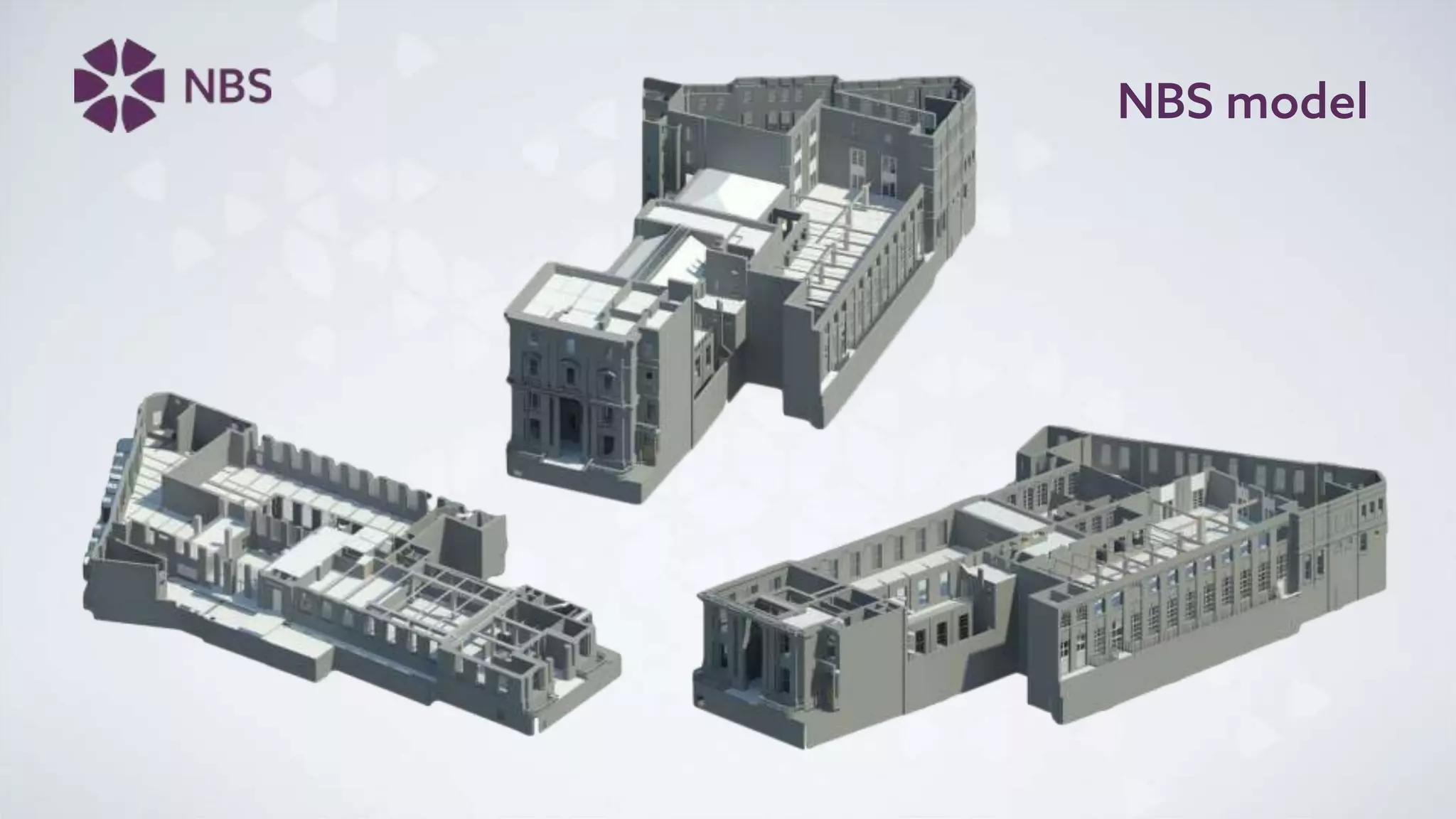
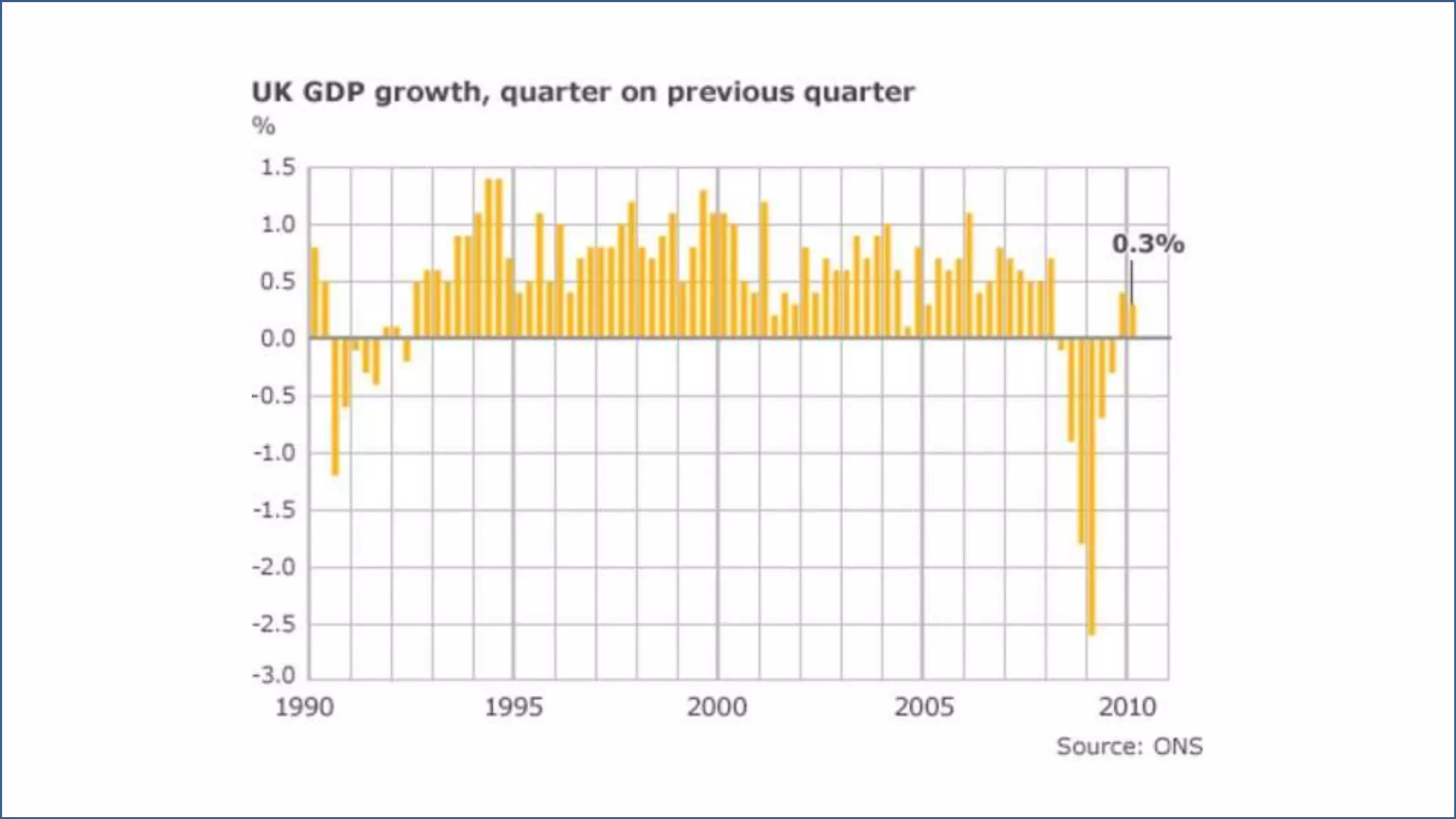
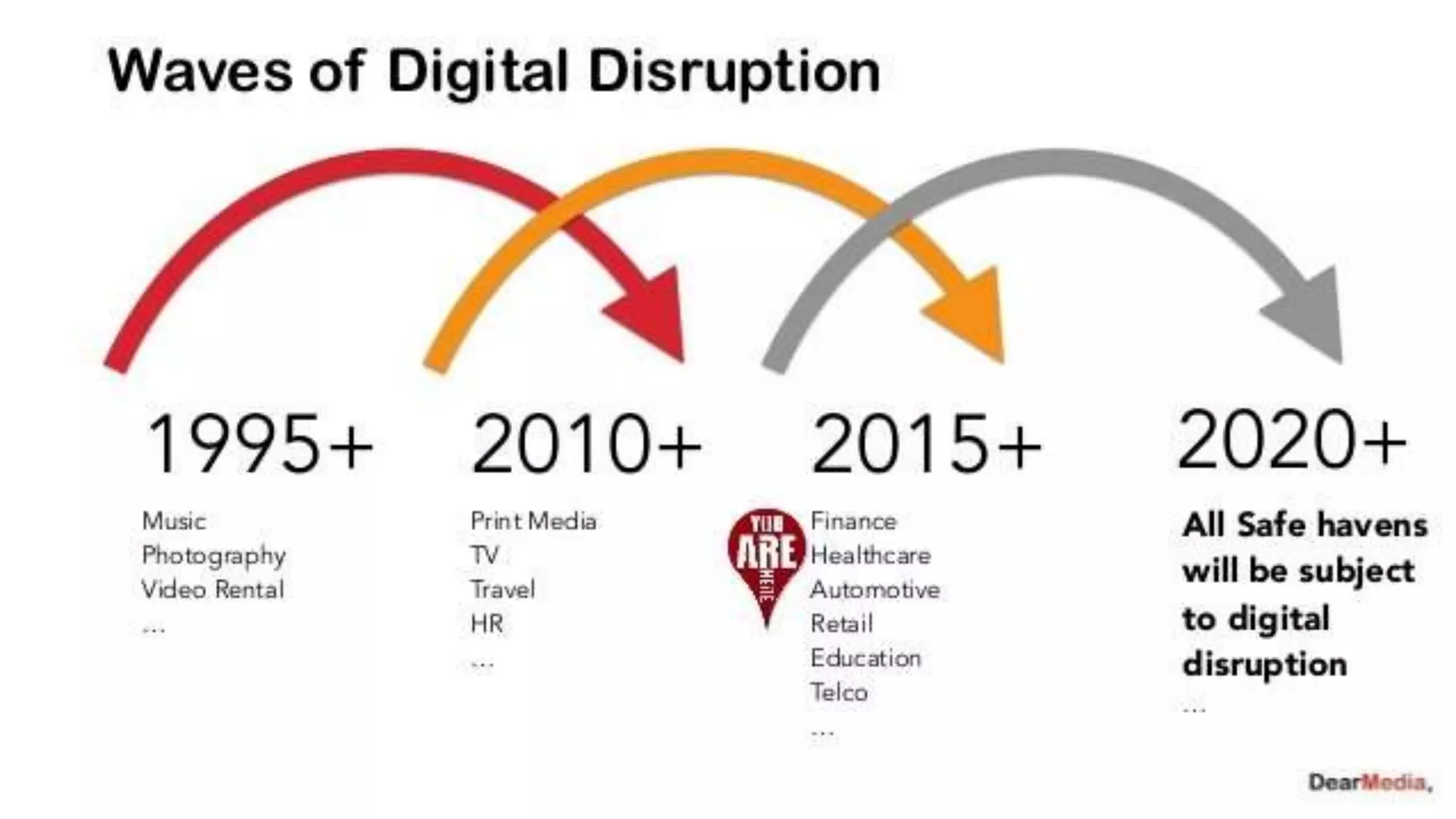
