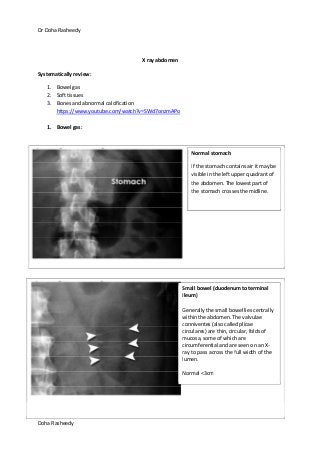
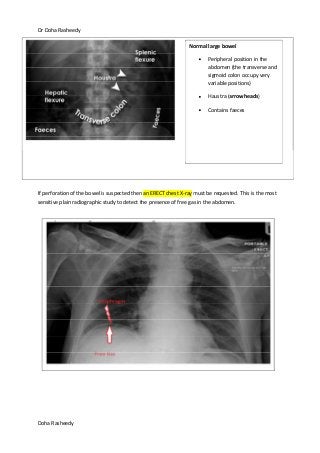
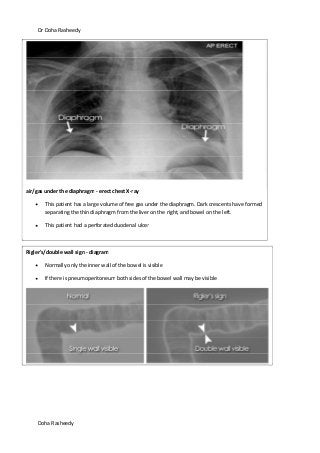
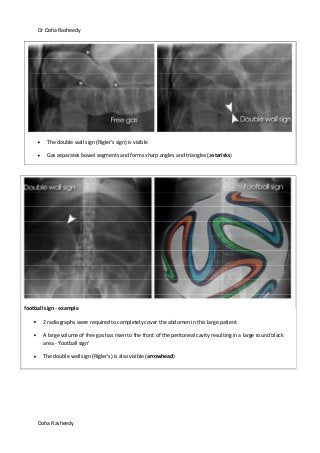
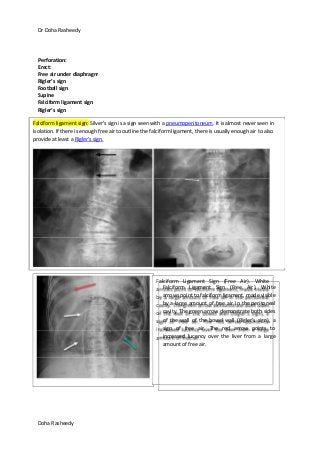
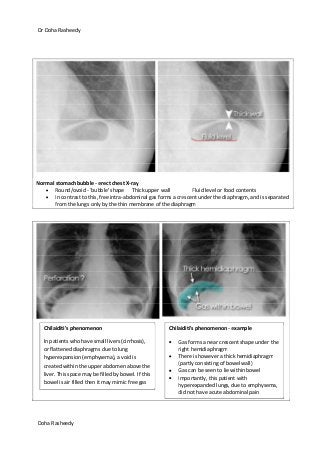
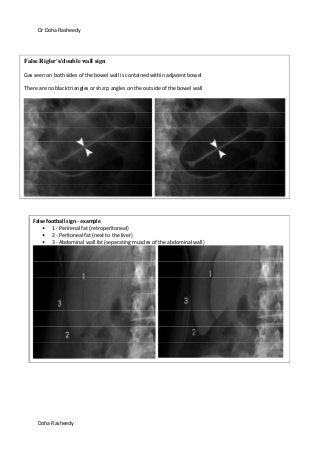
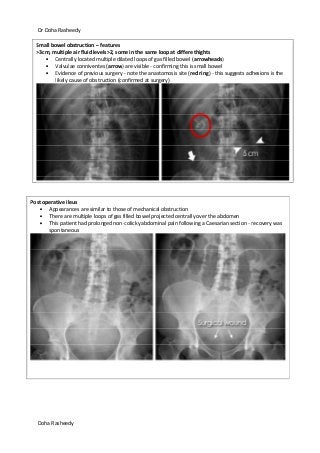
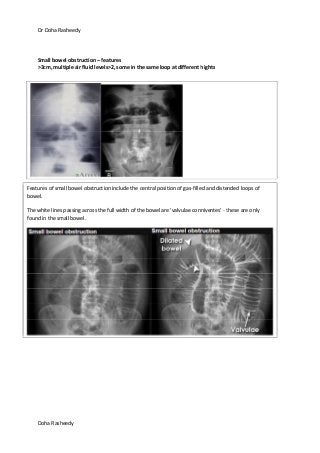
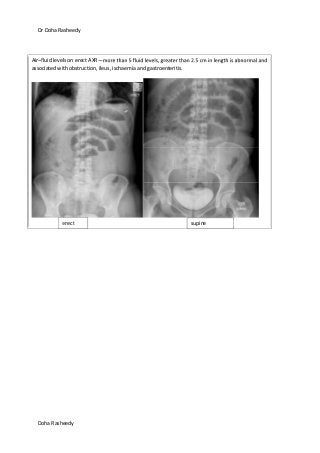
