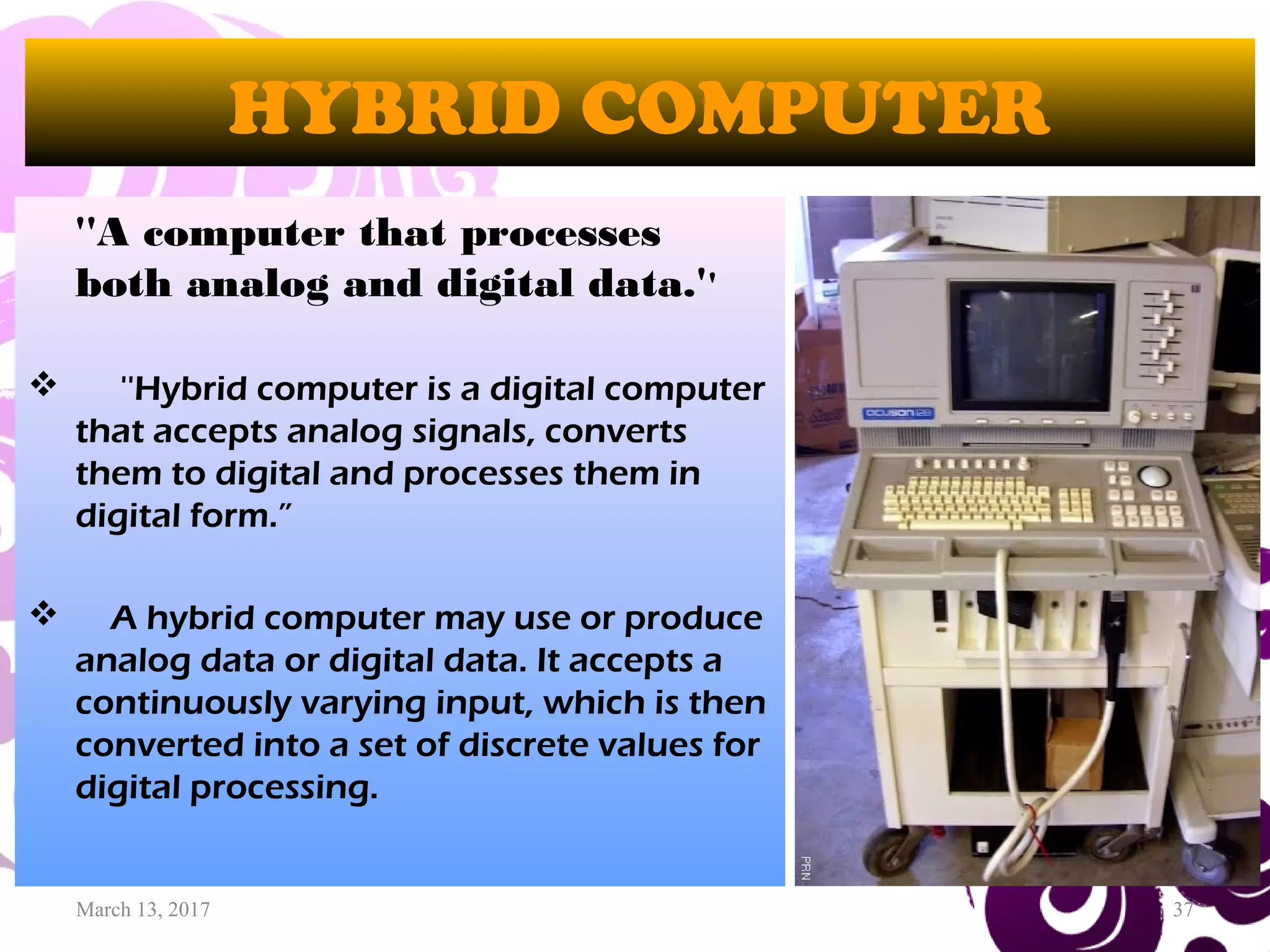
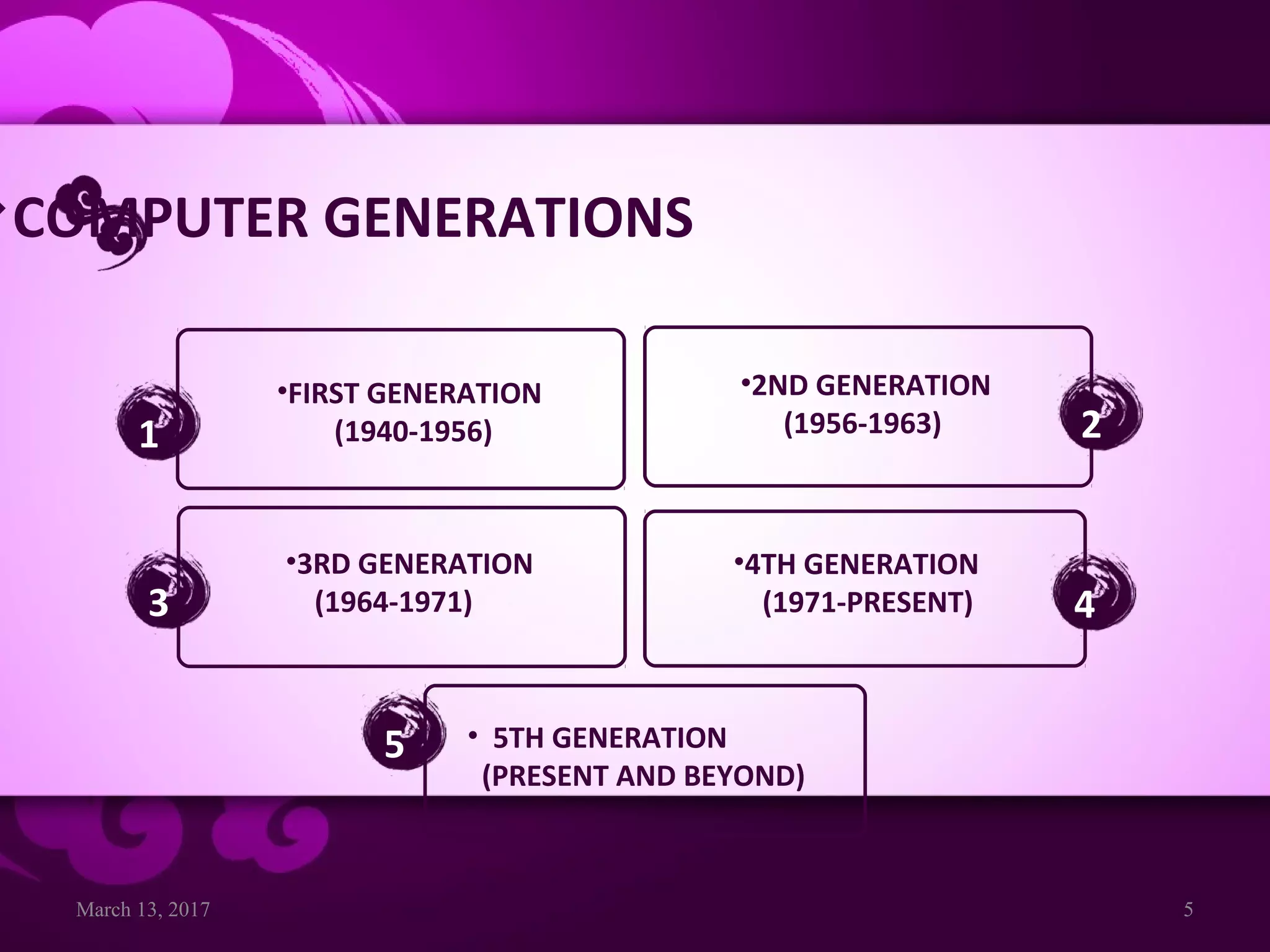
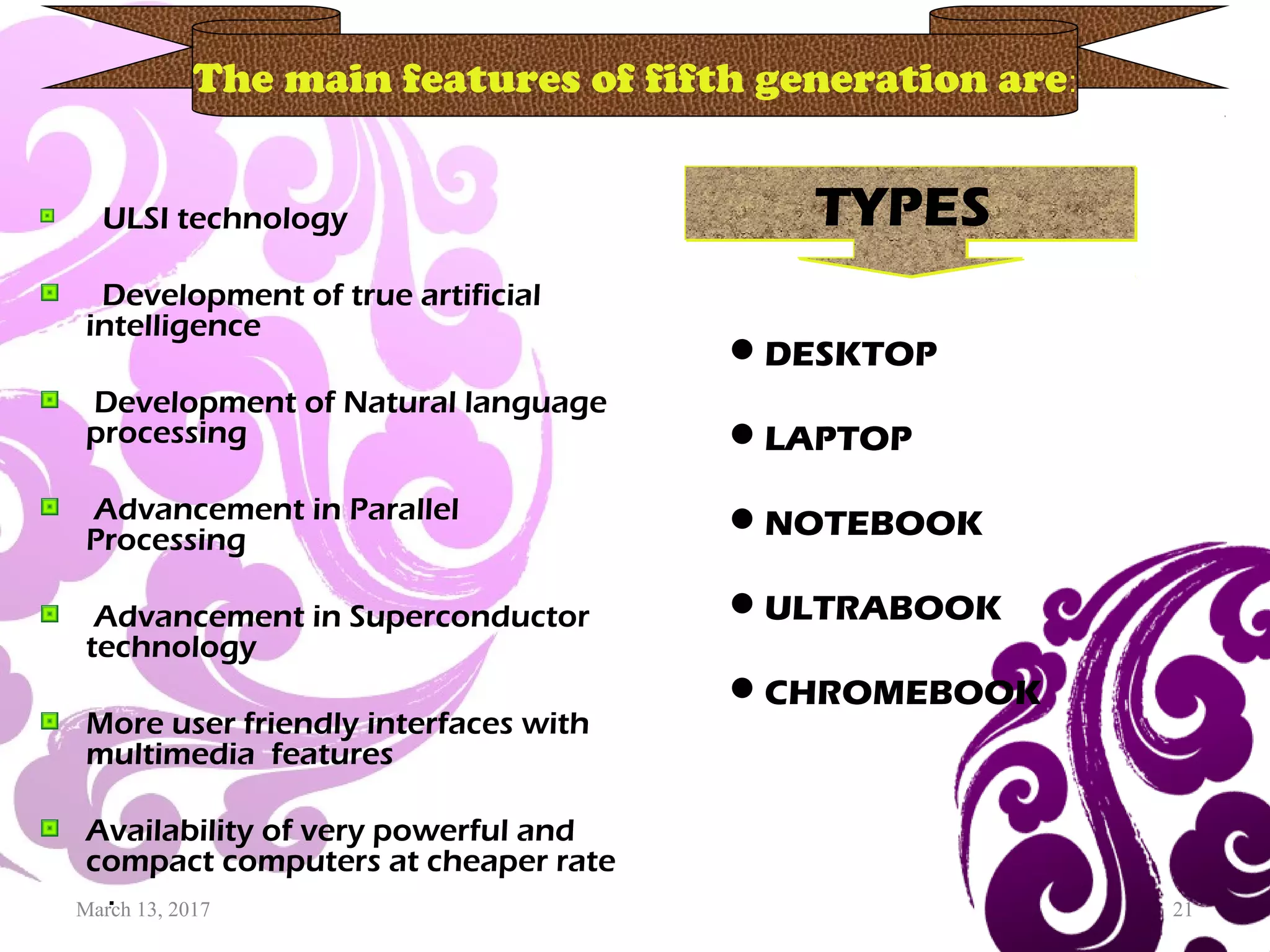
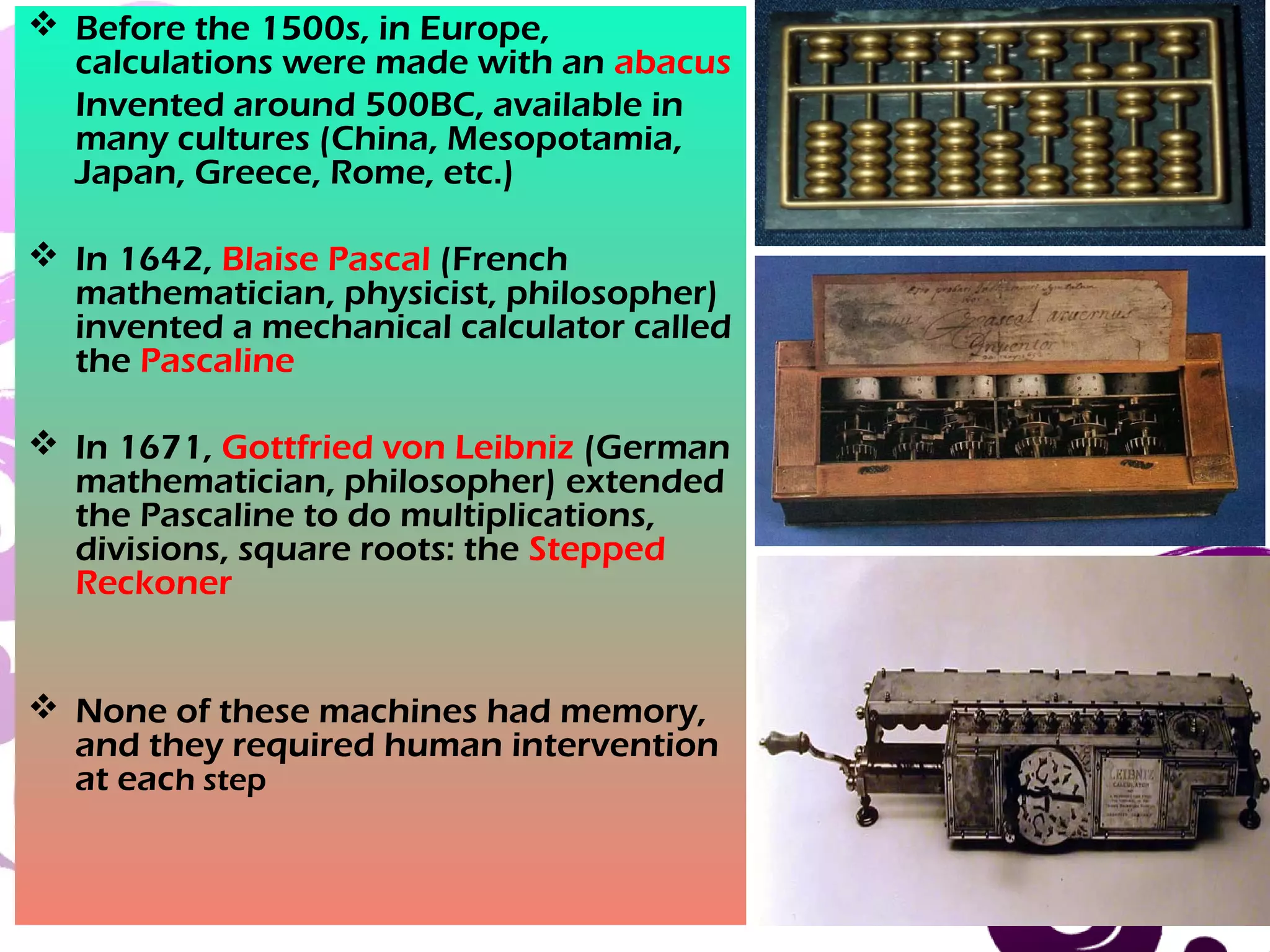
