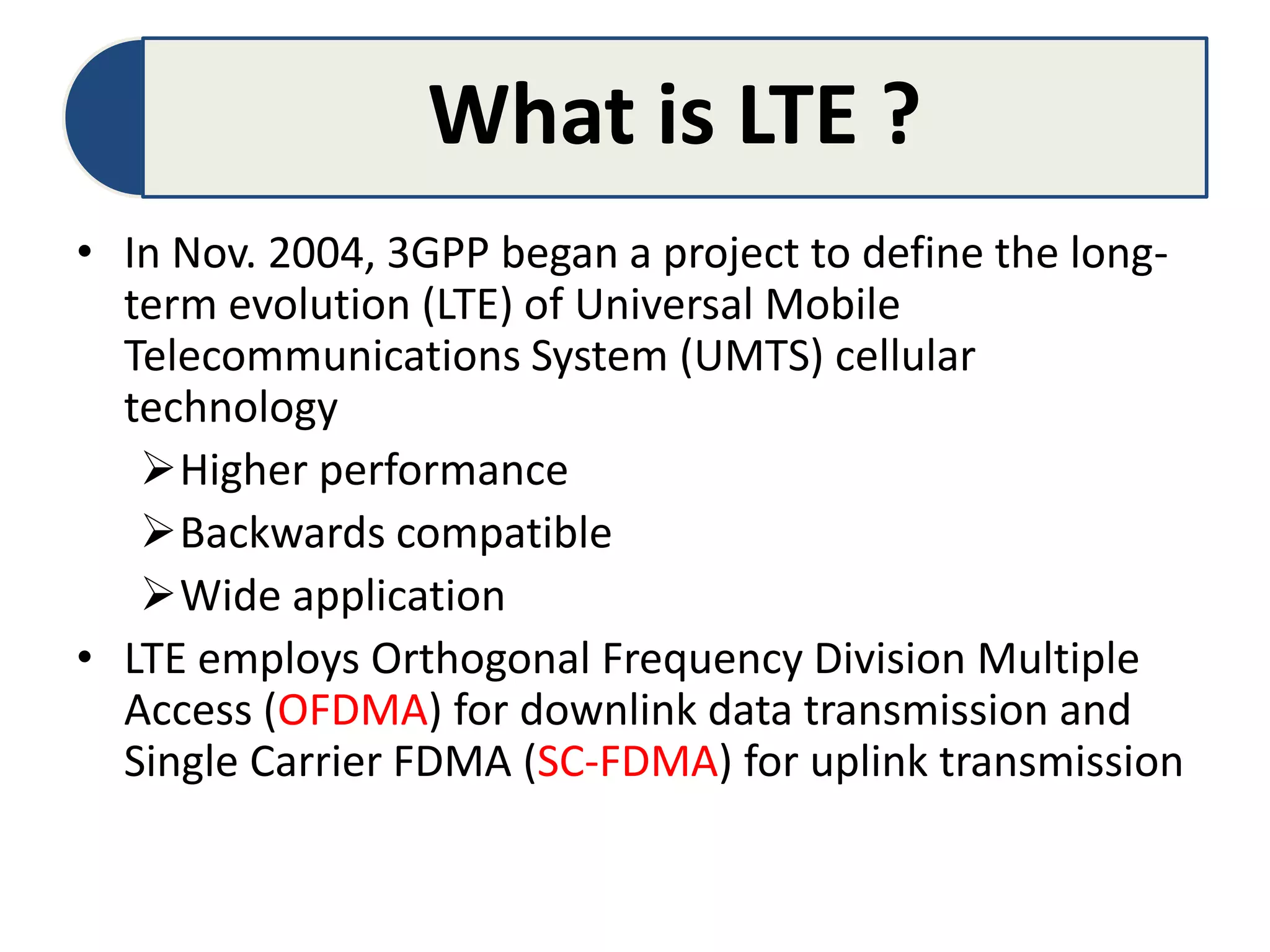
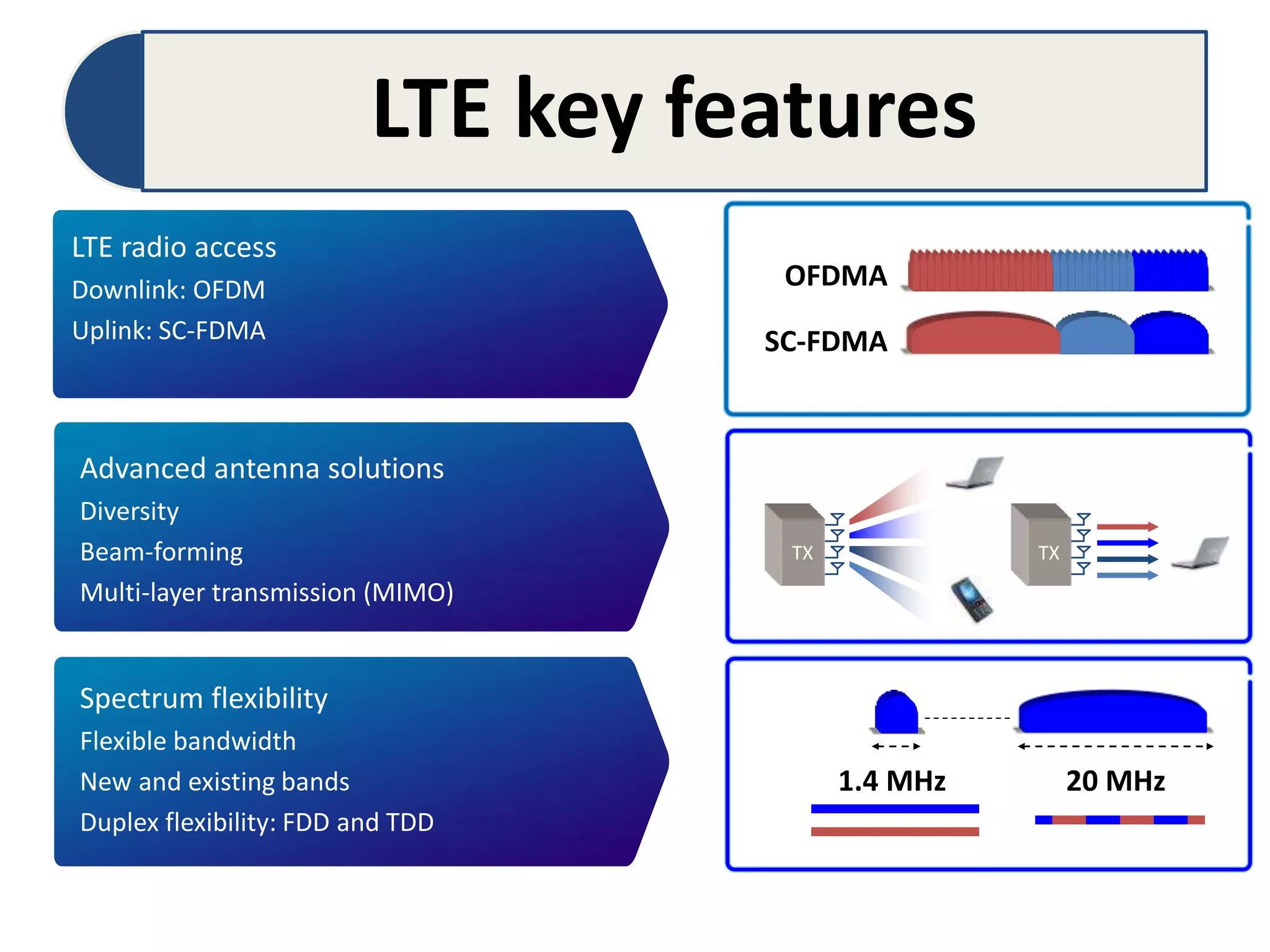
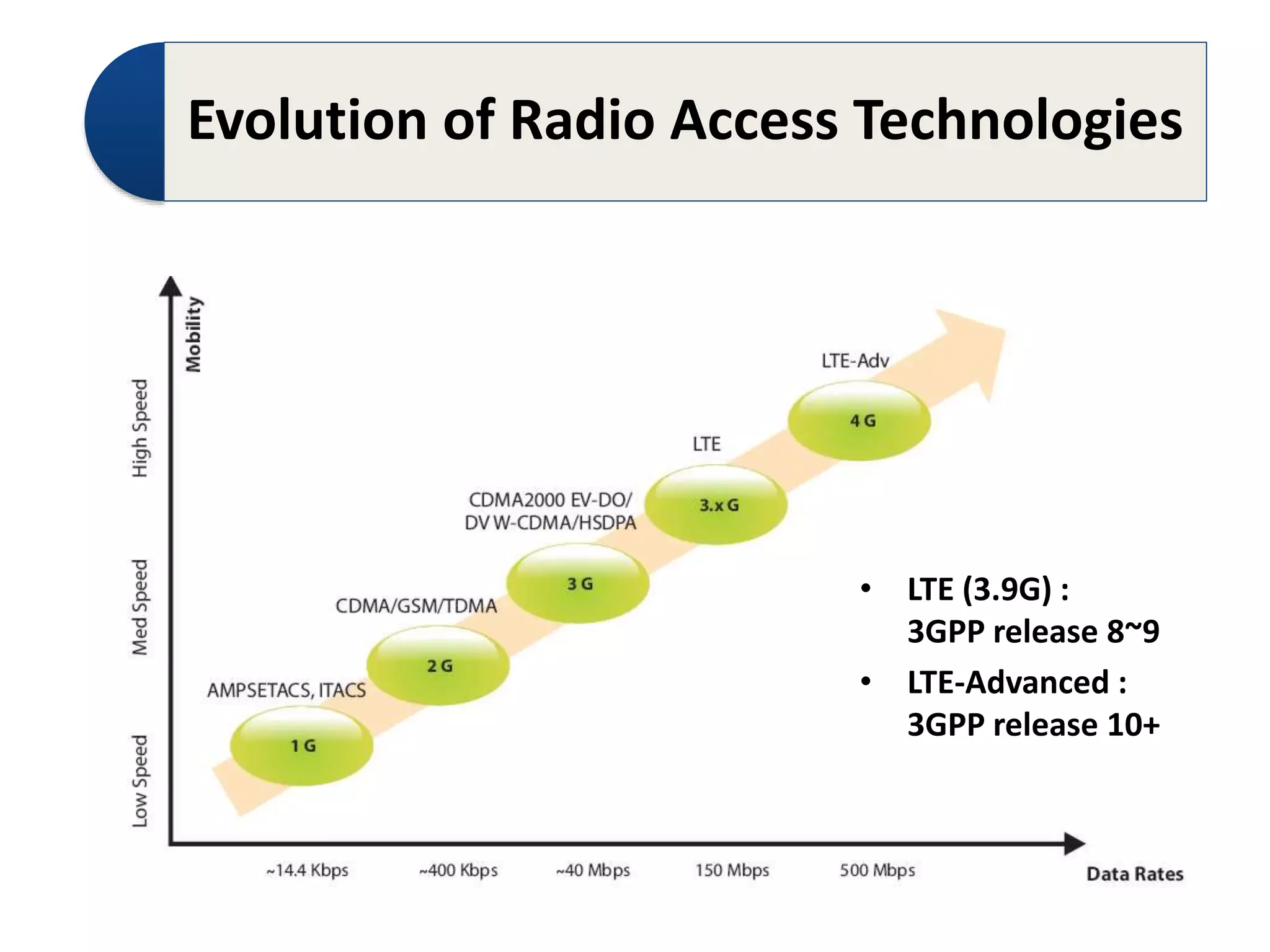
