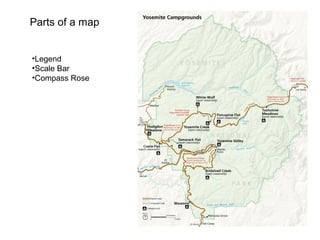
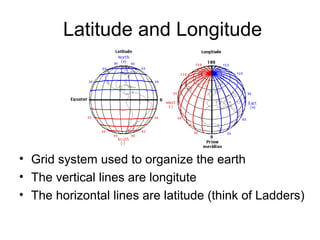
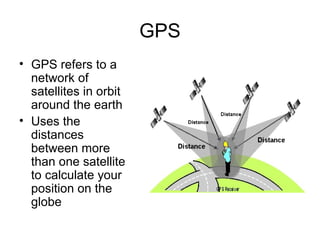
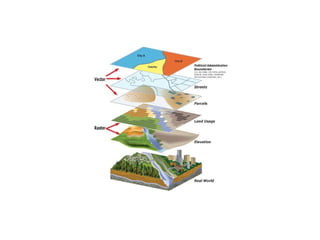
Tools used in geography include maps, globes, GPS, remote sensing, and GIS. Maps show physical features and are printed on paper, while globes model the spherical earth accurately. GPS uses satellite distances to determine position. Remote sensing studies objects from afar using tools like aerial photography. GIS digitally analyzes and displays geographic data, allowing overlay of different data layers.