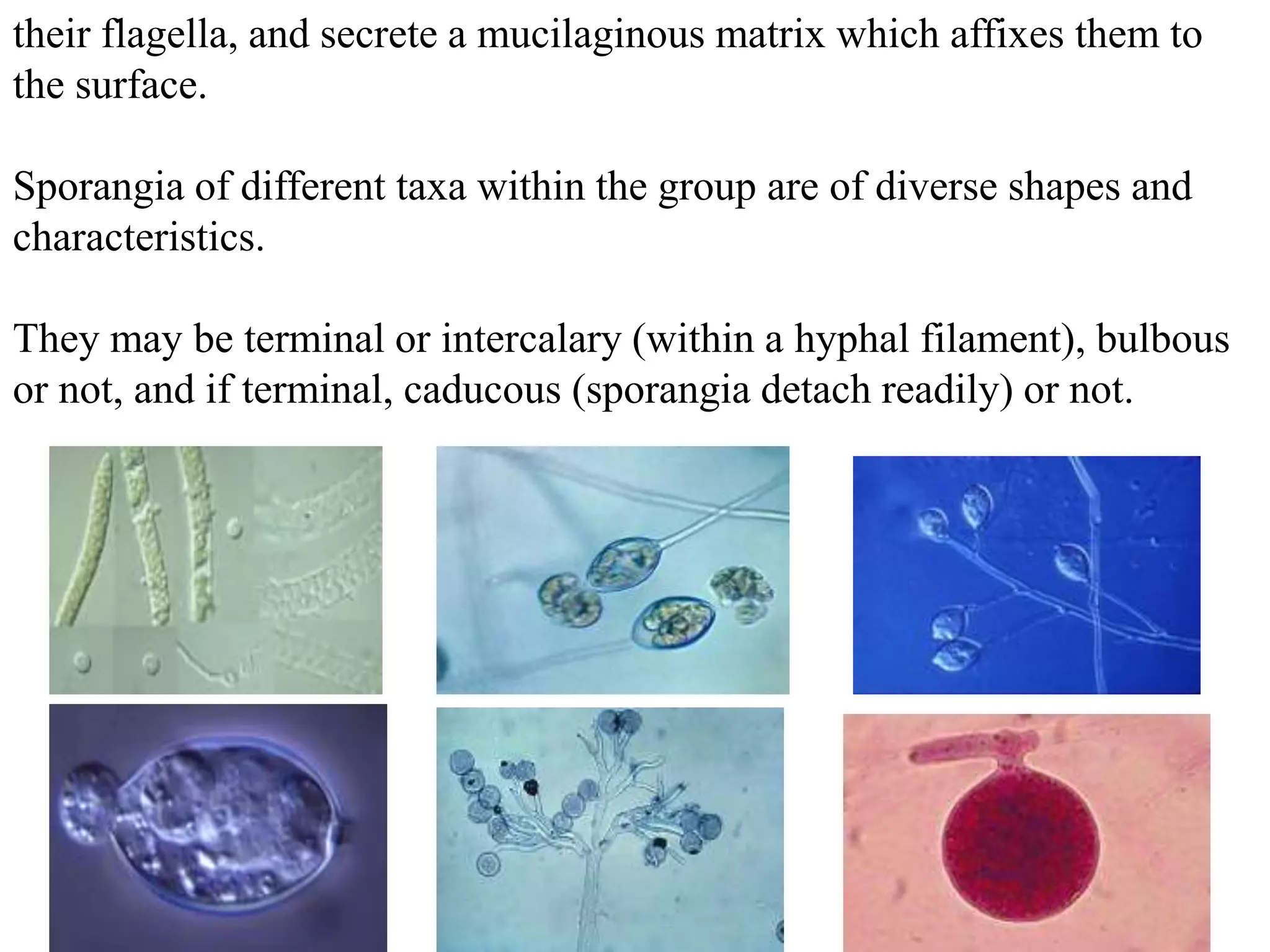
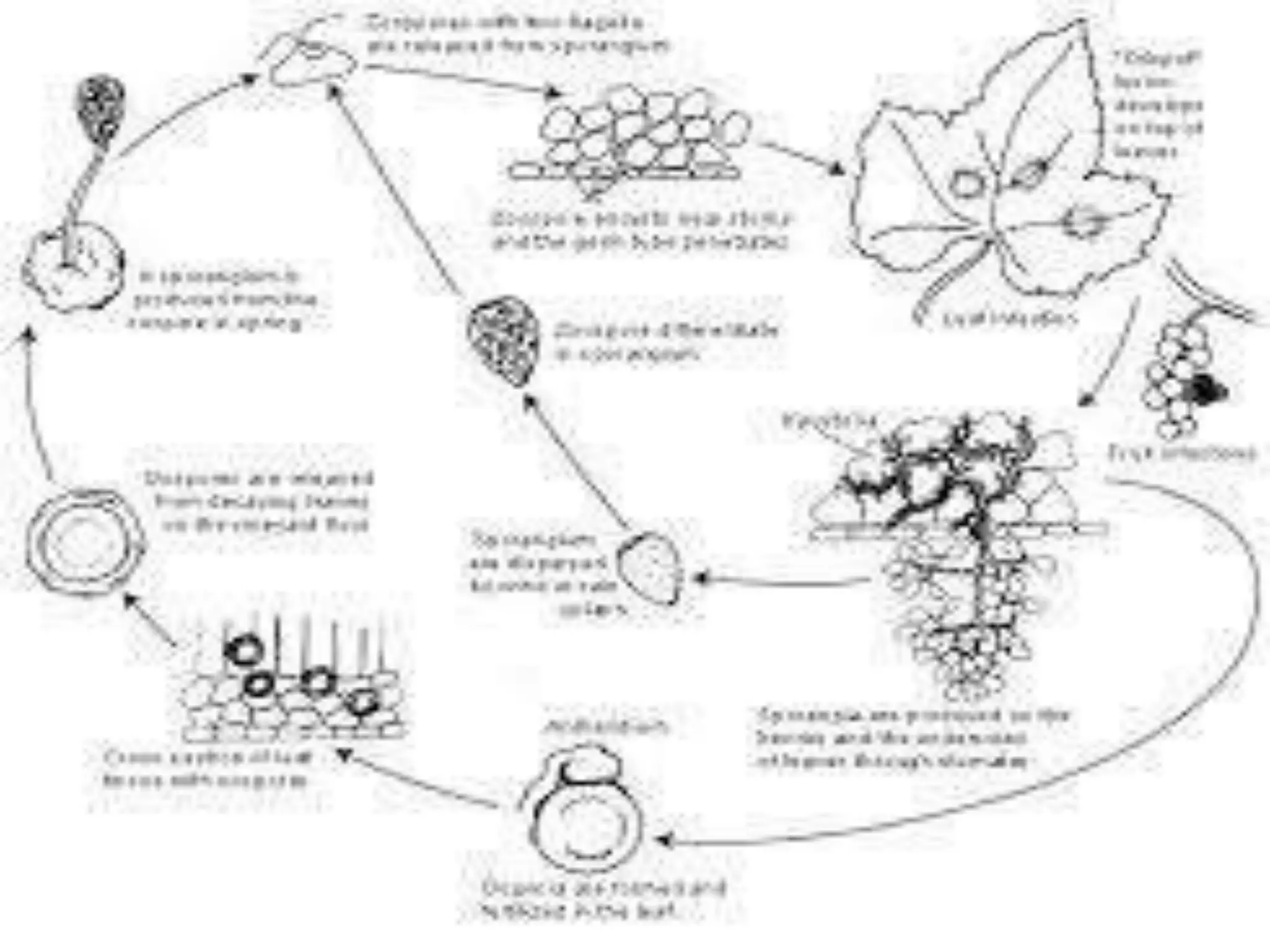
Oomycetes, commonly known as water molds, are eukaryotic organisms that are closely related to algae. They include some of the most devastating plant pathogens, causing diseases like late blight of potato and downy mildew of grapevines. Oomycetes reproduce both sexually, through the formation of gametangia and fertilization leading to thick-walled oospores, and asexually via motile zoospores or non-motile sporangia. While they were long classified as fungi, genetic evidence shows they are more closely related to algae and plants. Key differences from true fungi include having cell walls composed of cellulose and lacking chitin.