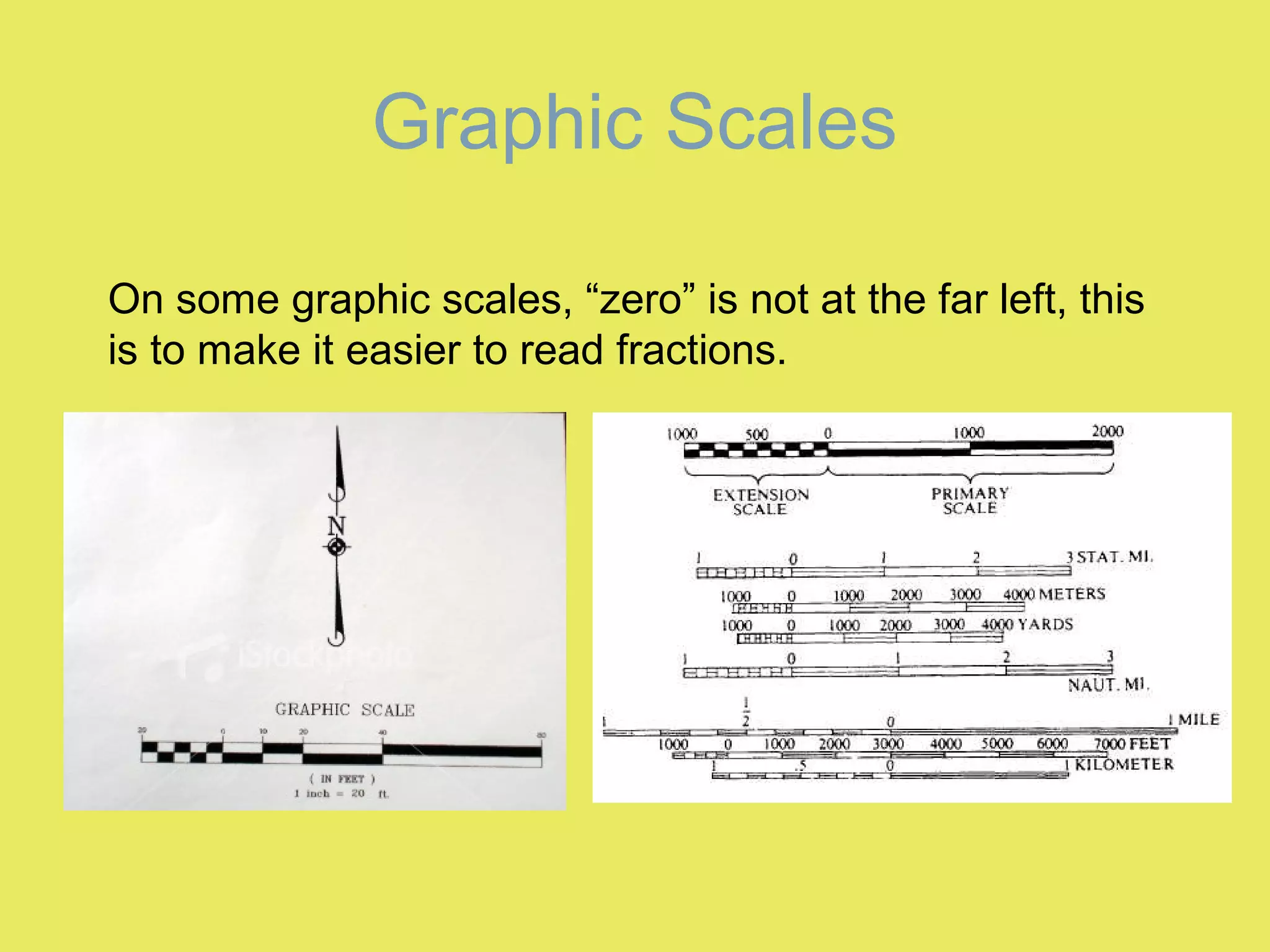
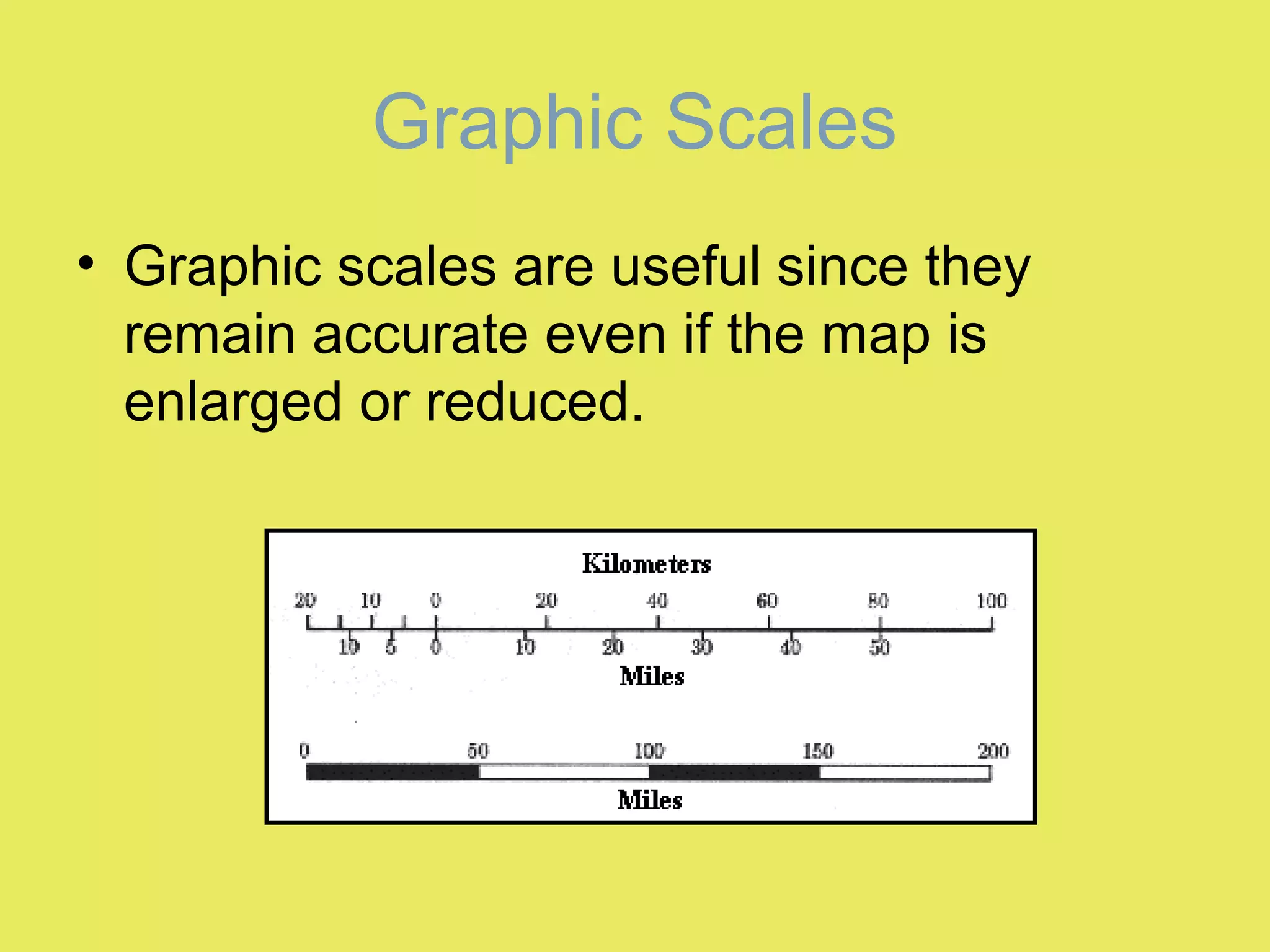
