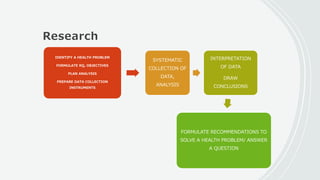
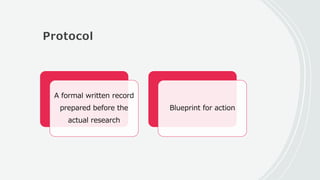
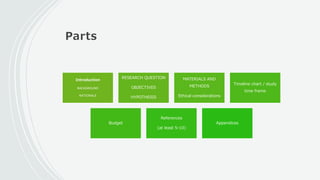
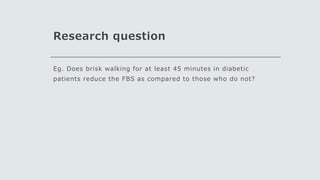
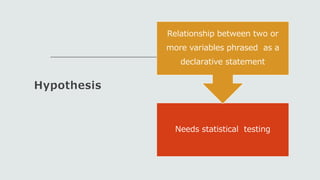
This document outlines the key components of a research protocol, including identifying a health problem, formulating research questions and objectives, planning data collection and analysis, and drawing conclusions. It discusses that a research protocol provides a formal written plan and blueprint for conducting research. The major sections covered are introduction, research question/hypothesis, objectives, review of literature, materials and methods, sample size calculation, data collection plan, data analysis plan, implementation plan, ethical considerations, timeline, and references. The goal of a protocol is to clarify the research question and design a scientifically sound methodology to properly address the question.