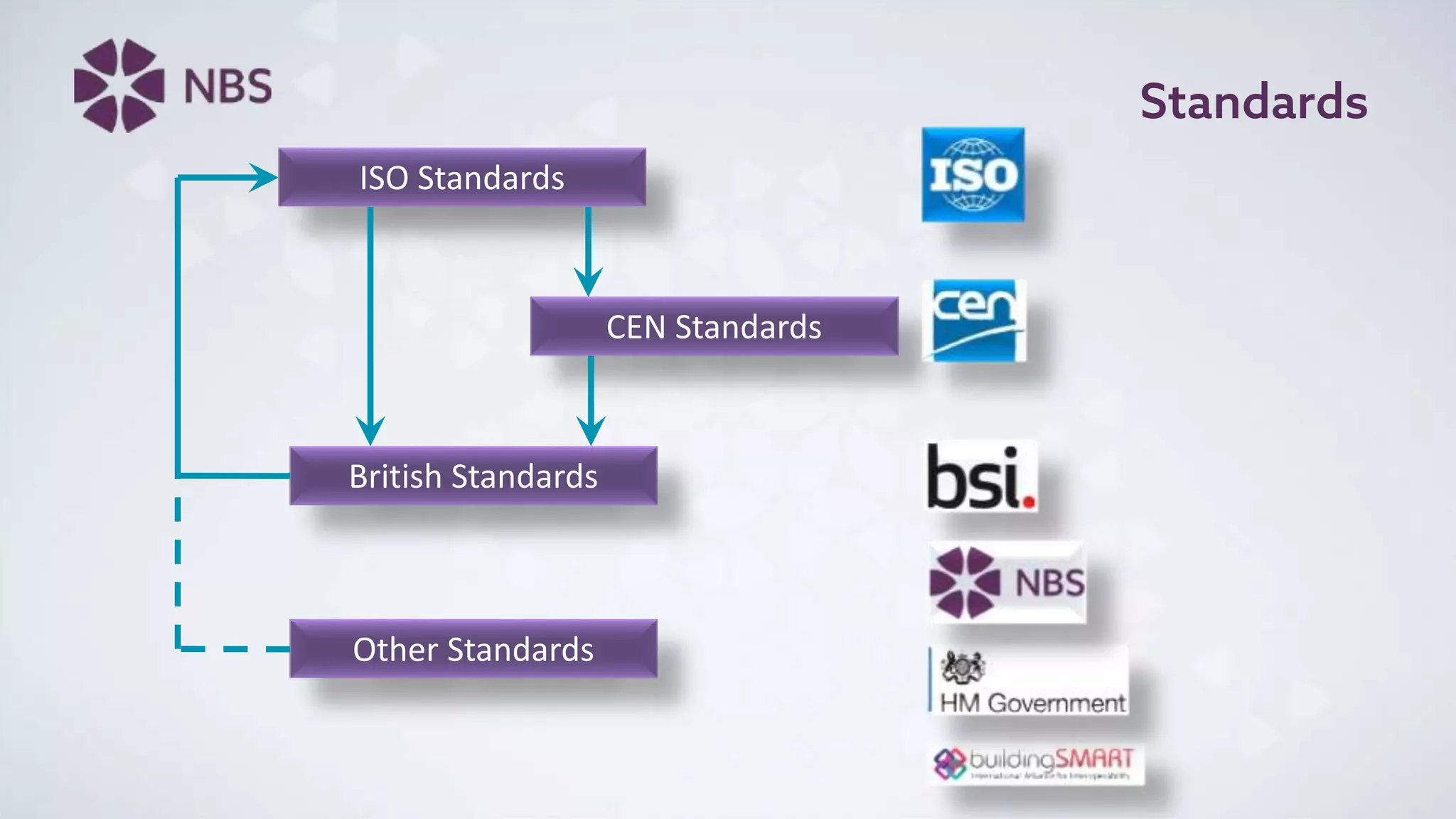
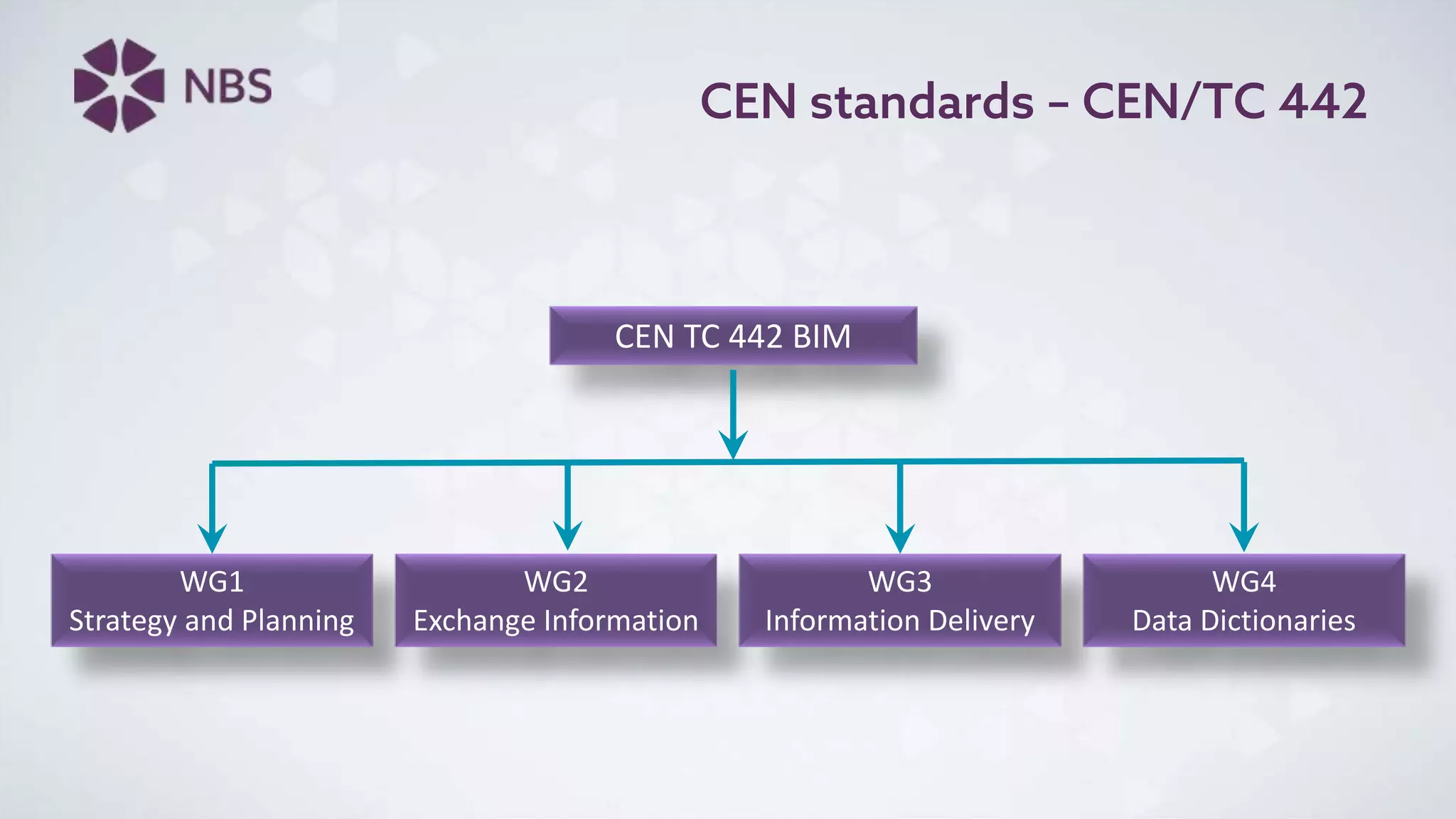
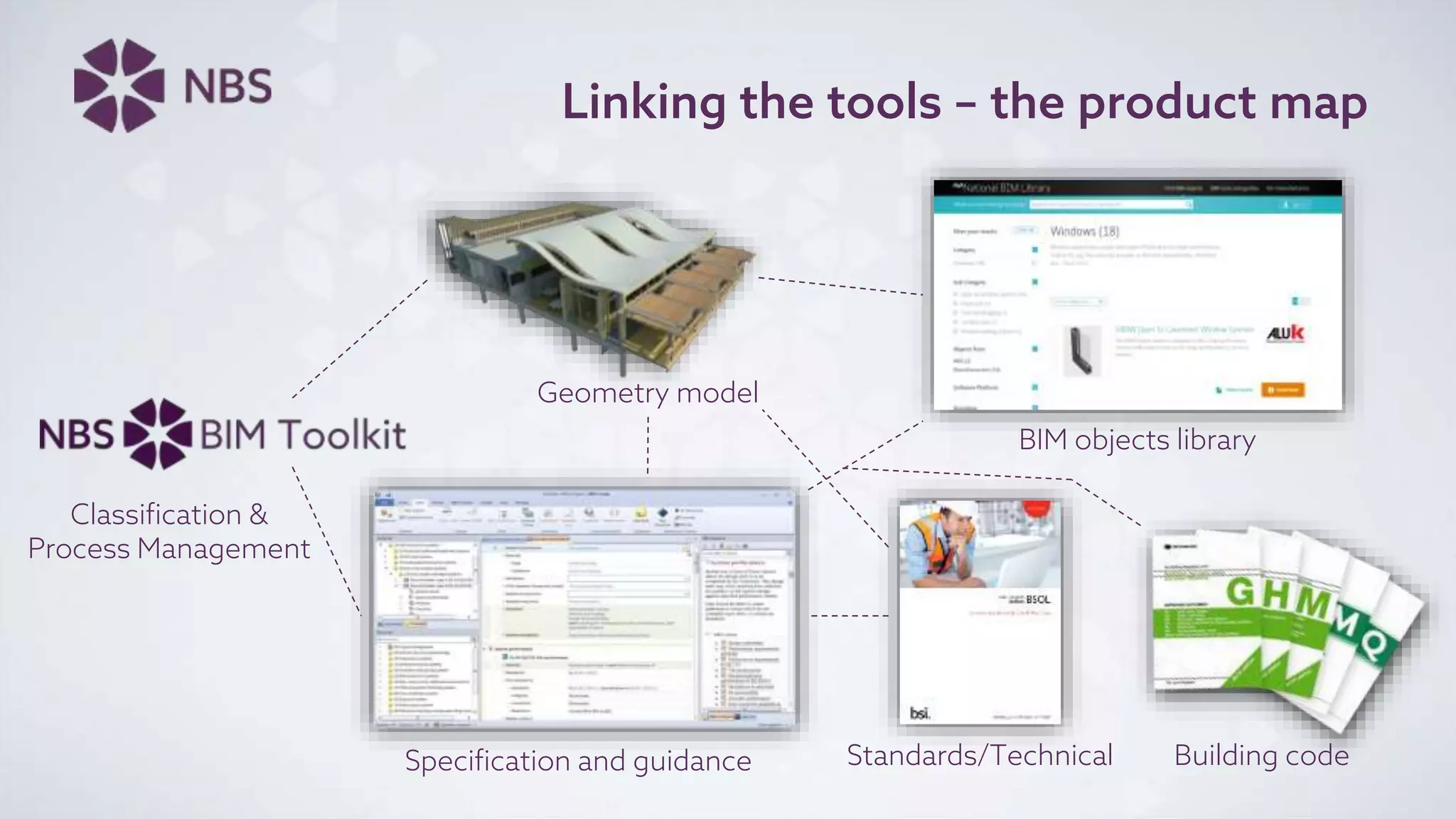
