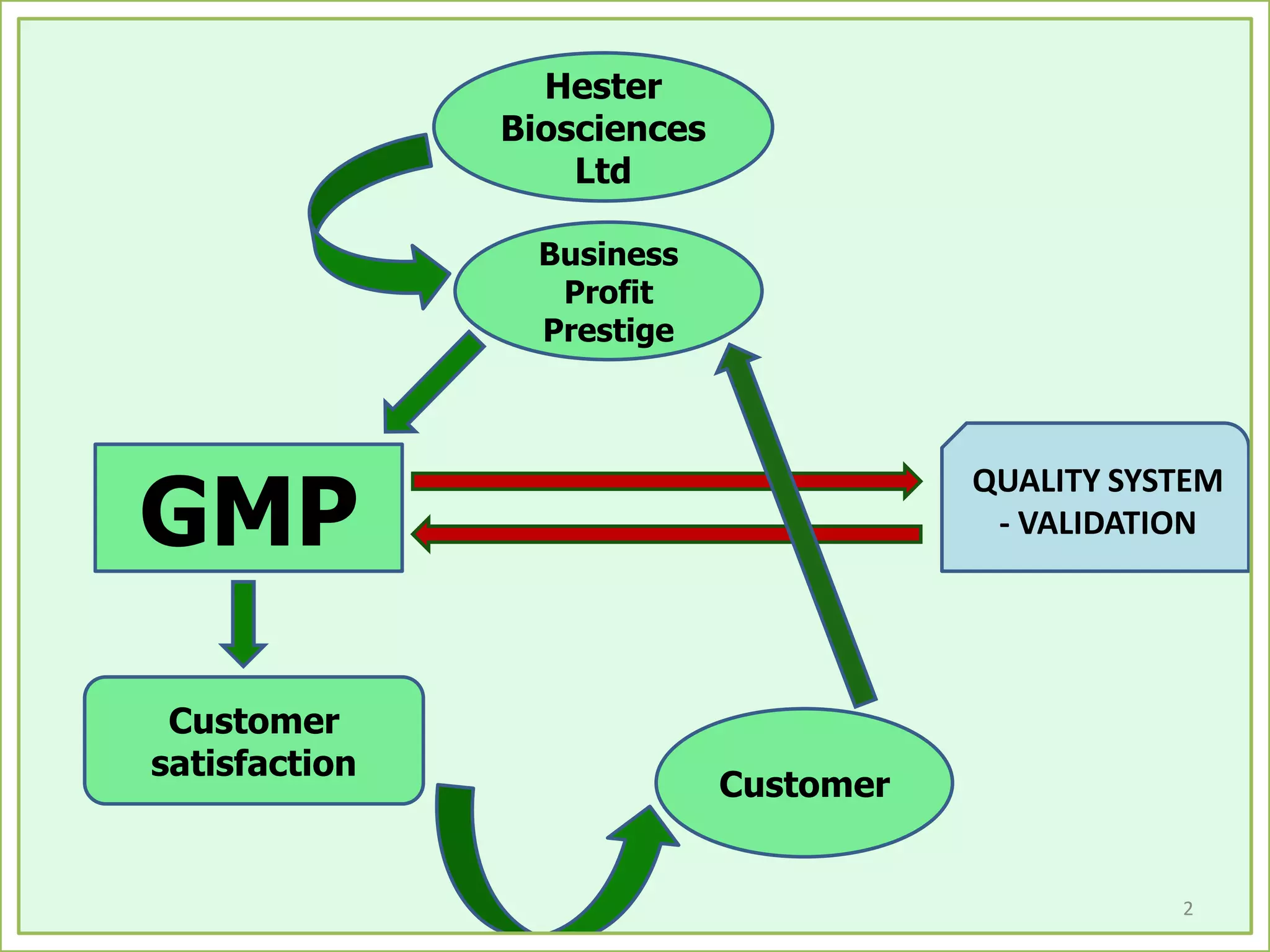
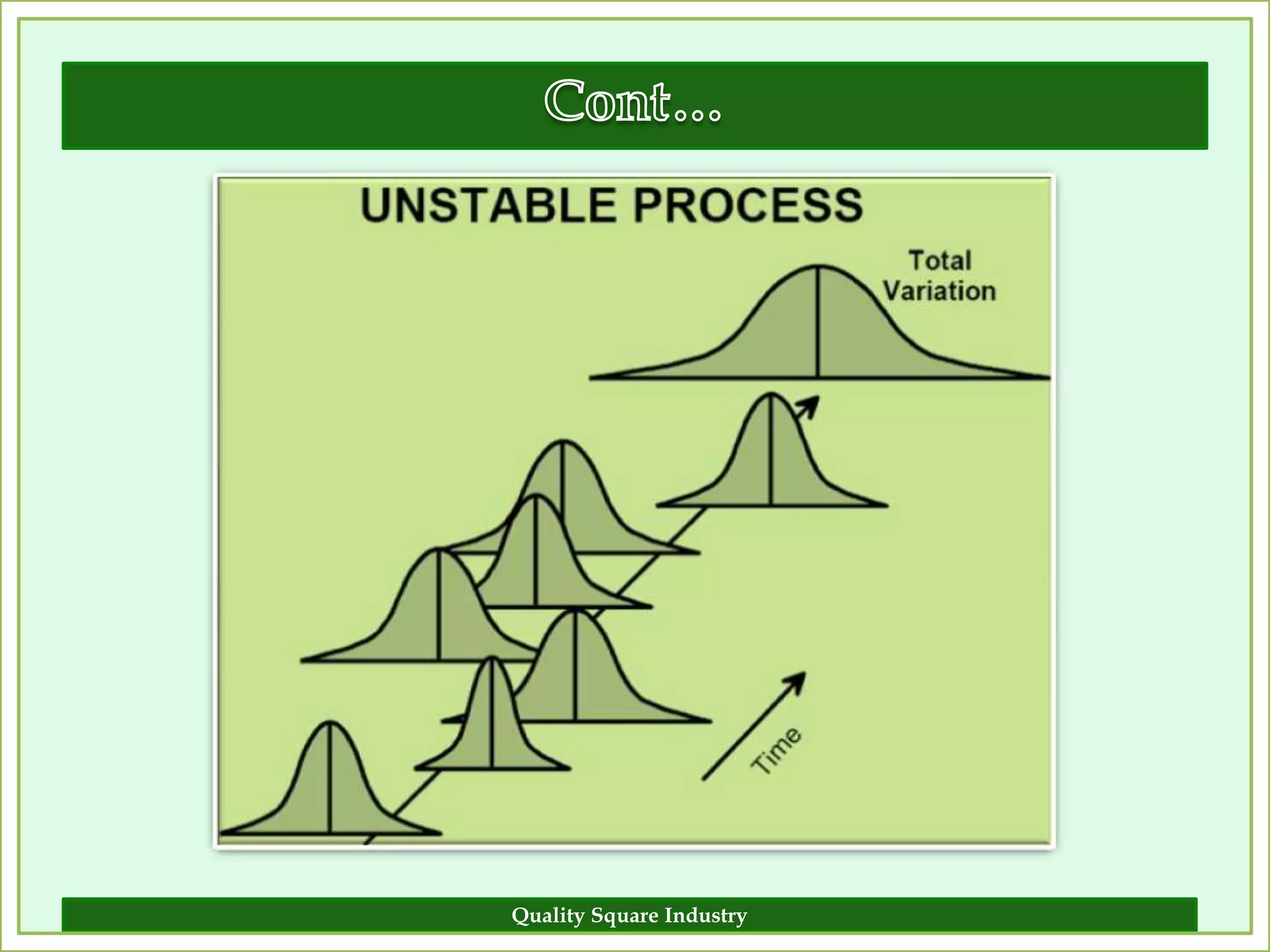
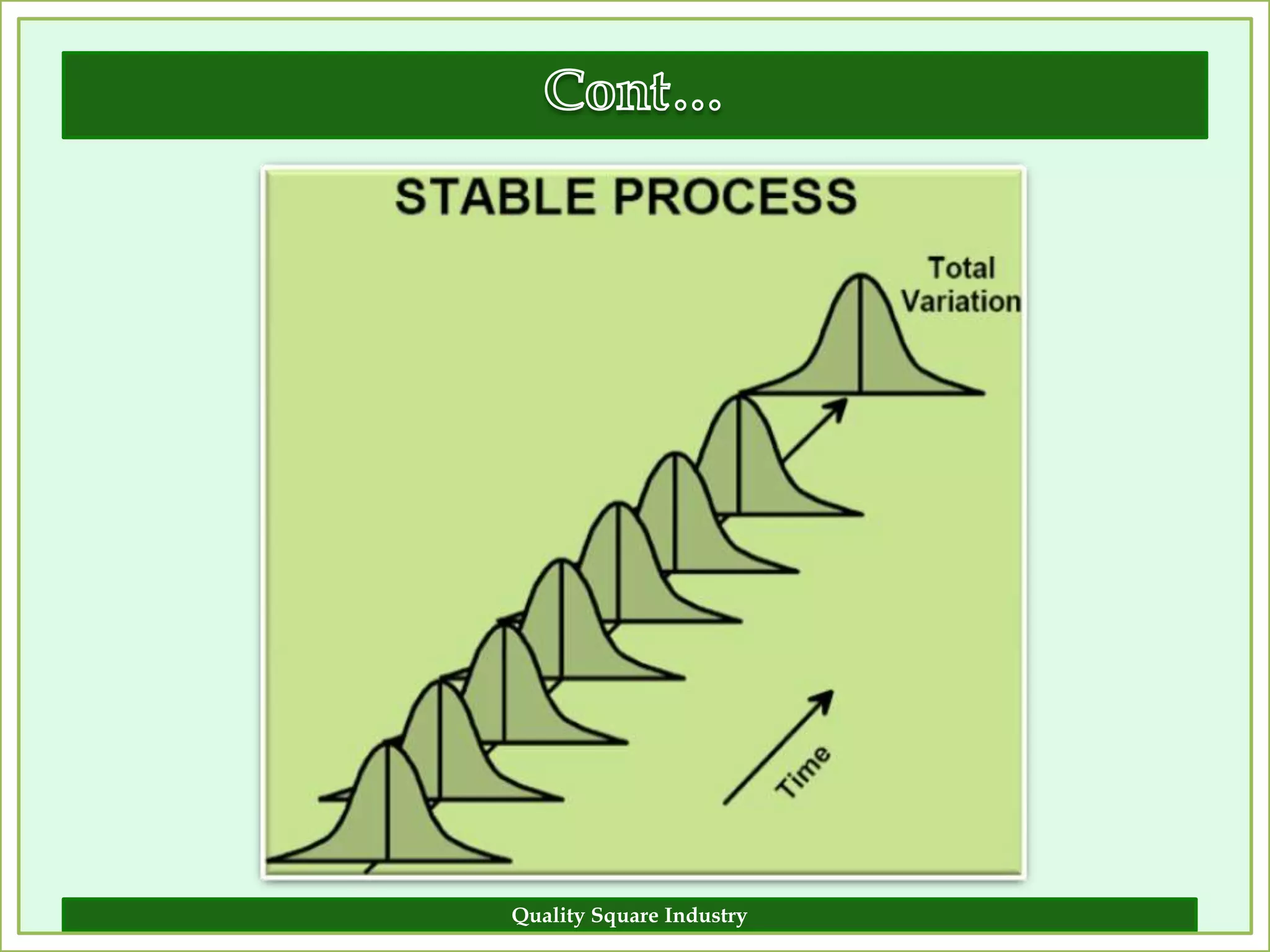
