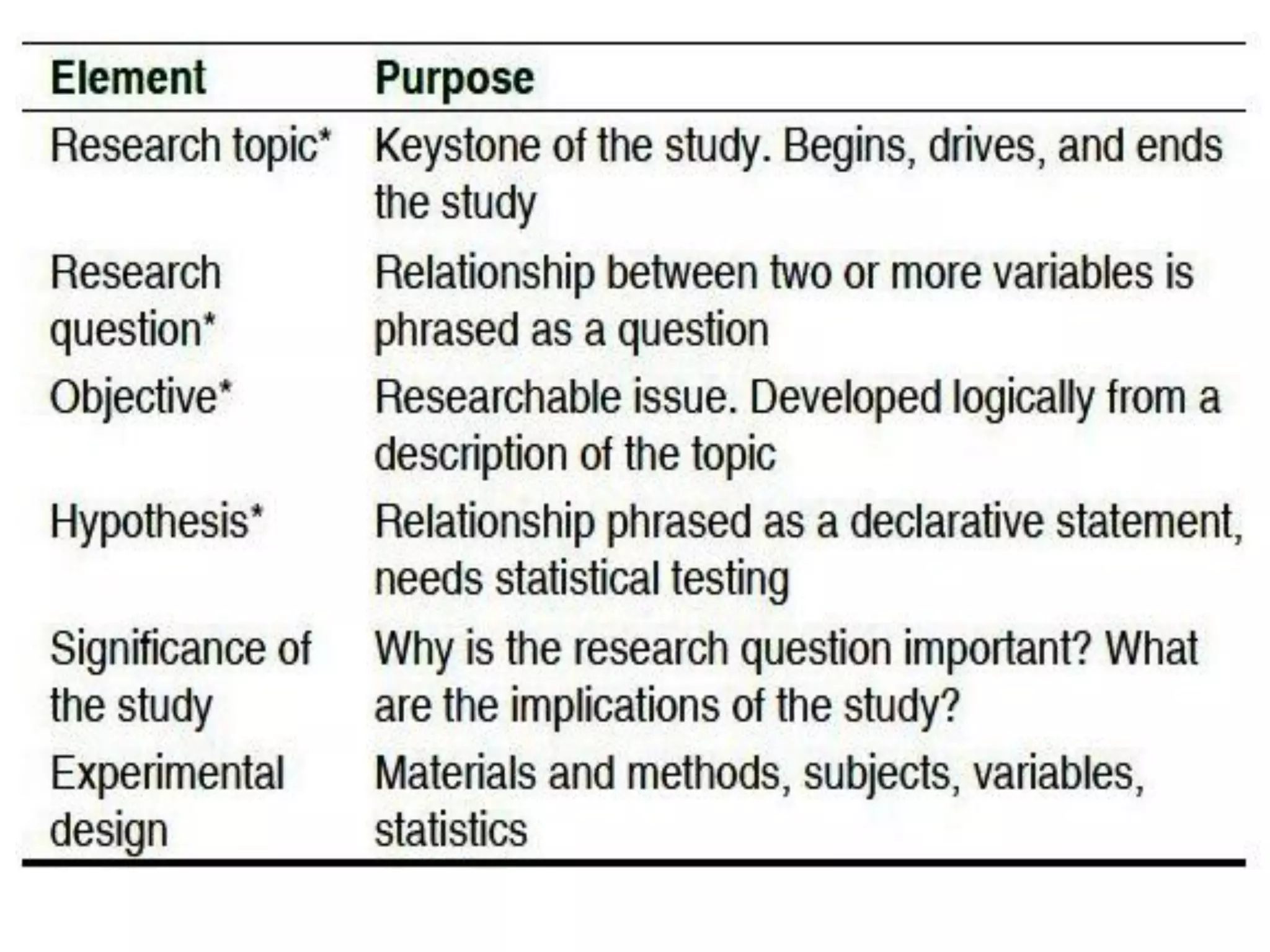
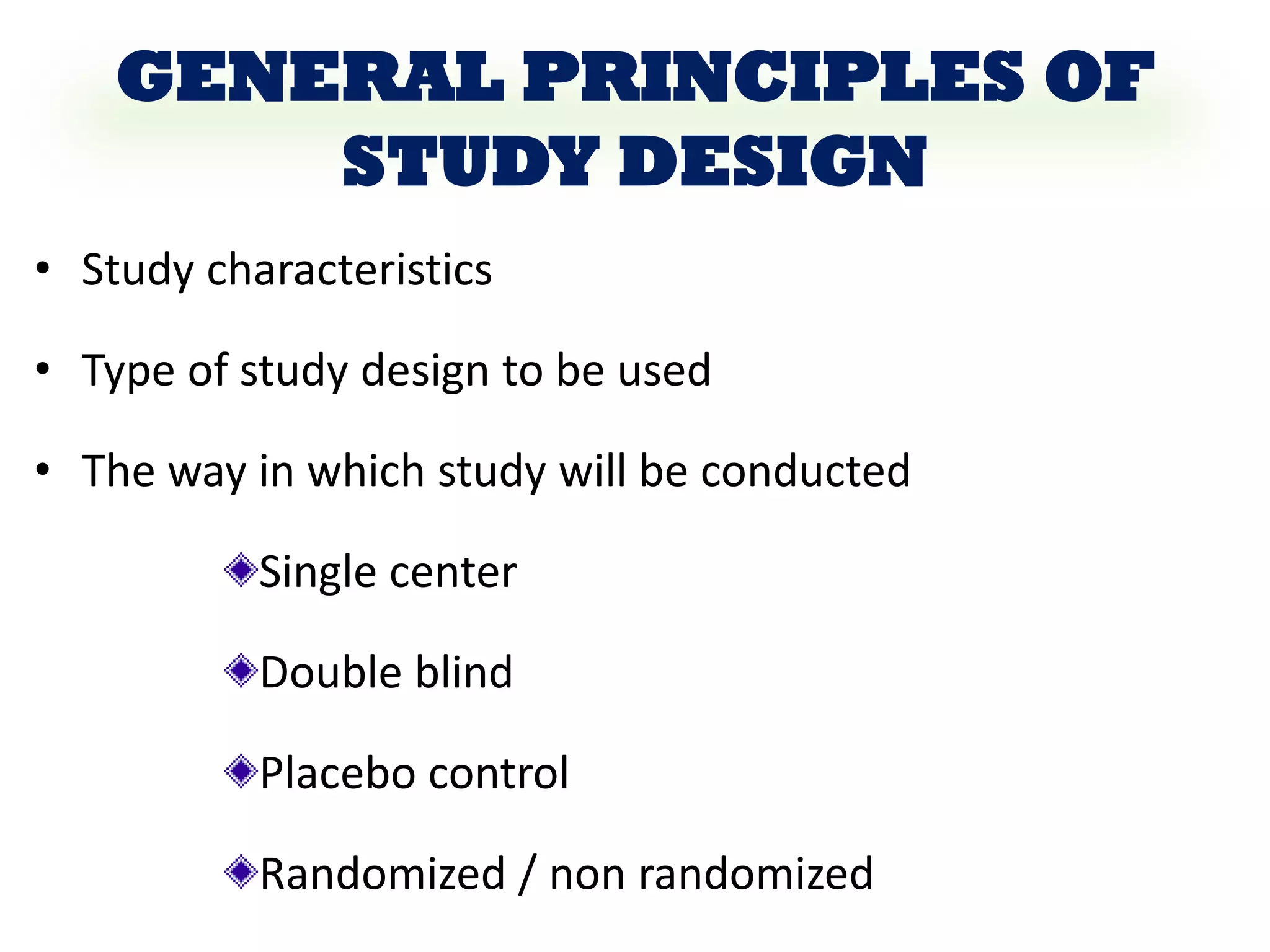
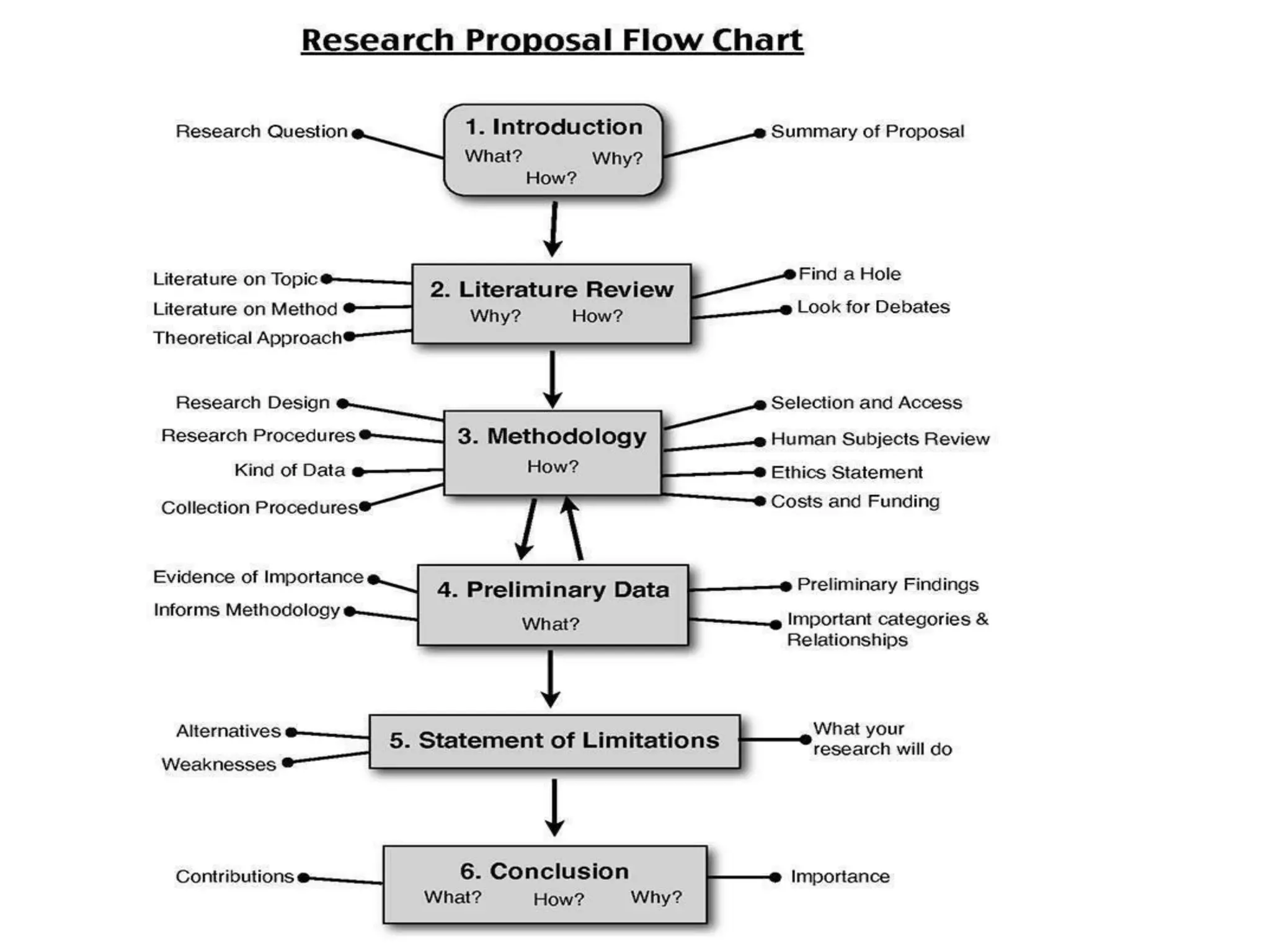
The document outlines the key components of writing a research protocol, including defining research, the purpose of a protocol, and the typical parts of a protocol. It discusses that a protocol should clarify the research question, compile existing knowledge, form a hypothesis and objectives. The typical parts are an introduction with the problem and background, methodology covering the research design and data collection/analysis, and ethical considerations. It provides guidance on writing each section, such as making the introduction concise and specific, clearly linking objectives to the research problem, and describing the study design and statistical analysis plan in the methodology.