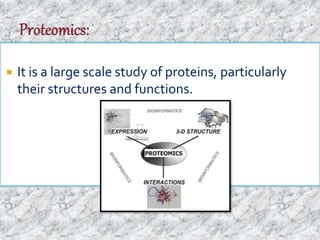
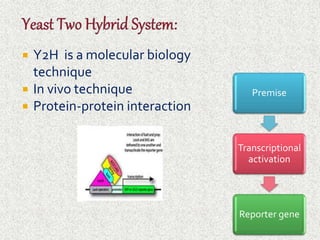
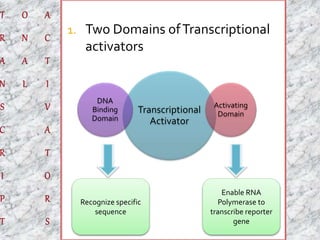
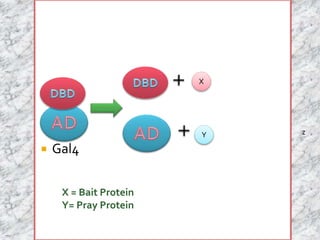
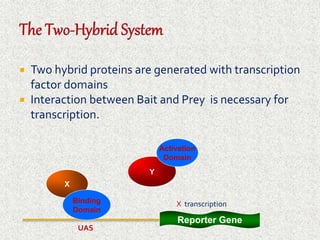
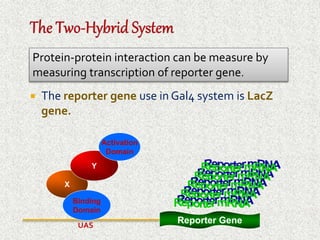
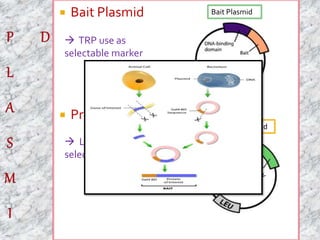
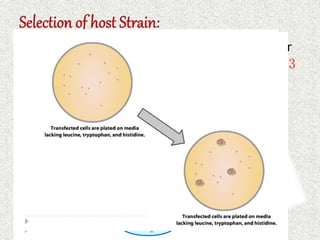
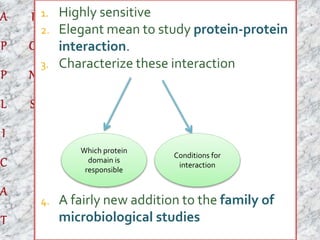
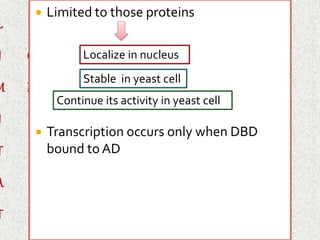
The document discusses the yeast two-hybrid system, which is a technique used to detect protein-protein interactions in vivo. It involves fusing a bait protein to a DNA-binding domain and a prey protein to an activating domain; if the bait and prey proteins interact, they bring the domains together and activate transcription of a reporter gene. This allows researchers to efficiently study protein interactions, characterize the domains involved, and identify conditions required for interaction. However, the yeast two-hybrid system is limited to proteins that can localize and function properly in the yeast cell.