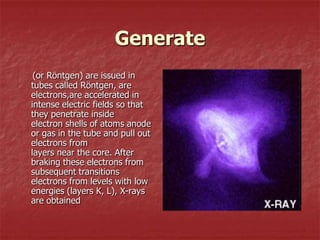
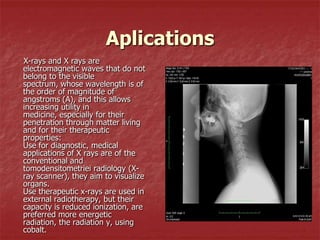
X-rays are electromagnetic waves with wavelengths comparable to the size of atoms that are generated when high-speed electrons collide with a metal target in an X-ray tube. X-rays can penetrate materials like human tissue and be detected using devices like gas detectors, proportional counters, and photodetectors. Digital detectors used in medical imaging can detect X-rays and create images of internal structures. X-rays have various medical applications including diagnostic radiography, fluoroscopy, and radiation therapy due to their ability to pass through matter and ionize materials.