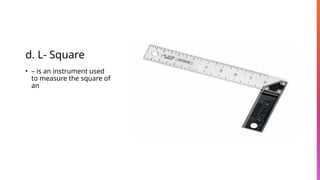
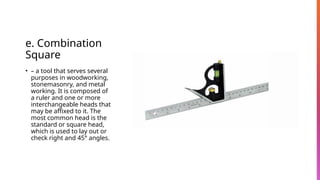
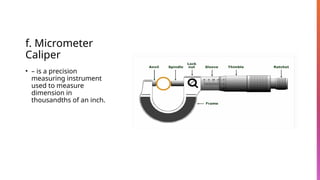
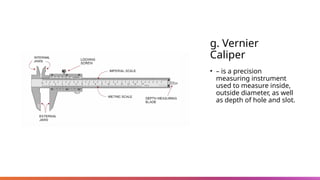
The document provides an overview of basic hand tools used in shielded metal arc welding, classified into categories such as measuring tools, cutting tools, driving tools, and more. Each category is described with examples, detailing their purposes and specific types, including push-pull rules, hacksaws, pliers, and multi-meters. The document emphasizes the importance of these tools for various welding and metalworking tasks.