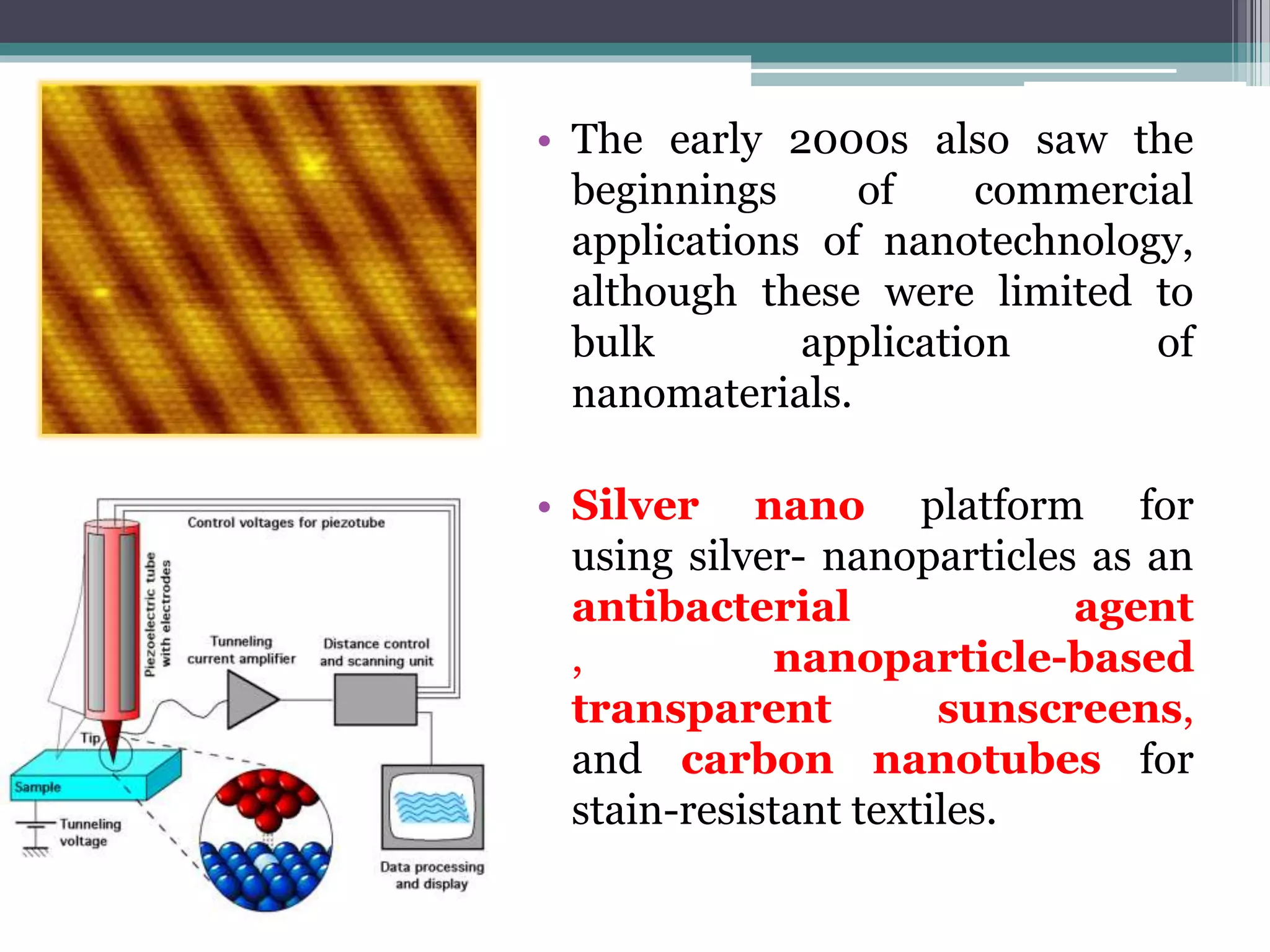
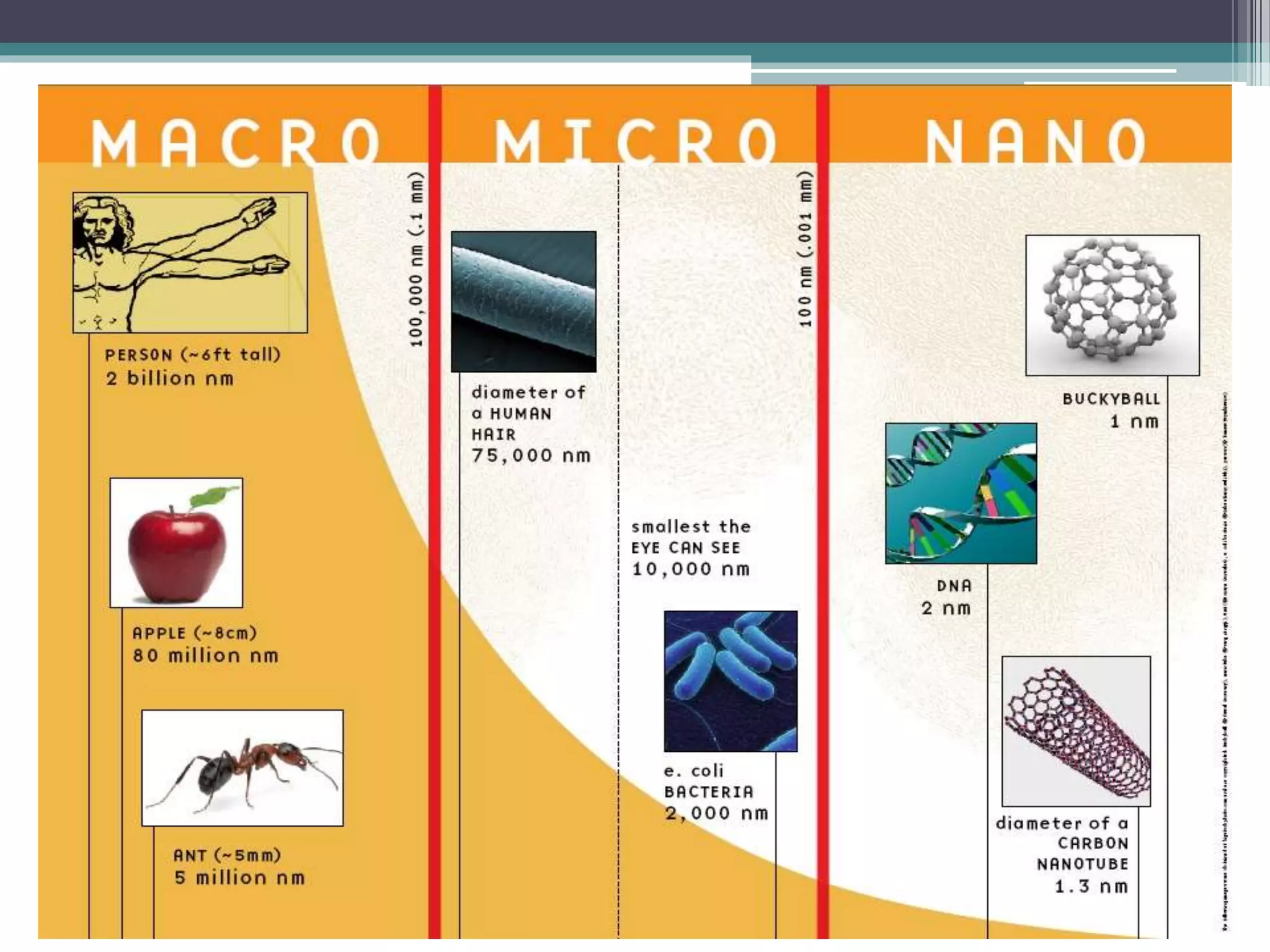
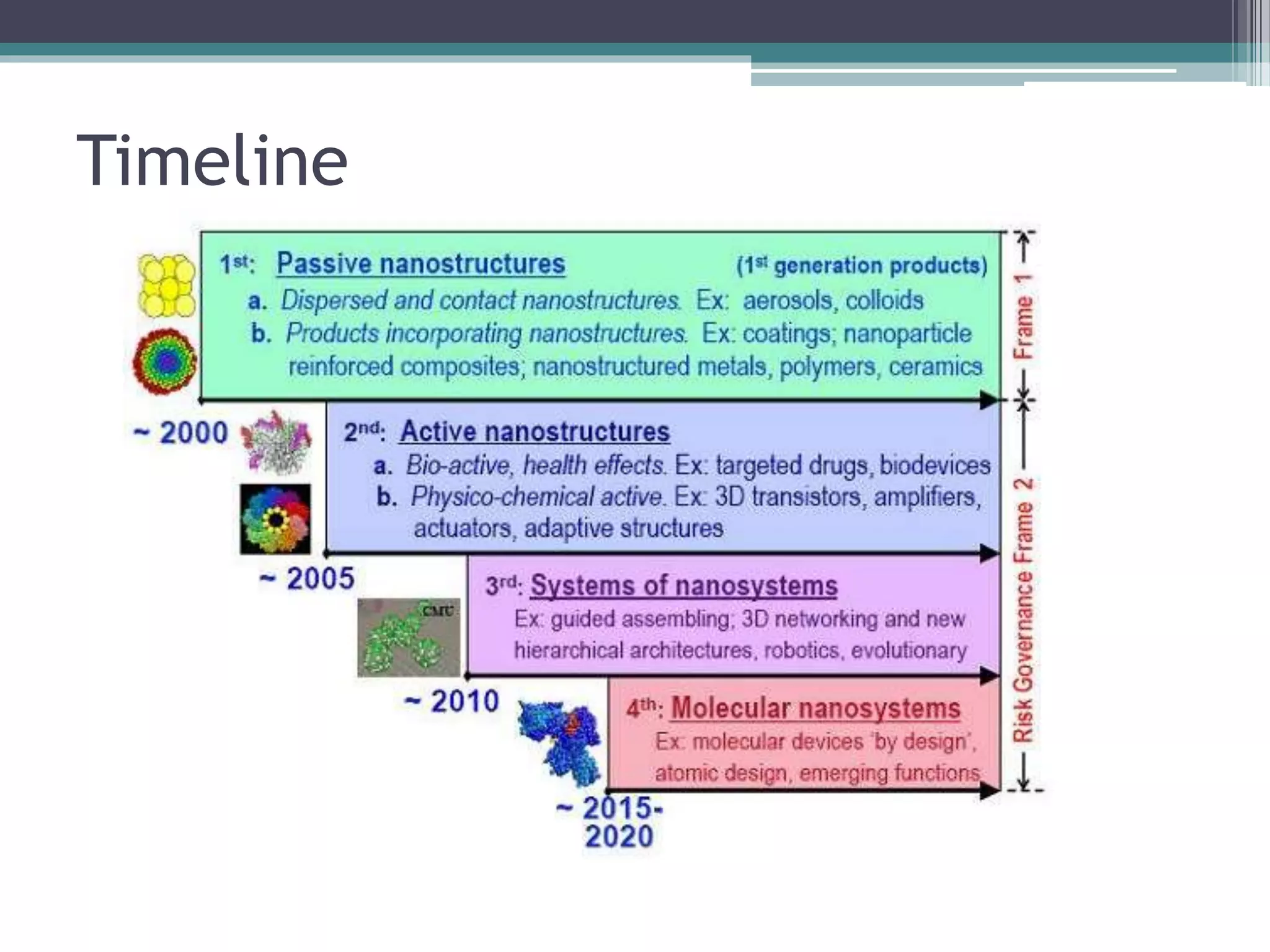
