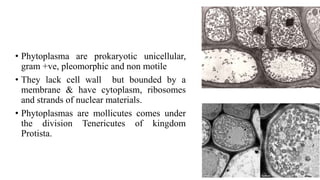
Phytoplasma are prokaryotic, cell-wall less bacteria that infect the phloem of plants and are transmitted by insect vectors. They lack the ability to be cultured independently and are pleomorphic, ranging from 0.17-0.25 μm in size. Phytoplasma cause diseases in hundreds of plant species and are characterized by symptoms such as phyllody, yellowing, witches' brooms, and little leaf. They are detected using PCR and fluorescent staining. Major phytoplasma diseases include little leaf disease of brinjal, sesame phyllody, and lethal yellowing of coconut.