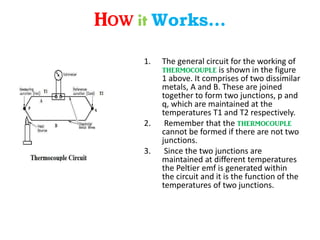
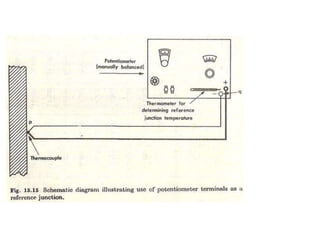
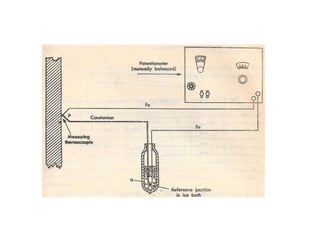
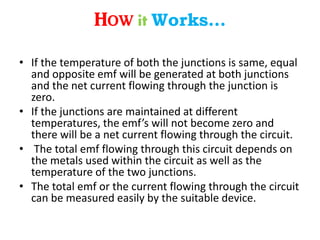
A thermocouple measures temperature by using the Seebeck effect produced between two different metals that are joined together at two points. One junction is placed at the body being measured (hot junction) while the other is placed at a reference body of known temperature (cold junction). This generates a voltage based on the temperature difference between the two junctions. The thermocouple works by using the Seebeck, Peltier, and Thomson effects - where a voltage is produced due to the temperature difference across the two junctions of dissimilar metals. The voltage produced can then be measured to determine the temperature of the hot junction relative to the cold junction.