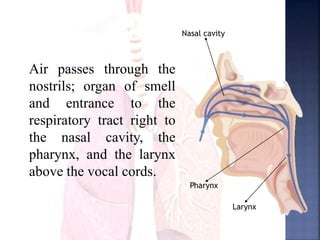
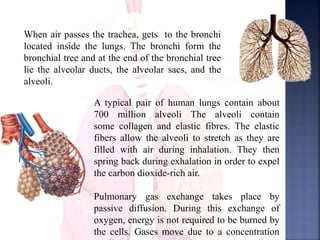
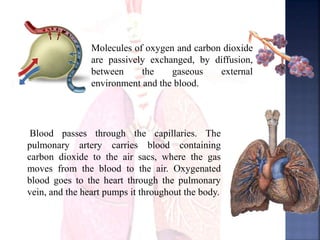
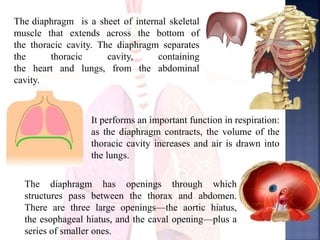
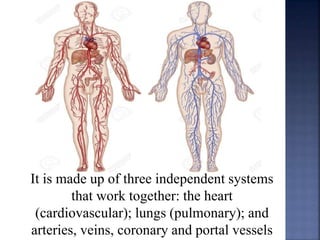
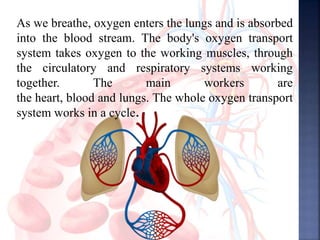
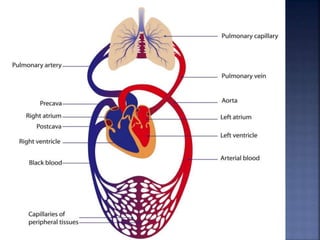
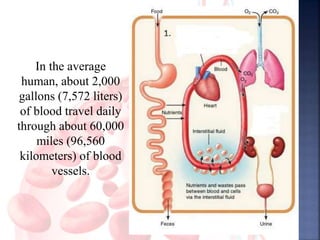
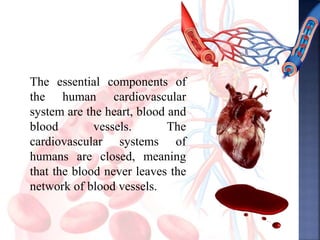
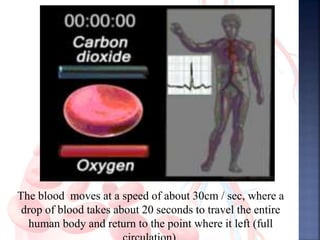
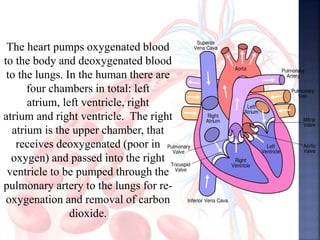
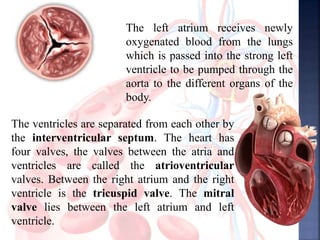
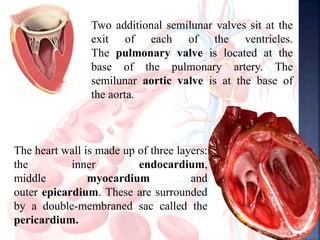
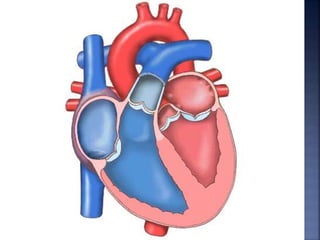
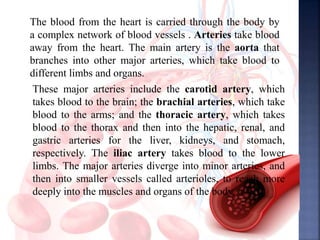
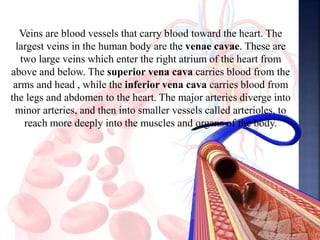
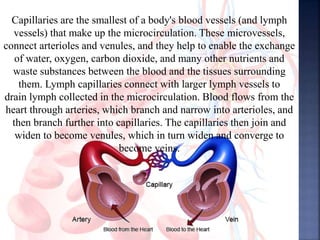
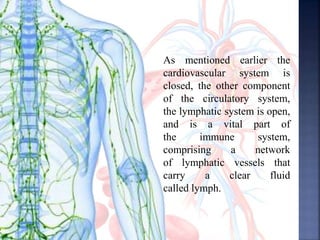
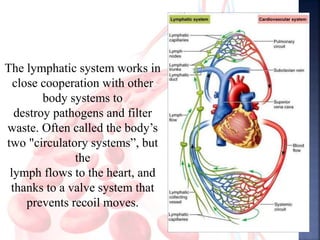
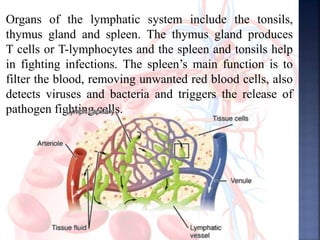
The document provides an overview of the human respiratory and cardiovascular systems, detailing the processes involved in oxygen absorption and carbon dioxide expulsion. It describes the structures and functions of the lungs, heart, blood vessels, and the lymphatic system, highlighting their roles in gas exchange and nutrient transport. Overall, the systems work in coordination to maintain homeostasis and support bodily functions.