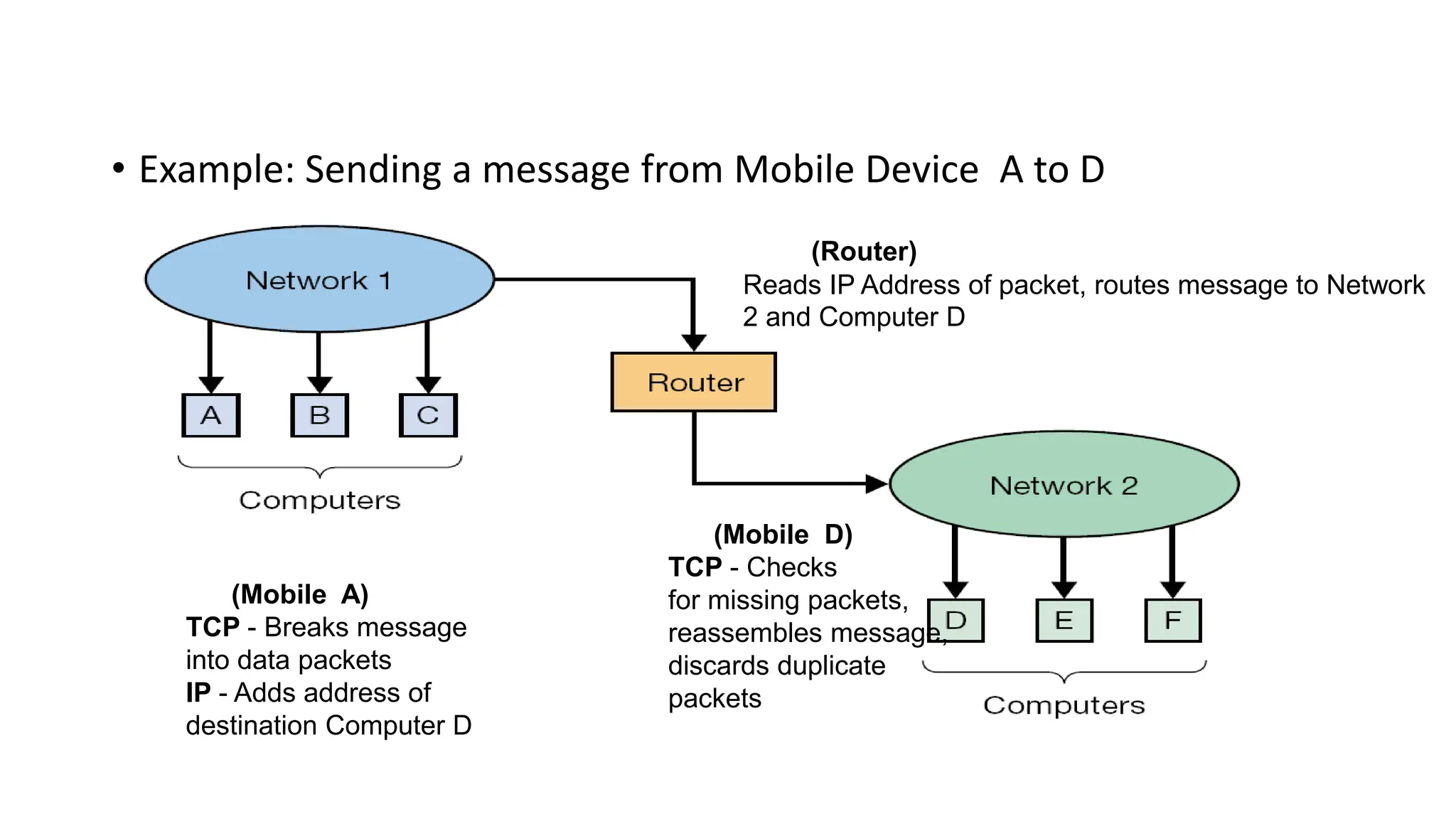
1. TCP/IP is the protocol used to break messages into packets and route them between mobile devices and networks using IP addresses and routers.
