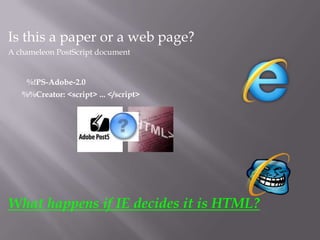
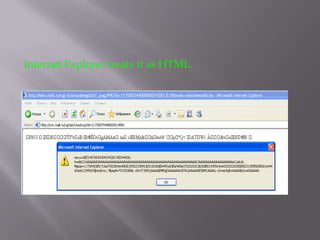
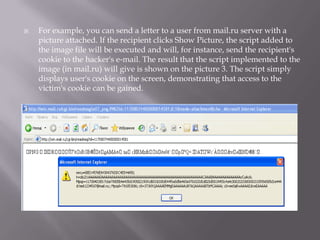
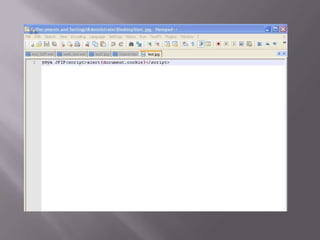
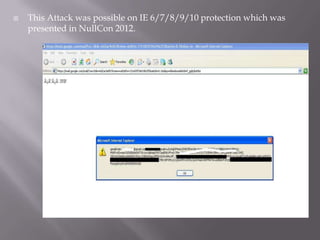
The document discusses content sniffing vulnerabilities in web browsers. It explains that browsers try to determine the true content type of a file, even if the server provides the wrong content type header. This allows an attacker to craft a file, like an image, that is also valid HTML containing JavaScript. When the browser content sniffs the file and treats it as HTML, the JavaScript will execute in the context of the vulnerable website. The document provides examples of how this can be used to steal cookies from users and perform cross-site scripting attacks. It recommends server and browser fixes like ensuring correct content type headers and adding headers to disable content sniffing.