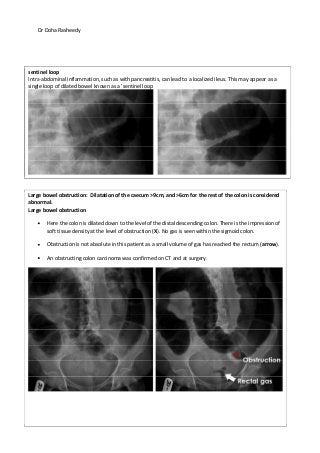
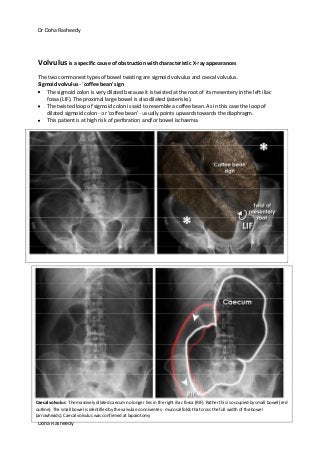
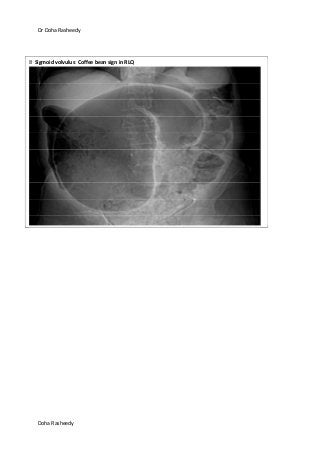
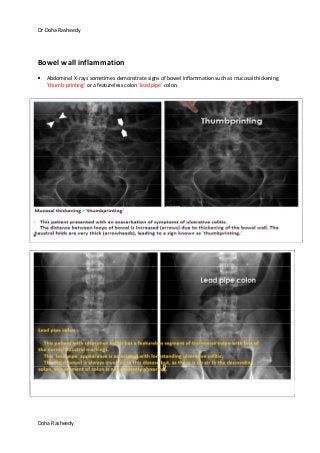
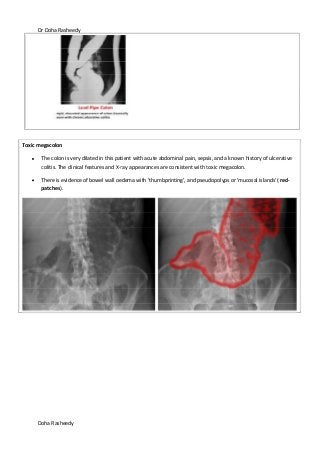
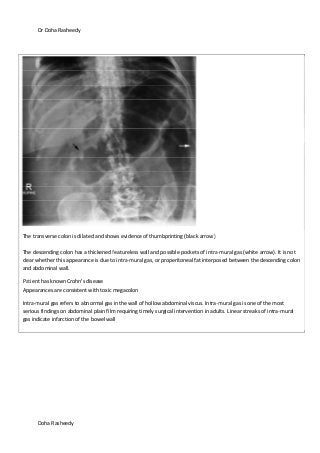
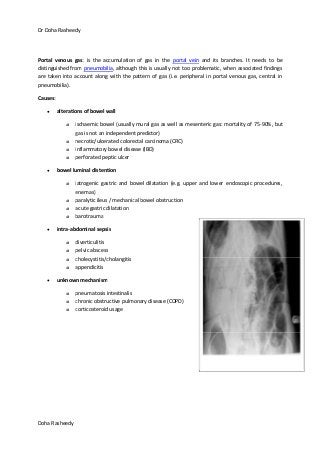
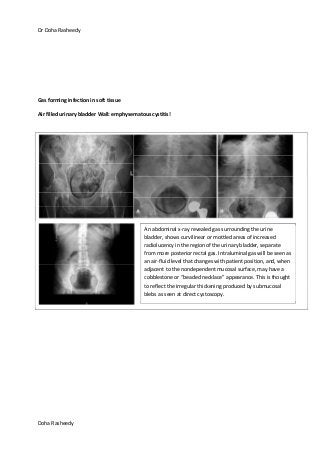
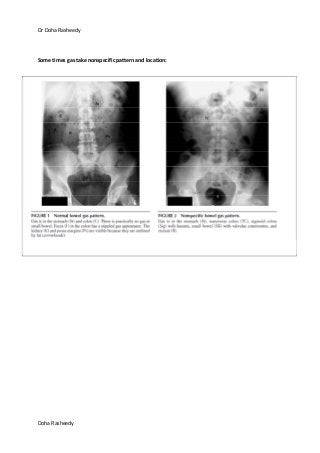