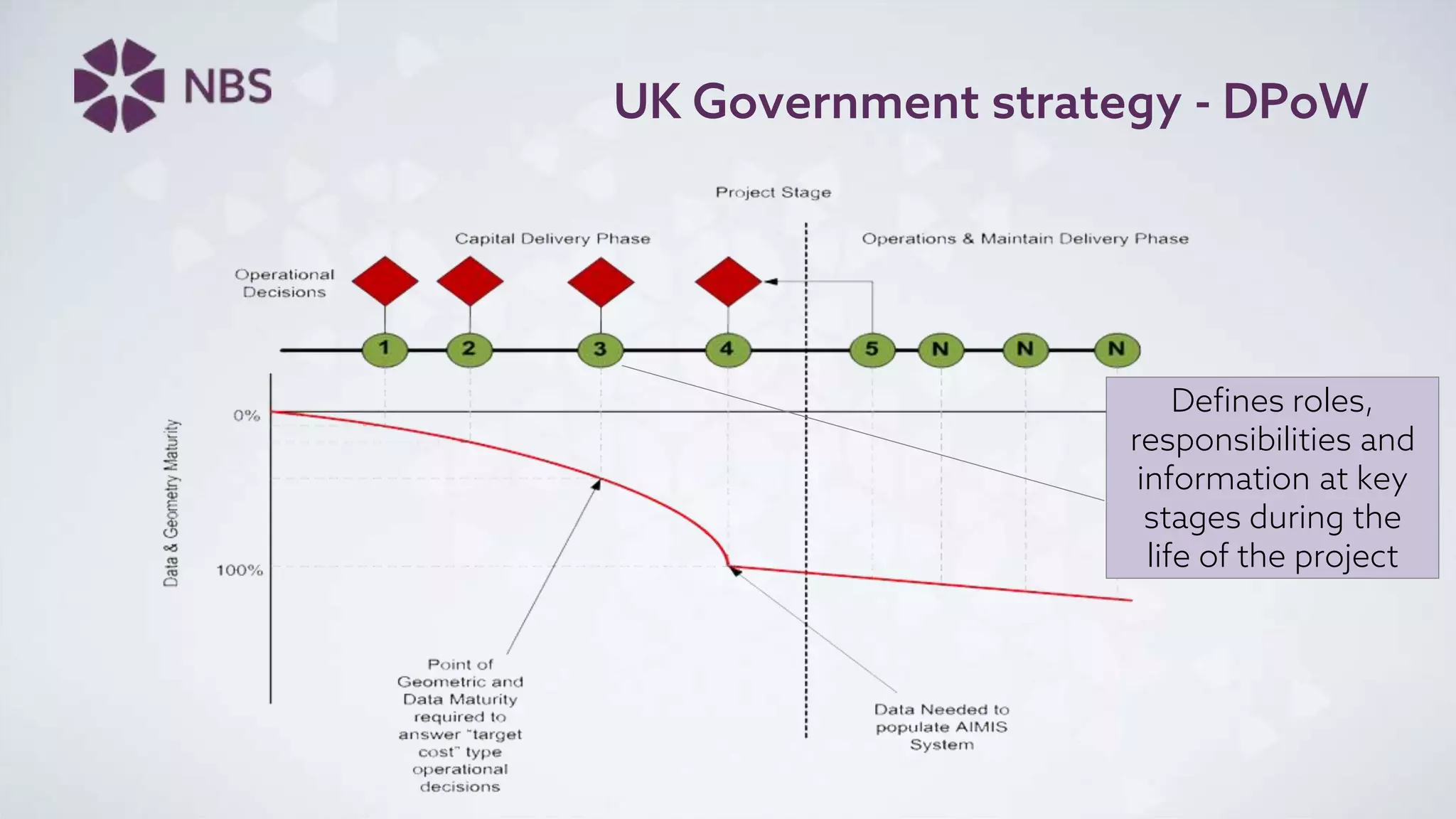
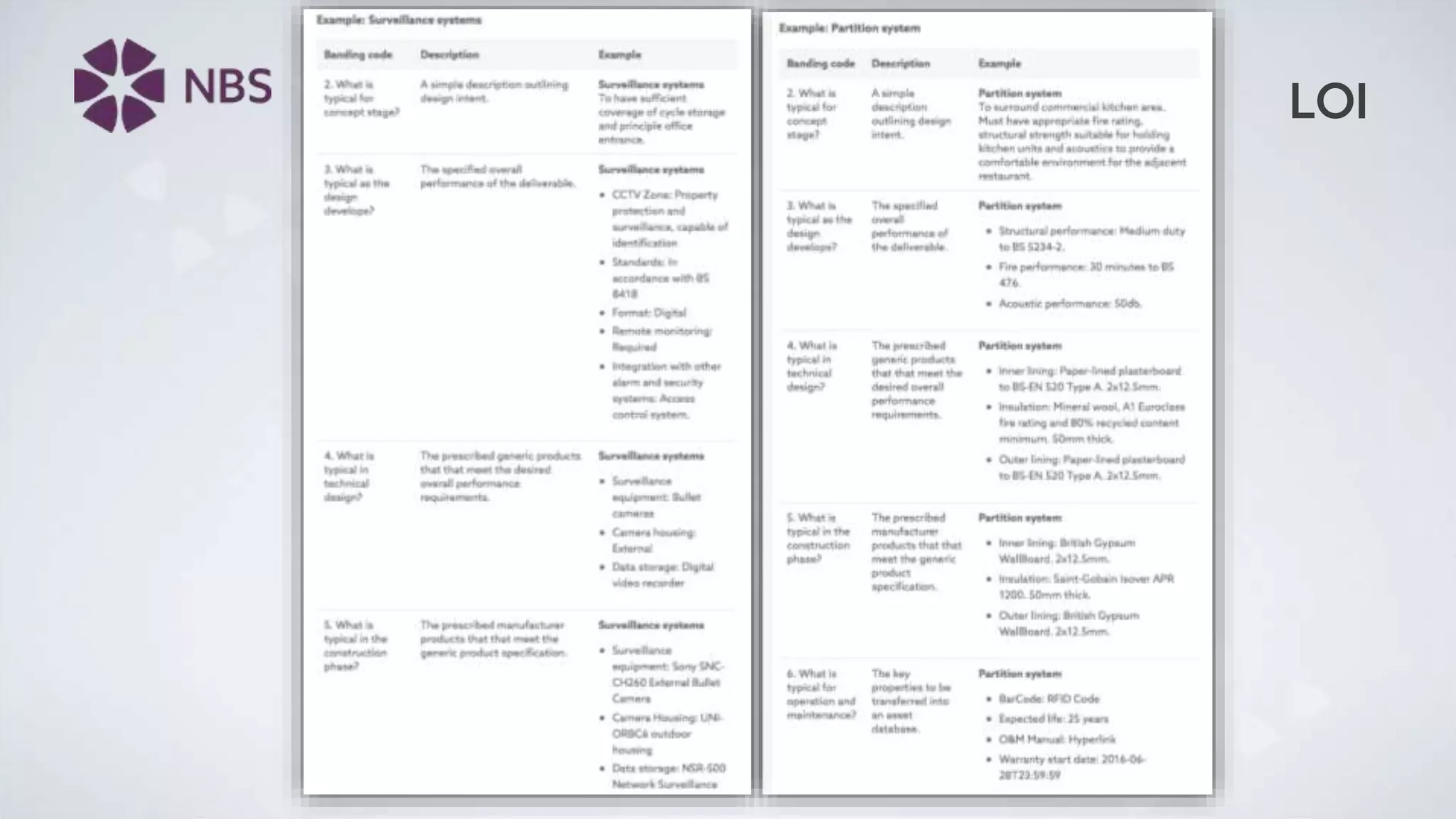