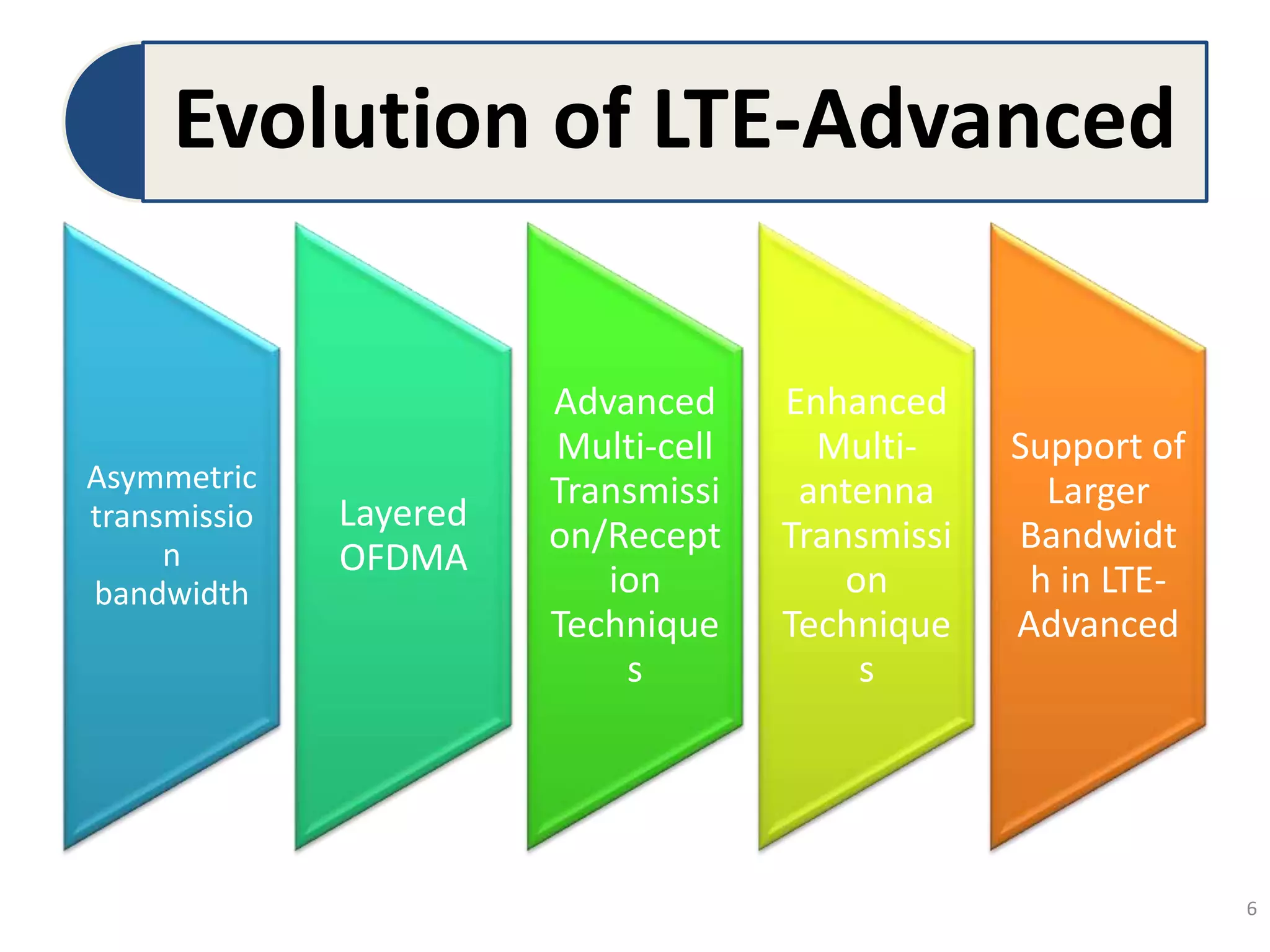
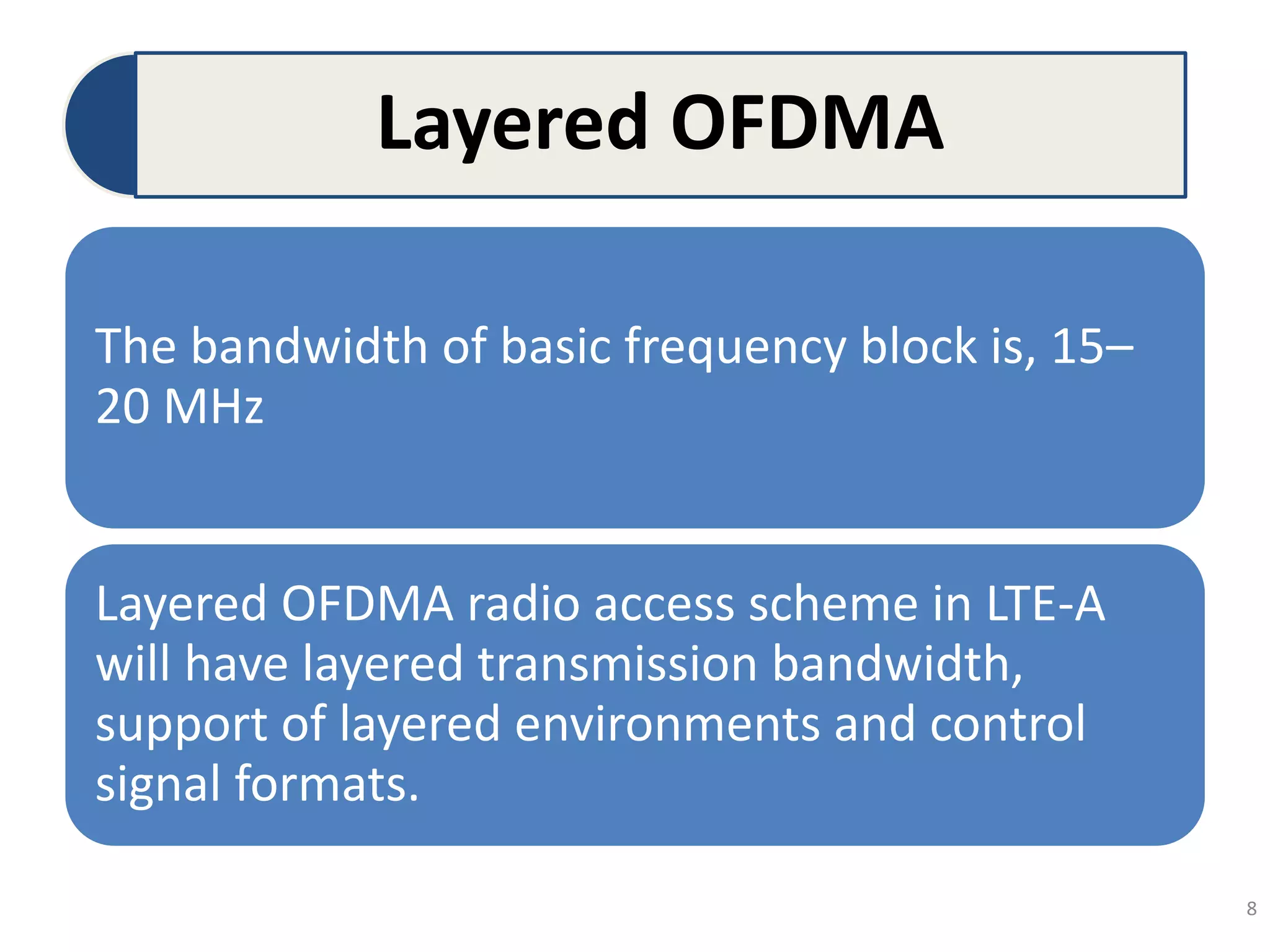
