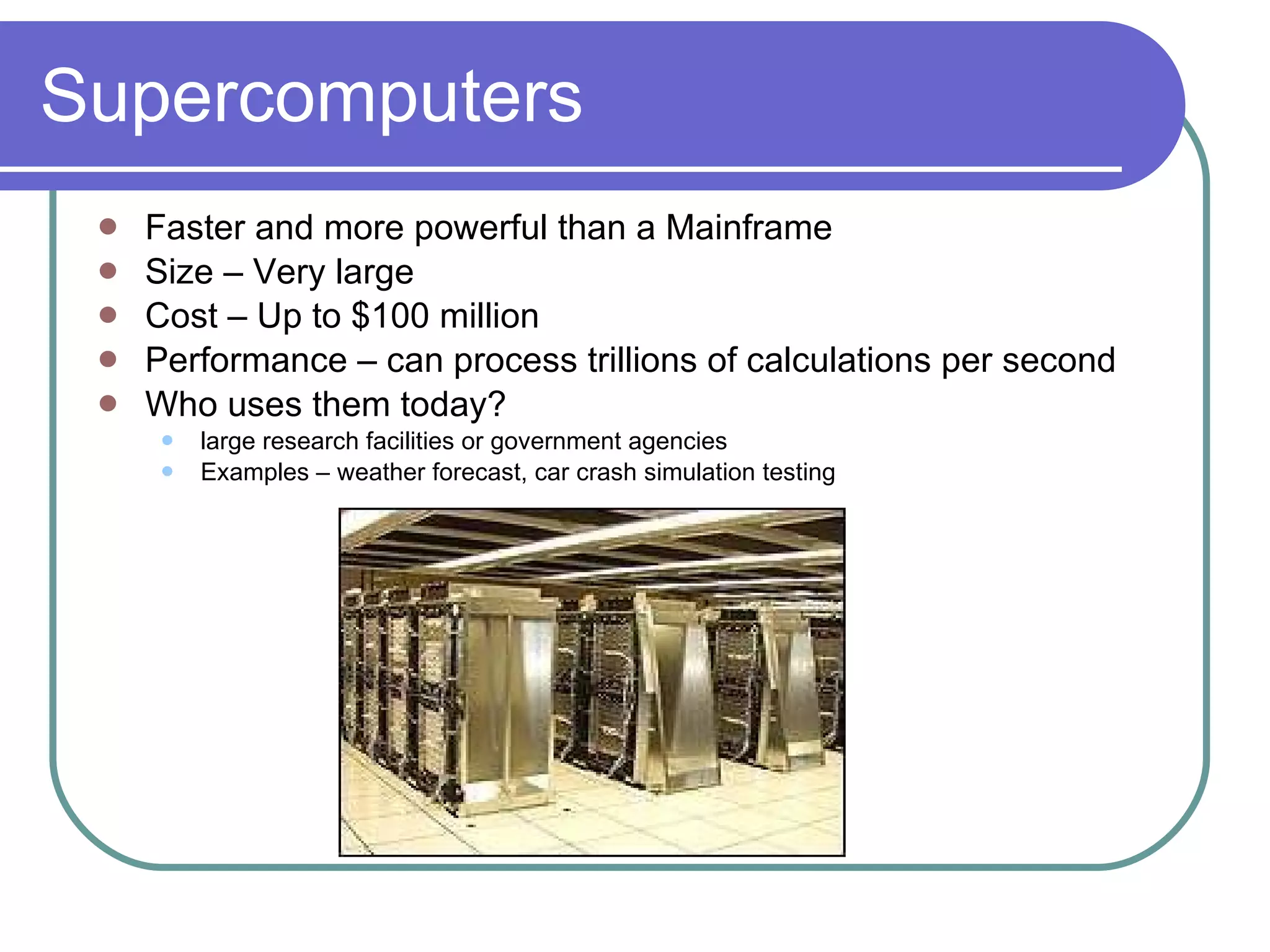
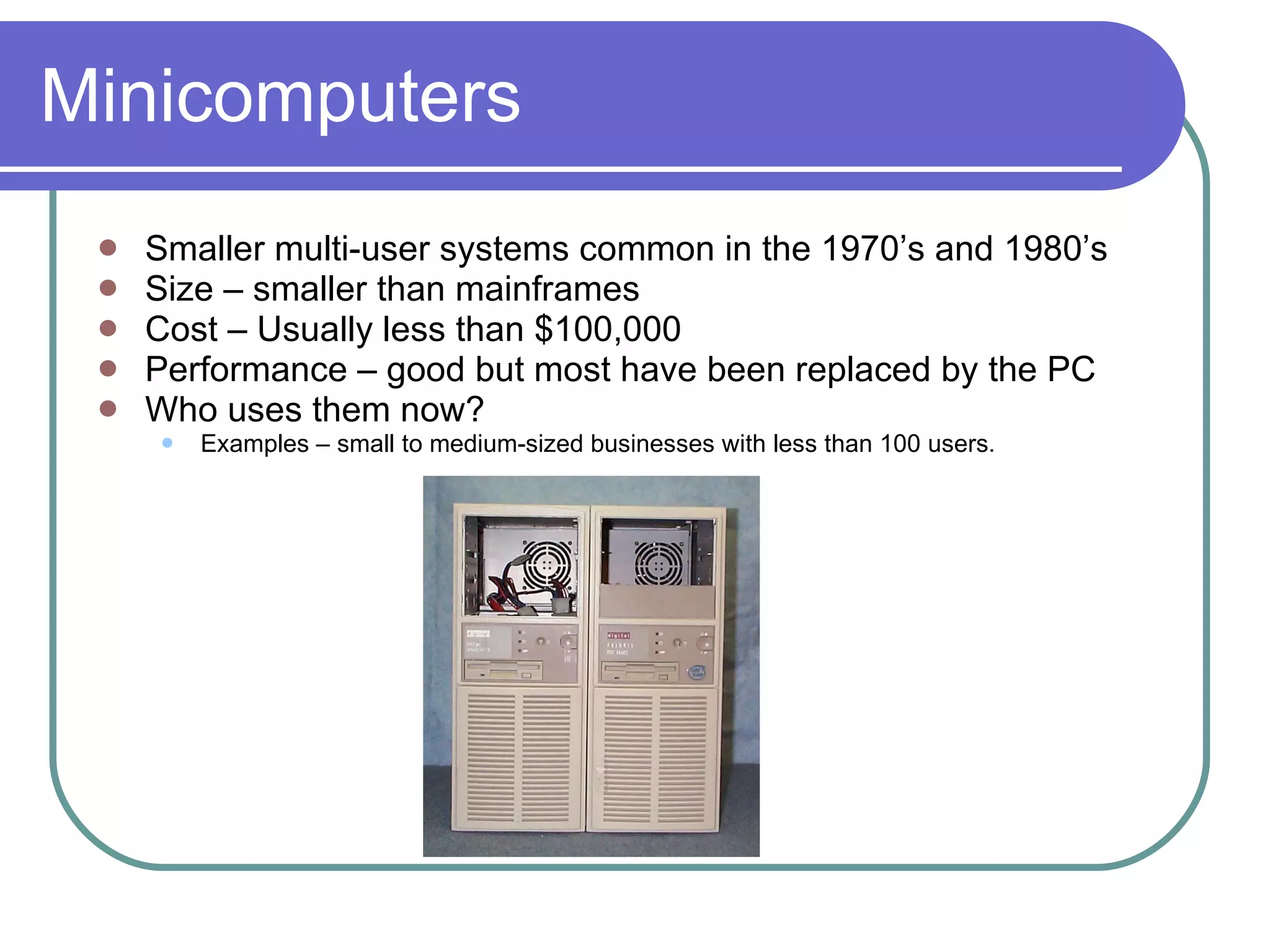
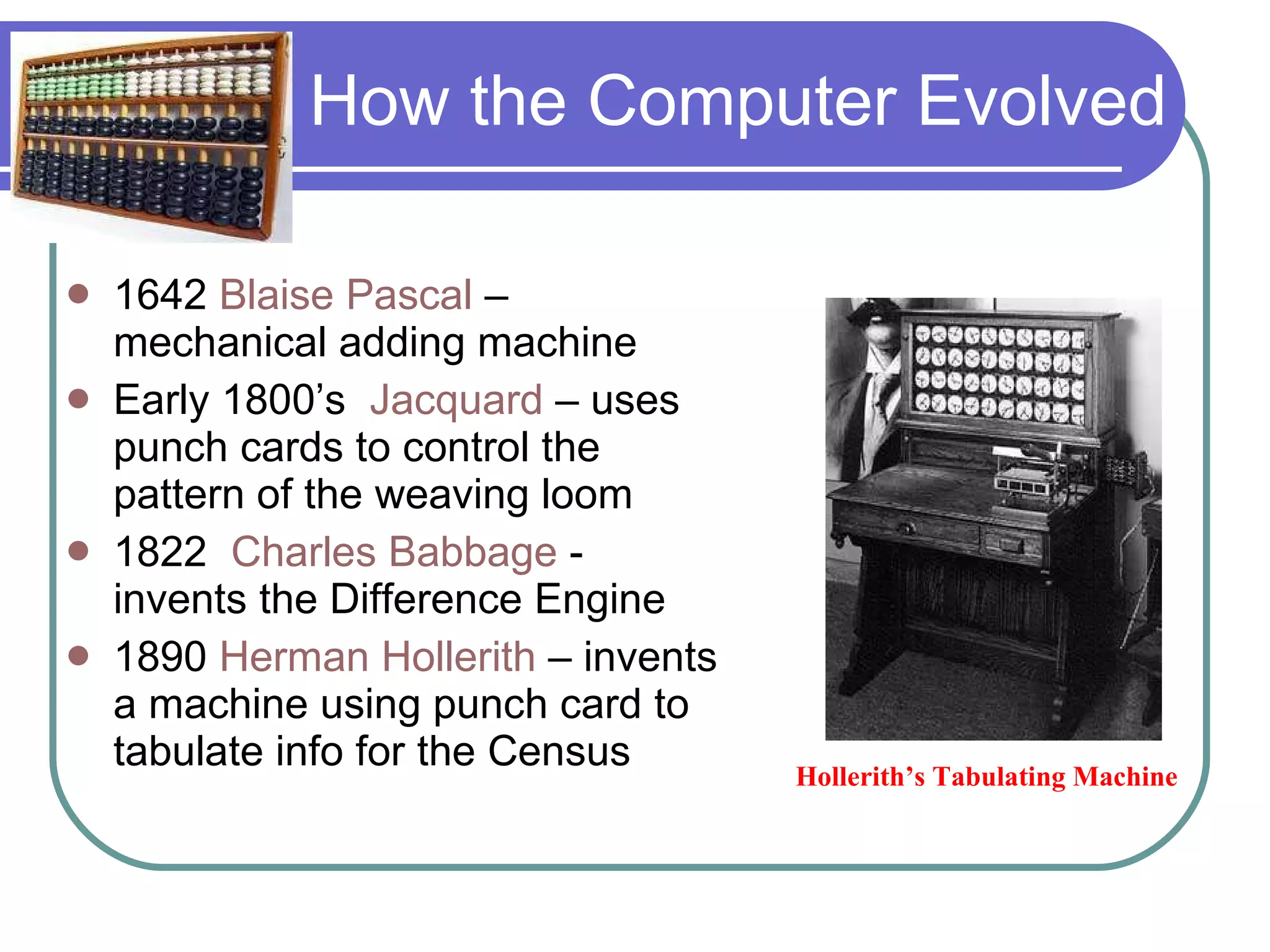
The document discusses the evolution of different types of computers from the past to present. It begins with the largest and most powerful computers - supercomputers - used for complex calculations. It then discusses mainframe computers, which were the first used by businesses in the 1950s. Minicomputers followed and were common until the 1980s. Personal computers emerged in the 1970s and are now ubiquitous, while workstations fill a performance gap between personal computers and more powerful systems. The document provides details on the size, cost, performance and typical users of each type of computer through history to help students understand how computers have progressed.