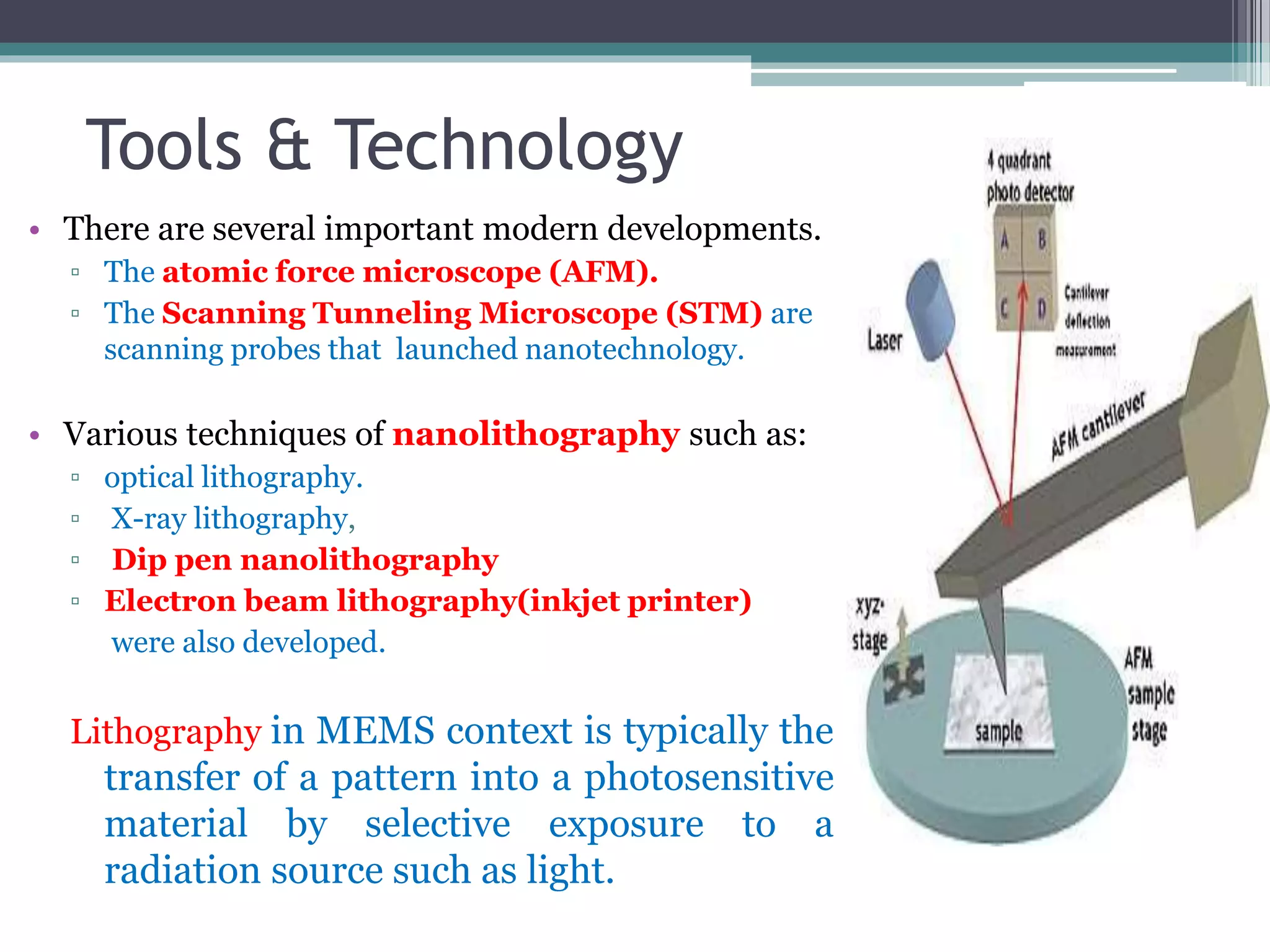
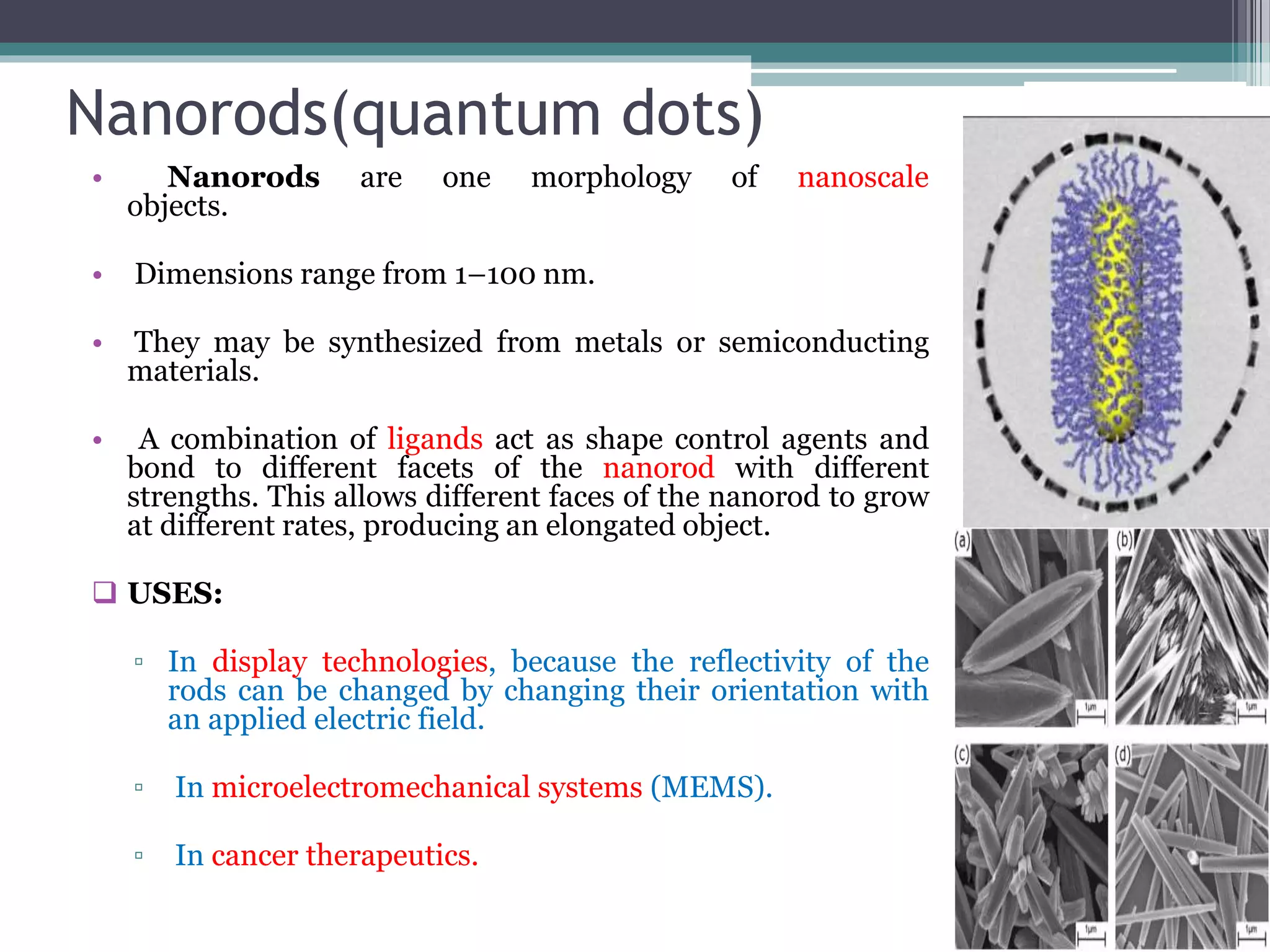
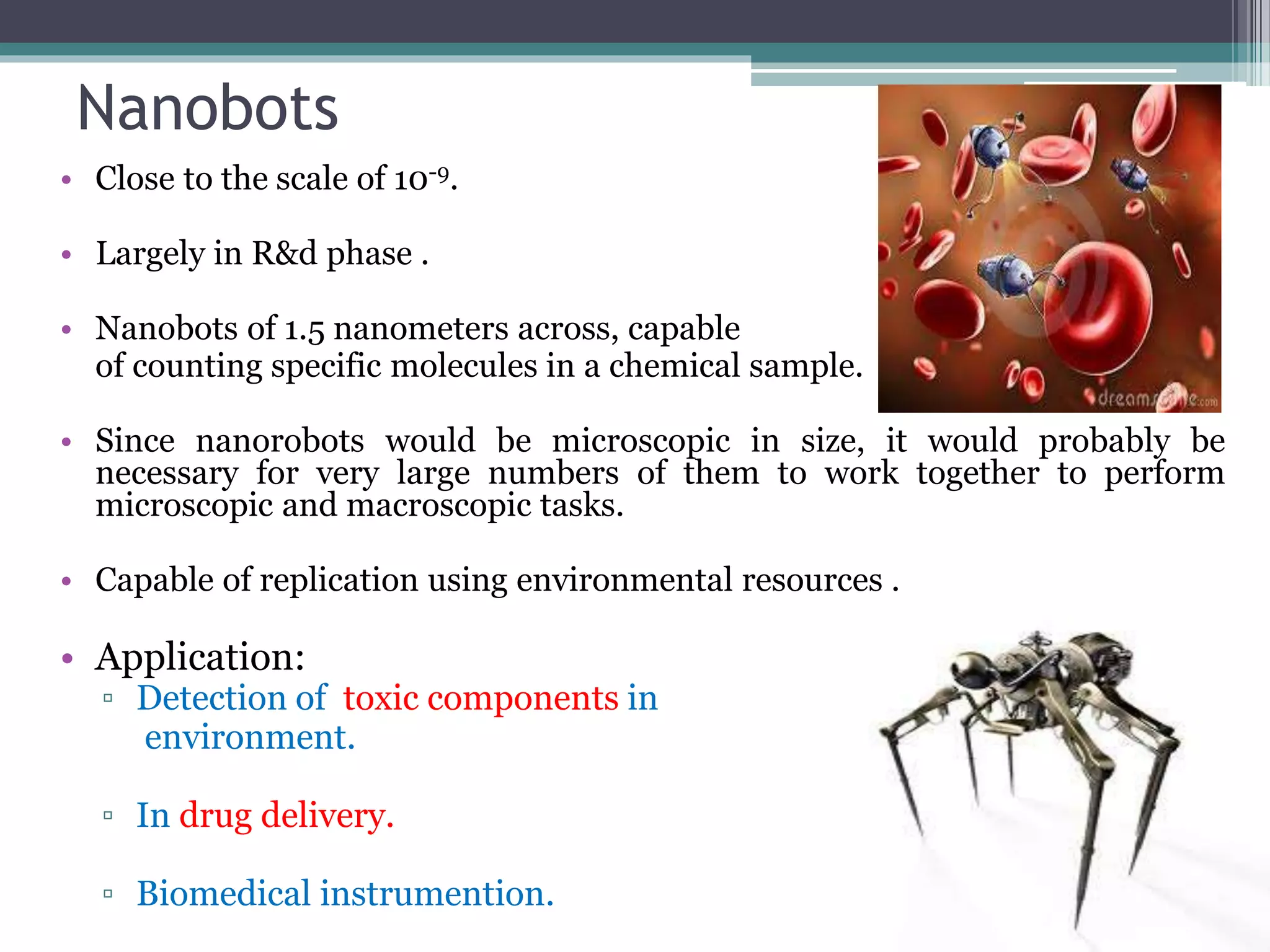
