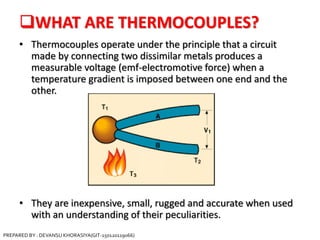
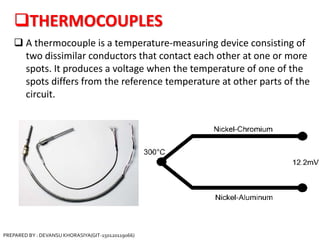
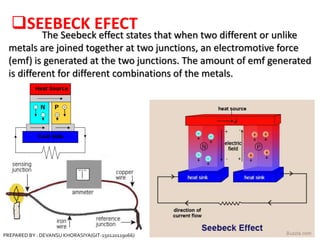
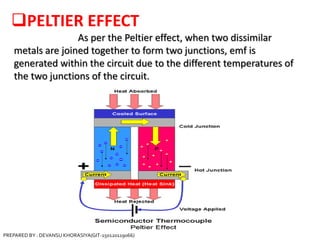
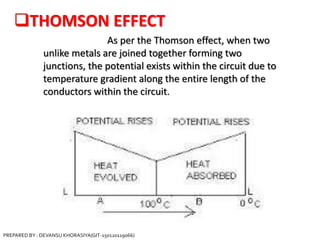
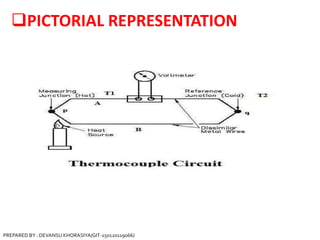
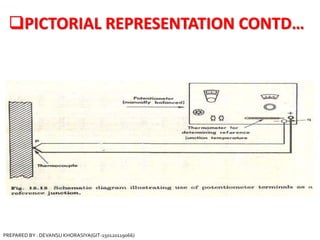
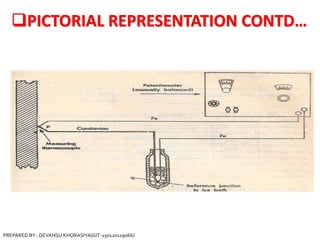
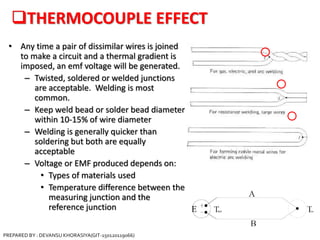
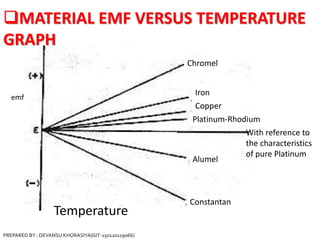
The document is a presentation on thermocouples, detailing their definition, operating principles, types, and applications. It explains how thermocouples measure temperature using two dissimilar metals, generating an electromotive force based on temperature differences. Key concepts discussed include the Seebeck, Peltier, and Thomson effects, along with various applications in industries such as steel manufacturing and gas safety.