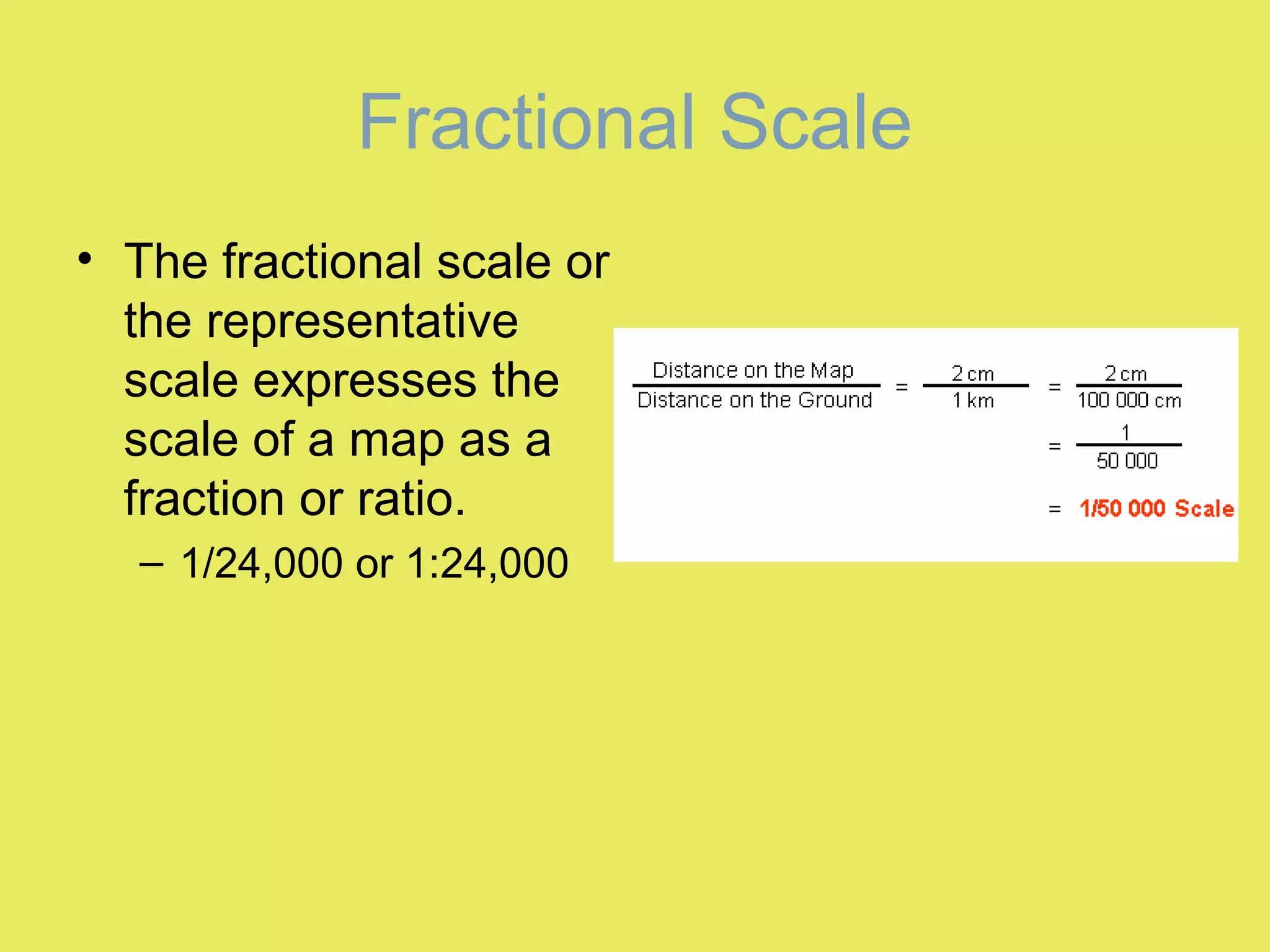
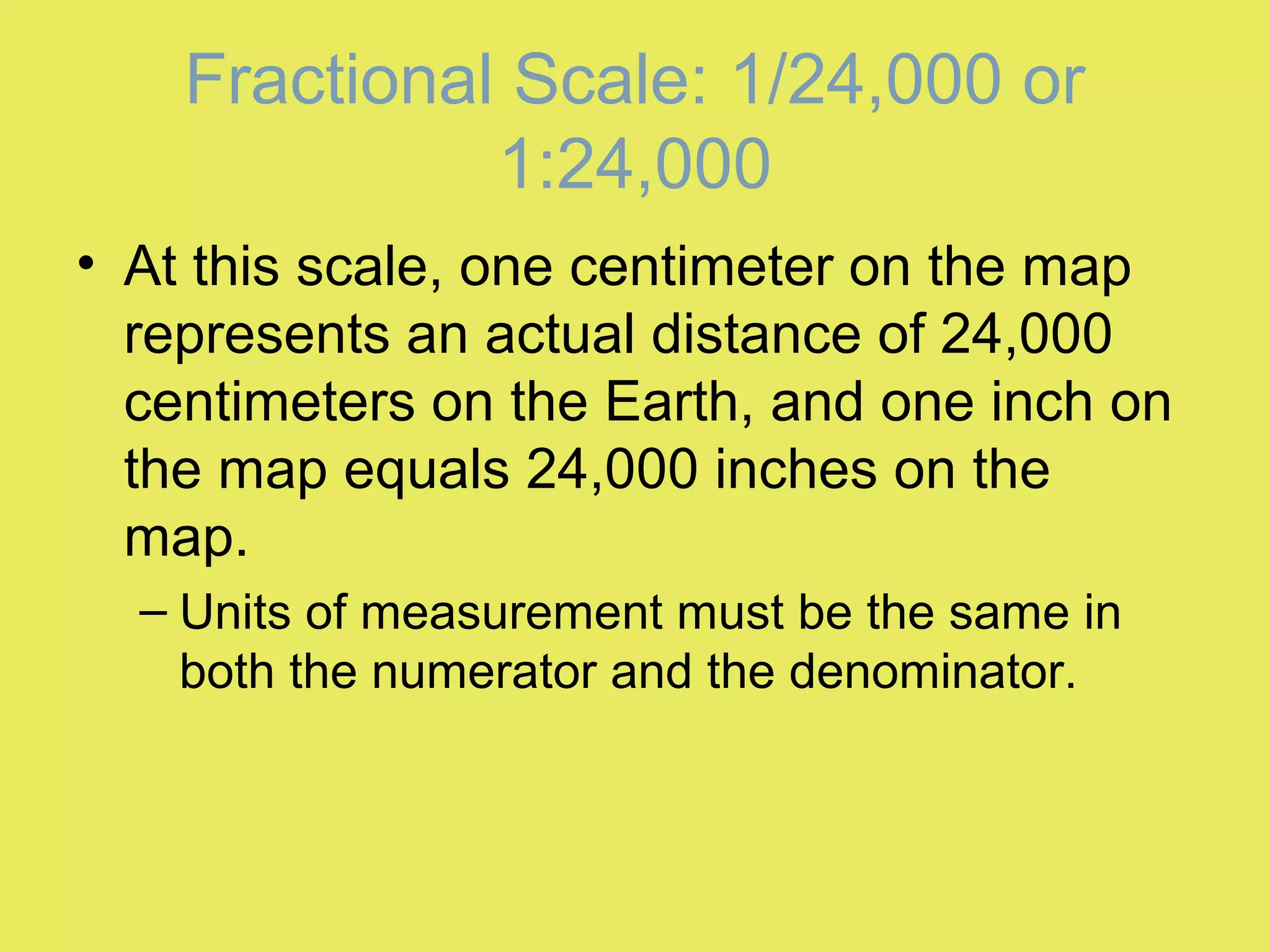