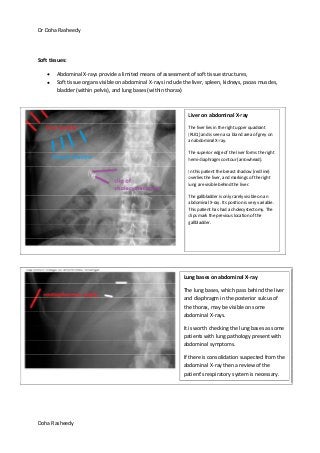
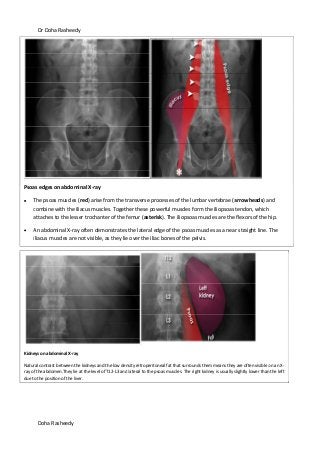
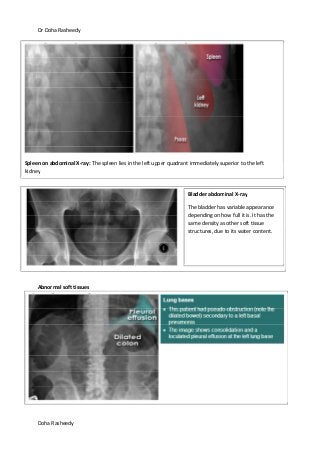
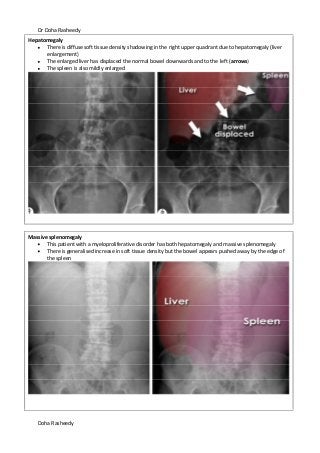
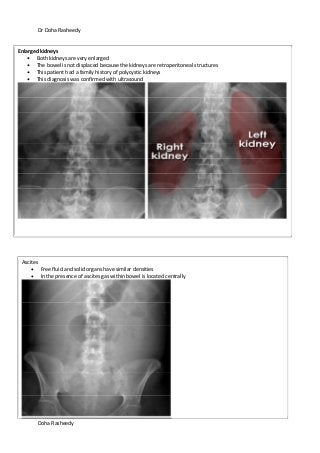
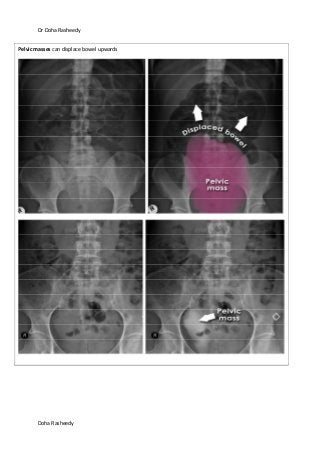
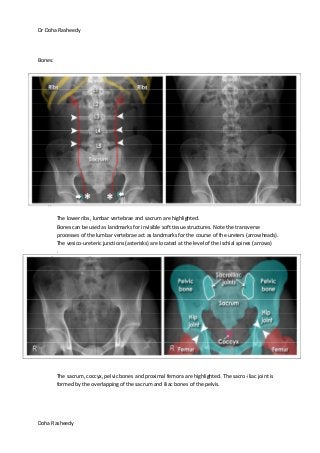
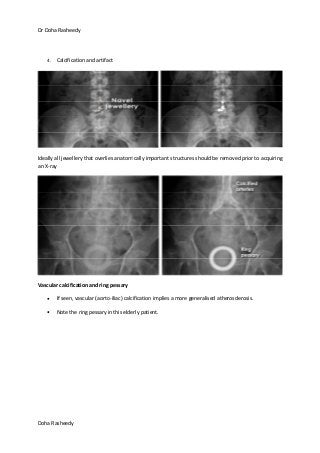
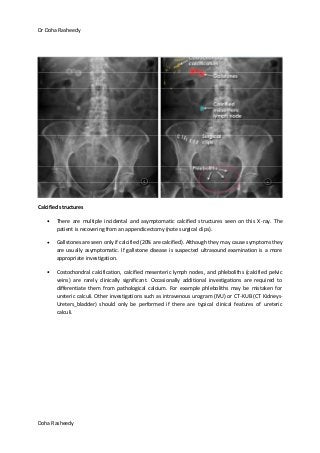
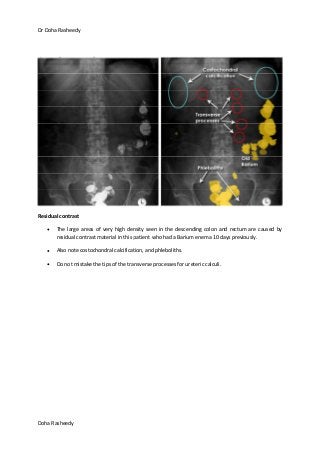
