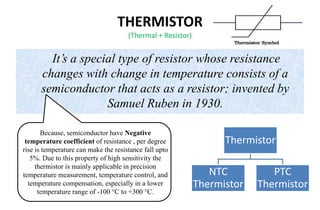
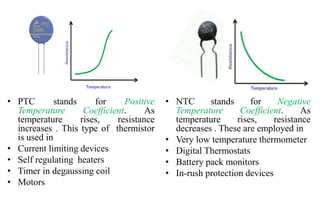
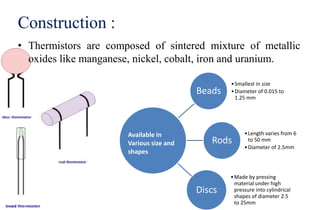
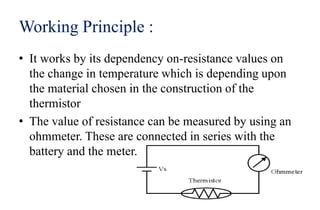
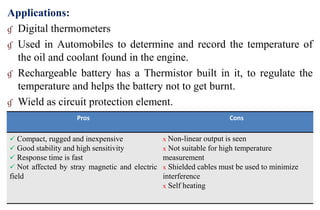
Thermistors are a type of resistor whose resistance changes significantly with temperature. They are made of semiconducting materials like metal oxides and their resistance decreases with rising temperature (NTC thermistors) or increases with rising temperature (PTC thermistors). NTC thermistors are used in applications like temperature sensors and overcurrent protection, while PTC thermistors are used in self-regulating heaters and current-limiting devices. Thermistors have a fast response time, are compact and inexpensive but have non-linear resistance-temperature characteristics and may self-heat.