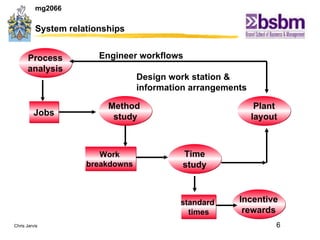
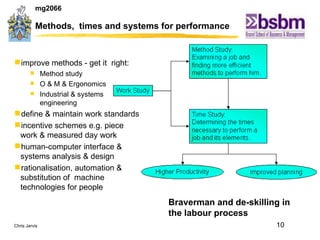
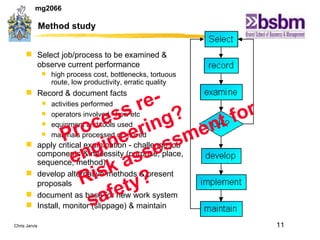
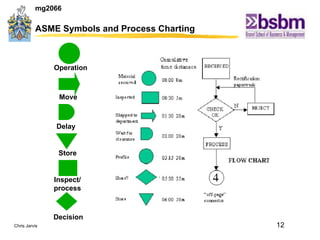
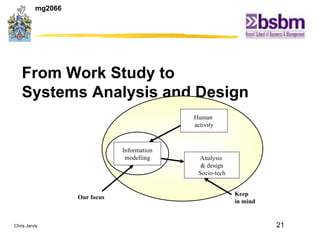
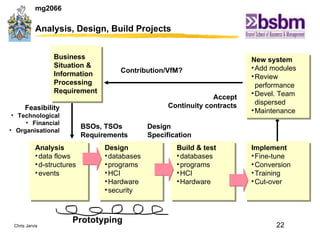
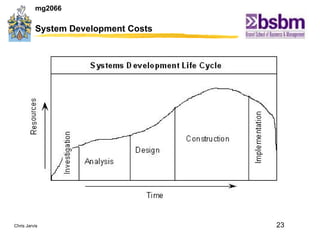
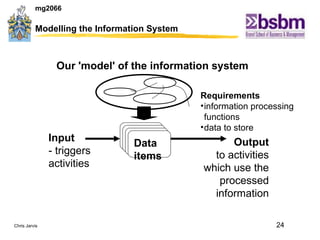
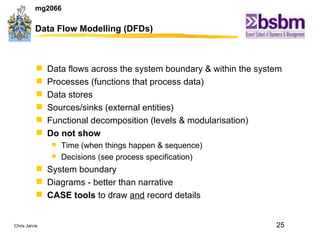
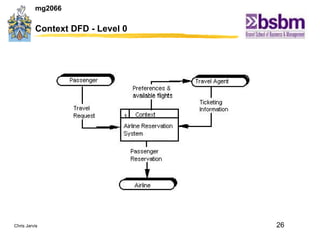
The document discusses various techniques for improving work efficiency, processes, and productivity, including method study, work measurement, ergonomics, and productivity analysis. It covers the history and basic concepts of work study, how to conduct method studies and time studies, and how to establish work standards and incentive plans. The document also examines how work study concepts apply to systems analysis, design of workstations, business process reengineering, and modeling information systems.