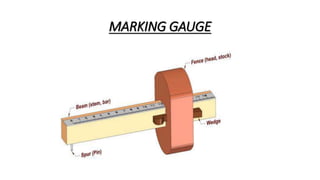
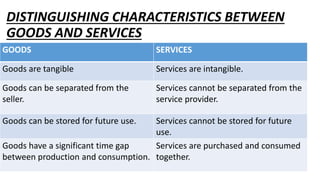
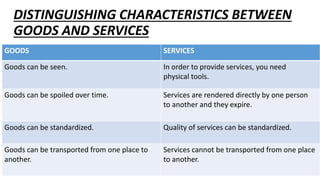
This document discusses various measuring and marking tools used in construction, manufacturing, and other fields. It describes common tools like rulers, tape measures, calipers, levels, and marking tools. It explains what each tool is used for and provides examples of applications. Maintaining tools by cleaning, lubricating, and proper storage is also mentioned to keep them in good working condition.