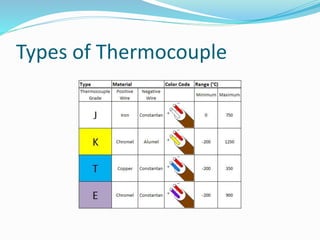
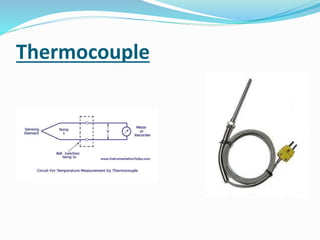
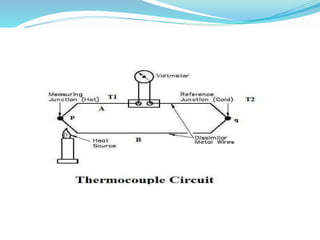
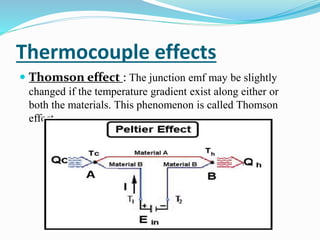
A thermocouple is an electrical device consisting of two dissimilar metals joined together that produces a voltage dependent on the temperature difference between the junctions. Thermocouples operate based on the Seebeck effect and Peltier effect to measure a wide range of temperatures from -270°C to 3000°C. They are commonly used to monitor temperatures in industrial processes like kilns but are less accurate than other sensors for measuring small temperature differences with high precision.