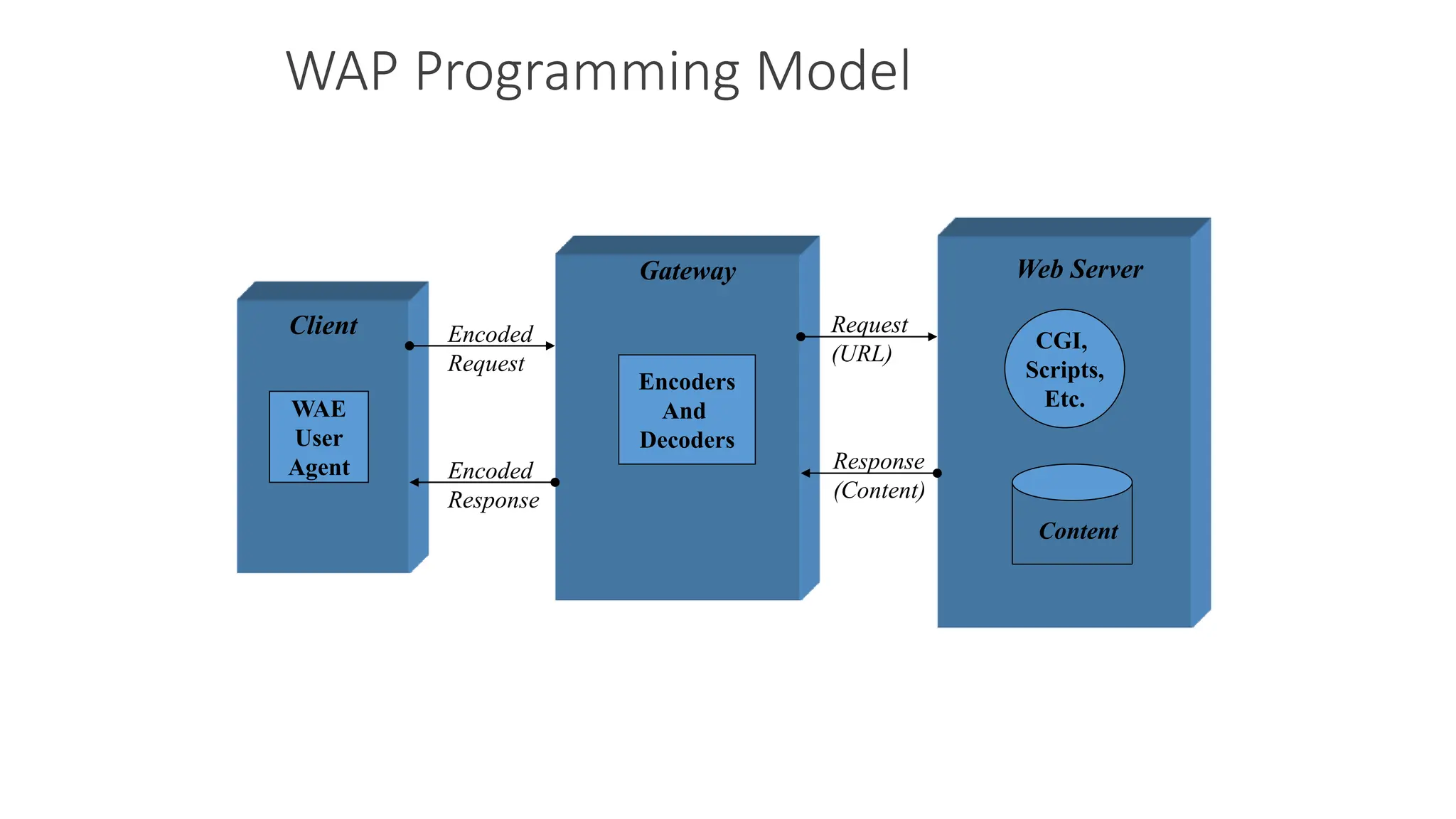
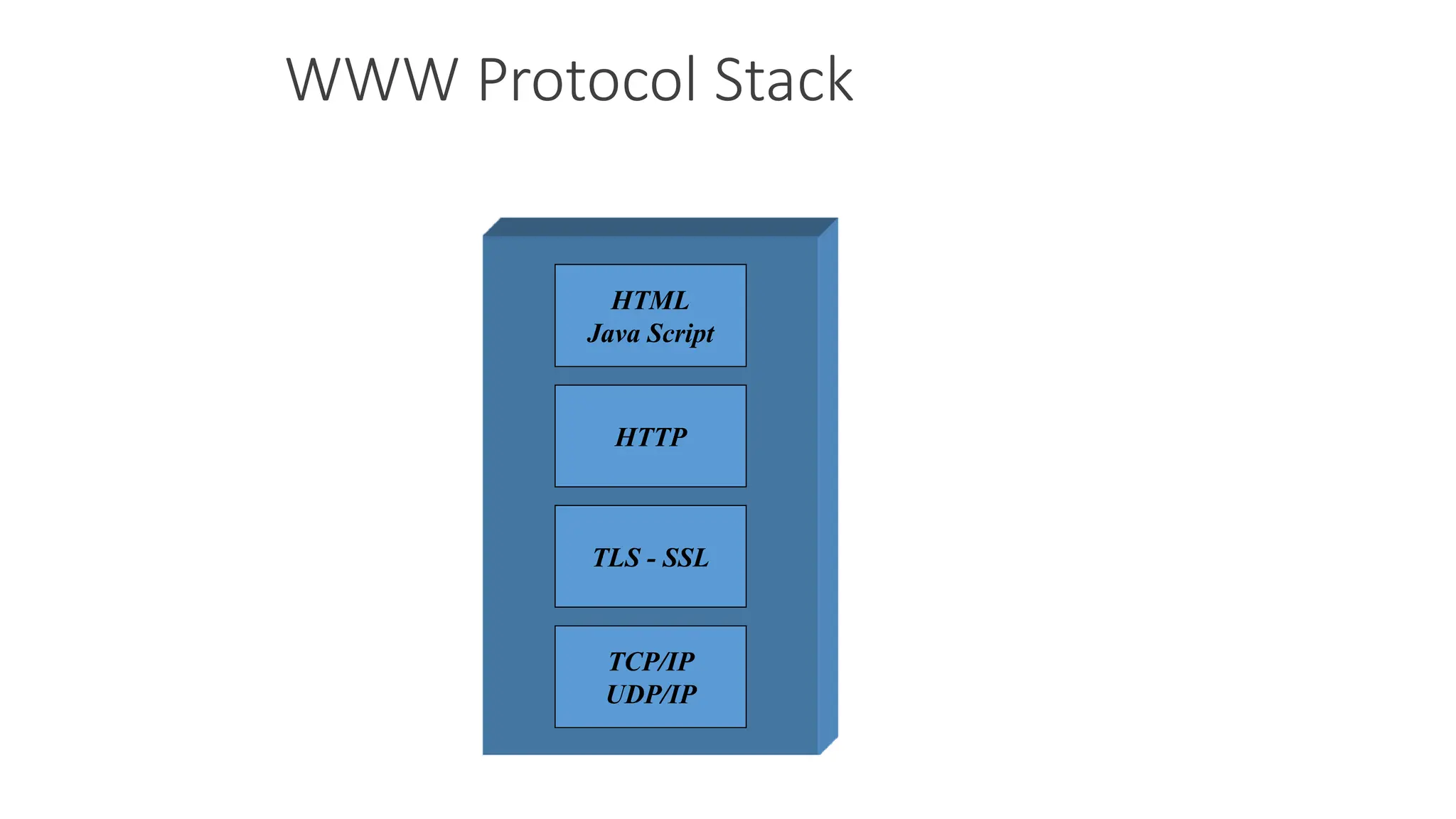
2. WAP allows users to access internet content and services on mobile devices by encoding requests and responses for transmission and decoding them on the other end.