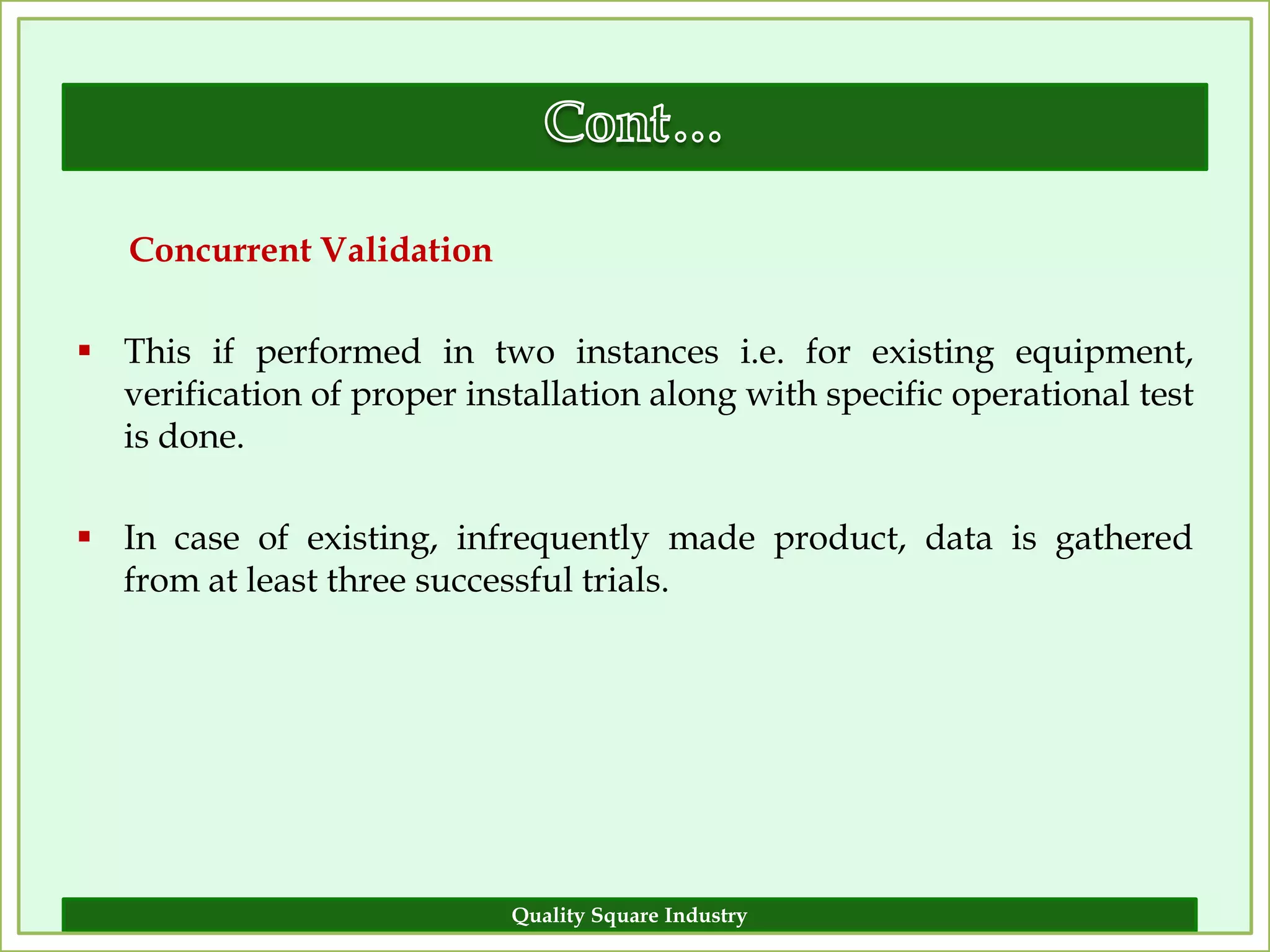
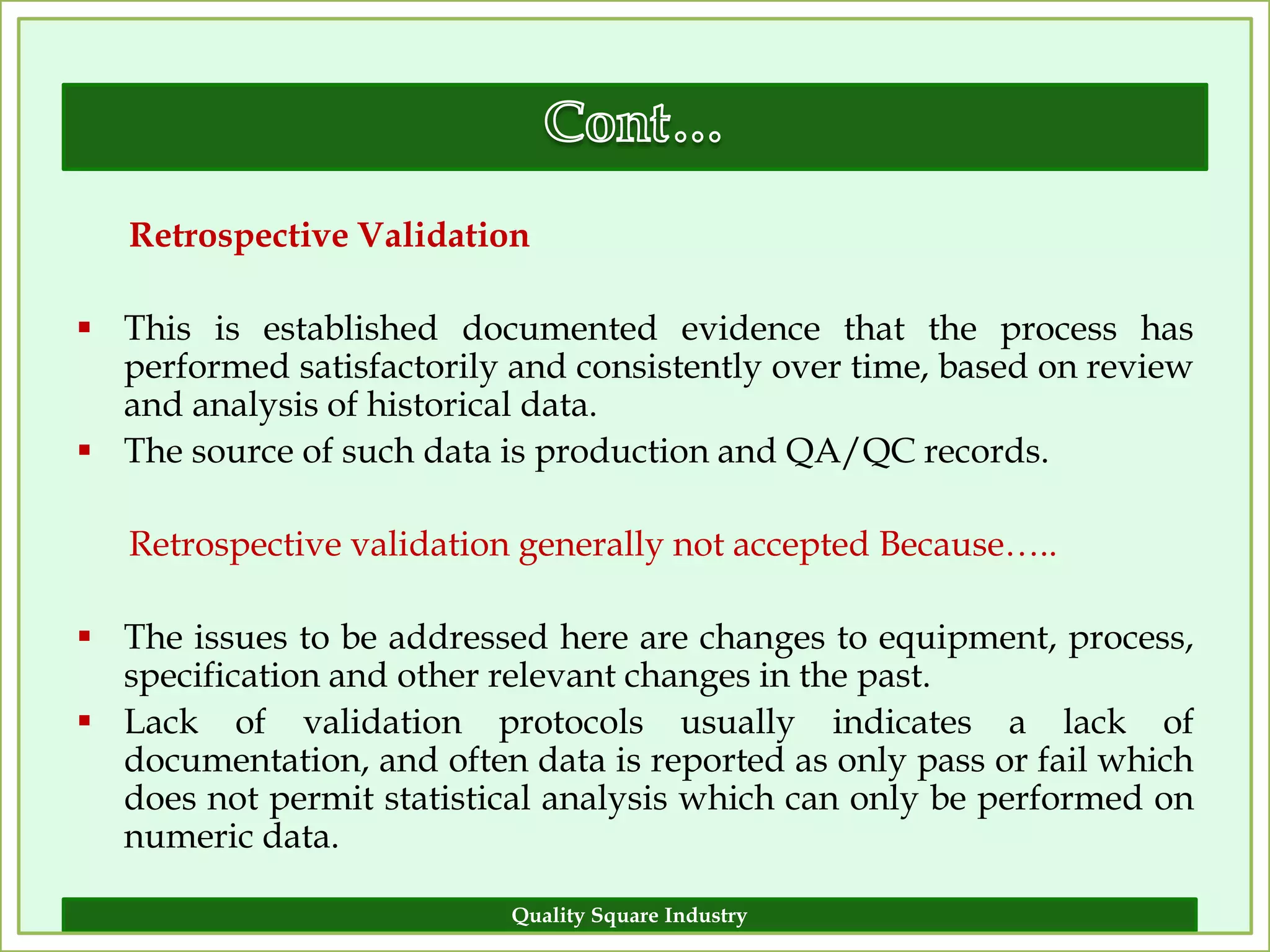
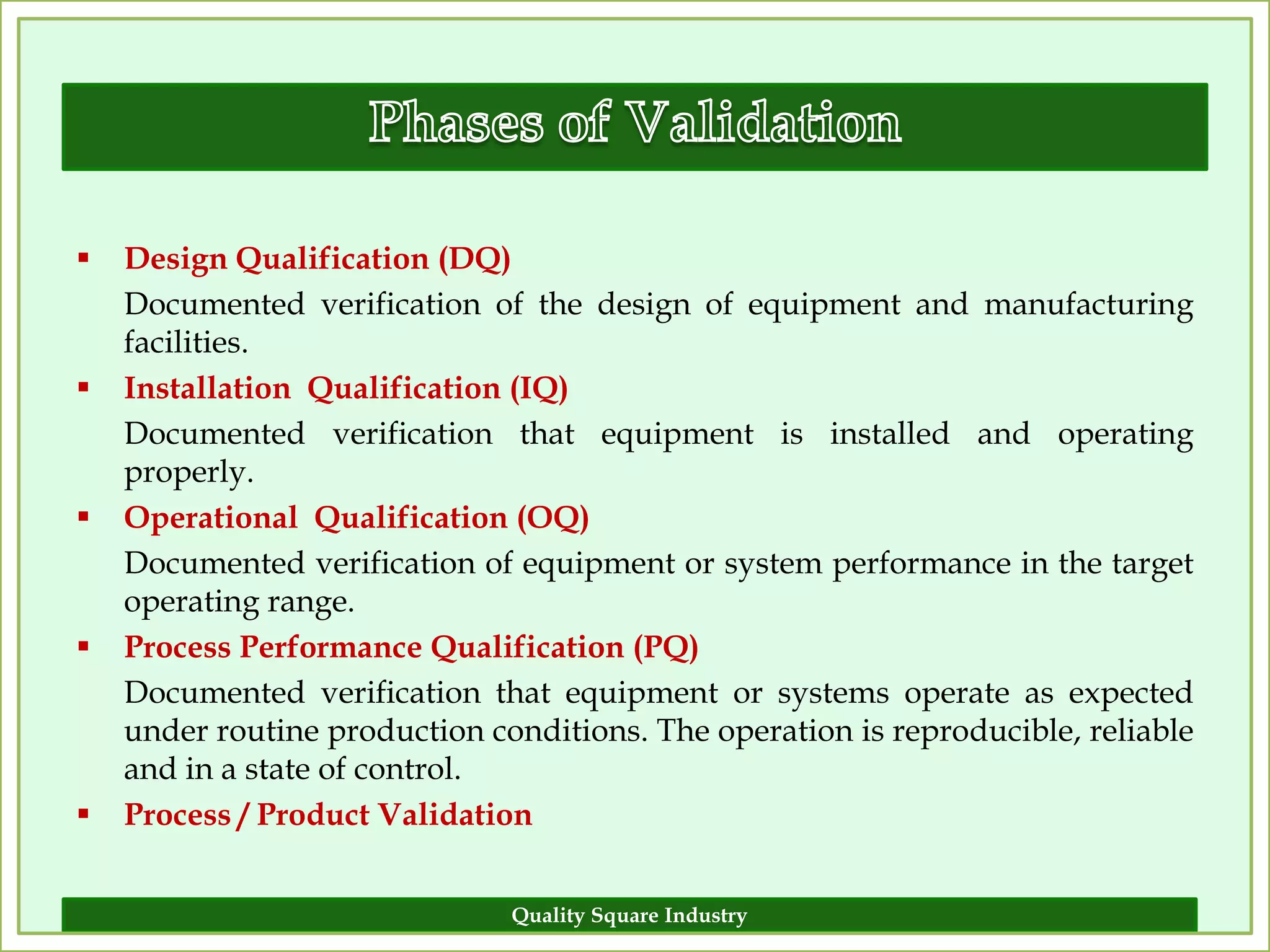
