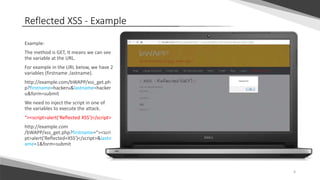
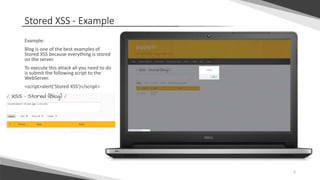
Cross-site scripting (XSS) vulnerabilities allow attackers to inject client-side scripts into web pages viewed by other users. There are three main types of XSS attacks: stored XSS, where malicious scripts are permanently stored on the target servers; reflected XSS, where scripts are reflected off the web server in response to user requests; and DOM-based XSS, where scripts are executed after a page loads due to unsafe JavaScript handling of untrusted data. To prevent XSS, output variables should be encoded using the htmlentities function to replace special characters that could be parsed as active content.