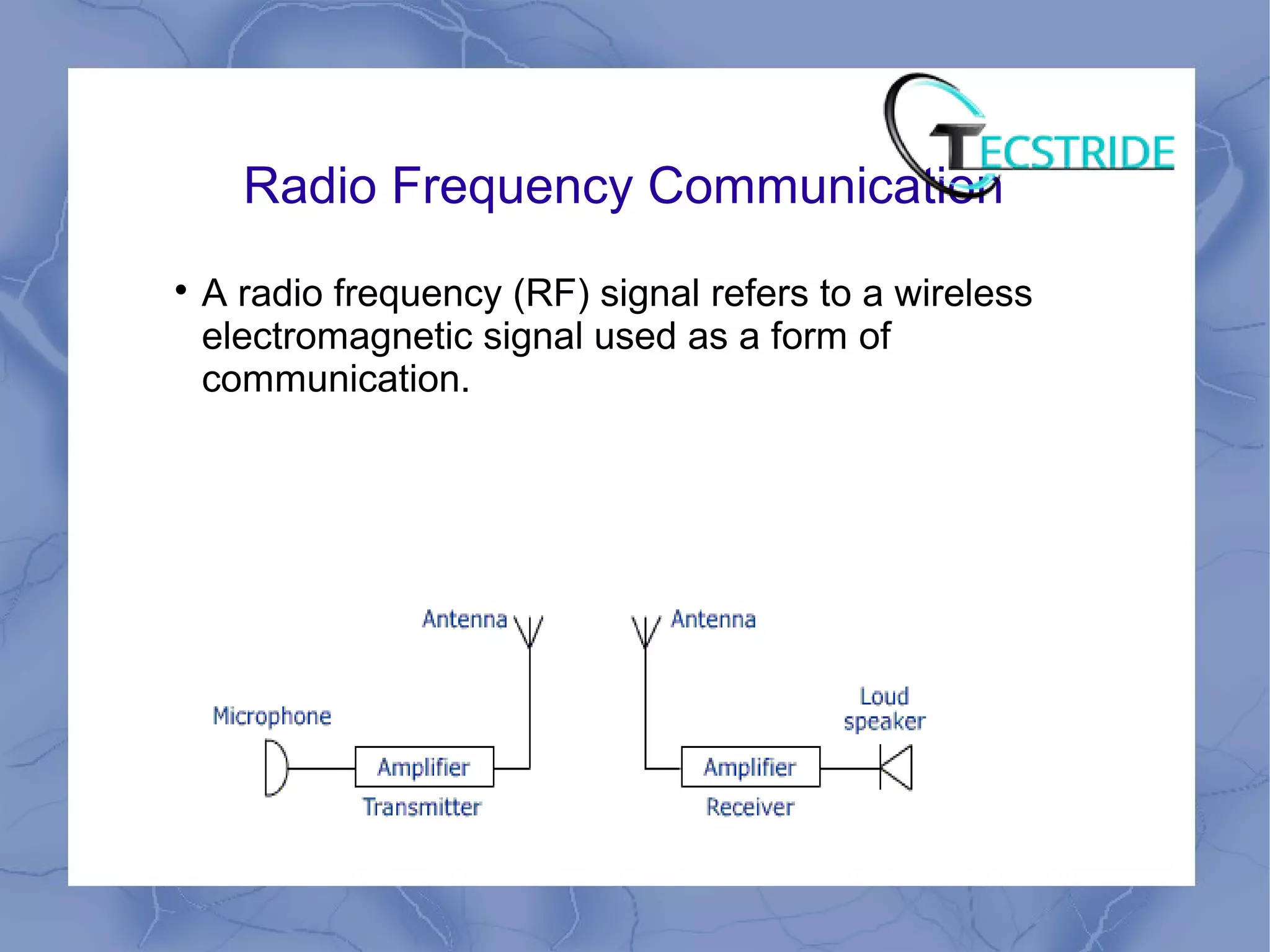
Wireless communication transmits information over distances without wires, using technologies like microwave, radio frequency, and infrared. Each mode has advantages, such as long-distance coverage, mobility, and low power usage. Various applications include point-to-point communication, broadcasting, and cellular networks.