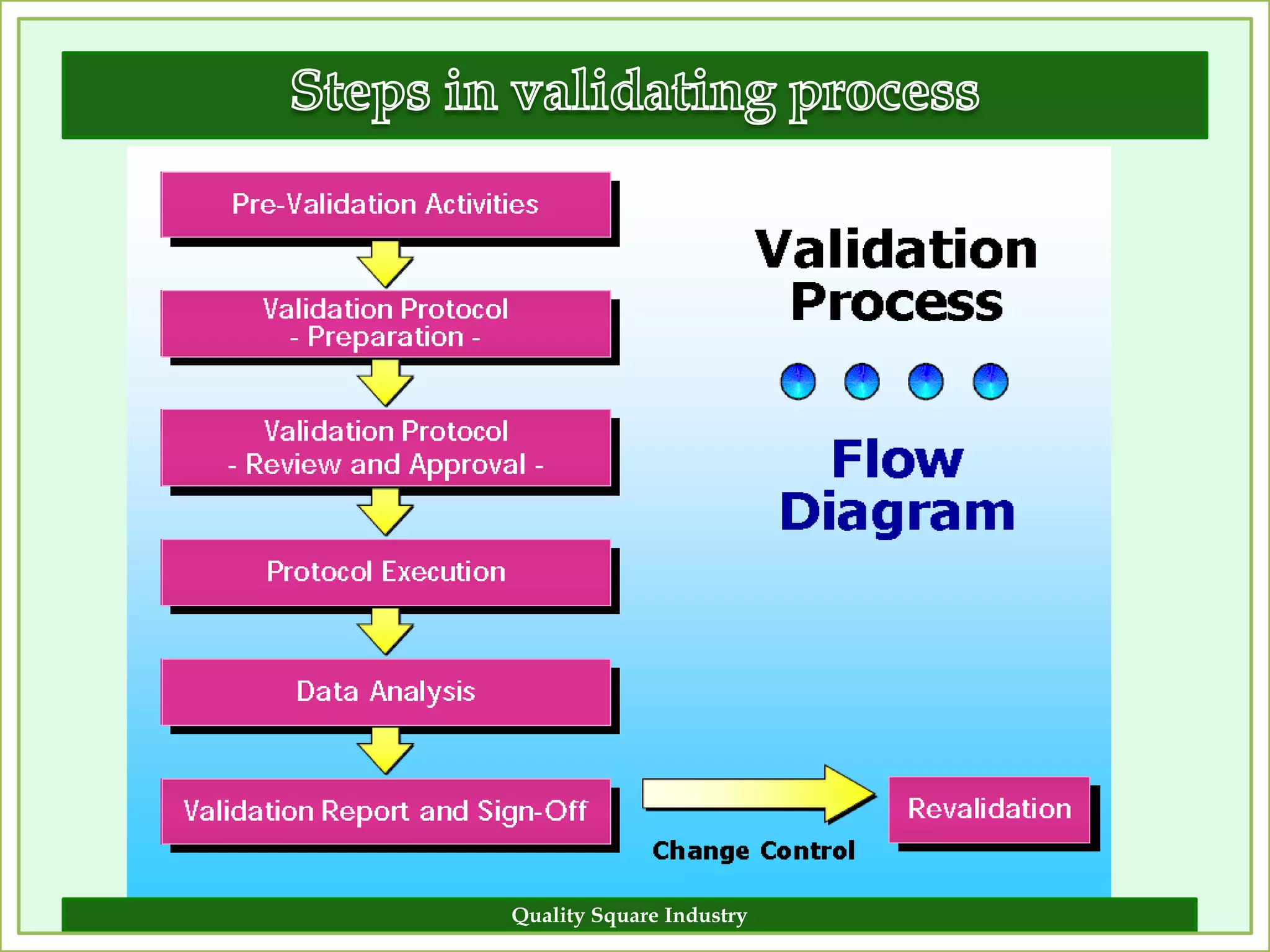
The document outlines the importance of validation in the quality assurance processes within industries like pharmaceuticals and biotechnology, illustrating various types of validation such as prospective, concurrent, and retrospective. It highlights the need for thorough documentation and procedural adherence to ensure product integrity and compliance with regulatory standards. Additionally, it discusses the cost-efficiency and customer satisfaction benefits that effective validation can bring to an organization.