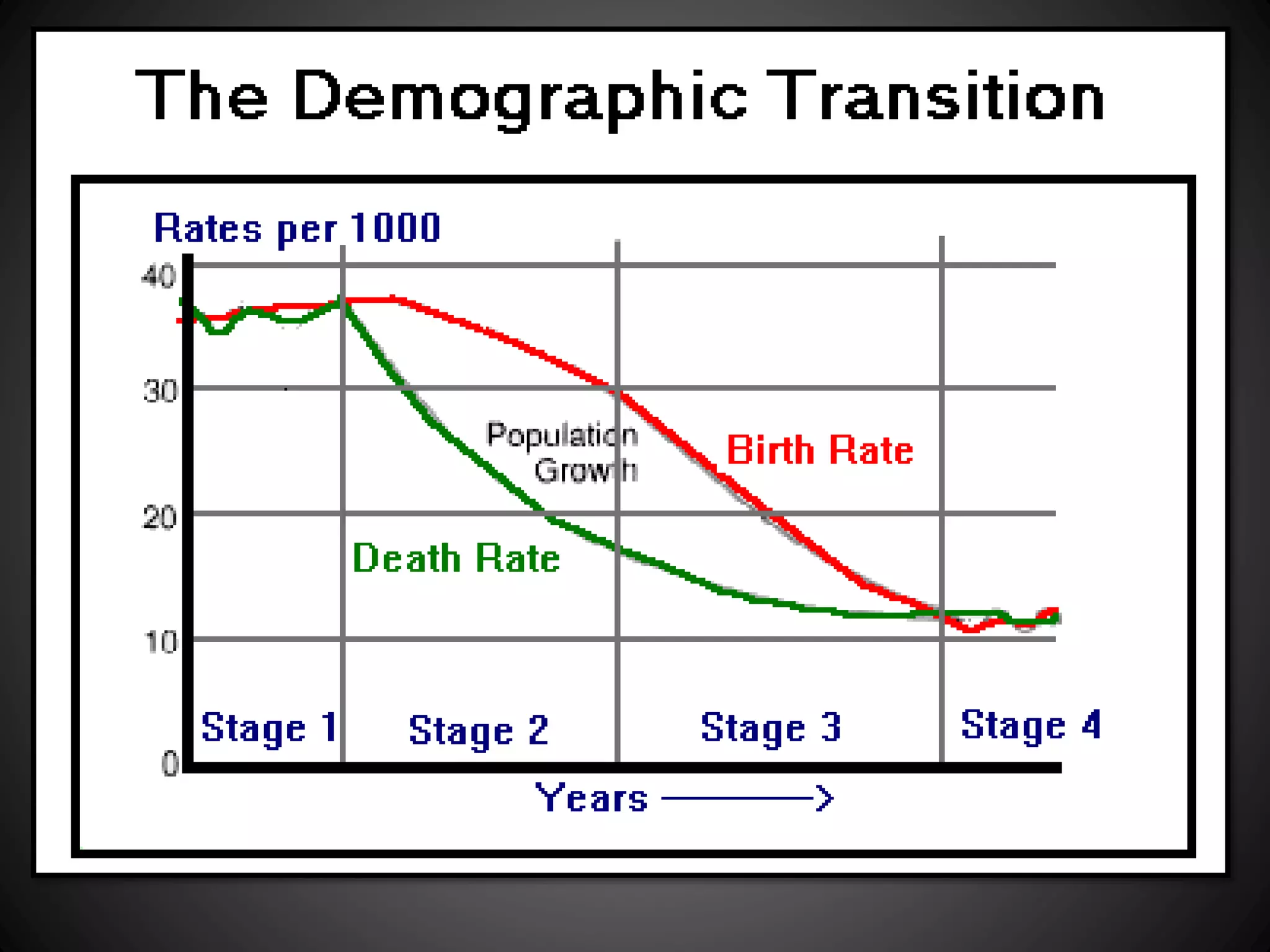
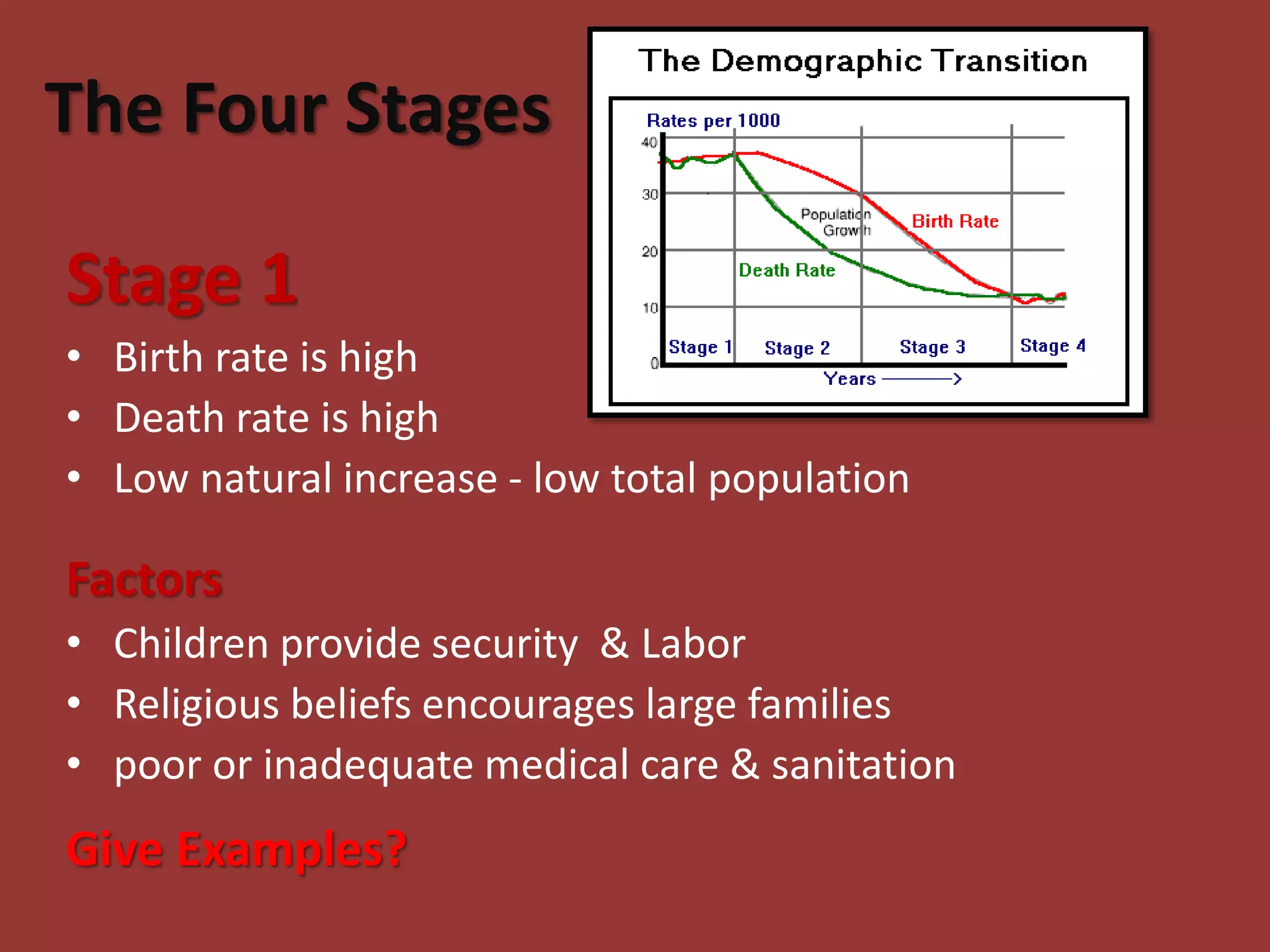
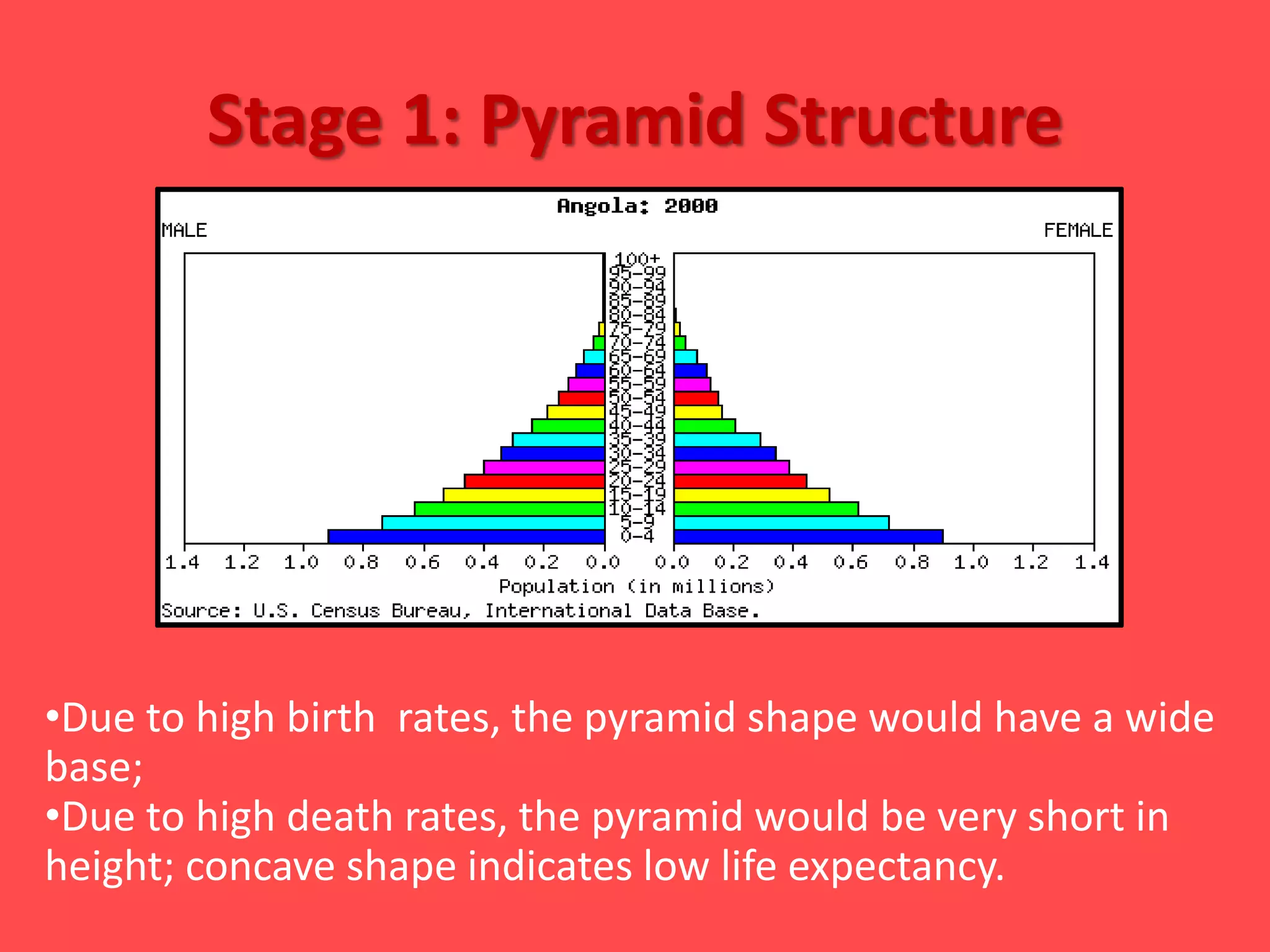