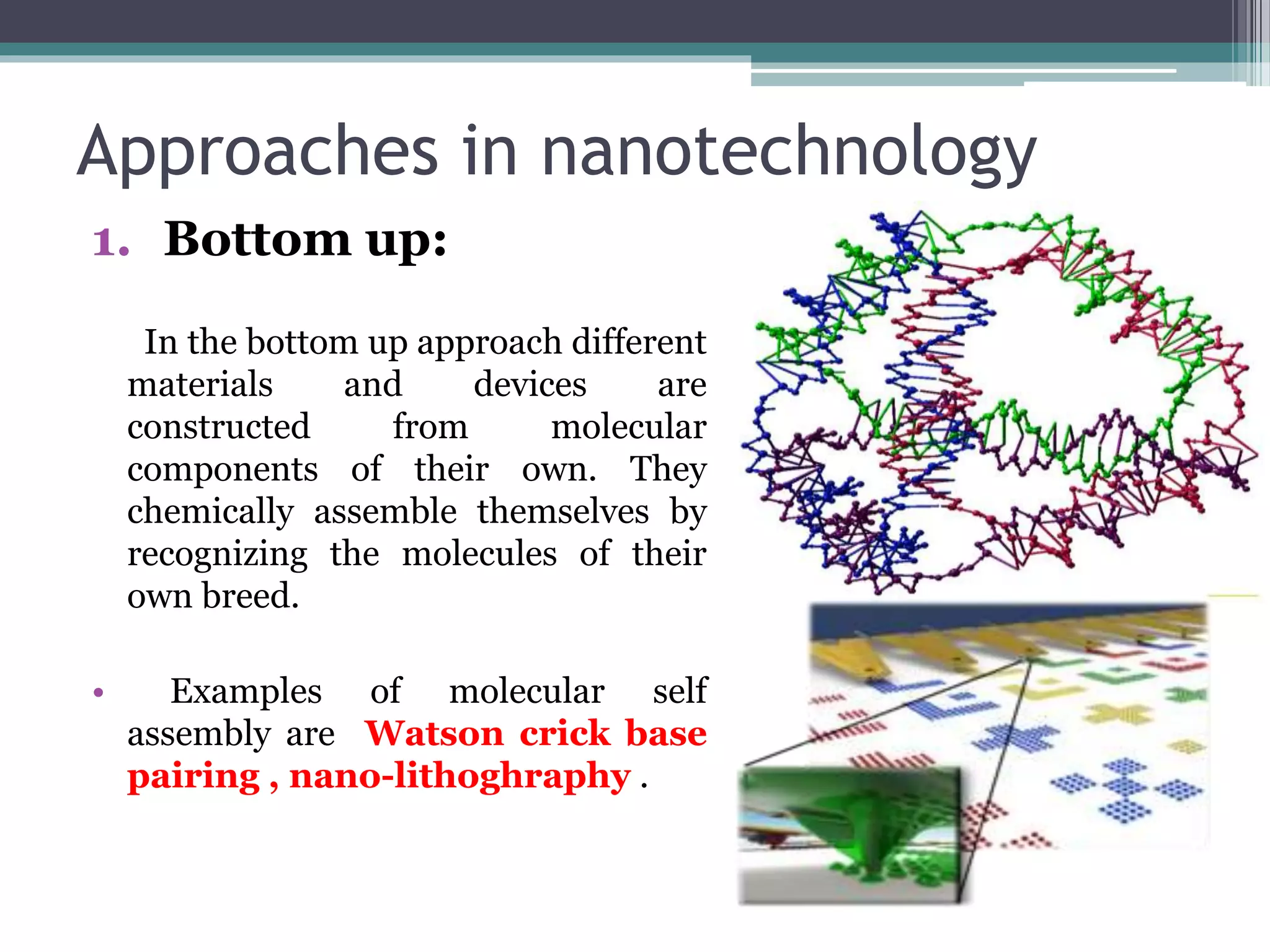
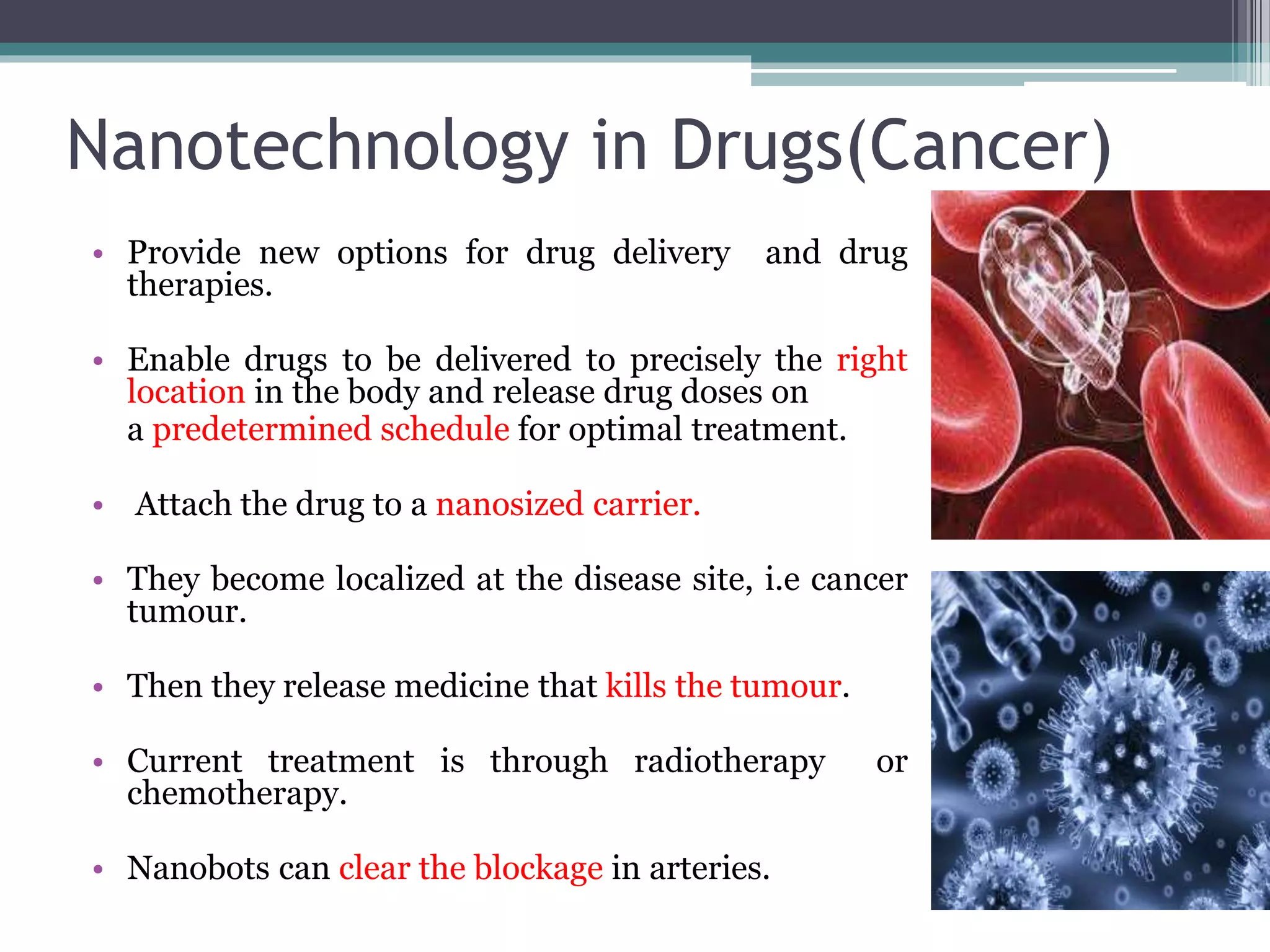
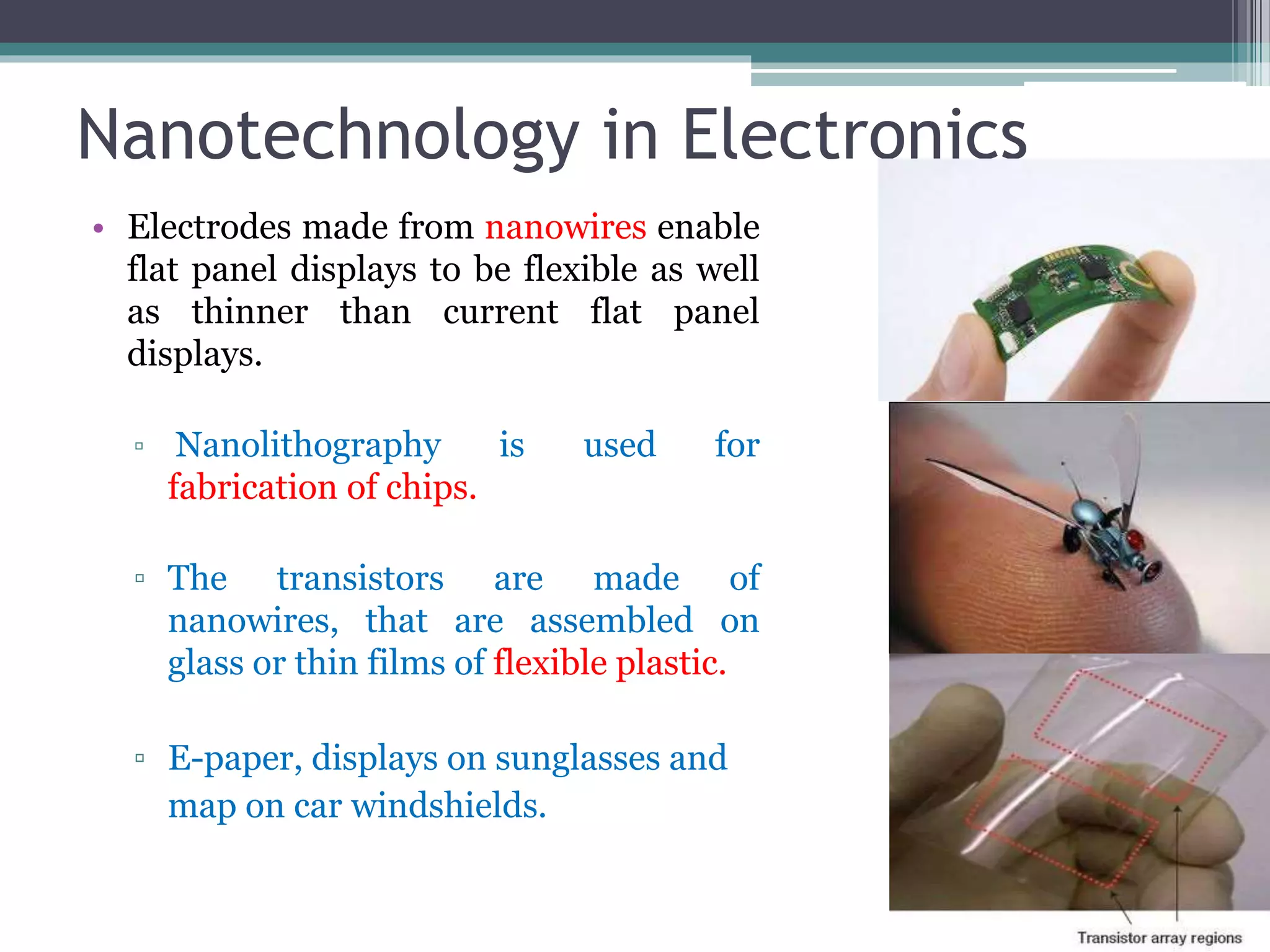
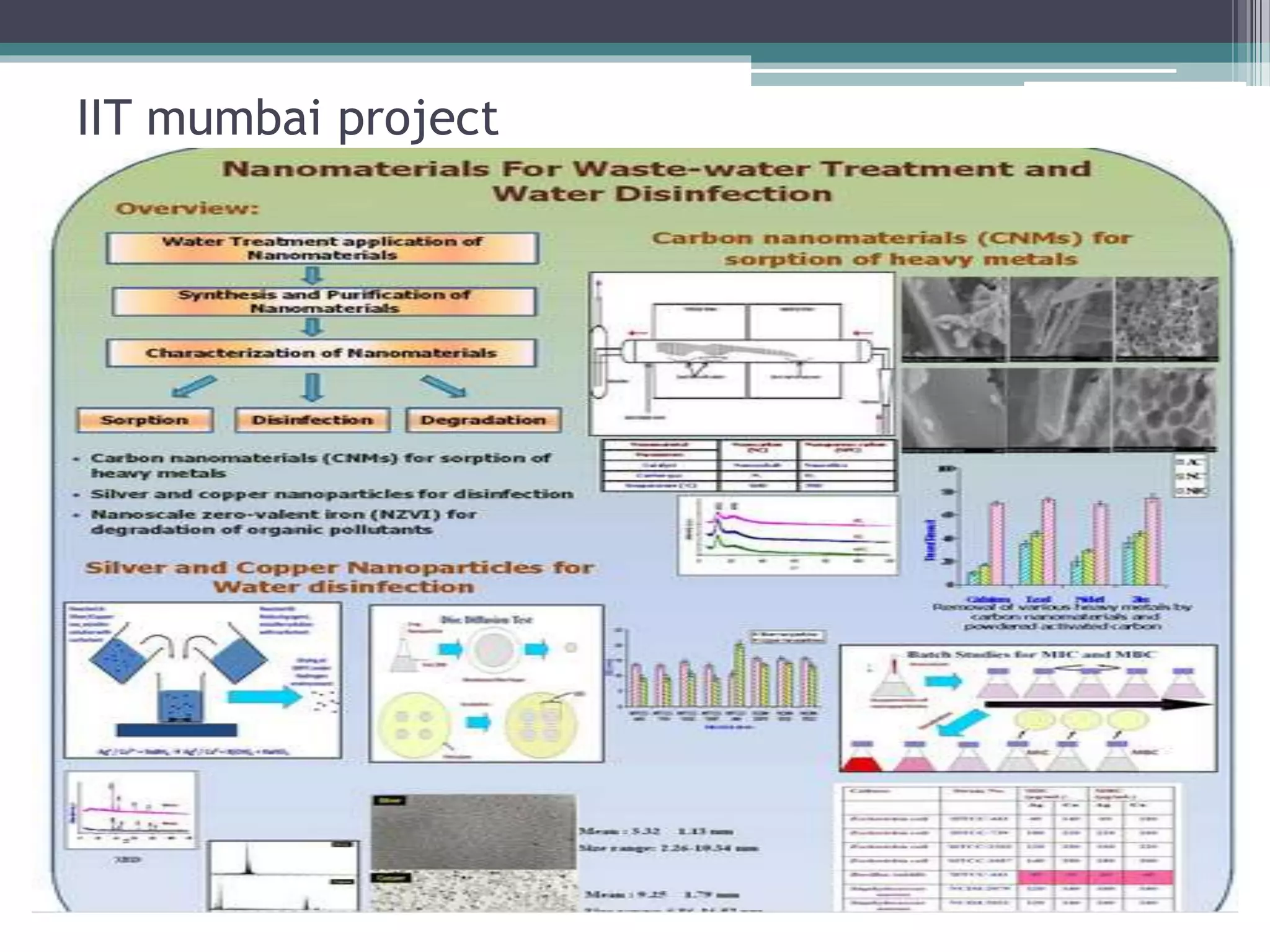
This document provides an overview of nanotechnology, including definitions, history, tools and techniques, materials used, and applications. Nanotechnology involves manipulating matter at the atomic scale (1-100 nanometers). Key developments include the scanning tunneling microscope in 1981 and carbon nanotubes. Tools like atomic force microscopes and lithography are used. Approaches include top-down (larger to smaller) and bottom-up (molecular self-assembly). Applications include drugs, fabrics, electronics, and computers. The future may bring nanorobots and programmable materials. Risks include health effects of nanoparticles.