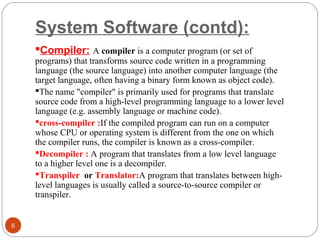
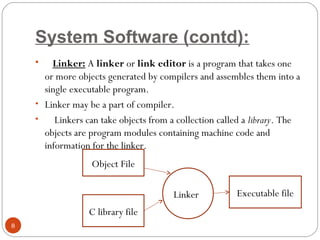
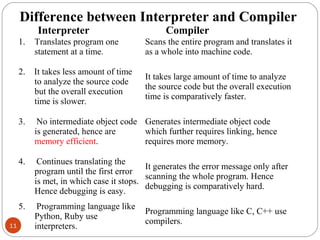
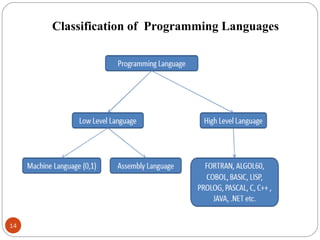
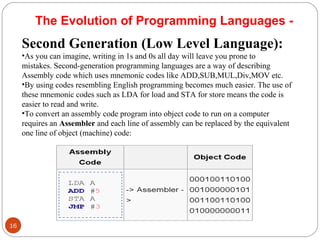
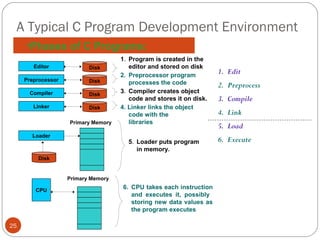
The document discusses the evolution of programming languages from first to third generation languages. First generation languages were machine code using binary, while second generation introduced assembly language with mnemonic codes. Third generation languages brought features like loops and conditionals, making code easier to write but requiring compilers or interpreters to convert to machine code. Some examples of early third generation languages discussed are FORTRAN, BASIC, COBOL, and PASCAL.