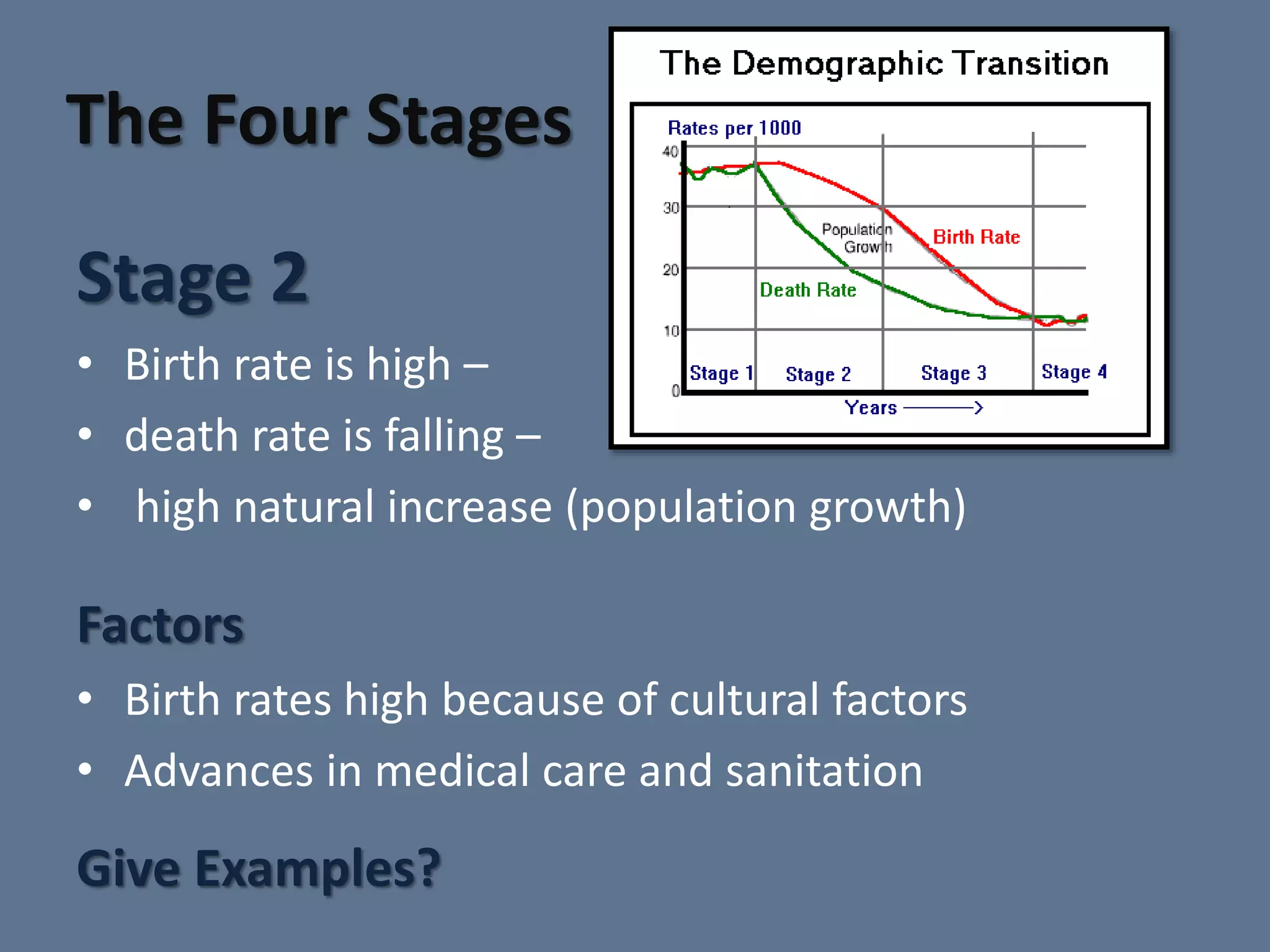
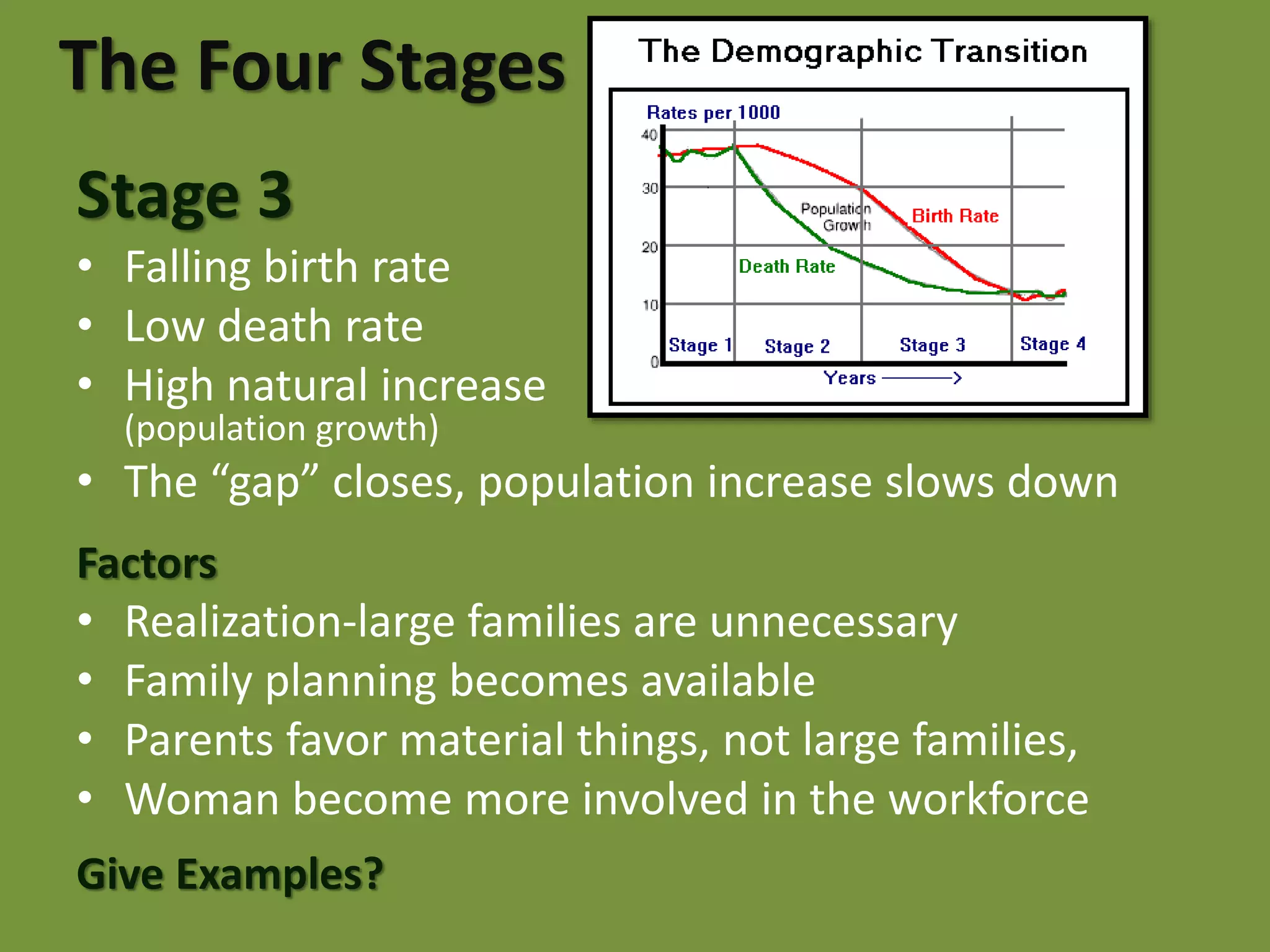
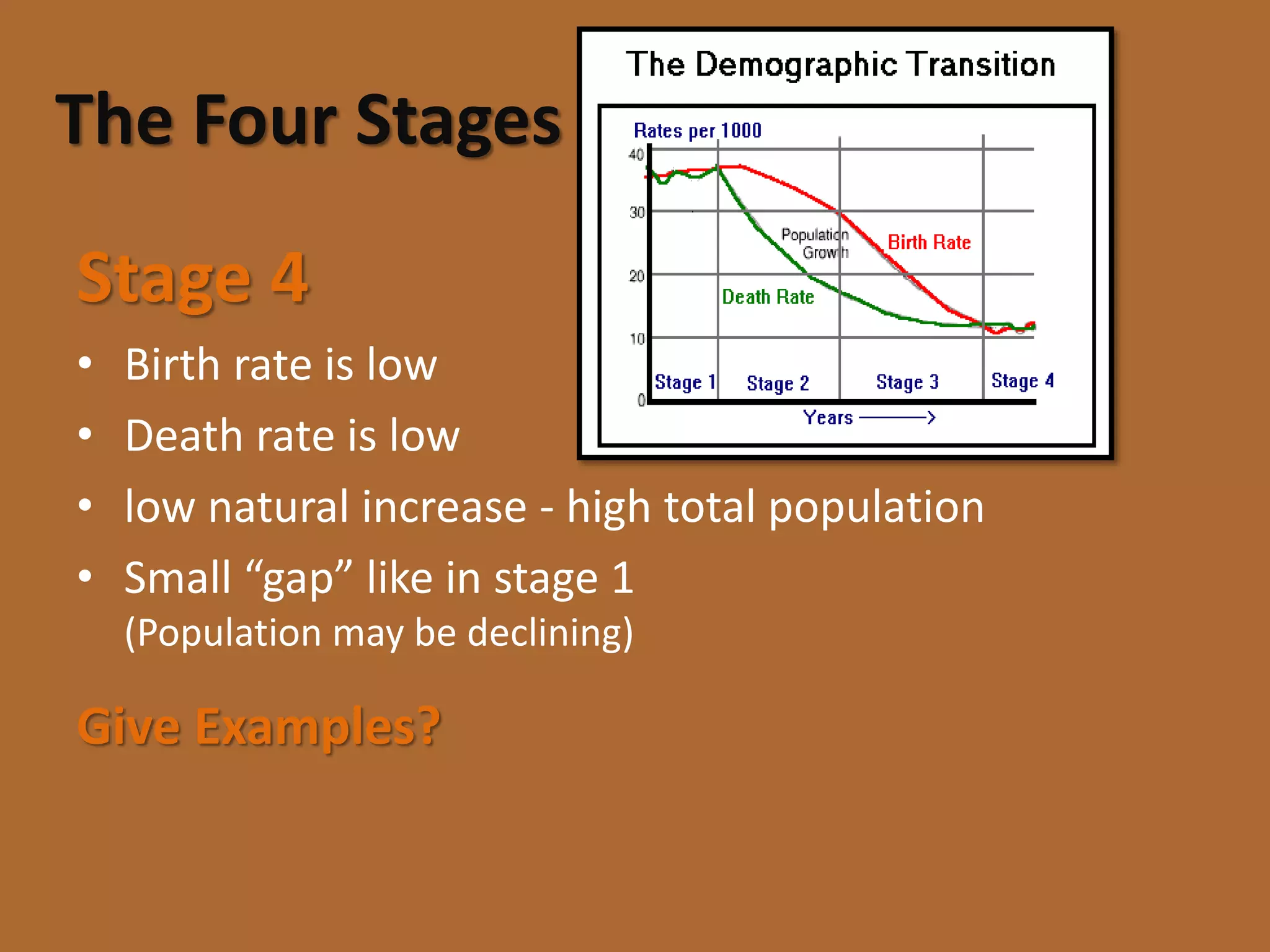
