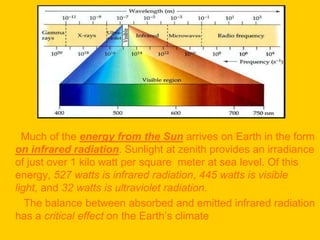
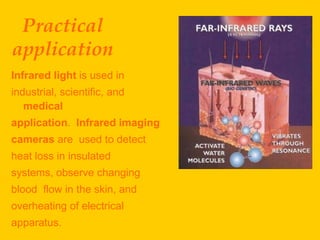
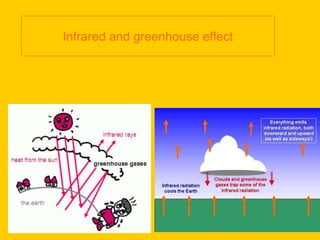
Infrared radiation was discovered in the early 19th century by William Herschel. Infrared radiation is an electromagnetic radiation with a wavelength longer than visible light. Infrared radiation includes most of the thermal radiation emitted by objects near room temperature through molecular rotational and vibrational movements. Infrared light is used in various applications like infrared cameras to detect heat loss, observe blood flow, and detect overheating equipment. It also allows astronomy observations of objects obscured by interstellar dust. Night vision devices using infrared illumination allow observation without detection. The Earth absorbs visible and invisible radiation from the sun and re-emits much of the energy as infrared radiation, which is absorbed by greenhouse gases in the atmosphere and re-radiated to warm