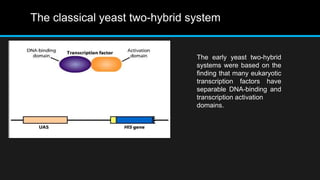
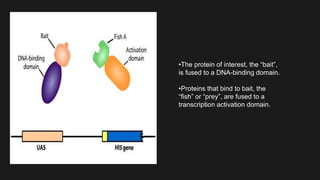
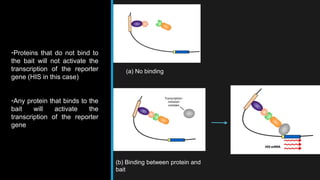
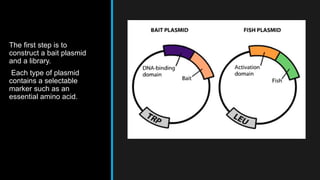
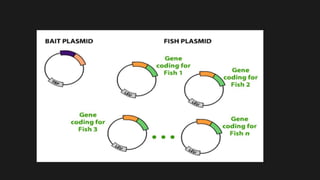
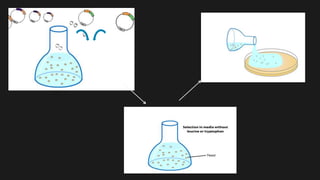
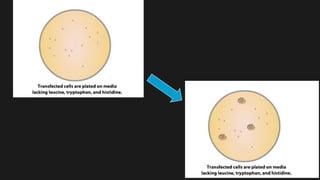
The yeast two-hybrid system allows researchers to study protein-protein interactions (PPIs) in vivo. It involves fusing a "bait" protein to a DNA-binding domain and fusing potential binding partners ("prey") to an activation domain. If the bait and prey interact, transcription of a reporter gene is activated, revealing the interaction. This system is useful because it can identify novel PPIs and protein networks in yeast, resembles higher eukaryotes more than bacteria, and requires only cDNA rather than purified proteins. However, false positives can occur if the bait induces transcription on its own.