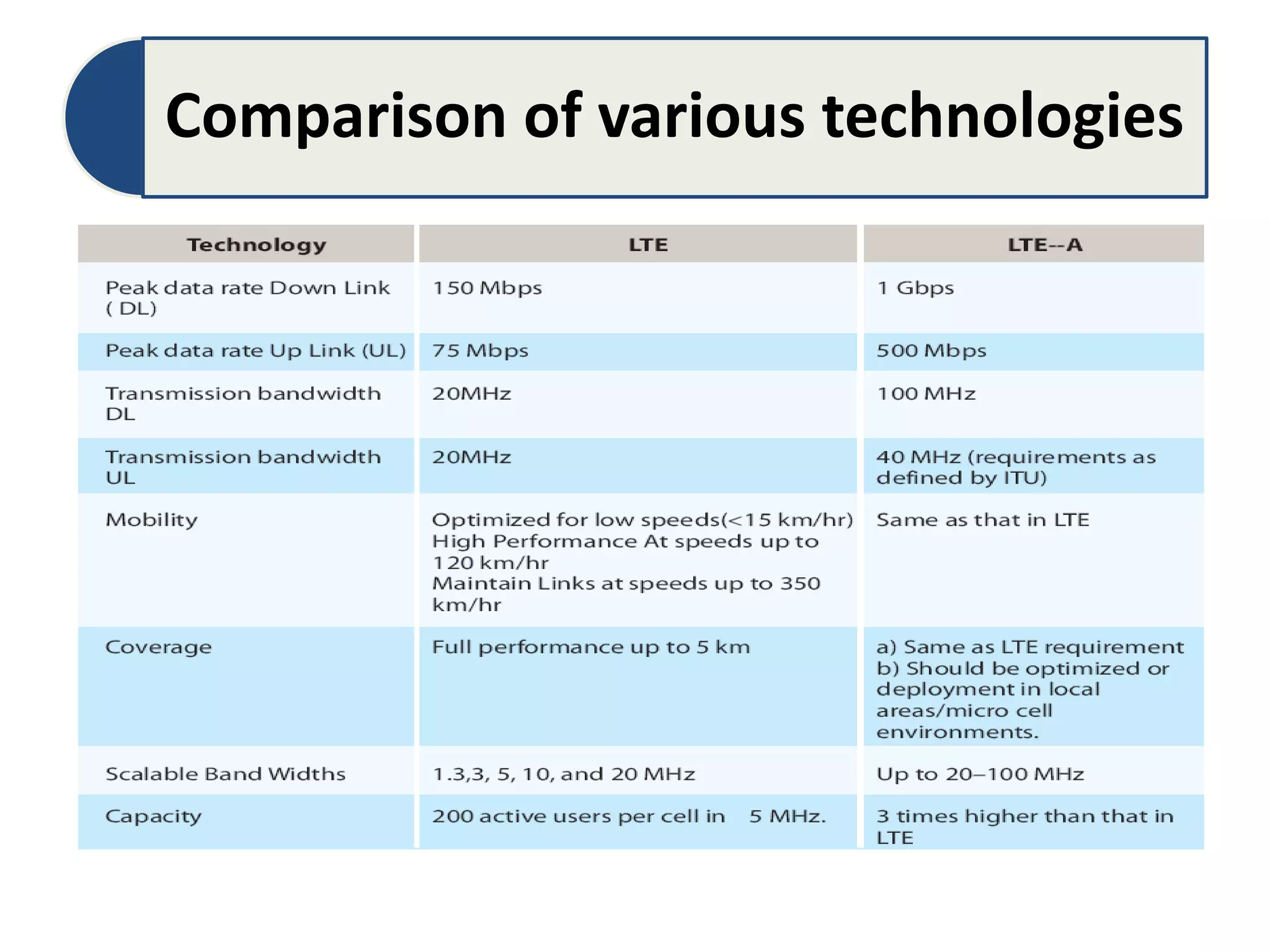
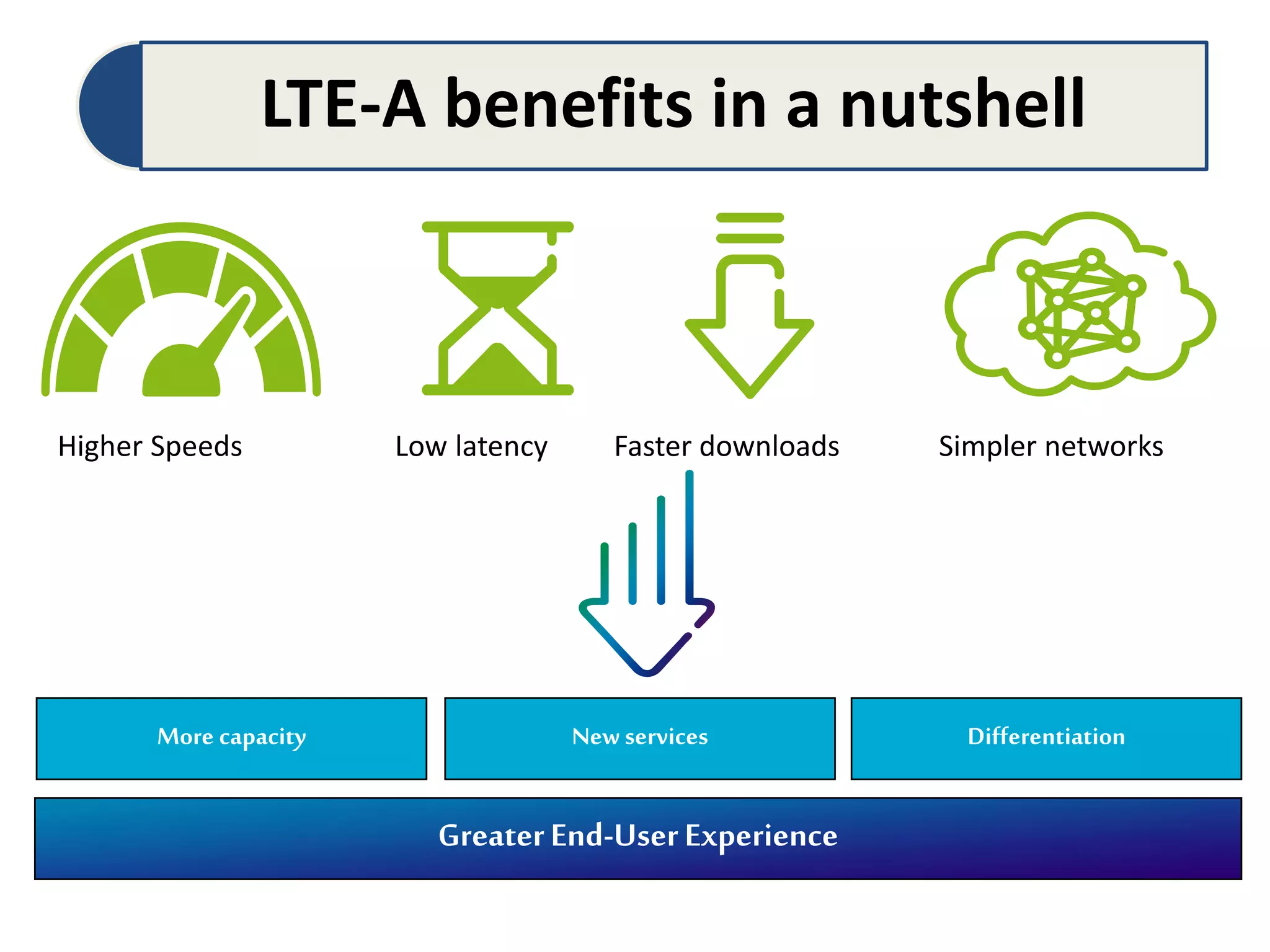
The document discusses Long-Term Evolution (LTE) technology, detailing its inception, key features, and advancements into LTE-Advanced. It highlights improvements such as increased bandwidth capacity, enhanced multi-antenna techniques, and support for larger bandwidths, aiming for peak data rates exceeding 1 Gbps. The benefits of LTE-A include higher speeds, lower latency, improved user experience, and greater network capacity.