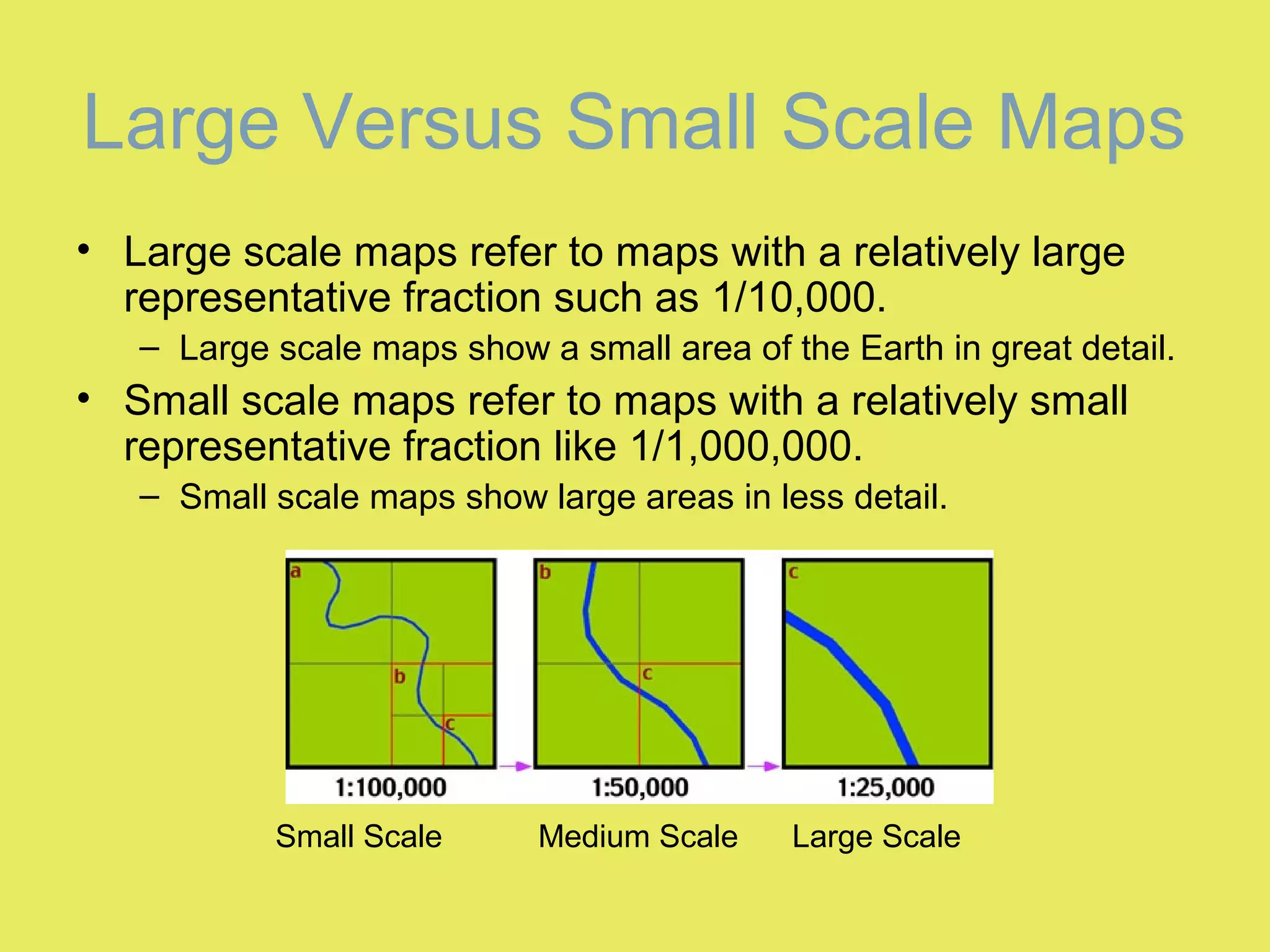
1) Map scale indicates the ratio between the distance on a map and the actual distance on Earth. It is expressed either graphically with a bar scale or fractionally as a ratio like 1:24,000.