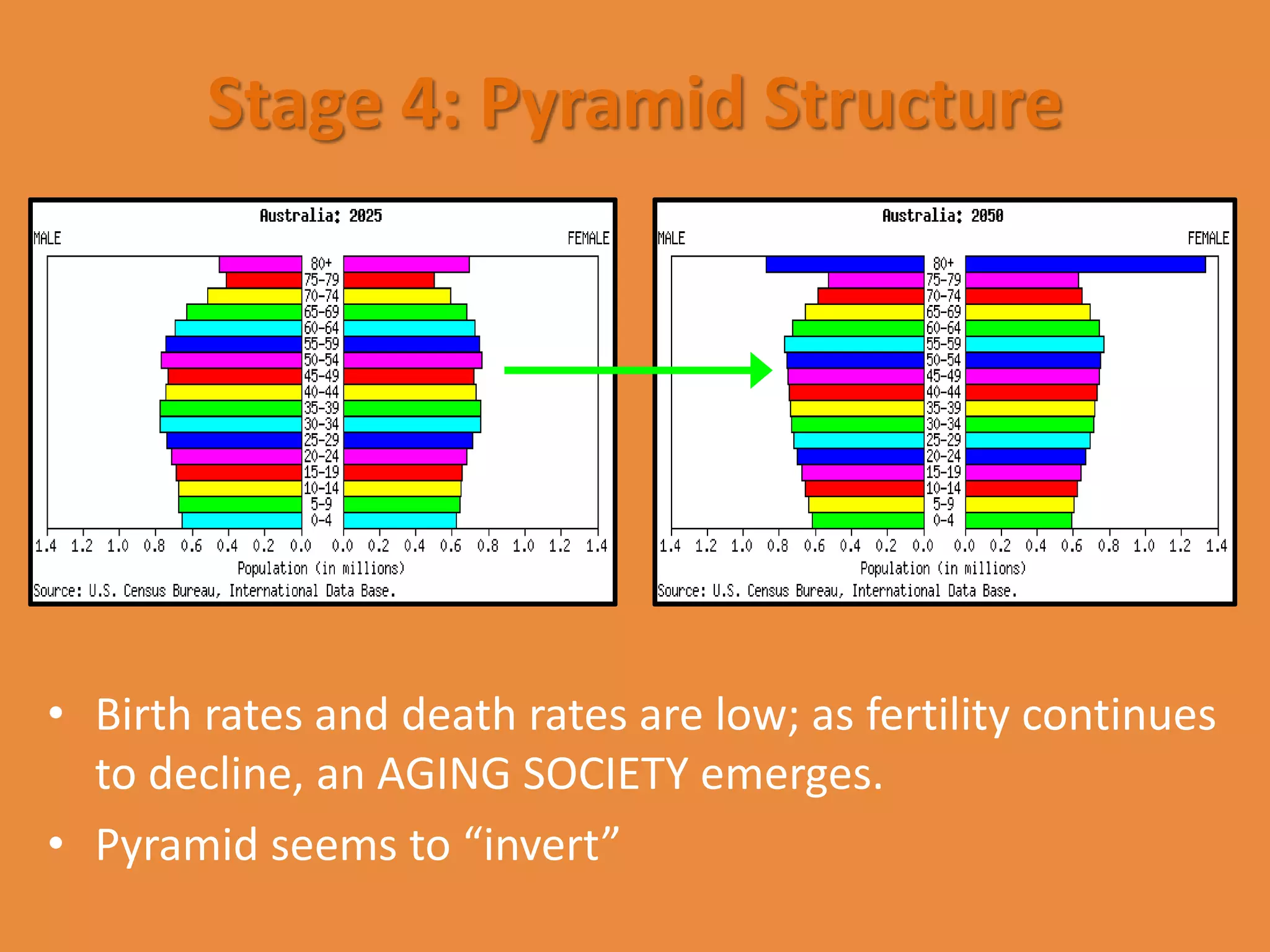
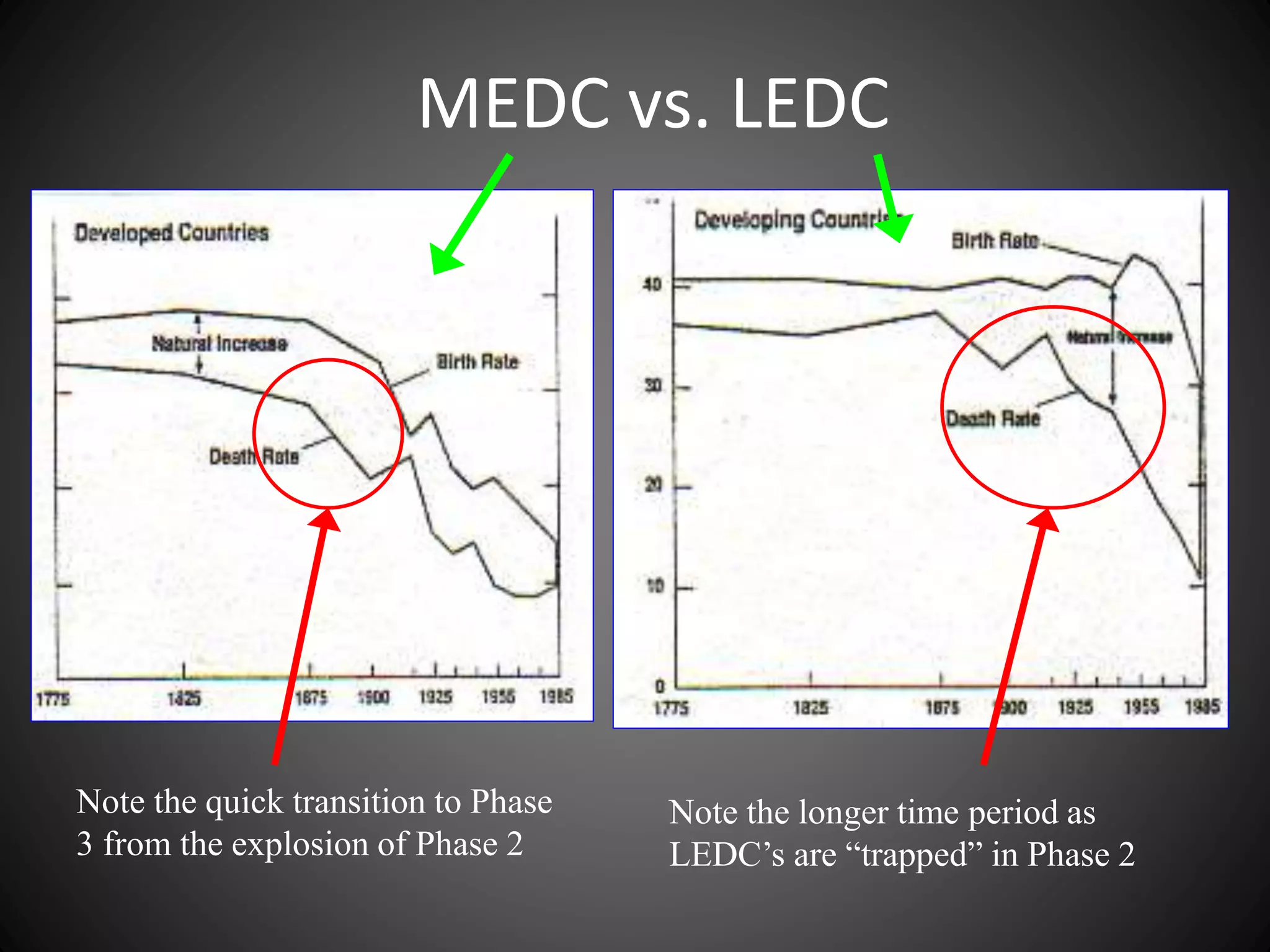
The document discusses the Demographic Transition Model, which