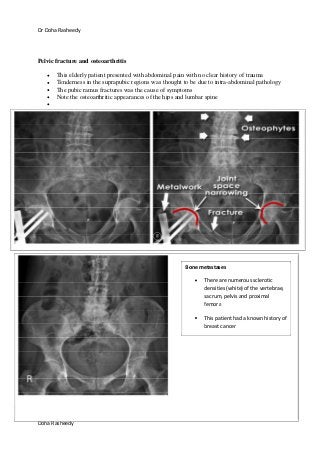
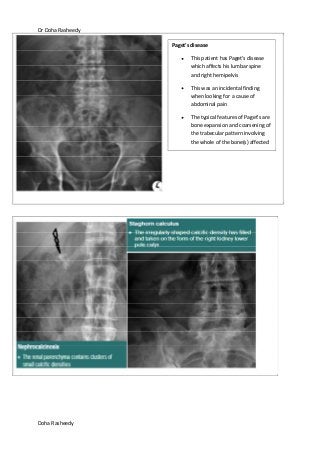
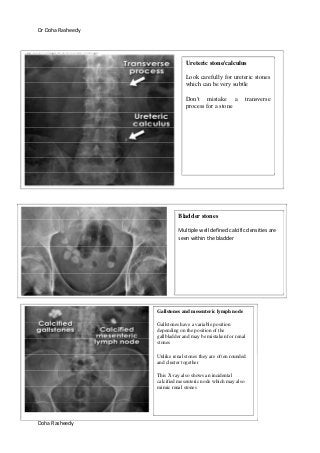
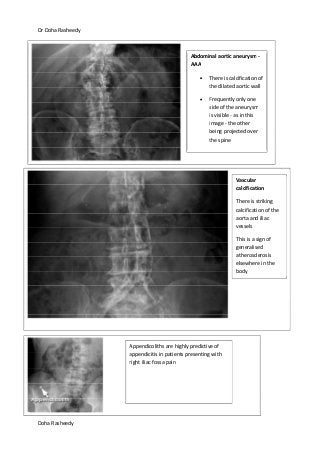
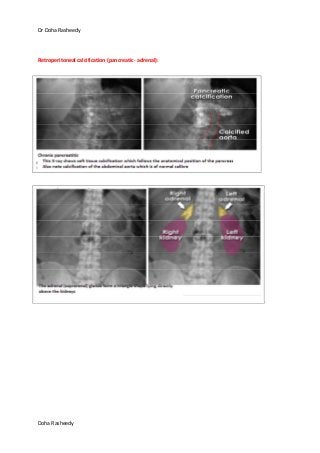
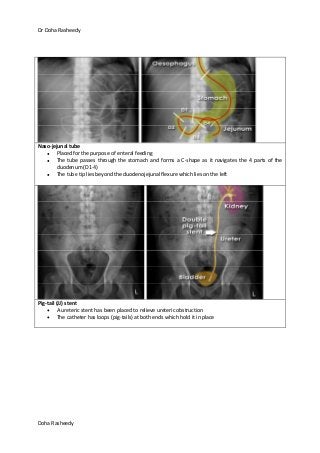
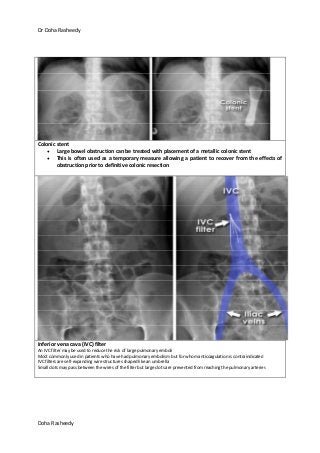
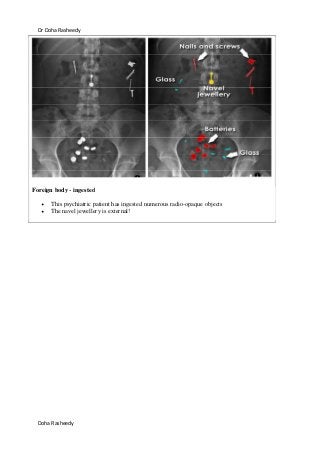
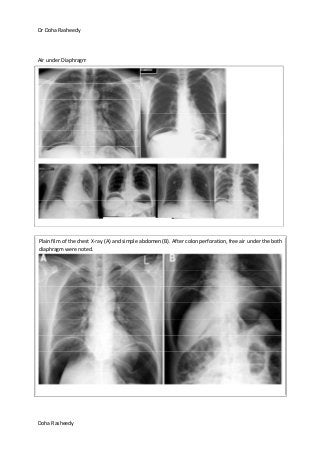
