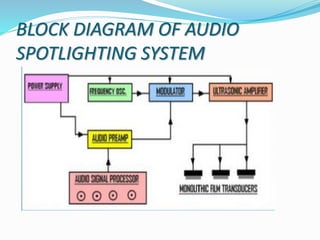
Audio spotlighting uses ultrasonic waves to create a narrow, focused beam of sound. It was invented by Dr. F. Joseph Pompei and allows specific listeners to hear sound without others nearby. It works by modulating an audio signal with ultrasonic frequencies, which through the nonlinearity of air generates new audible frequencies that can be focused into a beam. Its applications include targeted communication for safety officials in crowds and descriptive audio for museum exhibits without disturbing other listeners.