attempts to show how population changes as a country develops. The model divides development into four stages:
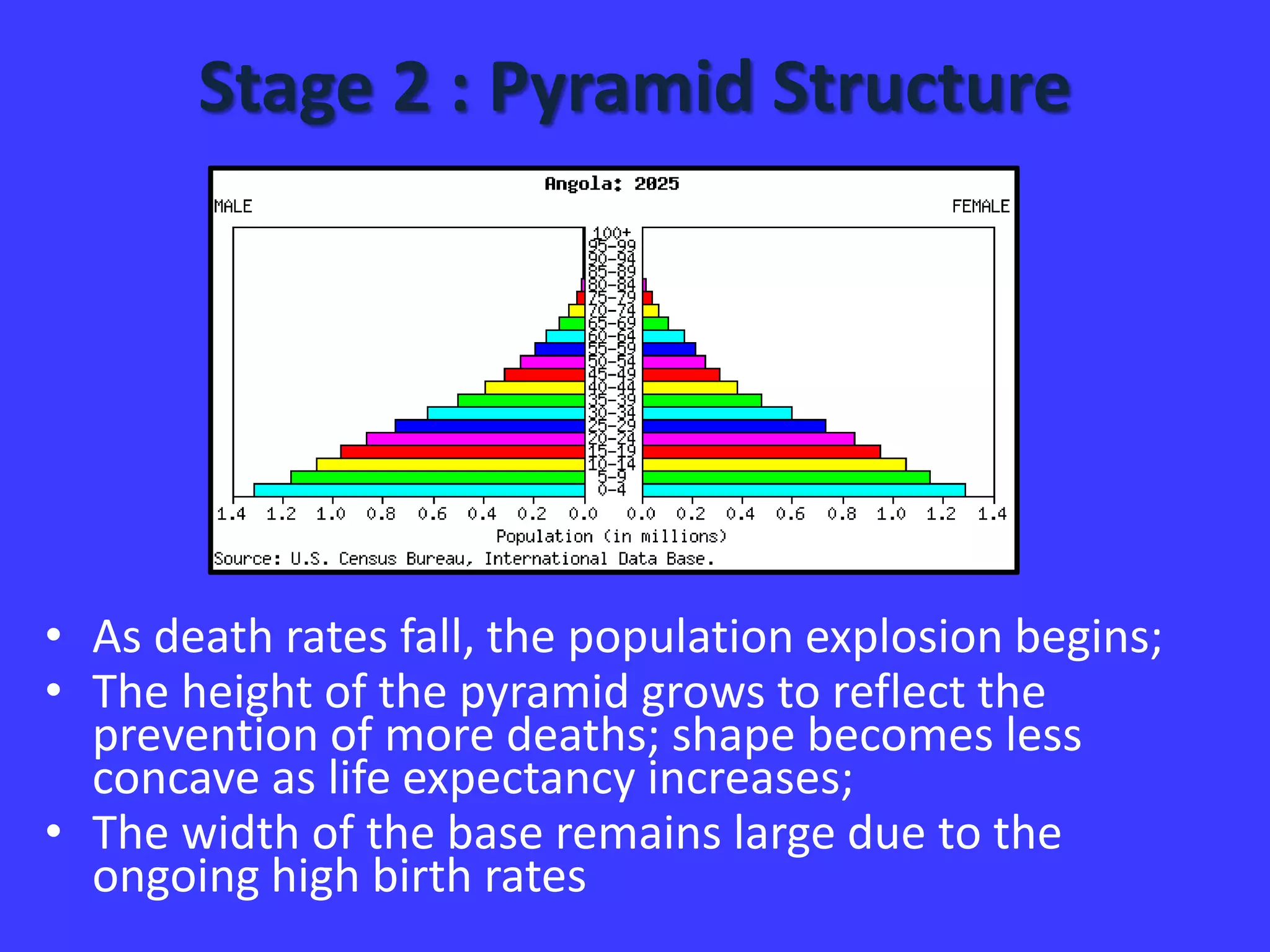
