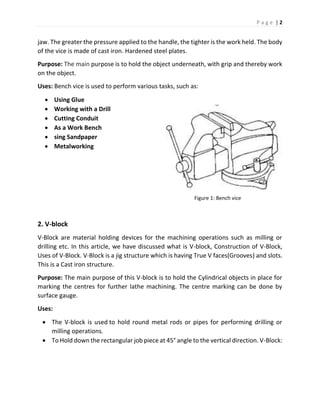
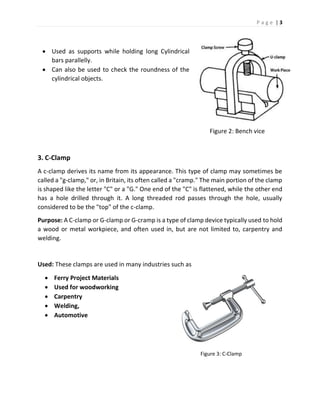
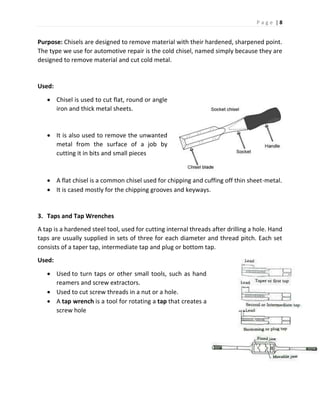
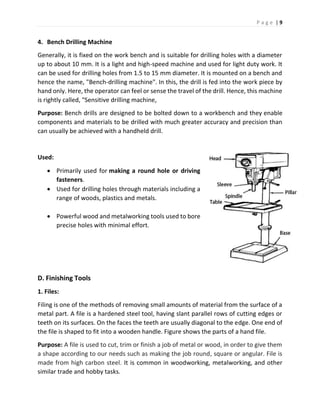
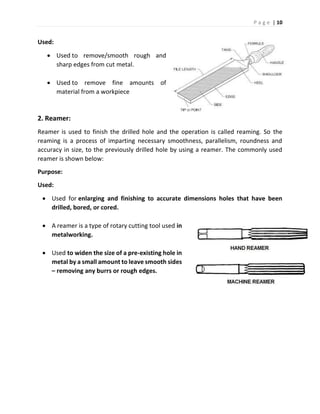
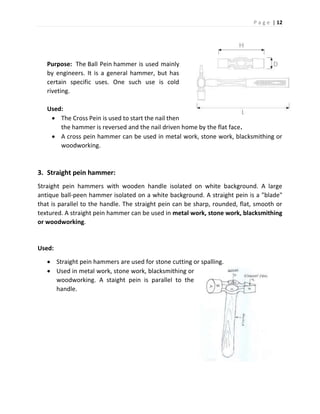
The document discusses different types of hand tools used in a workshop. It describes four main categories of tools: work holding tools, marking tools, cutting tools, and finishing tools. Under work holding tools it discusses bench vices, V-blocks, and C-clamps. Marking tools covered include surface plates, dot punches, and center punches. Cutting tools described are hacksaws, chisels, and taps/tap wrenches. The document provides details on the purpose and uses of each individual tool.