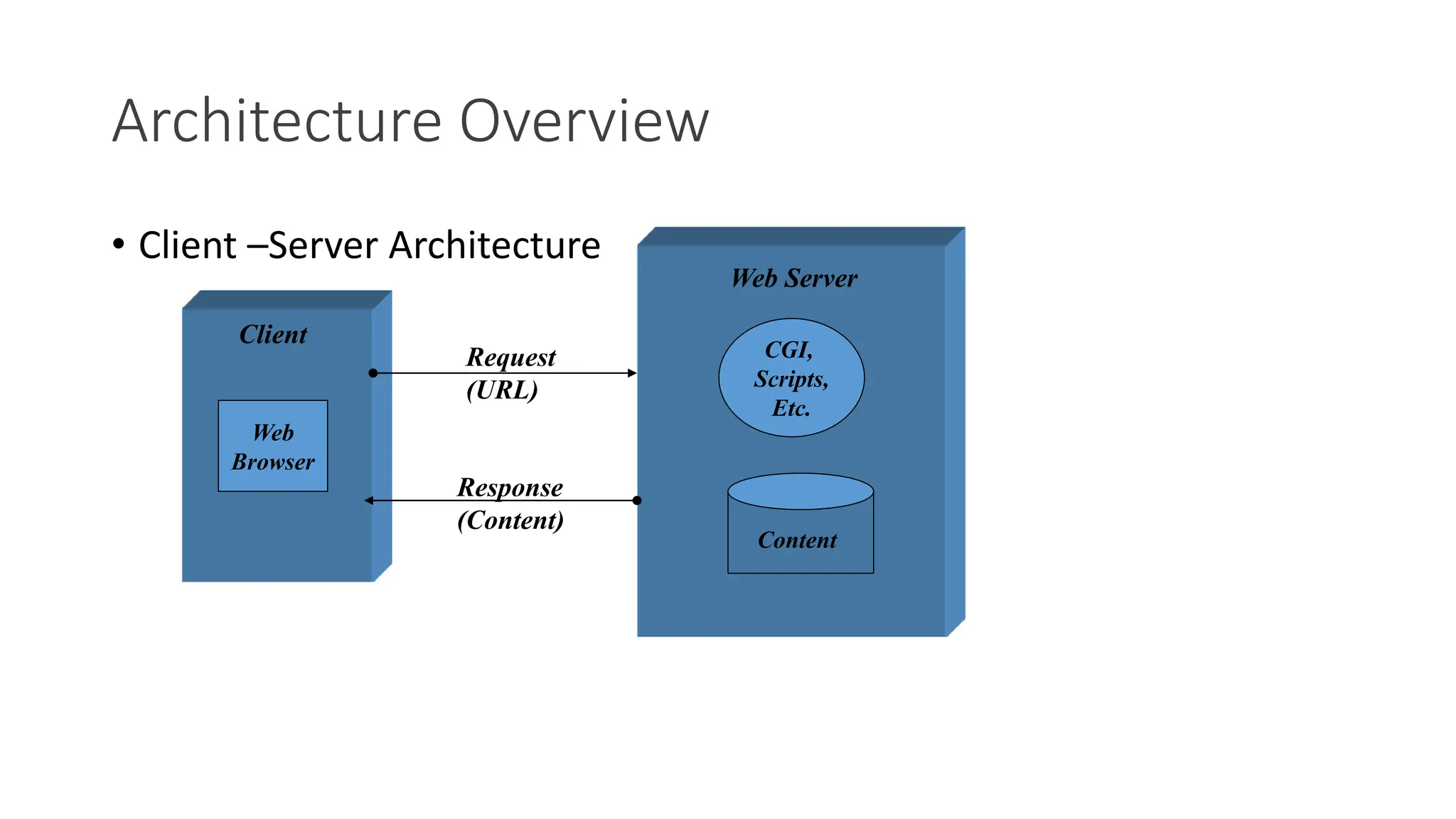
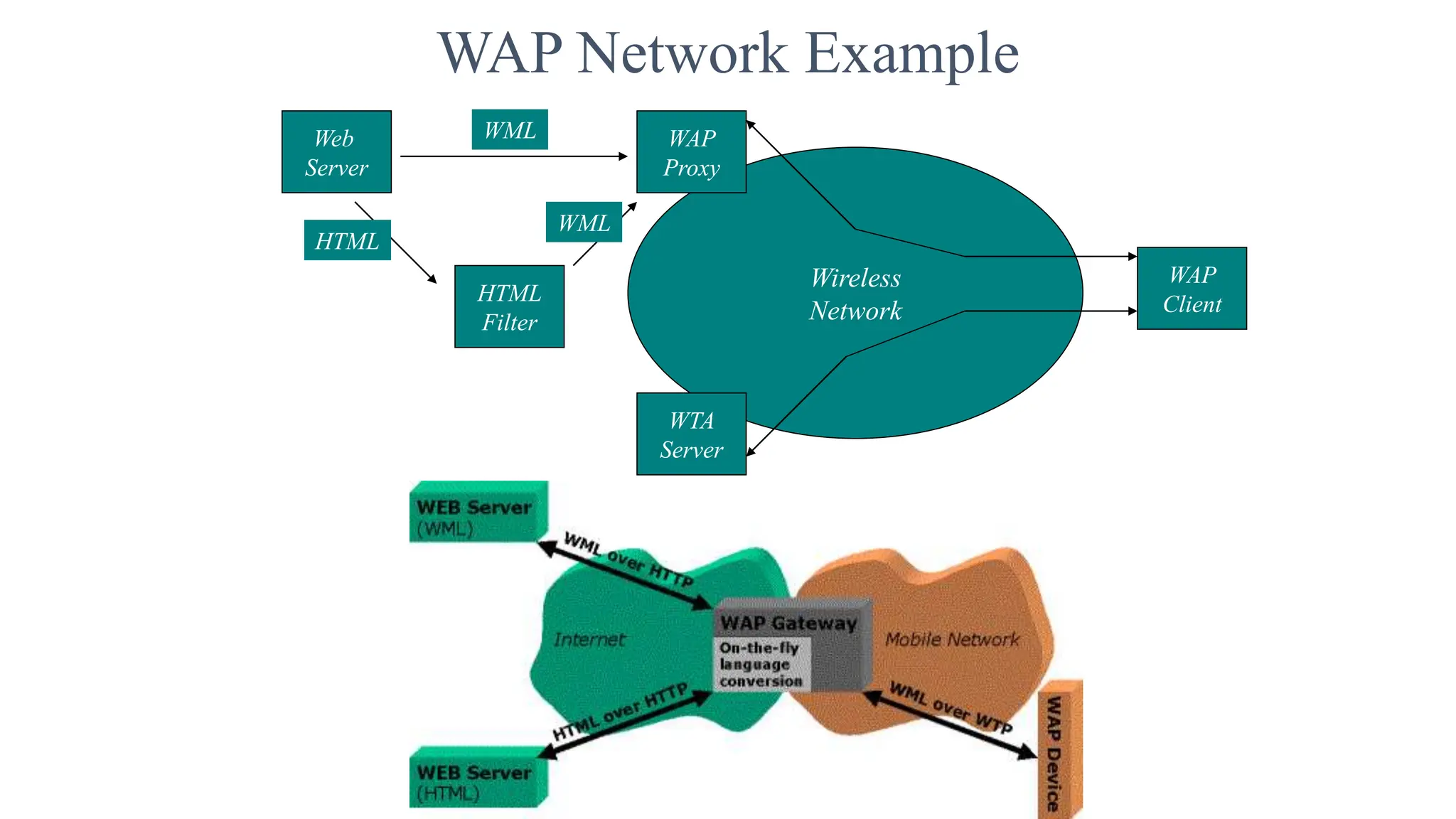
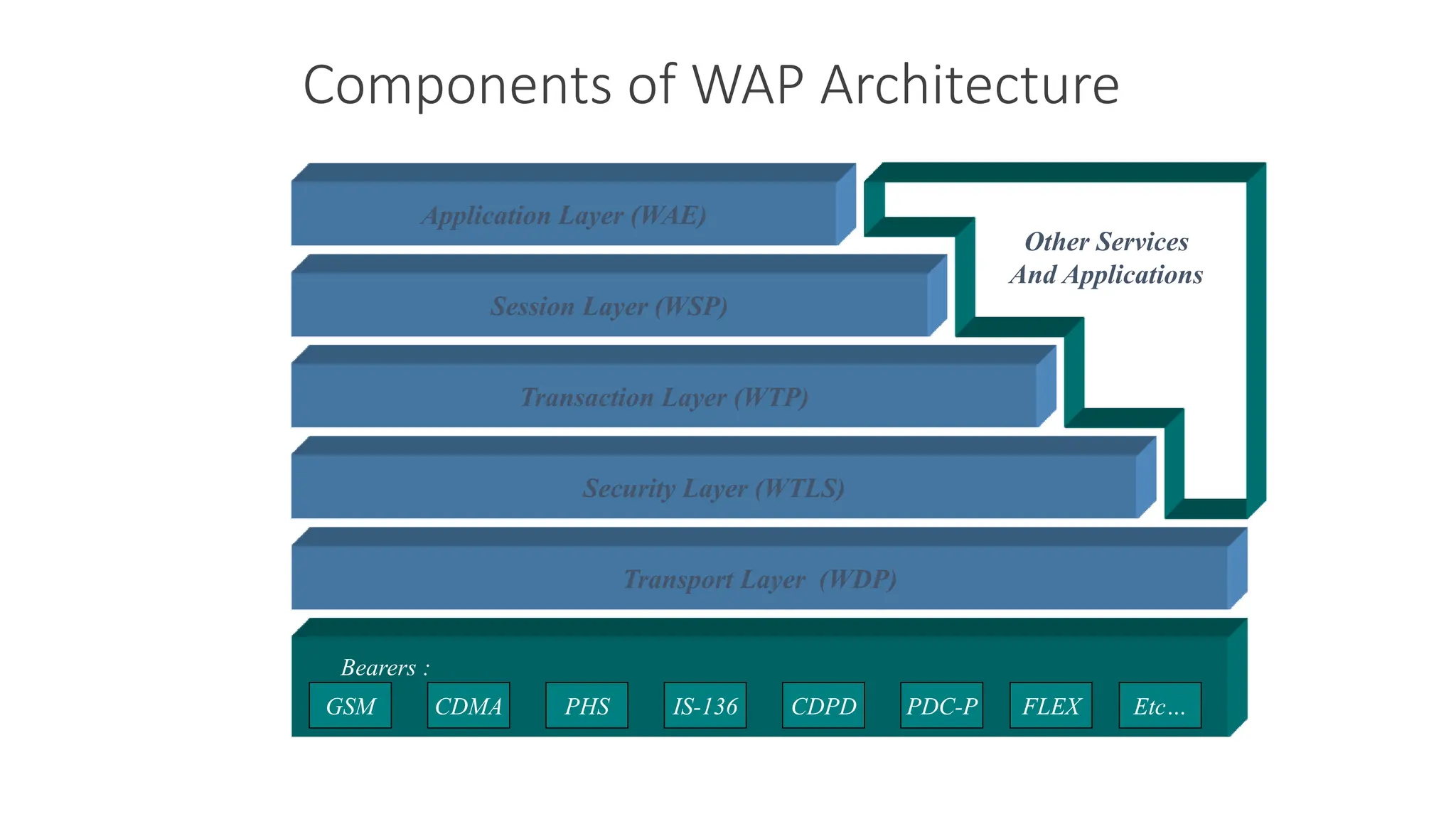
3. The WAP architecture includes WAP devices, clients, servers, proxies, and gateways that allow mobile devices to communicate with the internet through wireless networks using protocols like WAP, WML, and WTA.