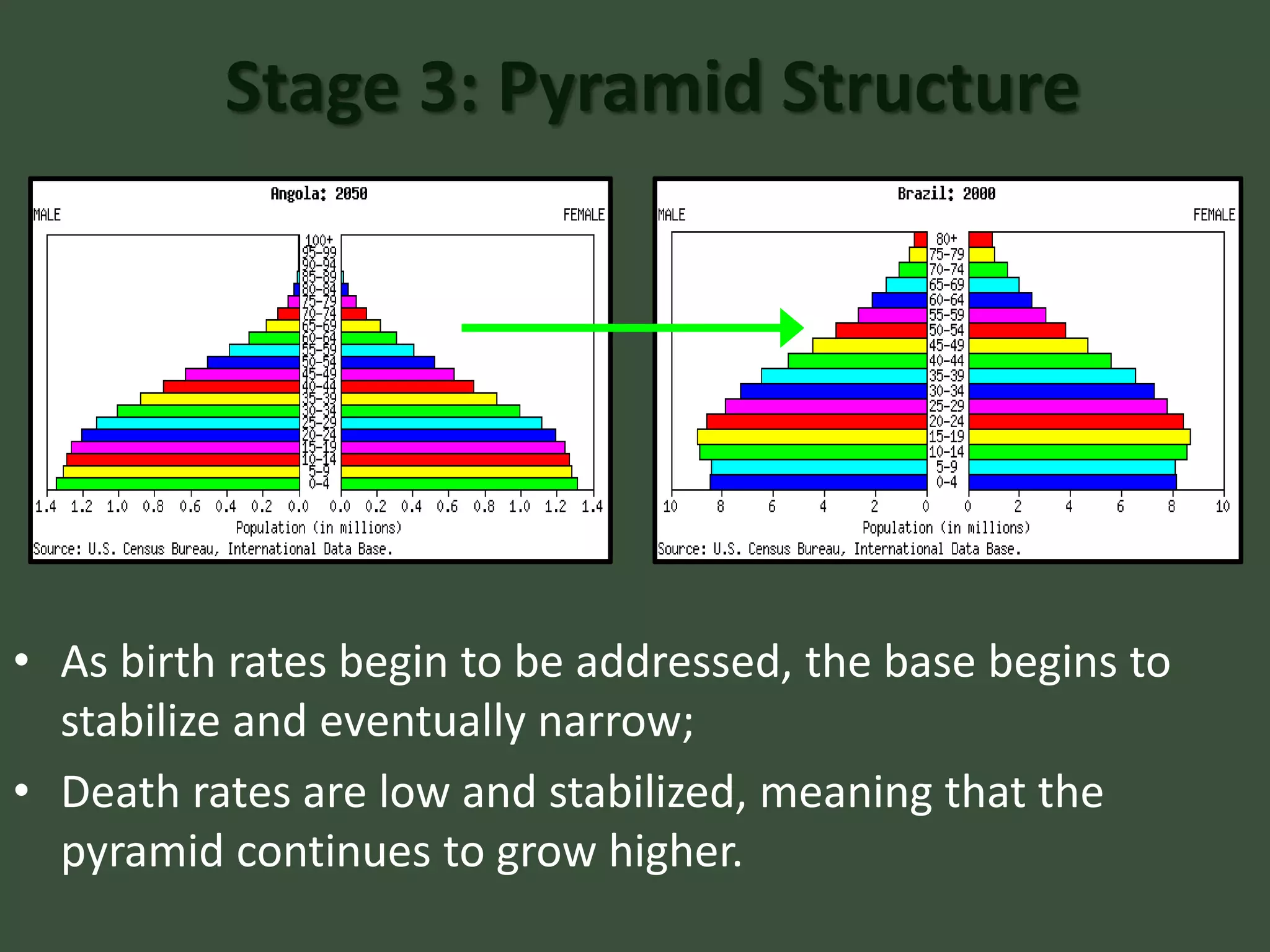
Stage 1 has high birth and death rates, leading to low population growth. Stages 2 and 3 see birth rates remain high while death rates fall dramatically, resulting in rapid population increase. Stage 4 is characterized by low birth and death rates, leading again to low population growth. The model shows these stages through a country's population pyramid shape. However, the model is an overgeneralization and does not consider exceptions like war or political issues.