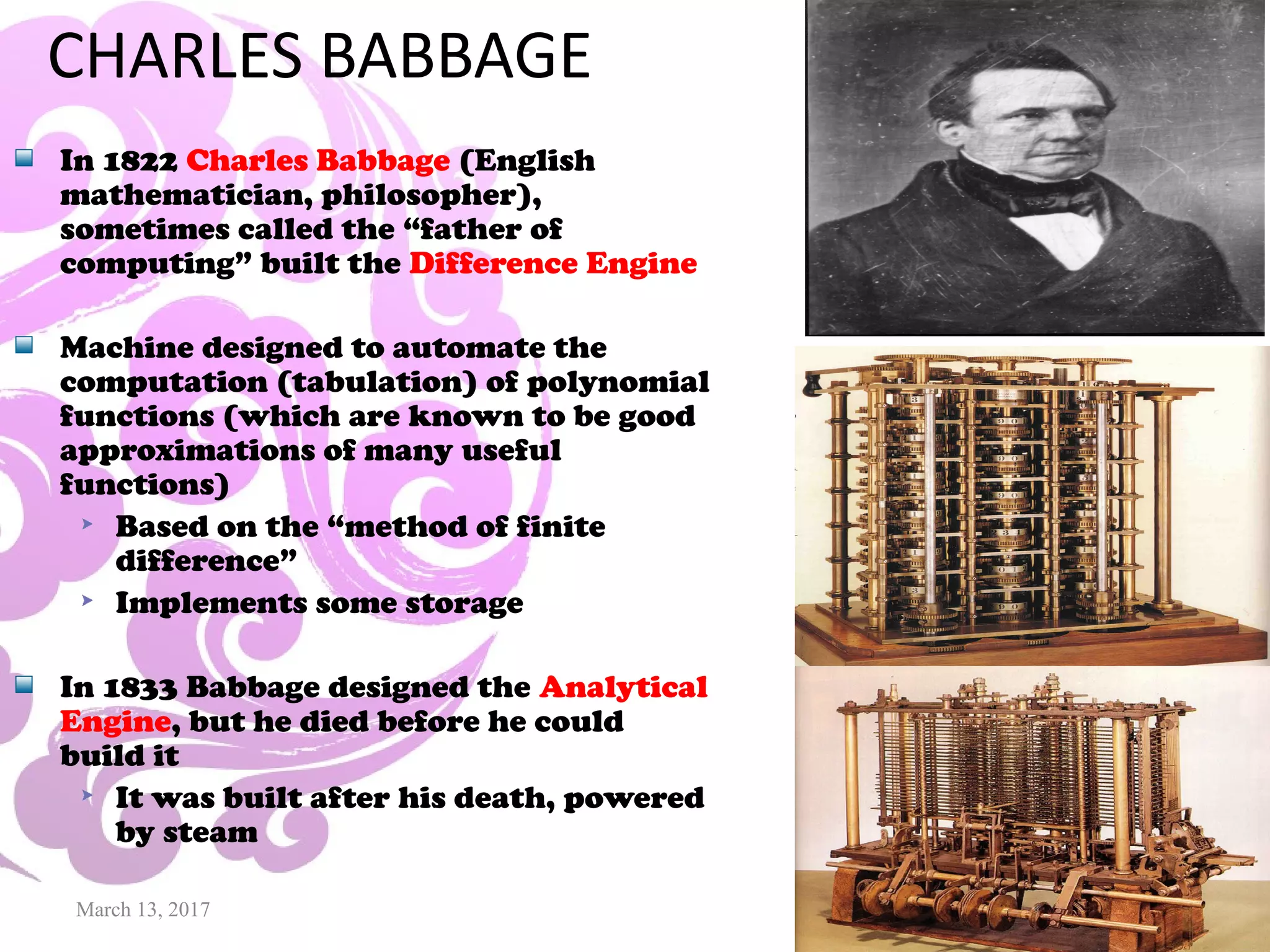
This document provides an overview of computer generations, types of computers, and the history of computers. It discusses the five generations of computers from the first generation using vacuum tubes to the current fifth generation using artificial intelligence. It also describes the main types of computers as analog, digital, and hybrid. Finally, it outlines some of the major developments in computer history from early mechanical calculators to modern devices, showing how technology has progressed rapidly from vacuum tubes to semiconductors to microprocessors.






















