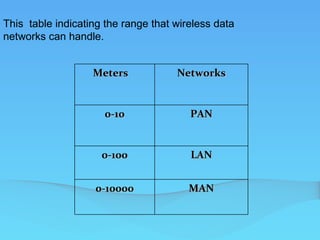
This document discusses wireless technology and wireless networks. It defines wireless as technology that does not require wires and describes various wireless systems including radio, satellite radio and TV, and wireless internet access. It provides a brief history of wireless networks and defines types of wireless networks including WPANs, WLANs, WMANs, and WWANs. It also discusses wireless access points, wireless routers, and different wireless communication technologies such as radio transmission, microwave transmission, infrared waves, and light wave transmission.