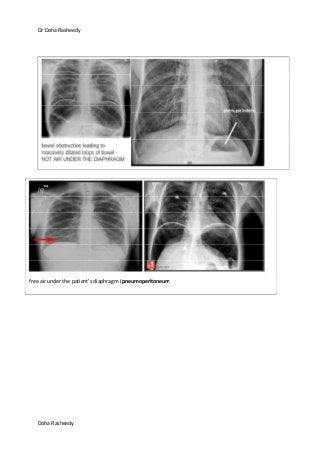
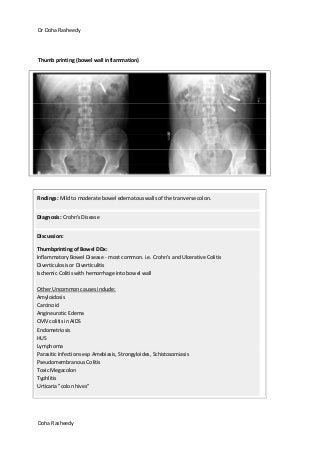
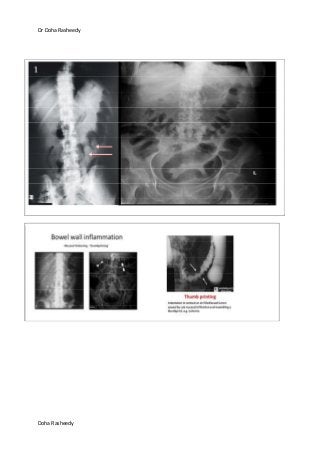
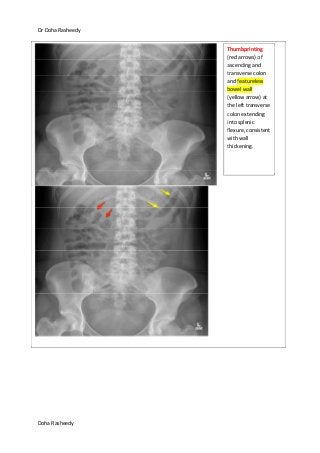
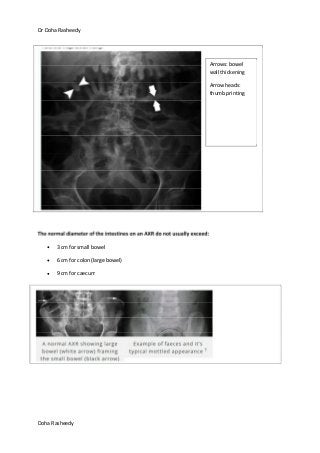
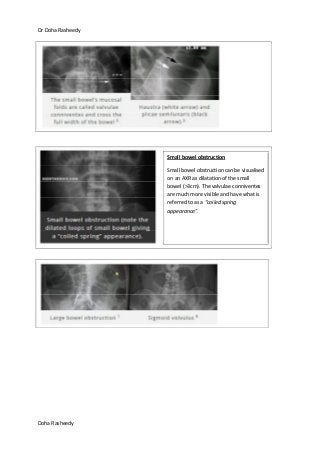
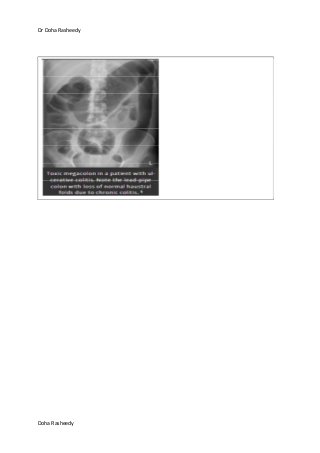
This document provides an overview of how to systematically review an x-ray of the abdomen. It discusses normal bowel gas patterns and positions. It then describes signs of perforation including free air under the diaphragm, the Rigler's sign, and football sign. Other topics covered include small bowel obstruction features, large bowel obstruction including volvulus, toxic megacolon, and other sources of aberrant air such as pneumobilia. Images are included illustrating many of these findings.