![March 13, 2017 33
“a short summary''
(first telegraph message sent by Samuel Morse, 1844Samuel Morse, 1844)
Electronic and computing technology quickly progressed—at an
ever-accelerating pace—
from vacuum tubes (Lee de Forrest, the audion, 1907Lee de Forrest, the audion, 1907)
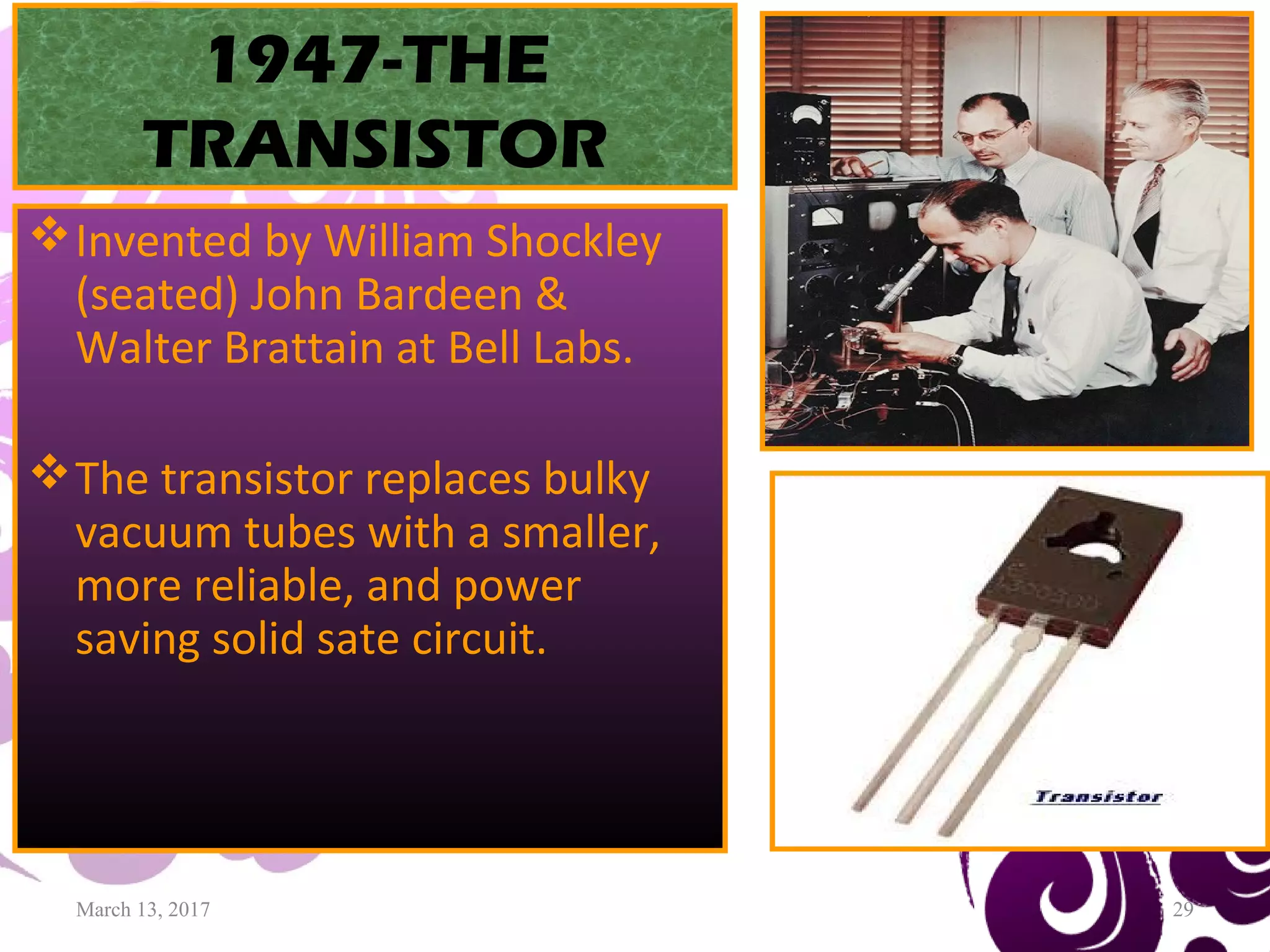
to transistors (William Shockley et al. 1947)William Shockley et al. 1947)
to semiconductors (Jack Kilby & Robert Noyce, 1958Jack Kilby & Robert Noyce, 1958)
to microprocessors (M.E. “Ted” Hoff, 1971M.E. “Ted” Hoff, 1971)
to networking and the Internet (Vinton Cerf & Robert Kahn,Vinton Cerf & Robert Kahn,
19821982]
to the World Wide Web (Tim Berners-Lee, 1991Tim Berners-Lee, 1991)
and beyond…
Whatever next?…Whatever next?…](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/computerhistorygenerationsanditstypes-170313171625/75/Computer-history-generations-and-its-types-33-2048.jpg)