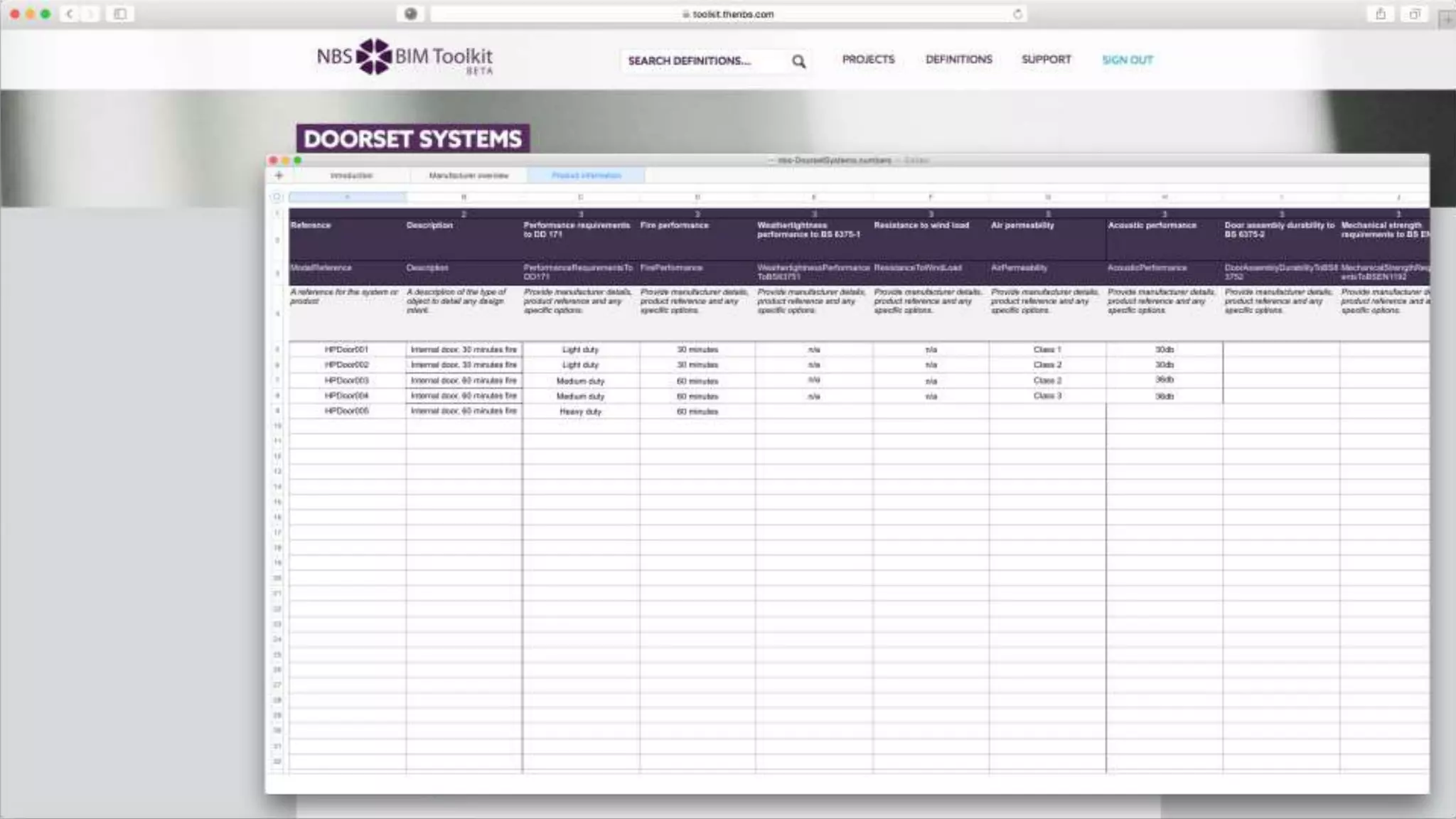
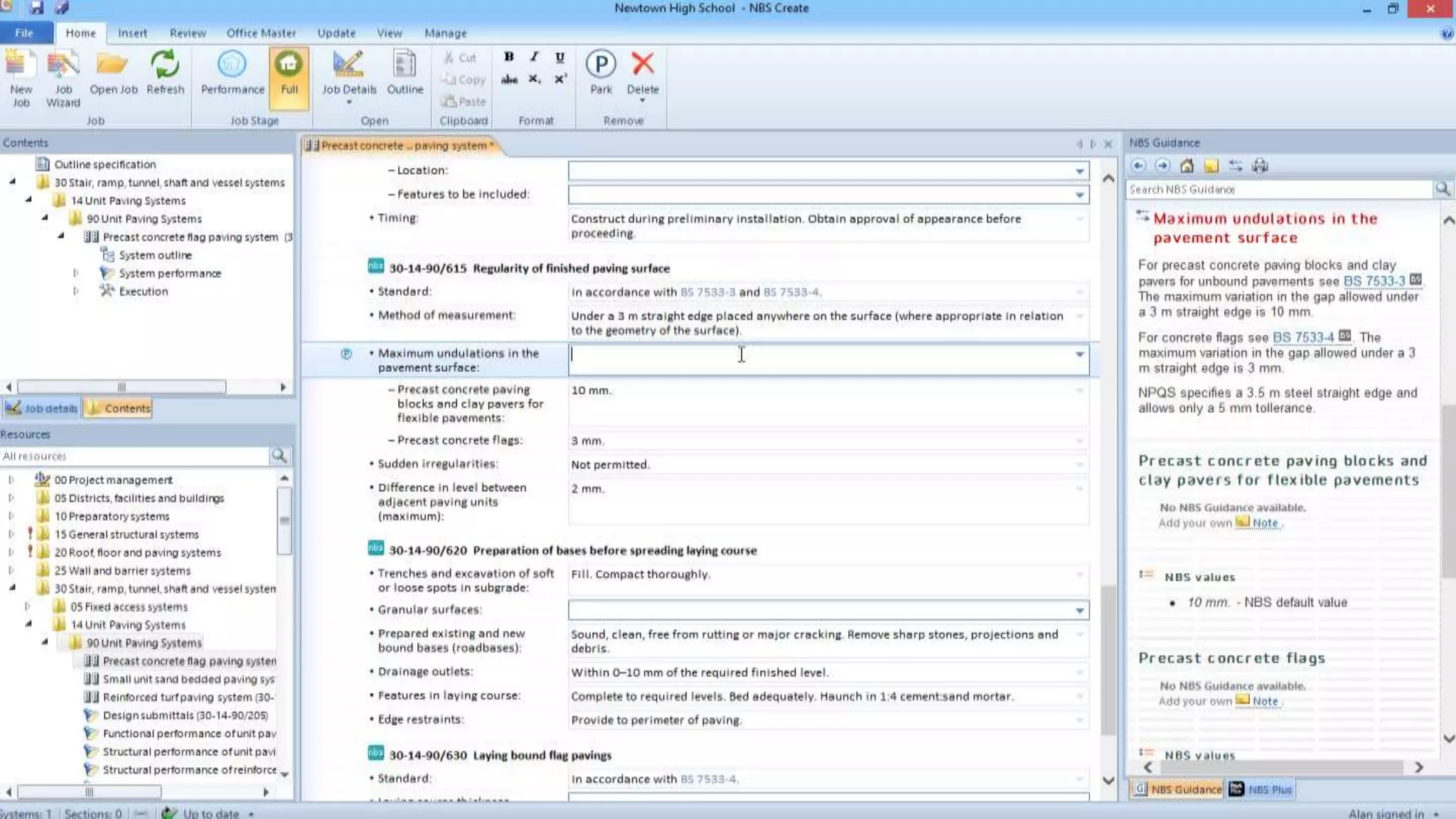
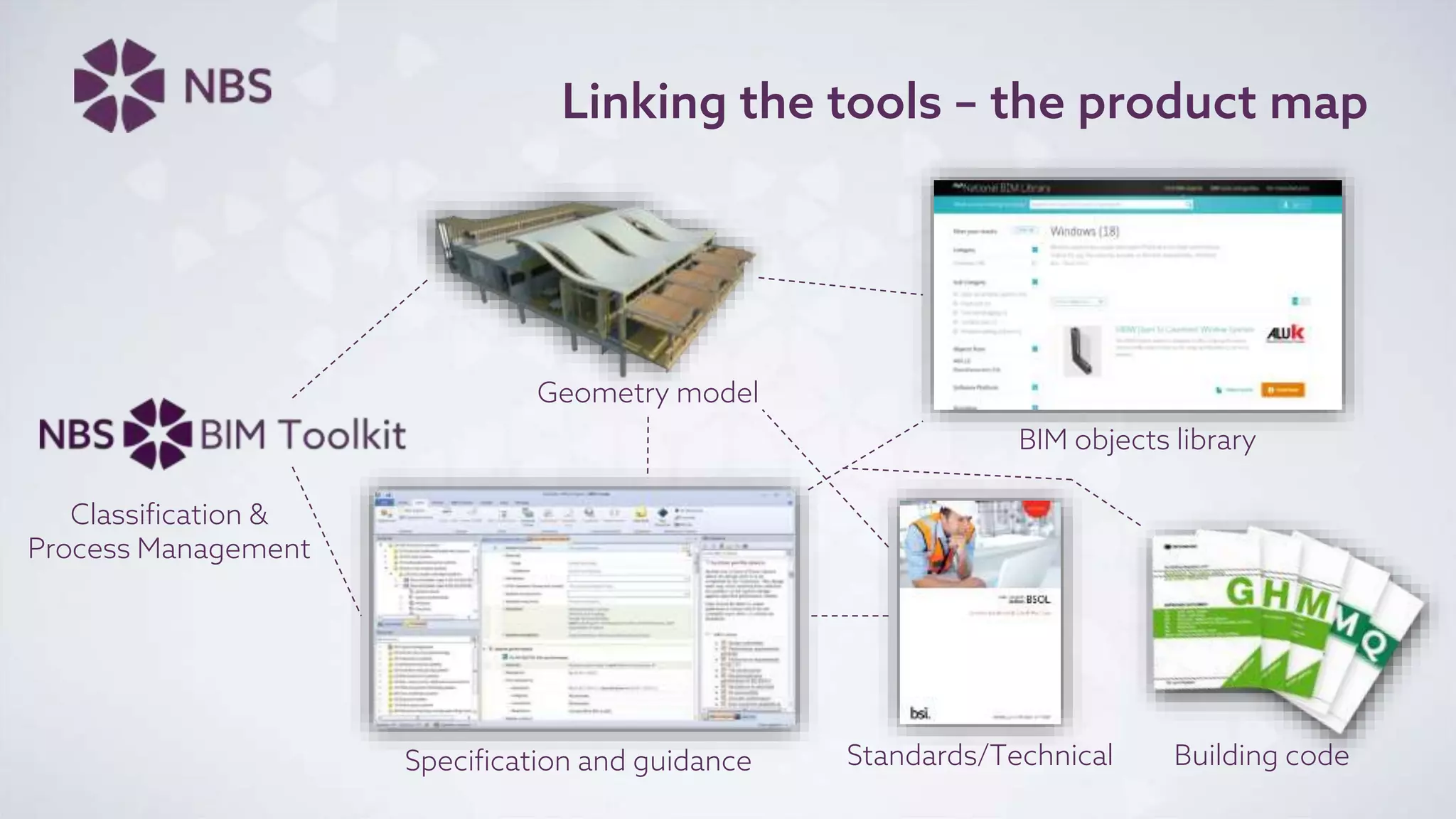
The document discusses Building Information Modeling (BIM) and its impact on the construction industry, emphasizing the importance of collaboration among designers and constructors to unlock efficiencies. It outlines the UK government's BIM strategy, including objectives for cost reduction, emissions reduction, and faster project delivery by 2025. Additionally, it highlights international standards and mandates for BIM adoption to improve construction practices globally.