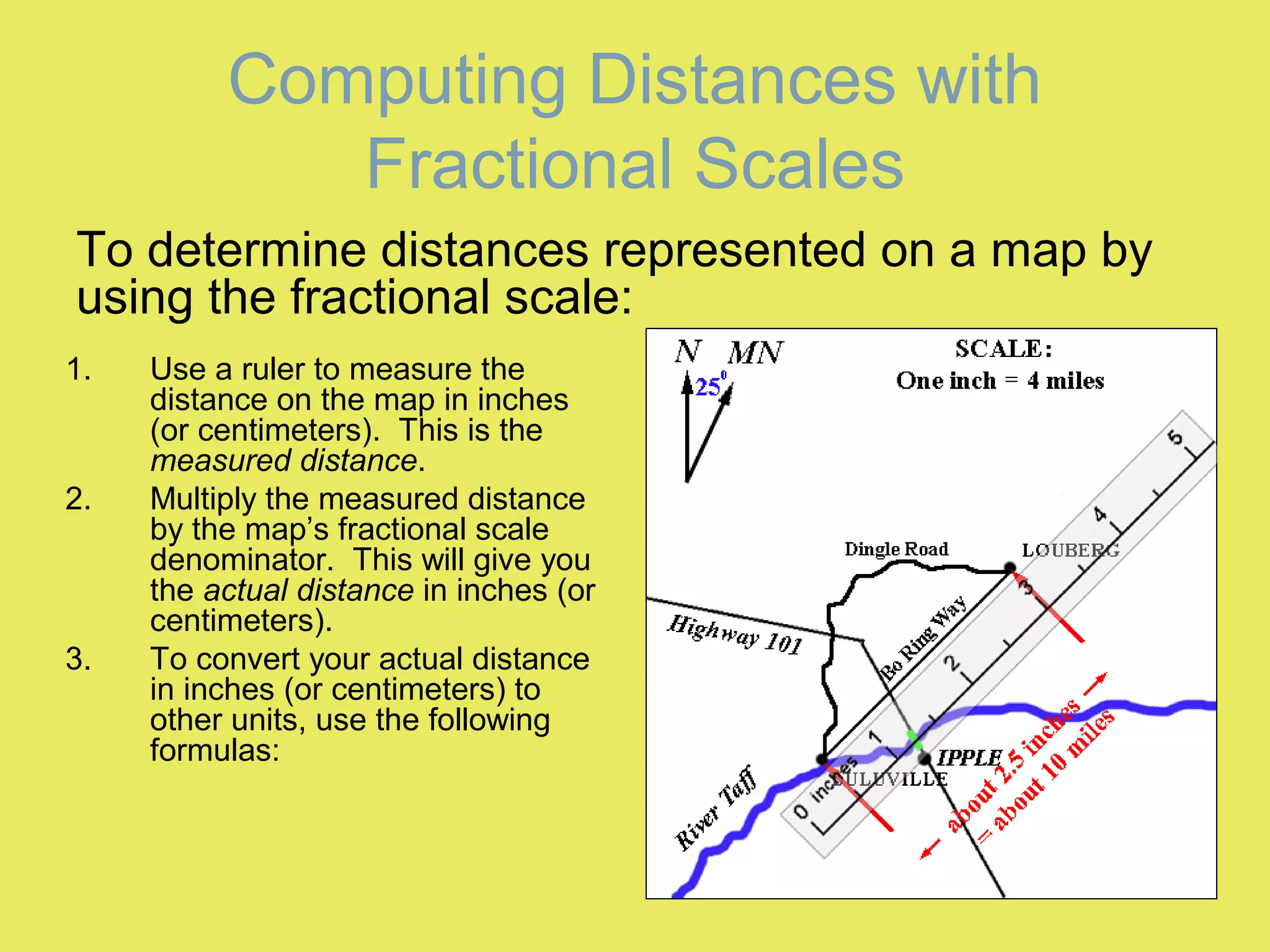
2) Graphic scales allow direct measurement of distances on a map. Fractional scales require calculating the actual distance by multiplying the measured distance by the denominator of the scale ratio.
3) Examples show how to use fractional scales to determine distances in other units like feet, miles, or meters based on the map's scale ratio.